- 1创意信息联席CTO:学习财务思维,打造100位技术大咖_马双涛
- 2IDEA 创建scala spark的Mvn项目_idea 创建一个 scala +spark的maven项目
- 3学习笔记之Yarn命令_yern 使用
- 4文件服务器FastDFS
- 5微信小程序笔记_this.selectcomponent
- 6算法思想和实际应用场景总结_经典算法思想在实际场景中的应用 研究报告
- 7【自动化测试】Pytest框架 —— Pytest测试框架介绍_pytest框架详解
- 8Docker AIGC等大模型深度学习环境搭建(完整详细版)_有哪些开源ai模型适合docker 部署
- 9应用VBA在Excel表中执行统计_excel vba宏运行次数统计
- 10linux重置root密码的两种方法_linux重置root密码步骤
MessageBox调用--Shellcode_messageboxa 弹框的shellcode 怎么写
赞
踩
首先,拓展一下寄存器简括:
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zys-simon/p/9221384.html
C语言MessageBox()函数简单调用:
源代码:
MessageBox()函数拓展:
MessageBoxA函数是Windows系统提供的API函数,需要引入user32.lib这个库,同时还需要手动声明一下函数原型。MessageBoxA函数中最后一个参数为对话框风格,通过设置这个参数不同值,可以实现显示MessageBoxA的不同组态。具体参数含义可以参考微软官方手册。链接地址:https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows/desktop/api/winuser/nf-winuser-messagebox
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<windows.h>
-
- void main()
- {
- printf("begin\n");
- ::MessageBox(NULL,"test shellcode","test",MB_OK);//test shellcode是弹框内容,test是弹框名字
- printf("end\n");
- }
反汇编
查看汇编代码:
(1)、printf函数:
- 6: printf("begin\n");
- 00401028 68 40 20 42 00 push offset string "begin\n" (00422040)
- ;将字符串格式压堆栈,以便输入输出使用。由上可知压入的是4bit
- 0040102D E8 5E 00 00 00 call printf (00401090)
- 00401032 83 C4 04 add esp,4
- ;由于之前push入栈压入了四个字节,当调用结束后我们需要将其堆栈恢复
拓展:
call/ret指令:
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u014421422/article/details/79471396
举例:求两个数的和
拓展:
esp是栈指针,是cpu机制决定的,push、pop指令会自动调整esp的值;
ebp只是存取某时刻的esp,这个时刻就是进入一个函数内后,cpu会将esp的值赋给ebp,此时就可以通过ebp对栈进行操作,比如获取函数参数,局部变量等。
首先,将3和4压入堆栈,
- push 3
- push 4
- call add_num
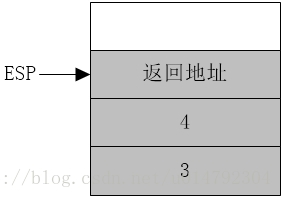
执行call指令前:(如图)
其中ESP为x86CPU使用的堆栈指针,每进行一次入栈操作,ESP要减4(32位CPU)(图上堆栈向上地址减小,向下地址增加) 明显的是,add_num只需要把堆栈中相应的变量取出来使用就可以了。堆栈参数传递的确也是这么做,但是却要稍稍费事一点。
给出add_num过程:
-
- add_num proc
- push ebp
- mov ebp,esp
- mov eax,[ebp+8]
- add eax,[ebp+12]
- pop ebp
- ret
- add_num endp
指令:
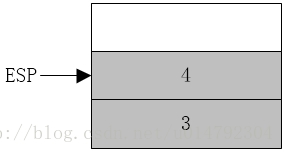
call add_num执行call add_num时,ESP减4后将add_num过程的返回地址压入堆栈,即当前指令指针EIP的值(该值为主程序中call指令的下一条指令(不是push ebp)的地址)
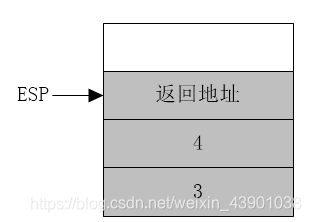
-
- push ebp
- ;将esp的值赋予ebp。而将ebp压入堆栈是为了保护ebp,在add_num过程结束后还要恢复ebp的值。
-
- mov ebp,esp
- ;此时esp指向堆栈中的ebp,而将esp赋予ebp后,ebp便指向了堆栈中自己被保护的值。此时ebp的主要作用是为参数读取提供绝对地址。比如参数4比ebp所在地址高8Byte(堆栈一个单元是4Byte),则过程中要使用参数4时,使用基址-偏移量寻址即可,即[ebp+8]。
-
- mov eax,[ebp+8]
- add eax,[ebp+12]
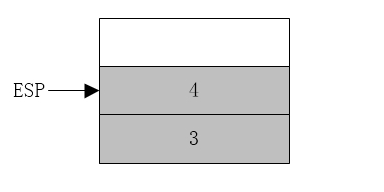
此时已经进入了add_num过程了。
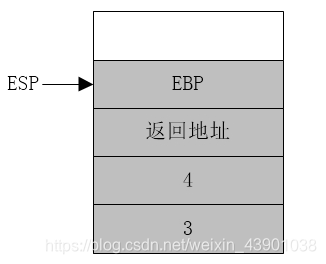
- pop ebp
- ;此时ebp弹出,ebp恢复调用前的值
- ret
- ;最后弹出返回地址,程序返回到主程序中并执行下一条指令
- call 标号
- 1.将下一条指令的偏移地址入栈
- 2.转到标号出执行指令
- ret
- 将栈顶的值出栈,赋值给IP
(2)、MessageBox()函数:
- 7: ::MessageBox(NULL,"test shellcode","test",MB_OK);//test shellcode是弹框内容,test是弹框名字
-
-
- 00401035 8B F4 mov esi,esp
- ;esi指向栈顶,在函数调用前用esi保留esp寄存器
-
- 00401037 6A 00 push 0 ;传参,默认遵从__cdecl调用规则
- 00401039 68 2C 20 42 00 push offset string "test" (0042202c)
- 0040103E 68 CC 2F 42 00 push offset string "test shellcode" (00422fcc)
- 00401043 6A 00 push 0
- 00401045 FF 15 AC A2 42 00 call dword ptr [__imp__MessageBoxA@16 (0042a2ac)]
- ;取iat表中的函数地址,调用。
-
- 0040104B 3B F4 cmp esi,esp
- 0040104D E8 BE 00 00 00 call __chkesp (00401110)
- ;用于检测堆栈是否被破坏,只在调试阶段存在,发行版本不存在。

代码:mov esi esp具体解析:
- 00401037 6A 00 push 0
- 00401039 68 2C 20 42 00 push offset string "test" (0042202c)
- 0040103E 68 CC 2F 42 00 push offset string "test shellcode" (00422fcc)
- 00401043 6A 00 push 0
- 00401045 FF 15 AC A2 42 00 call dword ptr [__imp__MessageBoxA@16 (0042a2ac)]
如上代码类似于:
MessageBox(NULL,"test shellcode","test",MB_OK);即将Messagebox的对应的参数元素倒序逐一push压入栈中,(即MB_OK先入栈,然后“test”,“test shellcode”,并且由汇编可知,字符串机器码也是倒叙)
- call dword ptr [__imp__MessageBoxA@16 (0042a2ac)]
- ;取iat表中的函数地址,调用。
这里的call 用来调用子过程,跳转到子程序,dword指的是双字型,ptr是将左边的类型(dword)赋给右边的变量,(类似于interesting i),【】中的0042a2ac是一个内存地址,即我们要调用的子过程的首地址。
拓展:
(1)、IAT的全称是Import Address Table。
IAT表是执行程序或者dll为了实现动态加载和重定位函数地址,用到的一个导入函数地址表。这里面记录了每个导入函数的名字和所在的dll名称,在pe加载的时候系统会加载这些dll到用户的地址空间然后把函数地址覆盖这个表里的函数地址,然后重构所有用到这个表的代码,让其调用直接指向实际函数地址(PE是否覆盖不确定,驱动会这么做),PE的IAT表会留在内存,驱动的就丢弃了。
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/gd-luojialin/p/7581106.html
(2)、WiINAPI是一个宏名,定义如下:
#define WINAPI _stdcall;而std_call是新标准c/c++函数的调用方法,他是采用自动清栈的方式,而标准c调用(_cdecl方法,cdecl是C declare的缩写)采用的是手工清栈的方式。
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/lisfaf/article/details/98990043
- 0040104B 3B F4 cmp esi,esp
- 0040104D E8 BE 00 00 00 call __chkesp (00401110)
cmp指令是减法操作,操作之后会设置标志位寄存器所以也就是判断指令,注意进行减法运算后并不会对两个寄存器里的值产生任何影响,结果会存放到通用寄存器当中,并根据通用寄存器的值来设置标志位!
__RTC_CheckEsp函数是检查某内存缓冲区是否溢出的。调用此函数检查00401110h内存缓冲区是否溢出!(VC++编译器在每个API函数调用用后都会生成一个call _chkesp,调试版才有)
绕过 _chkesp函数检查:https://blog.csdn.net/lixiangminghate/article/details/46612119
汇编语言:
方法一:
- char* a = "test shellcode";
- char* b = "test";
- _asm
- {
- push MB_OK
- push b
- push a
- push 0
- call dword ptr[MessageBoxA]
- }
方法二:
- char* a = "test shellcode";
- char* b = "test";
- _asm
- {
- push MB_OK
- push b
- push a
- push 0
- mov eax,7666EA71h; // 假设 0x7666EA71 是 MessageBoxA 的地址
- call eax
- }
PS:方法三:间接获取messagebox的地址:
- // test0218——5.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
- //
-
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include <windows.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- printf("Hello World!\n");
-
- LoadLibraryA("user32.dll"); //载入指定的动态链接库,并将它映射到当前进程使用的地址空间。一旦载入,即可访问库内保存的资源
- HMODULE hmd=GetModuleHandleW(L"user32.dll"); //hmd就是user32.dll在这个实例的内存基址
- ULONG addr=(ULONG)GetProcAddress(hmd,"MessageBoxA"); //hmd就是user32.dll在这个实例的内存基址
-
-
- char* aa="这是内联汇编,哈哈!";
- char* bb="提示"; //aa bb是2个字符串的首地址
-
- //MessageBoxA(0,aa,bb,MB_OK|MB_ICONINFORMATION); //如果取消屏蔽你会看到一模一样的弹框
- __asm
- {
- push 0x40 //最后一个参数
- mov eax,bb //标题
- push eax
- mov eax,aa //内容
- push eax
- push 0 //句柄
- mov eax,addr //messagebox的地址,我们不能直接call addr要给他放一个寄存器里面再call寄存器这样一个过程就完成了
- call eax //call这个地址
-
- }
-
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
-

错误示例:以下采用的是lea指令,可以弹框,但是弹出我们制定好的内容
- char* a = "test shellcode";
- char* b = "test";
- _asm
- {
- push MB_OK
- lea eax,b
- push eax
- lea eax,a
- push eax
- push 0
- call dword ptr[MessageBox]
- }
shellcode 的提取:
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/manu18/articles/9445130.html
理解:指一组计算机能直接执行(不需要点击和编译),实现我们想要功能的机器代码,通常以十六进制数组的形式存在。
(1)、弹出MessageBox()
源代码:
- // 2.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
- //
-
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include "stdio.h"
- #include "windows.h"
-
- char shellcode[]="\x90\x90\x90\x33\xDB\x53\x68\x64\x63\x62\x61\x68\x68\x67\x66\x65\x8B\xC4\x53\x50\x50\x53\xB8\xEA\x07\xD5\x77\xFF\xD0";
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- printf("begin\n");
- HINSTANCE libHandle;
- char *dll="user32.dll";
- libHandle=LoadLibrary(dll);
- /*
- __asm
- {
- sub sp,0x454
- xor ebx,ebx
- push ebx
- push 0x61626364
- push 0x65666768
- mov eax,esp
- push ebx
- push eax
- push eax
- push ebx
- mov eax,0x77d507ea
- call eax
-
- }
-
- */
- __asm
- {
- lea eax,shellcode
- push eax
- ret
-
- }
-
- return 0;
- }

代码解析:
sub sp, 0x454给栈区分配一段空间
xor ebx, ebx将ebx清零
- push ebx ;esp-4,作为字符串的的最后一个‘\0’字符
- push 0x61626364 ;元素入栈“abcdefgh”
- push 0x65666768
- mov eax,esp ;将栈顶指针赋值给eax
- push ebx ;元素入栈,实现MessageBox()的功能
- push eax
- push eax
- push ebx
- mov eax,0x77d507ea
- call eax
实验MessageBox()功能。然后反汇编,将机器码保存,每个机器码前面加上‘\x’ 代表十六进制。
(2)、弹出cmd程序
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include<windows.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- printf("Hello World!\n");
- HINSTANCE libHandle;
- char* dll = "kernel32.dll";
- libHandle = LoadLibrary(dll);
- WinExec("cmd.exe",SW_SHOW);
- return 0;
- }