热门标签
热门文章
- 1Java接口,超详细整理,适合新手入门_java 接口
- 2闲话Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC(连载4)——IO资源_hrio和hpio
- 3uni-app配置开发、测试、生产等多环境,process.env_uniapp process.env
- 4深入理解外观模式(Facade Pattern)及其实际应用
- 5git分支合并冲突解决_ugit 冲突文件
- 6XILINX 7系列FPGA_SelectIO_xilinx selectio
- 7龙蜥操作系统上安装MySQL:步骤详解与常见问题解决_龙蜥安装mysql
- 8Navicat实现 MYSQL数据库备份图文教程_navicat备份数据库
- 9【数据结构】线性表:顺序表
- 10ARIMA参数判定_如何通过acf和pacf判断arima的参数
当前位置: article > 正文
13.hadoop系列之MapReduce排序实践_mapreduce降序输出
作者:酷酷是懒虫 | 2024-06-22 23:27:52
赞
踩
mapreduce降序输出
本文我们学习MapReduce的全排序、二次排序以及区内排序
1.MapReduce概述
- MapTask和ReduceTask均会对数据按照key进行排序。该操作属于hadoop的默认行为。任何应用程序中的数据均会被排序,而不管逻辑上是否需要
- 默认排序是按照字典顺序排序,通过快速排序实现
- 对于MapTask,它会将处理结果暂时放到环形缓冲区中,当环形缓冲区使用率达到一定阈值后(默认80%),对缓冲区中的数据进行一次快速排序,并将这些有序数据溢写到磁盘上,而当数据处理完后,对磁盘上的所有文件进行归并排序
- 对于ReduceTask,会从每个MapTask上远程拷贝相应数据文件,如果文件大小超过阈值,则溢写磁盘上,否则存储到内存中;如果磁盘上文件数据达到阈值,则进行归并排序生成更大文件,如果内存中文件大小或数据超过阈值,则合并后溢写到磁盘
- 当所有数据拷贝完后,ReduceTask统一对内存和磁盘上的所有数据进行一次归并排序
2.全排序
最终输出结果只有一个,且文件内部有序。
// 我们主要实现WritableComparable接口重写compareTo方法即可
public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean> {
private long upFlow; // 上行流量
private long downFlow; // 下行流量
private long totalFlow; // 总流量
public FlowBean() {}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(upFlow);
out.writeLong(downFlow);
out.writeLong(totalFlow);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.upFlow = in.readLong();
this.downFlow = in.readLong();
this.totalFlow = in.readLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "FlowBean{" +
"upFlow=" + upFlow +
", downFlow=" + downFlow +
", totalFlow=" + totalFlow +
'}';
}
public long getUpFlow() {
return upFlow;
}
public void setUpFlow(long upFlow) {
this.upFlow = upFlow;
}
public long getDownFlow() {
return downFlow;
}
public void setDownFlow(long downFlow) {
this.downFlow = downFlow;
}
public long getTotalFlow() {
return totalFlow;
}
public void setTotalFlow() {
this.totalFlow = this.upFlow + this.downFlow;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(FlowBean o) {
// 按照总流量倒序排序
if (this.totalFlow > o.totalFlow) {
return -1;
}
if (this.totalFlow < o.totalFlow) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
// 注意我们将FlowBean作为键用于排序
public class FlowMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, FlowBean, Text> {
private FlowBean keyOut = new FlowBean();
private Text valueOut = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, FlowBean, Text>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String[] split = line.split(" ");
String phone = split[1];
String up = split[3];
String down = split[4];
valueOut.set(phone);
keyOut.setUpFlow(Long.parseLong(up));
keyOut.setDownFlow(Long.parseLong(down));
keyOut.setTotalFlow();
context.write(keyOut, valueOut);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
public class FlowReduce extends Reducer<FlowBean, Text, Text, FlowBean> {
private FlowBean valueOut = new FlowBean();
@Override
protected void reduce(FlowBean key, Iterable<Text> values, Reducer<FlowBean, Text, Text, FlowBean>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Text value : values) {
context.write(value, key);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
public class FlowDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "flowSort");
job.setJarByClass(FlowDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(FlowMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowReduce.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
观察输出结果,可以看到已按结果降序输出

3.二次排序
在自定义排序过程中,如果compareTo中判断条件为两个即为二次排序
public int compareTo(FlowBean o) {
// 按照总流量倒序排序
if (this.totalFlow > o.totalFlow) {
return -1;
}
if (this.totalFlow < o.totalFlow) {
return 1;
}
// 按照下行流量倒序排序
if (this.downFlow > o.downFlow) {
return -1;
}
if (this.downFlow < o.downFlow) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17

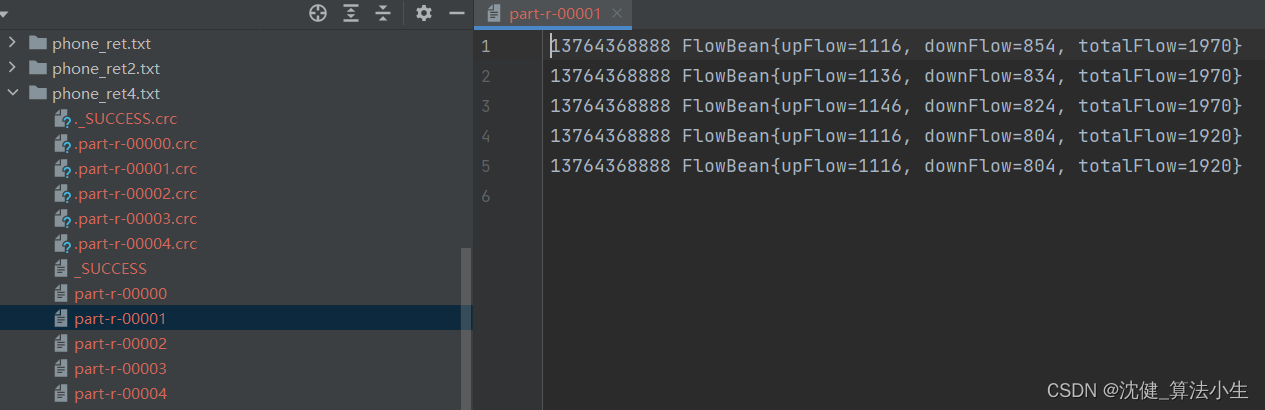
4.区内排序
MapReduce根据输入记录的键对数据集排序。保证输出的每个文件内部有序
// 注意FlowBean导入为排序的呢个类,最好新建包
public class ProvincePartitioner extends Partitioner<FlowBean, Text> {
@Override
public int getPartition(FlowBean flowBean, Text text, int numPartitions) {
// Text是手机号
String phone = text.toString().substring(0, 3);
// 注意分区号需要连续,从0开始分区
int partition;
if ("136".equals(phone)) {
partition = 0;
} else if ("137".equals(phone)) {
partition = 1;
} else if ("138".equals(phone)) {
partition = 2;
} else if ("139".equals(phone)) {
partition = 3;
} else {
partition = 4;
}
return partition;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
public class FlowPartitionerDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "flowPartitionerSort");
job.setJarByClass(FlowPartitionerDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(FlowMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowReduce.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
// 关联自定义分区类
job.setPartitionerClass(ProvincePartitioner.class);
// 设置ReduceTask任务数,保持与分区数一致
job.setNumReduceTasks(5);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
欢迎关注公众号算法小生与我沟通交流
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/酷酷是懒虫/article/detail/747976
推荐阅读
相关标签


