热门标签
热门文章
- 1AI服务器市场火爆,价格飙升20倍的背后有何因素?_影响ai行情的因素
- 2STM32——SDIO的学习(驱动SD卡)(实战篇)_sdio cmd命令
- 3利用深度学习来预测股票价格变动_utility = utilityfunction(kind="ucb", kappa=2.5, x
- 4克服当众讲话紧张的12种方法_调节当众讲话紧张的十七种方法
- 5自然语言处理NLTK(一):NLTK和语料库_import nltk
- 6编译遇到 Could not determine the dependencies of task ‘:xxxxx:compileDebugAidl‘.
- 7extjs学习总结_textfield 设置 禁止缓存
- 8VASP6.1.0以上版本中VASPsol的修改及编译方法
- 9[实践]YOLOv5提升10倍推理速度:利用TensorRT 在Jetson NX上的模型部署
- 10错误C4996 'scanf': This function or variable may be unsafe. Consider using scanf_s instead. 最高效解决办法!!_c4996'scanf': this function or variable may be uns
当前位置: article > 正文
kaggle competition 实践学习 文本分类 keras实现 模型基于yoon kim 的 Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Class_keras与nltk的关系
作者:菜鸟追梦旅行 | 2024-03-31 23:24:14
赞
踩
keras与nltk的关系
比赛链接实例
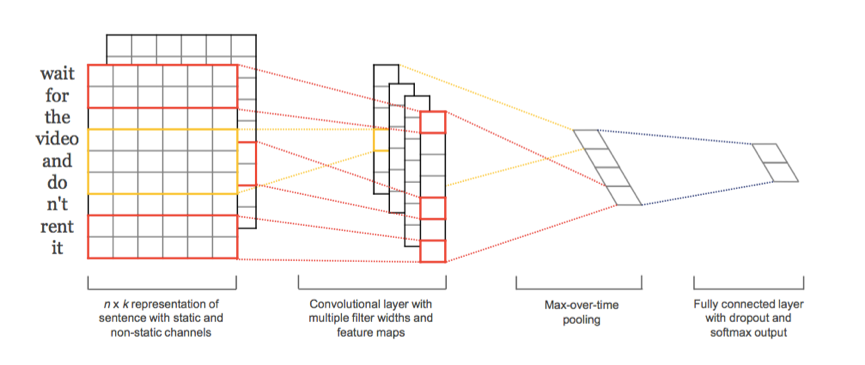
《 Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Class》论文链接
yoon kim 的《Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification》。(2014 Emnlp会议)
还有一下其他利用卷积神经网络的例子讲解
那个比赛就是对文本进行分类,一共五类
预处理是利用了nltk,gensim和pandas进行数据处理
其中pandas读取csv文本文件,这样就可以通过下标访问内容
nltk是对自然语言处理的一个很有用的库,pip 安装之后需要执行nltk.download()然后安装其数据库
然后这里用到了stopwords用来分词,还加入了标点符号分词,然后利用SnowballStemmer提取词的主干
代码用到了一个keras的序列处理的方法,会自动进行切割文本,当大于一定长度
然后用到了新的层Embedding,就是用来将一个词转化为n维向量,处理后一个长l的句子会变成 l*n 的矩阵,每一行代表一个单词
然后用一维的序列卷积,注意其实是长度为n的二维卷积,图像的2d卷积其实是加上维度的3维卷积,这点需要注意
下面是代码,也不难,注释掉的部分是用lstm实现的效果也差不多,在那个比赛均能达到0.62的准确度
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
-
- from gensim import corpora
- from nltk.corpus import stopwords
- from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
- from nltk.stem import SnowballStemmer
-
- import keras
- from keras.preprocessing import sequence
- from keras.utils import np_utils
- from keras.models import Sequential
- from keras.models import Model
- #from keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten
- from keras.layers import *
- from keras.optimizers import Adam
- from keras import callbacks
- from keras import backend as K
- from keras import metrics
- from keras import regularizers
-
- np.random.seed(0)
-
- if __name__ == "__main__":
-
- #load data
- train_df = pd.read_csv('./data/train.tsv', sep='\t', header=0)
- test_df = pd.read_csv('./data/test.tsv', sep='\t', header=0)
-
- raw_docs_train = train_df['Phrase'].values
- raw_docs_test = test_df['Phrase'].values
- sentiment_train = train_df['Sentiment'].values
- num_labels = len(np.unique(sentiment_train))
-
- #text pre-processing
- stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
- stop_words.update(['.', ',', '"', "'", ':', ';', '(', ')', '[', ']', '{', '}'])
- stemmer = SnowballStemmer('english')
- print stemmer
-
- print "pre-processing train docs..."
- processed_docs_train = []
- for doc in raw_docs_train:
- tokens = word_tokenize(doc)
- filtered = [word for word in tokens if word not in stop_words]
- stemmed = [stemmer.stem(word) for word in filtered]
- processed_docs_train.append(stemmed)
-
- print "pre-processing test docs..."
- processed_docs_test = []
- for doc in raw_docs_test:
- tokens = word_tokenize(doc)
- filtered = [word for word in tokens if word not in stop_words]
- stemmed = [stemmer.stem(word) for word in filtered]
- processed_docs_test.append(stemmed)
- print len(processed_docs_train),len(processed_docs_test)
- processed_docs_all = np.concatenate((processed_docs_train, processed_docs_test), axis=0)
-
- print len(processed_docs_all)
- dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(processed_docs_all)
- dictionary_size = len(dictionary.keys())
- print "dictionary size: ", dictionary_size
- #dictionary.save('dictionary.dict')
- #corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(doc) for doc in processed_docs]
-
- print "converting to token ids..."
- word_id_train, word_id_len = [], []
- for doc in processed_docs_train:
- word_ids = [dictionary.token2id[word] for word in doc]
- word_id_train.append(word_ids)
- word_id_len.append(len(word_ids))
-
- word_id_test, word_ids = [], []
- for doc in processed_docs_test:
- word_ids = [dictionary.token2id[word] for word in doc]
- word_id_test.append(word_ids)
- word_id_len.append(len(word_ids))
-
- seq_len = np.round((np.mean(word_id_len) + 2*np.std(word_id_len))).astype(int)
- print seq_len,np.mean(word_id_len),2*np.std(word_id_len)
- #pad sequences
- word_id_train = sequence.pad_sequences(np.array(word_id_train), maxlen=seq_len)
- word_id_test = sequence.pad_sequences(np.array(word_id_test), maxlen=seq_len)
- y_train_enc = np_utils.to_categorical(sentiment_train, num_labels)
-
- # #LSTM
- # print "fitting LSTM ..."
- # # model = Sequential()
- # # model.add(Embedding(dictionary_size, 128, dropout=0.2))
- # # model.add(LSTM(128, dropout_W=0.2, dropout_U=0.2))
- # # model.add(Dense(num_labels))
- # # model.add(Activation('softmax'))
- # seq_len=12
- # dictionary_size=10000
- # num_labels=10
- myInput=Input(shape=(seq_len,))
- print myInput.shape
-
- WORD_VECSIZE=128
- x = Embedding(output_dim=WORD_VECSIZE, input_dim=dictionary_size,dropout=0.2)(myInput)
-
- print x.shape
- filterNum=64
- b=Conv1D(filterNum/2, 2)(x)
- c=Conv1D(filterNum/4, 3)(x)
- d=Conv1D(filterNum/4, 4)(x)
- e=Conv1D(filterNum/4, 5)(x)
- f=Conv1D(filterNum/8, 6)(x)
- # b=Conv1D(filterNum/8, 2)(x)
- # c=Conv1D(filterNum/4, 3)(x)
- # d=Conv1D(filterNum/4, 4)(x)
- # e=Conv1D(filterNum/2, 5)(x)
- # f=Conv1D(filterNum, 6)(x)
-
-
- ba=Activation('relu')(b)
- ca=Activation('relu')(c)
- da=Activation('relu')(d)
- ea=Activation('relu')(e)
- fa=Activation('relu')(f)
- print ba.shape,fa.shape
- b2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -1 ))(ba)
- c2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -2 ))(ca)
- d2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -3 ))(da)
- e2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -4 ))(ea)
- f2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -5 ))(fa)
-
- fb=Flatten()(b2)
- fc=Flatten()(c2)
- fd=Flatten()(d2)
- fe=Flatten()(e2)
- ff=Flatten()(f2)
-
- all_flatten=concatenate([fb,fc,fd,fe,ff])
- # flatten=Flatten()(all_pool)
- dp=Dropout(0.5)(all_flatten)
- # fc1=Dense(64,activation='relu')(dp)
- # dp2=Dropout(0.5)(fc1)
- out=Dense(num_labels,activation='softmax',kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.005))(dp)
- # out=Dense(NUM_CLASS,activation='softmax')(dp)
-
- model = Model(inputs=myInput,outputs=out)
- model.compile(optimizer='adam',
- loss='categorical_crossentropy',
- # metrics=['accuracy',metrics.categorical_accuracy])
- metrics=['accuracy'])
-
- model.fit(word_id_train, y_train_enc, nb_epoch=5, batch_size=256, verbose=1)
-
- test_pred = model.predict(word_id_test)
-
- test_pred=test_pred.tolist()
- test_label =[i.index(max(i)) for i in test_pred]
-
- #make a submission
- test_df['Sentiment'] = np.array(test_label).reshape(-1,1)
- header = ['PhraseId', 'Sentiment']
- test_df.to_csv('./lstm_sentiment.csv', columns=header, index=False, header=True)

后面我又参考《A C-LSTM Neural Network for Text Classification》(arXiv preprint arXiv)这篇文章改了一下,在cnn后面加上了lstm,发现效果和原来差不多。上涨了0.001.。
模型差不多,就加了一层lstm
- myInput=Input(shape=(seq_len,))
- print myInput.shape
-
- WORD_VECSIZE=128
- x = Embedding(output_dim=WORD_VECSIZE, input_dim=dictionary_size)(myInput)
-
- print x.shape
- filterNum=128
- b=Conv1D(filterNum/2, 2)(x)
- c=Conv1D(filterNum/2, 3)(x)
- d=Conv1D(filterNum, 4)(x)
- e=Conv1D(filterNum, 5)(x)
- f=Conv1D(filterNum, 6)(x)
- # b=Conv1D(filterNum/8, 2)(x)
- # c=Conv1D(filterNum/4, 3)(x)
- # d=Conv1D(filterNum/4, 4)(x)
- # e=Conv1D(filterNum/2, 5)(x)
- # f=Conv1D(filterNum, 6)(x)
-
-
- ba=Activation('relu')(b)
- ca=Activation('relu')(c)
- da=Activation('relu')(d)
- ea=Activation('relu')(e)
- fa=Activation('relu')(f)
-
- b2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -1 ))(ba)
- c2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -2 ))(ca)
- d2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -3 ))(da)
- e2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -4 ))(ea)
- f2=MaxPooling1D(pool_size=(seq_len -5 ))(fa)
- print b2.shape,f2.shape
-
- all_pool=concatenate([b2,c2,d2,e2,f2])
- # flatten=Flatten()(all_pool)
- # print all_pool.shape
- # res=Reshape(1)
- # print type(res),type(all_flatten)
- lstm=LSTM(128,return_sequences=True)(all_pool)
-
- print lstm.shape
- flatten=Flatten()(lstm)
- dp=Dropout(0.5)(flatten)
- # fc1=Dense(64,activation='relu')(dp)
- # dp2=Dropout(0.5)(fc1)
- out=Dense(num_labels,activation='softmax',kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.005))(dp)
- # out=Dense(NUM_CLASS,activation='softmax')(dp)
-
- model = Model(inputs=myInput,outputs=out)
- model.compile(optimizer='adam',
- loss='categorical_crossentropy',
- # metrics=['accuracy',metrics.categorical_accuracy])
- metrics=['accuracy'])

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/菜鸟追梦旅行/article/detail/346375
推荐阅读
相关标签