- 1让 new bing 使用 GPT-4 编写一个令人满意的程序全过程赏析_bing写代码
- 2能用HTML/CSS解决的问题就不要使用JS_html点击导航栏切换内容不用js
- 3非计算机科班如何丝滑转码?小白我来说说看法_非科班计算机何去何从
- 4vue+Element实现静态旅游网站
- 5RHEL常用 Linux命令操作_用less命令分屏查看文件profile的内容,注意练习less命令的各个子命令,如b、p、q等
- 6Transformer 介绍_transformer有什么用
- 74G LTE 频率表_4g频段与band对照表
- 8随笔杂记(一)——小语种nlp文本预处理——数据清洗
- 9人工智能算法综述 (一)
- 10人工智能|机器学习——K-means系列聚类算法k-means/ k-modes/ k-prototypes/ ......(划分聚类)_kmeans聚类算法属于哪一门学科
YOLOv8+SAHI小目标检测:使用ONNX模型进行推理_使用yolov8 和 sahi 进行切片推理
赞
踩
SAHI:精准的小目标检测方法
简介
SAHI(Github) 是一个开源的图像检测库,专为高质量图片检测和小目标检测而设计。通过将大图像切片(Slice)处理,对每个切片进行目标检测,然后将检测结果聚合(Aggregate)回原始图像尺寸,以提高对小目标的检测精度。
SAHI的原理
图像切片
SAHI首先将大尺寸的图像切割成多个小尺寸的图像块。这些图像块的尺寸通常小于原图,以适应目标检测模型的输入尺寸要求。切片过程中可以设置重叠区域,以避免目标被边缘切割导致的检测不准确。
单独检测
对于每个图像切片,SAHI使用预先选定的目标检测模型(如YOLOv8等)进行独立的目标检测。每个切片都被当做一个独立的图像进行分析,模型将输出该切片中所有检测到的目标的类别、位置和置信度。
结果聚合
检测完成后,SAHI将从所有图像切片中得到的检测结果聚合到原始图像中。这一步骤考虑了切片之间的重叠区域,并通过特定的算法处理重叠区域中的冗余检测结果,如通过非最大抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression, NMS)等技术来合并或选择最佳的检测框。
- 实现过程展示
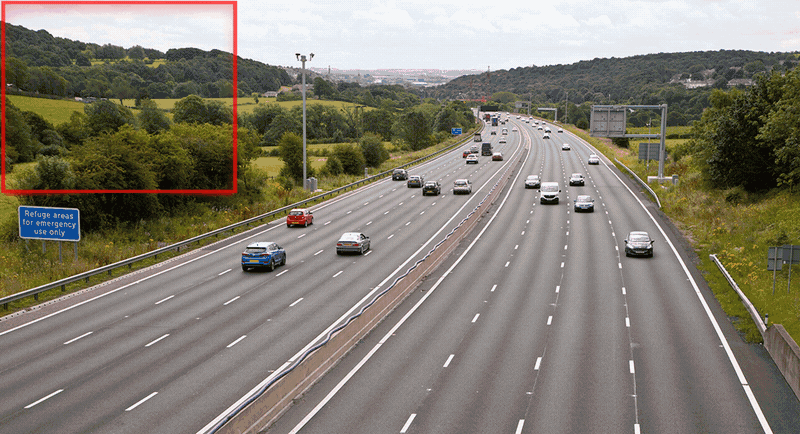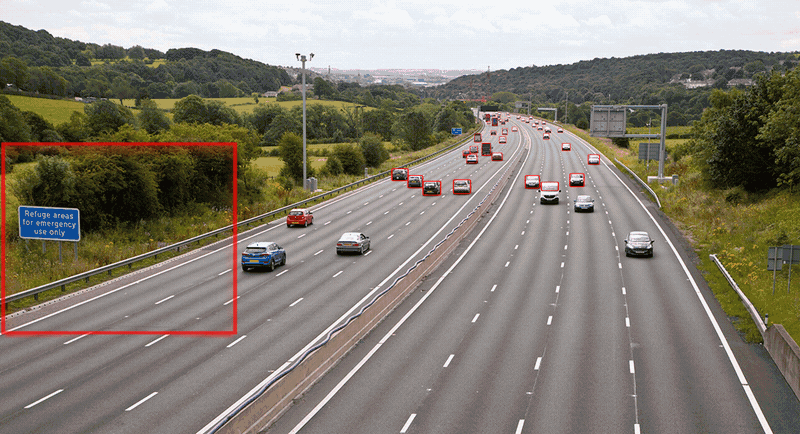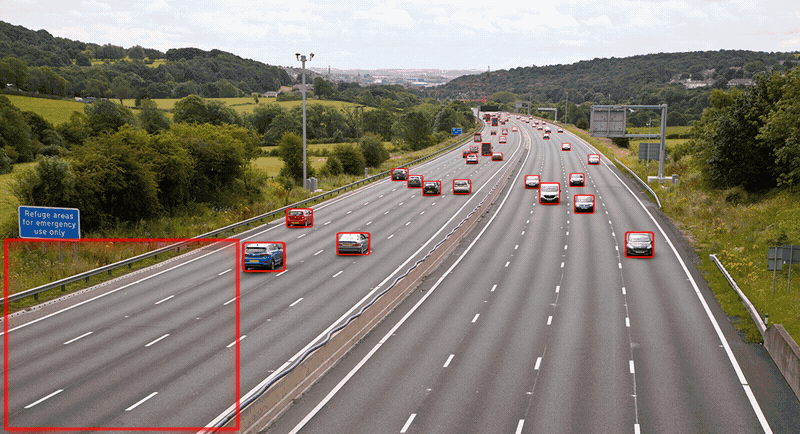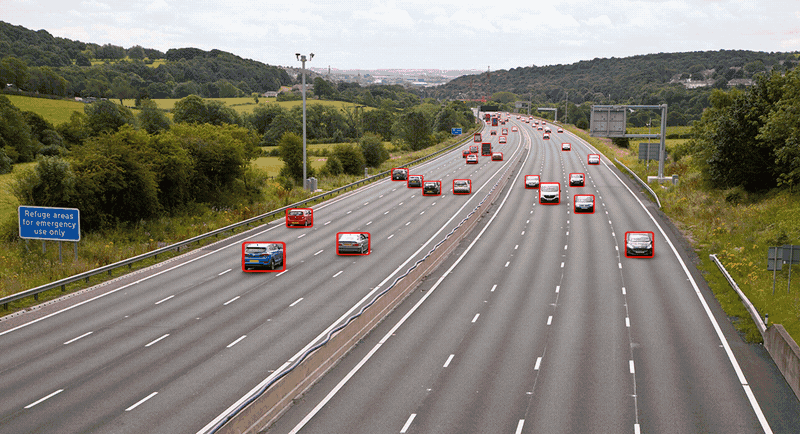
SAHI的优缺点
优点
- 高精度小目标检测: SAHI通过切片技术,能够在大尺寸图像中精确检测小尺寸目标,特别是在遥感图像、城市监控、医学影像等领域,这一方法展现了较高的实用价值。
- 灵活的模型支持: 支持多种目标检测模型,如YOLOv8,用户可以根据需要选择合适的权重文件。
- 自定义性强: 切片参数可根据实际项目需求调整,以达到最优检测效果。
缺点
- 速度较慢: 由于需要对图像进行切片处理,然后对每个切片进行检测,因此检测速度相比直接对整个图像进行检测要慢。
什么时候使用SAHI
当你需要在大尺寸图像中精确检测小目标时,SAHI是一个理想的选择。它特别适用于:
- 高质量图像检测
- 小目标检测
- 在精度要求高于速度的场景下
为什么使用SAHI
SAHI通过图像切片和切片检测结果的智能合并,大幅提升了小目标的检测精度。虽然这种方法牺牲了一定的检测速度,但在需要高精度检测的应用场景中,如遥感图像分析、医学影像处理等,SAHI提供了一个有效的解决方案。
具体实现方法
环境配置
在详细描述环境配置和安装步骤之前,请确保您的系统已经安装了Python和pip。下面是详细的环境配置步骤,适用于基于YOLOv8模型进行目标检测的项目。
1. 安装必要的Python库
pip install onnxruntime-gpu==1.13.1 opencv-python==4.7.0.68 numpy==1.24.1 sahi==0.11.15 typing_extensions==4.4.0 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
- 1
如果您没有GPU或者不打算使用GPU,可以安装onnxruntime而不是onnxruntime-gpu:
pip install onnxruntime==1.13.1 opencv-python==4.7.0.68 numpy==1.24.1 sahi==0.11.15 typing_extensions==4.4.0 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
- 1
小贴士
- 如果您在安装过程中遇到任何问题,可能需要更新pip到最新版本:
pip install --upgrade pip。 - 对于使用NVIDIA GPU的用户,确保您的系统已安装CUDA和cuDNN。
onnxruntime-gpu要求系统预装这些NVIDIA库以利用GPU加速。
模型权重下载
模型权重可以从以下百度网盘链接下载:
YOLOv8的ONNX模型加sahi方法进行检测,代码如下:
import onnxruntime import cv2 import numpy as np from sahi.predict import get_sliced_prediction, ObjectPrediction from sahi.utils.compatibility import fix_full_shape_list, fix_shift_amount_list from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional, Tuple import time category_mapping = {'0': 'person', '1': 'bicycle', '2': 'car', '3': 'motorcycle', '4': 'airplane', '5': 'bus', '6': 'train', '7': 'truck', '8': 'boat', '9': 'traffic light', '10': 'fire hydrant', '11': 'stop sign', '12': 'parking meter', '13': 'bench', '14': 'bird', '15': 'cat', '16': 'dog', '17': 'horse', '18': 'sheep', '19': 'cow', '20': 'elephant', '21': 'bear', '22': 'zebra', '23': 'giraffe', '24': 'backpack', '25': 'umbrella', '26': 'handbag', '27': 'tie', '28': 'suitcase', '29': 'frisbee', '30': 'skis', '31': 'snowboard', '32': 'sports ball', '33': 'kite', '34': 'baseball bat', '35': 'baseball glove', '36': 'skateboard', '37': 'surfboard', '38': 'tennis racket', '39': 'bottle', '40': 'wine glass', '41': 'cup', '42': 'fork', '43': 'knife', '44': 'spoon', '45': 'bowl', '46': 'banana', '47': 'apple', '48': 'sandwich', '49': 'orange', '50': 'broccoli', '51': 'carrot', '52': 'hot dog', '53': 'pizza', '54': 'donut', '55': 'cake', '56': 'chair', '57': 'couch', '58': 'potted plant', '59': 'bed', '60': 'dining table', '61': 'toilet', '62': 'tv', '63': 'laptop', '64': 'mouse', '65': 'remote', '66': 'keyboard', '67': 'cell phone', '68': 'microwave', '69': 'oven', '70': 'toaster', '71': 'sink', '72': 'refrigerator', '73': 'book', '74': 'clock', '75': 'vase', '76': 'scissors', '77': 'teddy bear', '78': 'hair drier', '79': 'toothbrush'} color_palette = np.random.uniform(100, 255, size=(len(category_mapping), 3)) def non_max_supression(boxes: np.ndarray, scores: np.ndarray, iou_threshold: float) -> np.ndarray: """Perform non-max supression. Args: boxes: np.ndarray Predicted bounding boxes, shape (num_of_boxes, 4) scores: np.ndarray Confidence for predicted bounding boxes, shape (num_of_boxes). iou_threshold: float Maximum allowed overlap between bounding boxes. Returns: np.ndarray: Filtered bounding boxes """ # Sort by score sorted_indices = np.argsort(scores)[::-1] keep_boxes = [] while sorted_indices.size > 0: # Pick the last box box_id = sorted_indices[0] keep_boxes.append(box_id) # Compute IoU of the picked box with the rest ious = compute_iou(boxes[box_id, :], boxes[sorted_indices[1:], :]) # Remove boxes with IoU over the threshold keep_indices = np.where(ious < iou_threshold)[0] # print(keep_indices.shape, sorted_indices.shape) sorted_indices = sorted_indices[keep_indices + 1] return keep_boxes def compute_iou(box: np.ndarray, boxes: np.ndarray) -> float: """Compute the IOU between a selected box and other boxes. Args: box: np.ndarray Selected box, shape (4) boxes: np.ndarray Other boxes used for computing IOU, shape (num_of_boxes, 4). Returns: float: intersection over union """ # Compute xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax for both boxes xmin = np.maximum(box[0], boxes[:, 0]) ymin = np.maximum(box[1], boxes[:, 1]) xmax = np.minimum(box[2], boxes[:, 2]) ymax = np.minimum(box[3], boxes[:, 3]) # Compute intersection area intersection_area = np.maximum(0, xmax - xmin) * np.maximum(0, ymax - ymin) # Compute union area box_area = (box[2] - box[0]) * (box[3] - box[1]) boxes_area = (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) * (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) union_area = box_area + boxes_area - intersection_area # Compute IoU iou = intersection_area / union_area return iou def xywh2xyxy(x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray: """Convert bounding box (x, y, w, h) to bounding box (x1, y1, x2, y2) Args: x: np.ndarray Input bboxes, shape (num_of_boxes, 4). Returns: np.ndarray: (num_of_boxes, 4) """ y = np.copy(x) y[..., 0] = x[..., 0] - x[..., 2] / 2 y[..., 1] = x[..., 1] - x[..., 3] / 2 y[..., 2] = x[..., 0] + x[..., 2] / 2 y[..., 3] = x[..., 1] + x[..., 3] / 2 return y class DetectionModel: def __init__( self, model_path: Optional[str] = None, model: Optional[Any] = None, config_path: Optional[str] = None, mask_threshold: float = 0.5, confidence_threshold: float = 0.3, category_mapping: Optional[Dict] = None, category_remapping: Optional[Dict] = None, load_at_init: bool = True, image_size: int = None, ): """ Init object detection/instance segmentation model. Args: model_path: str Path for the instance segmentation model weight config_path: str Path for the mmdetection instance segmentation model config file mask_threshold: float Value to threshold mask pixels, should be between 0 and 1 confidence_threshold: float All predictions with score < confidence_threshold will be discarded category_mapping: dict: str to str Mapping from category id (str) to category name (str) e.g. {"1": "pedestrian"} category_remapping: dict: str to int Remap category ids based on category names, after performing inference e.g. {"car": 3} load_at_init: bool If True, automatically loads the model at initalization image_size: int Inference input size. """ self.model_path = model_path self.config_path = config_path self.model = None self.mask_threshold = mask_threshold self.confidence_threshold = confidence_threshold self.category_mapping = category_mapping self.category_remapping = category_remapping self.image_size = image_size self._original_predictions = None self._object_prediction_list_per_image = None # automatically load model if load_at_init is True if load_at_init: if model: self.set_model(model) else: self.load_model() def check_dependencies(self) -> None: """ This function can be implemented to ensure model dependencies are installed. """ pass def load_model(self): """ This function should be implemented in a way that detection model should be initialized and set to self.model. (self.model_path, self.config_path) """ raise NotImplementedError() def set_model(self, model: Any, **kwargs): """ This function should be implemented to instantiate a DetectionModel out of an already loaded model Args: model: Any Loaded model """ raise NotImplementedError() def unload_model(self): """ Unloads the model from CPU/GPU. """ self.model = None def perform_inference(self, image: np.ndarray): """ This function should be implemented in a way that prediction should be performed using self.model and the prediction result should be set to self._original_predictions. Args: image: np.ndarray A numpy array that contains the image to be predicted. """ raise NotImplementedError() def _create_object_prediction_list_from_original_predictions( self, shift_amount_list: Optional[List[List[int]]] = [[0, 0]], full_shape_list: Optional[List[List[int]]] = None, ): """ This function should be implemented in a way that self._original_predictions should be converted to a list of prediction.ObjectPrediction and set to self._object_prediction_list. self.mask_threshold can also be utilized. Args: shift_amount_list: list of list To shift the box and mask predictions from sliced image to full sized image, should be in the form of List[[shift_x, shift_y],[shift_x, shift_y],...] full_shape_list: list of list Size of the full image after shifting, should be in the form of List[[height, width],[height, width],...] """ raise NotImplementedError() def _apply_category_remapping(self): """ Applies category remapping based on mapping given in self.category_remapping """ # confirm self.category_remapping is not None if self.category_remapping is None: raise ValueError("self.category_remapping cannot be None") # remap categories for object_prediction_list in self._object_prediction_list_per_image: for object_prediction in object_prediction_list: old_category_id_str = str(object_prediction.category.id) new_category_id_int = self.category_remapping[old_category_id_str] object_prediction.category.id = new_category_id_int def convert_original_predictions( self, shift_amount: Optional[List[int]] = [0, 0], full_shape: Optional[List[int]] = None, ): """ Converts original predictions of the detection model to a list of prediction.ObjectPrediction object. Should be called after perform_inference(). Args: shift_amount: list To shift the box and mask predictions from sliced image to full sized image, should be in the form of [shift_x, shift_y] full_shape: list Size of the full image after shifting, should be in the form of [height, width] """ self._create_object_prediction_list_from_original_predictions( shift_amount_list=shift_amount, full_shape_list=full_shape, ) if self.category_remapping: self._apply_category_remapping() @property def object_prediction_list(self): return self._object_prediction_list_per_image[0] @property def object_prediction_list_per_image(self): return self._object_prediction_list_per_image @property def original_predictions(self): return self._original_predictions class Yolov8OnnxDetectionModel(DetectionModel): def __init__(self, *args, iou_threshold: float = 0.7, **kwargs): """ Args: iou_threshold: float IOU threshold for non-max supression, defaults to 0.7. """ super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.iou_threshold = iou_threshold def load_model(self, ort_session_kwargs: Optional[dict] = {}) -> None: """Detection model is initialized and set to self.model. Options for onnxruntime sessions can be passed as keyword arguments. """ try: options = onnxruntime.SessionOptions() for key, value in ort_session_kwargs.items(): setattr(options, key, value) ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(self.model_path, sess_options=options, providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider']) self.set_model(ort_session) except Exception as e: raise TypeError("model_path is not a valid onnx model path: ", e) def set_model(self, model: Any) -> None: """ Sets the underlying ONNX model. Args: model: Any A ONNX model """ self.model = model # set category_mapping if not self.category_mapping: raise TypeError("Category mapping values are required") def _preprocess_image(self, image: np.ndarray, input_shape: Tuple[int, int]) -> np.ndarray: """Prepapre image for inference by resizing, normalizing and changing dimensions. Args: image: np.ndarray Input image with color channel order RGB. """ input_image = cv2.resize(image, input_shape) input_image = input_image / 255.0 input_image = input_image.transpose(2, 0, 1) image_tensor = input_image[np.newaxis, :, :, :].astype(np.float32) return image_tensor def _post_process( self, outputs: np.ndarray, input_shape: Tuple[int, int], image_shape: Tuple[int, int] ): image_h, image_w = image_shape input_w, input_h = input_shape predictions = np.squeeze(outputs[0]).T # Filter out object confidence scores below threshold scores = np.max(predictions[:, 4:], axis=1) predictions = predictions[scores > self.confidence_threshold, :] scores = scores[scores > self.confidence_threshold] class_ids = np.argmax(predictions[:, 4:], axis=1) boxes = predictions[:, :4] # Scale boxes to original dimensions input_shape = np.array([input_w, input_h, input_w, input_h]) boxes = np.divide(boxes, input_shape, dtype=np.float32) boxes *= np.array([image_w, image_h, image_w, image_h]) boxes = boxes.astype(np.int32) # Convert from xywh two xyxy boxes = xywh2xyxy(boxes).round().astype(np.int32) # Perform non-max supressions indices = non_max_supression(boxes, scores, self.iou_threshold) # Format the results prediction_result = [] for bbox, score, label in zip(boxes[indices], scores[indices], class_ids[indices]): bbox = bbox.tolist() cls_id = int(label) prediction_result.append([bbox[0], bbox[1], bbox[2], bbox[3], score, cls_id]) # prediction_result = [torch.tensor(prediction_result)] prediction_result = [prediction_result] return prediction_result def perform_inference(self, image: np.ndarray): """ Prediction is performed using self.model and the prediction result is set to self._original_predictions. Args: image: np.ndarray A numpy array that contains the image to be predicted. 3 channel image should be in RGB order. """ # Confirm model is loaded if self.model is None: raise ValueError("Model is not loaded, load it by calling .load_model()") # Get input/output names shapes model_inputs = self.model.get_inputs() model_output = self.model.get_outputs() input_names = [model_inputs[i].name for i in range(len(model_inputs))] output_names = [model_output[i].name for i in range(len(model_output))] input_shape = model_inputs[0].shape[2:] # w, h image_shape = image.shape[:2] # h, w # Prepare image image_tensor = self._preprocess_image(image, input_shape) # Inference outputs = self.model.run(output_names, {input_names[0]: image_tensor}) # Post-process prediction_results = self._post_process(outputs, input_shape, image_shape) self._original_predictions = prediction_results @property def category_names(self): return list(self.category_mapping.values()) @property def num_categories(self): """ Returns number of categories """ return len(self.category_mapping) @property def has_mask(self): """ Returns if model output contains segmentation mask """ return False def _create_object_prediction_list_from_original_predictions( self, shift_amount_list: Optional[List[List[int]]] = [[0, 0]], full_shape_list: Optional[List[List[int]]] = None, ): """ self._original_predictions is converted to a list of prediction.ObjectPrediction and set to self._object_prediction_list_per_image. Args: shift_amount_list: list of list To shift the box and mask predictions from sliced image to full sized image, should be in the form of List[[shift_x, shift_y],[shift_x, shift_y],...] full_shape_list: list of list Size of the full image after shifting, should be in the form of List[[height, width],[height, width],...] """ original_predictions = self._original_predictions # compatilibty for sahi v0.8.15 shift_amount_list = fix_shift_amount_list(shift_amount_list) full_shape_list = fix_full_shape_list(full_shape_list) # handle all predictions object_prediction_list_per_image = [] for image_ind, image_predictions_in_xyxy_format in enumerate(original_predictions): shift_amount = shift_amount_list[image_ind] full_shape = None if full_shape_list is None else full_shape_list[image_ind] object_prediction_list = [] # process predictions # for prediction in image_predictions_in_xyxy_format.cpu().detach().numpy(): for prediction in image_predictions_in_xyxy_format: x1 = prediction[0] y1 = prediction[1] x2 = prediction[2] y2 = prediction[3] bbox = [x1, y1, x2, y2] score = prediction[4] category_id = int(prediction[5]) category_name = self.category_mapping[str(category_id)] # category_name = classes[category_id] # fix negative box coords bbox[0] = max(0, bbox[0]) bbox[1] = max(0, bbox[1]) bbox[2] = max(0, bbox[2]) bbox[3] = max(0, bbox[3]) # fix out of image box coords if full_shape is not None: bbox[0] = min(full_shape[1], bbox[0]) bbox[1] = min(full_shape[0], bbox[1]) bbox[2] = min(full_shape[1], bbox[2]) bbox[3] = min(full_shape[0], bbox[3]) # ignore invalid predictions if not (bbox[0] < bbox[2]) or not (bbox[1] < bbox[3]): print(f"ignoring invalid prediction with bbox: {bbox}") continue object_prediction = ObjectPrediction( bbox=bbox, category_id=category_id, score=score, bool_mask=None, category_name=category_name, shift_amount=shift_amount, full_shape=full_shape, ) object_prediction_list.append(object_prediction) object_prediction_list_per_image.append(object_prediction_list) self._object_prediction_list_per_image = object_prediction_list_per_image def apply_color_mask(image: np.ndarray, color: tuple): """ Applies color mask to given input image. """ r = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8) g = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8) b = np.zeros_like(image).astype(np.uint8) (r[image == 1], g[image == 1], b[image == 1]) = color colored_mask = np.stack([r, g, b], axis=2) return colored_mask # 将结果解析并画在图上 def visualize_object_predictions( image: np.array, object_prediction_list, rect_th: int = None, text_size: float = None, text_th: float = None, hide_labels: bool = False, hide_conf: bool = False, ): # set rect_th for boxes rect_th = rect_th or max(round(sum(image.shape) / 2 * 0.003), 2) # set text_th for category names text_th = text_th or max(rect_th - 1, 1) # set text_size for category names text_size = text_size or rect_th / 3 # add masks to image if present for object_prediction in object_prediction_list: # deepcopy object_prediction_list so that original is not altered object_prediction = object_prediction.deepcopy() # visualize masks if present if object_prediction.mask is not None: # deepcopy mask so that original is not altered mask = object_prediction.mask.bool_mask # set color color = color_palette[object_prediction.category.id] # draw mask rgb_mask = apply_color_mask(mask, color) image = cv2.addWeighted(image, 1, rgb_mask, 0.6, 0) # add bboxes to image if present for object_prediction in object_prediction_list: # deepcopy object_prediction_list so that original is not altered object_prediction = object_prediction.deepcopy() bbox = object_prediction.bbox.to_xyxy() category_name = object_prediction.category.name score = object_prediction.score.value # set color color = color_palette[object_prediction.category.id] # set bbox points p1, p2 = (int(bbox[0]), int(bbox[1])), (int(bbox[2]), int(bbox[3])) # visualize boxes cv2.rectangle( image, p1, p2, color=color, thickness=rect_th, ) if not hide_labels: # arange bounding box text location label = f"{category_name}" if not hide_conf: label += f" {score:.2f}" w, h = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=text_size, thickness=text_th)[0] # label width, height outside = p1[1] - h - 3 >= 0 # label fits outside box p2 = p1[0] + w, p1[1] - h - 3 if outside else p1[1] + h + 3 # add bounding box text cv2.rectangle(image, p1, p2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled cv2.putText( image, label, (p1[0], p1[1] - 2 if outside else p1[1] + h + 2), 0, text_size, (255, 255, 255), thickness=text_th, ) result_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) return result_image if __name__ == "__main__": CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD = 0.35 # 定义置信度阈值 IOU_THRESHOLD = 0.5 # 定义交并比(IoU)阈值 IMAGE_SIZE = 640 # 定义图像尺寸 YOLOV8N_ONNX_MODEL_PATH = "yolov8n.onnx" # 定义YOLOv8模型路径 # 初始化YOLOv8模型 yolov8_onnx_detection_model = Yolov8OnnxDetectionModel( model_path=YOLOV8N_ONNX_MODEL_PATH, # 模型路径 confidence_threshold=CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD, # 置信度阈值 iou_threshold=IOU_THRESHOLD, # 交并比阈值 category_mapping=category_mapping, # 类别映射 load_at_init=True, # 初始化时加载模型 image_size=IMAGE_SIZE, # 图像尺寸 ) mode = 1 # 定义模式,1为图片预测并显示结果图片;2为摄像头检测并实时显示FPS if mode == 1: image = cv2.imread("small-vehicles.jpg") # 读取图片 image_data = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # 将图片从BGR转换为RGB result = get_sliced_prediction( image_data, yolov8_onnx_detection_model, slice_height=256, # 切片高度 slice_width=256, # 切片宽度 overlap_height_ratio=0.25, # 高度重叠比率 overlap_width_ratio=0.25 # 宽度重叠比率 ) result_data = visualize_object_predictions(image_data, result.object_prediction_list) # 可视化检测结果 cv2.imshow("result_sahi", result_data) # 在窗口中显示当前帧 cv2.imwrite("result_sahi.jpg", result_data) # 保存图片 cv2.waitKey(0) # 等待按键以继续 elif mode == 2: # 摄像头检测 cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 返回当前时间 start_time = time.time() counter = 0 while True: # 从摄像头中读取一帧图像 ret, frame = cap.read() # 对读取的帧进行处理和检测 image_data = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) result = get_sliced_prediction( image_data, yolov8_onnx_detection_model, slice_height=256, slice_width=256, overlap_height_ratio=0.25, overlap_width_ratio=0.25 ) result_data = visualize_object_predictions(image_data, result.object_prediction_list) counter += 1 # 计算帧数 # 实时显示帧数 if (time.time() - start_time) != 0: cv2.putText(result_data, "FPS:{0}".format(float('%.1f' % (counter / (time.time() - start_time)))), (5, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, (255, 255, 255), 1) # 显示图像 cv2.imshow('result_sahi', result_data) if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): break # 释放资源 cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() elif mode == 3: # 输入视频路径 input_video_path = 'pedestrian.mp4' # 输出视频路径 output_video_path = 'pedestrian_sahi_det.mp4' # 打开视频文件 cap = cv2.VideoCapture(input_video_path) # 检查视频是否成功打开 if not cap.isOpened(): print("Error: Could not open video.") exit() # 读取视频的基本信息 frame_width = int(cap.get(3)) frame_height = int(cap.get(4)) fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) # 定义视频编码器和创建VideoWriter对象 fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v') # 根据文件名后缀使用合适的编码器 out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_video_path, fourcc, fps, (frame_width, frame_height)) # 初始化帧数计数器和起始时间 frame_count = 0 start_time = time.time() while True: ret, frame = cap.read() if not ret: print("Info: End of video file.") break # 对读入的帧进行对象检测 image_data = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) result = get_sliced_prediction( image_data, yolov8_onnx_detection_model, slice_height=256, slice_width=256, overlap_height_ratio=0.25, overlap_width_ratio=0.25 ) result_data = visualize_object_predictions(image_data, result.object_prediction_list) # 计算并打印帧速率 frame_count += 1 end_time = time.time() elapsed_time = end_time - start_time if elapsed_time > 0: fps = frame_count / elapsed_time print(f"FPS: {fps:.2f}") # 将处理后的帧写入输出视频 out.write(result_data) # (可选)实时显示处理后的视频帧 # cv2.imshow("Output Video", output_image) # if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): # break # 释放资源 cap.release() out.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() else: print("输入错误,请检查mode的赋值")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
- 431
- 432
- 433
- 434
- 435
- 436
- 437
- 438
- 439
- 440
- 441
- 442
- 443
- 444
- 445
- 446
- 447
- 448
- 449
- 450
- 451
- 452
- 453
- 454
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458
- 459
- 460
- 461
- 462
- 463
- 464
- 465
- 466
- 467
- 468
- 469
- 470
- 471
- 472
- 473
- 474
- 475
- 476
- 477
- 478
- 479
- 480
- 481
- 482
- 483
- 484
- 485
- 486
- 487
- 488
- 489
- 490
- 491
- 492
- 493
- 494
- 495
- 496
- 497
- 498
- 499
- 500
- 501
- 502
- 503
- 504
- 505
- 506
- 507
- 508
- 509
- 510
- 511
- 512
- 513
- 514
- 515
- 516
- 517
- 518
- 519
- 520
- 521
- 522
- 523
- 524
- 525
- 526
- 527
- 528
- 529
- 530
- 531
- 532
- 533
- 534
- 535
- 536
- 537
- 538
- 539
- 540
- 541
- 542
- 543
- 544
- 545
- 546
- 547
- 548
- 549
- 550
- 551
- 552
- 553
- 554
- 555
- 556
- 557
- 558
- 559
- 560
- 561
- 562
- 563
- 564
- 565
- 566
- 567
- 568
- 569
- 570
- 571
- 572
- 573
- 574
- 575
- 576
- 577
- 578
- 579
- 580
- 581
- 582
- 583
- 584
- 585
- 586
- 587
- 588
- 589
- 590
- 591
- 592
- 593
- 594
- 595
- 596
- 597
- 598
- 599
- 600
- 601
- 602
- 603
- 604
- 605
- 606
- 607
- 608
- 609
- 610
- 611
- 612
- 613
- 614
- 615
- 616
- 617
- 618
- 619
- 620
- 621
- 622
- 623
- 624
- 625
- 626
- 627
- 628
- 629
- 630
- 631
- 632
- 633
- 634
- 635
- 636
- 637
- 638
- 639
- 640
- 641
- 642
- 643
- 644
- 645
- 646
- 647
- 648
- 649
- 650
- 651
- 652
- 653
- 654
- 655
- 656
- 657
- 658
- 659
- 660
在这部分,你可以根据项目需求调整切片参数,选择最适合的权重文件(s, m, l, x),并通过mode参数控制是进行图片、摄像头还是视频检测,代码中切片参数可根据实际项目需求调整,以达到对应项目的最优检测效果。(代码可以复制直接运行)
结果对比
- 使用yolov8n的ONNX权重推理:

- 使用yolov8n的ONNX权重加sahi方法进行推理:
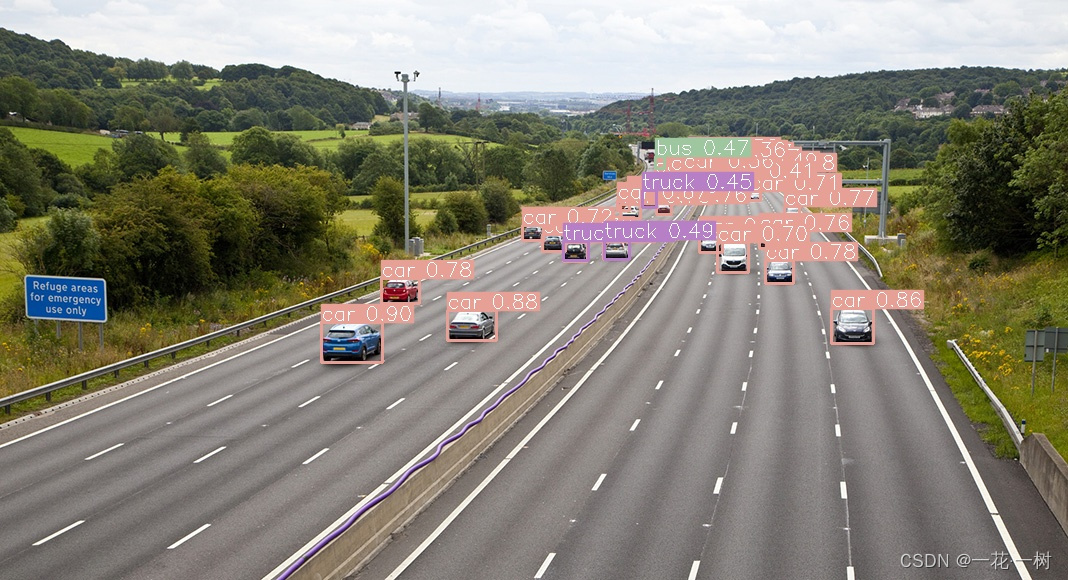
总结
SAHI是一个功能强大的小目标检测库,特别适合处理高质量图像中的小目标检测任务。尽管这种方法可能会导致处理时间增加,但它为需要高精度小目标检测的应用场景提供了一种有效的解决方案。希望本文能帮助你了解SAHI的使用场景和配置方法,如果有任何问题,欢迎留言讨论。



