热门标签
热门文章
- 1unity发布webGL压缩方式的gzip,使用nginx作为web服务器时的配置文件_unity gzip
- 2GitHub 上优质项目整理_github高质量项目
- 3Stable Diffusion with Diffusers 学习笔记: 原理+完整pipeline代码_stablediffusionpipeline
- 4Linux C语言 39-进程间通信IPC之管道_进程间通信ipc管道
- 5手写二叉树,二叉树的特性
- 6【深度学习】深度学习中的可解释性(1)_可解释深度学习
- 7Python - 深夜数据结构与算法之 Stack & Queue_python 栈 队列
- 8python可视化工具示例_python 2.7界面
- 930岁以后搞Java已经没有前途_30岁以后的java工程师前景
- 10简谈设计模式之代理模式
当前位置: article > 正文
Canny边缘检测-python_canny边缘检测算法代码
作者:运维做开发 | 2024-07-18 14:28:39
赞
踩
canny边缘检测算法代码
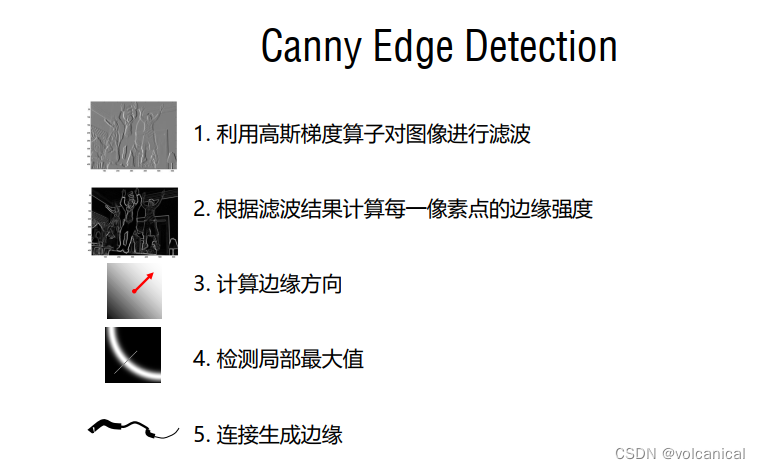
1.梯度强度计算与梯度方向计算
计算每个点的梯度强度与梯度方向
sobel_x = np.array([[1, 0, -1], [1, 0, -1], [1, 0, -1]])
sobel_y = np.array([[1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -1, -1]])
grad_x = signal.convolve2d(b, sobel_x, 'same')
grad_y = signal.convolve2d(b, sobel_y, 'same')
ans = grad_x**2 + grad_y**2
# 梯度强度矩阵
ans = ans**0.5
# np.set_printoptions(1)
degree = grad_y / grad_x
# 梯度方向矩阵
degree = np.arctan(degree)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
2.梯度方向离散化
将梯度方向离散化为四个方向
# 梯度方向矩阵离散化
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if degree[i, j] < 0:
degree[i, j] += np.pi
if degree[i, j] > 7 * np.pi / 8:
degree[i, j] = np.pi - degree[i, j]
if (np.pi / 8 > degree[i, j] >= -np.pi / 8):
degree[i, j] = 0
elif (3 * np.pi / 8 > degree[i, j] >= np.pi / 8):
degree[i, j] = np.pi / 4
elif (5 * np.pi / 8 > degree[i, j] >= 3 * np.pi / 8):
degree[i, j] = np.pi / 2
elif (7 * np.pi / 8 > degree[i, j] >= 5 * np.pi / 8):
degree[i, j] = 3 * np.pi / 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
3.极大值抑制
将梯度方向上不是最大值的点舍弃
# 极大值抑制
yizhi = np.zeros((row, col))
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if not np.isnan(degree[i, j]):
if degree[i, j] == 0:
if ans[i, j] > ans[i, max(0, j - 1)] and ans[i, j] > ans[
i, min(8, j + 1)]:
yizhi[i][j] = 1
if degree[i, j] == np.pi / 4:
if ans[i, j] > ans[max(0, i - 1),
min(8, j +
1)] and ans[i, j] > ans[min(8, i + 1),
max(0, j - 1)]:
yizhi[i][j] = 1
if degree[i, j] == np.pi / 2:
if ans[i, j] > ans[max(0, i - 1),
j] and ans[i, j] > ans[min(8, i + 1), j]:
yizhi[i][j] = 1
if degree[i, j] == 3 * np.pi / 4:
if ans[i, j] > ans[max(0, i - 1),
max(0, j -
1)] and ans[i, j] > ans[min(8, i + 1),
min(8, j + 1)]:
yizhi[i][j] = 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
4. 边缘连接
设置两个阈值,大于大的阈值可以直接被视为边缘点,介于两个阈值之间的边缘点需要看有没有绝对边缘点与其邻接,如果有可以视为边缘点,否则不视为边缘点。
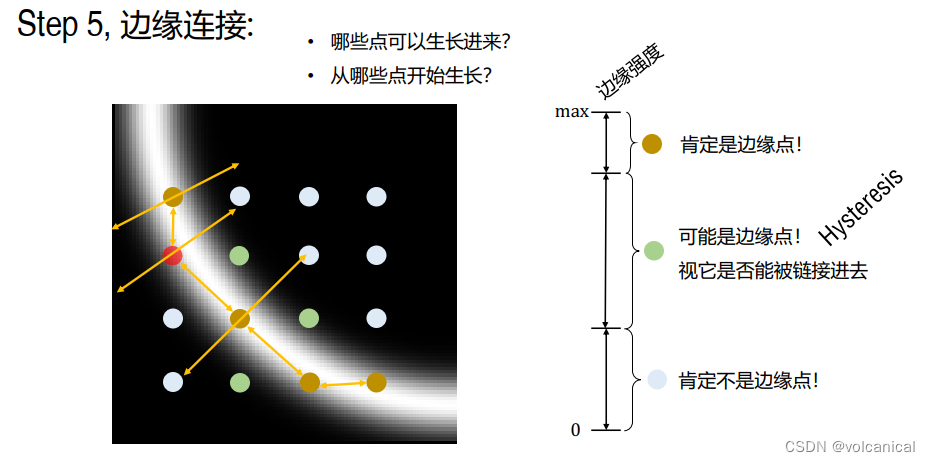
# step4. 双阈值算法检测、连接边缘
W3, H3 = yizhi.shape
DT = np.zeros([W3, H3])
# 定义高低阈值
TL = 0.2 * np.max(yizhi)
TH = 0.3 * np.max(yizhi)
for i in range(1, W3-1):
for j in range(1, H3-1):
if (yizhi[i, j] < TL):
DT[i, j] = 0
elif (yizhi[i, j] > TH):
DT[i, j] = 1
elif ((yizhi[i-1, j-1:j+1] < TH).any() or (yizhi[i+1, j-1:j+1]).any()
or (yizhi[i, [j-1, j+1]] < TH).any()):
DT[i, j] = 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
源代码:
TODO: arctan等于Nan的情况好像没有处理
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from scipy import signal
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import os
def file_name(file_dir):
L = []
N = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(file_dir):
for file in files:
if os.path.splitext(file)[1] == '.jpg':
L.append(os.path.join(root, file))
N.append(file)
return L, N
np.set_printoptions(1)
sobel_y = np.array([[1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -1, -1]])
name, filename = file_name('D:/Canny-publish/Images')
print(filename)
# 阈值
yuzhi = 5
b = Image.open(f'{name[1]}')
b = b.convert('L')
b = np.array(b)
sobel_x = np.array([[1, 0, -1], [1, 0, -1], [1, 0, -1]])
grad_x = signal.convolve2d(b, sobel_x, 'same')
grad_y = signal.convolve2d(b, sobel_y, 'same')
ans = grad_x**2 + grad_y**2
# 梯度强度矩阵
ans = ans**0.5
# np.set_printoptions(1)
degree = grad_y / grad_x
# 梯度方向矩阵
degree = np.arctan(degree)
row, col = b.shape
# 梯度方向矩阵离散化
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if degree[i, j] < 0:
degree[i, j] += np.pi
if degree[i, j] > 7 * np.pi / 8:
degree[i, j] = np.pi - degree[i, j]
if (np.pi / 8 > degree[i, j] >= -np.pi / 8):
degree[i, j] = 0
elif (3 * np.pi / 8 > degree[i, j] >= np.pi / 8):
degree[i, j] = np.pi / 4
elif (5 * np.pi / 8 > degree[i, j] >= 3 * np.pi / 8):
degree[i, j] = np.pi / 2
elif (7 * np.pi / 8 > degree[i, j] >= 5 * np.pi / 8):
degree[i, j] = 3 * np.pi / 4
# 极大值抑制
yizhi = np.zeros((row, col))
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
if not np.isnan(degree[i, j]) and ans[i, j] > yuzhi:
if degree[i, j] == 0:
if ans[i, j] > ans[i, max(0, j - 1)] and ans[i, j] > ans[
i, min(8, j + 1)]:
yizhi[i][j] = 1
if degree[i, j] == np.pi / 4:
if ans[i, j] > ans[max(0, i - 1),
min(8, j +
1)] and ans[i, j] > ans[min(8, i + 1),
max(0, j - 1)]:
yizhi[i][j] = 1
if degree[i, j] == np.pi / 2:
if ans[i, j] > ans[max(0, i - 1),
j] and ans[i, j] > ans[min(8, i + 1), j]:
yizhi[i][j] = 1
if degree[i, j] == 3 * np.pi / 4:
if ans[i, j] > ans[max(0, i - 1),
max(0, j -
1)] and ans[i, j] > ans[min(8, i + 1),
min(8, j + 1)]:
yizhi[i][j] = 1
yizhi = yizhi * ans
print(yizhi)
W3, H3 = yizhi.shape
DT = np.zeros([W3, H3])
# 定义高低阈值
TL = 0.2 * np.max(yizhi)
TH = 0.3 * np.max(yizhi)
for i in range(1, W3-1):
for j in range(1, H3-1):
if (yizhi[i, j] < TL):
DT[i, j] = 0
elif (yizhi[i, j] > TH):
DT[i, j] = 255
elif ((yizhi[i-1, j-1:j+1] > TH).any() or (yizhi[i+1, j-1:j+1] > TH).any()
or (yizhi[i, [j-1, j+1]] > TH).any()):
DT[i, j] = 255
print(DT)
DT = Image.fromarray(DT)
DT.convert('1')
DT.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/运维做开发/article/detail/846129
推荐阅读
相关标签



