- 1鸿蒙开发过程中(DevEco Studio)使用远程真机连接端口异常的解决办法_hdc: hdc_server_port must be set to a positive num
- 2IOS面试题编程机制 31-35
- 3AI作画的业界天花板被我找到了,AIGC模型揭秘 | 昆仑万维_singularity openapl
- 4分享63个微信小程序源代码总有一个是你想要的_微信小程序开源源代码
- 5Java LinkedList类和Vector类_mybug鞋
- 6HarmonyOS中利用overflow属性实现横向滚动失效的解决方法_横向滚动条失效
- 7vue+element实现树状表格的增删改查;使用el-table树形数据与懒加载实现树状表格增删改查_vue3树形表格添加数据
- 8遇见这些APP,我觉得世界都变得温柔了_devcheck csdn
- 9Python圣诞树_python圣诞树代码源码
- 10【DBeaver】建立连接报驱动问题can‘t load driver class ‘org.postgresql.Driver_dbeaver连接pg数据库缺少驱动
Transformer | DETR目标检测中的位置编码position_encoding代码详解_positionembeddingsine
赞
踩
本文主要描述的是DETR论文中的position_encoding,详细DETR论文解析可参考
论文篇 | 2020-Facebook-DETR :利用Transformers端到端的目标检测=>翻译及理解(持续更新中)_夏天|여름이다的博客-CSDN博客_dert目标检测
Transformer不像RNN可以根据位置顺序接受和处理单词,所以为了得到词的位置信息,将位置信息添加到每个词的嵌入向量中,这称为位置编码。DETR中提供了两种编码方式,一种是正弦编码(PositionEmbeddingSine),一种是可以学习的编码(PositionEmbeddingLearned),默认为正弦编码。
如图,在用作输入的嵌入向量作为transformer的输入之前,将位置编码的值相加,将嵌入向量作为编码器的输入之前添加位置编码值的过程如下:
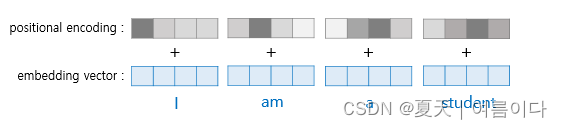
Transformer使用以下俩个函数来创建一个带有位置信息的值:
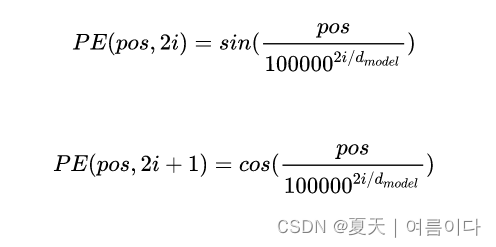
transformer把sine和cosine函数的值加入embedding向量,加上词序信息。embedding向量和位置编码的相加,是通过句子矩阵和位置编码矩阵的相加运算完成的,俩个矩阵是通过聚集embedding形成的向量。
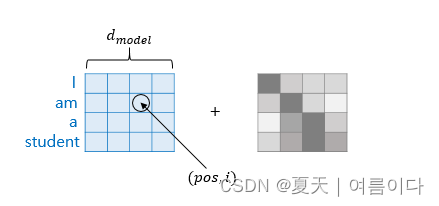
- pos: 表示嵌入向量在输入句子中的位置
- i :是嵌入向量中维度的索引
- d model:是transformer的一个超参数,是所有层的输出维度。在上图中为4,在论文《Attention is all you need》中为512.
根据上面的表达式,如果嵌入向量中每个维度的索引为偶数,则使用正弦函数的值,如果索引为奇数则使用余弦函数。
位置编码可视化
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pylab as plt
-
-
- def getPositionEncoding(seq_len, d, n=10000):
- P = np.zeros(((seq_len, d)), dtype=float)
- for k in range(seq_len):
- for i in np.arange(int(d/2)):
- denominator = np.power(n, 2*i/d)
- P[k, 2*i] = np.sin((k/denominator))
- P[k, 2*i+1] = np.cos(k/denominator)
- return P
-
- P = getPositionEncoding(seq_len=100, d=512, n=10000)
-
-
- print(P)
-
-
- cat = plt.matshow(P)
- plt.gcf().colorbar(cat)
- plt.show()

结果
1.正弦编码
取出mask,对mask进行取反,因为编码方式为二维编码,我们对行、和列分别进行累加,作为每一个维度的编码,并进行归一化,转化为角度。同时我们假设编码的每一维度都由一个128维的向量组成。然后,我们按照如下正弦编码方式进行编码,对奇数求余弦,偶数求正弦。编码后,x_emding,y_emding的维度均为batch*h*w*128 。
Transformer使用以下俩个函数来创建一个带有位置信息的值:

位置编码PE和词向量的维度需要保持一致,才能之后相加。其中pos是词的输入的位置,i是维度,
- import torch
-
- # 1d绝对sin_cos编码
- def create_1d_absolute_sin_cos_embedding(pos_len, dim):
- assert dim % 2 == 0, "wrong dimension!"
- position_emb = torch.zeros(pos_len, dim, dtype=torch.float)
- # i矩阵
- i_matrix = torch.arange(dim//2, dtype=torch.float)
- i_matrix /= dim / 2
- i_matrix = torch.pow(10000, i_matrix)
- i_matrix = 1 / i_matrix
- i_matrix = i_matrix.to(torch.long)
- # pos矩阵
- pos_vec = torch.arange(pos_len).to(torch.long)
- # 矩阵相乘,pos变成列向量,i_matrix变成行向量
- out = pos_vec[:, None] @ i_matrix[None, :]
- # 奇/偶数列
- emb_cos = torch.cos(out)
- emb_sin = torch.sin(out)
- # 赋值
- position_emb[:, 0::2] = emb_sin
- position_emb[:, 1::2] = emb_cos
- return position_emb
-
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- print(create_1d_absolute_sin_cos_embedding(4, 4))

- torch.arange():转为1维向量
- torch.pow() :实现张量和标量之间逐元素求指数操作,或者在可广播的张量之间逐元素求指数操作.
- torch.long:将tensor投射为long类型
2.DETR目标检测中的position_encoding.py
DETR中的Positional Embedding是一个固定值,Positional Embedding的代码如下,针对二维特征图的特点,DETR实现了自己的二维位置编码方式。
- # Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates. All Rights Reserved
- """
- Various positional encodings for the transformer.
- """
- import math
- import torch
- from torch import nn
-
- from util.misc import NestedTensor
-
-
- class PositionEmbeddingSine(nn.Module):
- """
- This is a more standard version of the position embedding, very similar to the one
- used by the Attention is all you need paper, generalized to work on images.
- """
- def __init__(self, num_pos_feats=64, temperature=10000, normalize=False, scale=None):
- super().__init__()
- self.num_pos_feats = num_pos_feats
- self.temperature = temperature
- self.normalize = normalize
- if scale is not None and normalize is False:
- raise ValueError("normalize should be True if scale is passed")
- if scale is None:
- scale = 2 * math.pi
- self.scale = scale
-
- def forward(self, tensor_list: NestedTensor):
- x = tensor_list.tensors
- mask = tensor_list.mask
- assert mask is not None
- not_mask = ~mask
- y_embed = not_mask.cumsum(1, dtype=torch.float32)
- x_embed = not_mask.cumsum(2, dtype=torch.float32)
- if self.normalize:
- eps = 1e-6
- y_embed = y_embed / (y_embed[:, -1:, :] + eps) * self.scale
- x_embed = x_embed / (x_embed[:, :, -1:] + eps) * self.scale
-
- dim_t = torch.arange(self.num_pos_feats, dtype=torch.float32, device=x.device)
- dim_t = self.temperature ** (2 * (dim_t // 2) / self.num_pos_feats)
-
- pos_x = x_embed[:, :, :, None] / dim_t
- pos_y = y_embed[:, :, :, None] / dim_t
- pos_x = torch.stack((pos_x[:, :, :, 0::2].sin(), pos_x[:, :, :, 1::2].cos()), dim=4).flatten(3)
- pos_y = torch.stack((pos_y[:, :, :, 0::2].sin(), pos_y[:, :, :, 1::2].cos()), dim=4).flatten(3)
- pos = torch.cat((pos_y, pos_x), dim=3).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
- return pos
-
-
- class PositionEmbeddingLearned(nn.Module):
- """
- Absolute pos embedding, learned.
- """
- def __init__(self, num_pos_feats=256):
- super().__init__()
- self.row_embed = nn.Embedding(50, num_pos_feats)
- self.col_embed = nn.Embedding(50, num_pos_feats)
- self.reset_parameters()
-
- def reset_parameters(self):
- nn.init.uniform_(self.row_embed.weight)
- nn.init.uniform_(self.col_embed.weight)
-
- def forward(self, tensor_list: NestedTensor):
- x = tensor_list.tensors
- h, w = x.shape[-2:]
- i = torch.arange(w, device=x.device)
- j = torch.arange(h, device=x.device)
- x_emb = self.col_embed(i)
- y_emb = self.row_embed(j)
- pos = torch.cat([
- x_emb.unsqueeze(0).repeat(h, 1, 1),
- y_emb.unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, w, 1),
- ], dim=-1).permute(2, 0, 1).unsqueeze(0).repeat(x.shape[0], 1, 1, 1)
- return pos
-
-
- def build_position_encoding(args):
- N_steps = args.hidden_dim // 2
- if args.position_embedding in ('v2', 'sine'):
- # TODO find a better way of exposing other arguments
- position_embedding = PositionEmbeddingSine(N_steps, normalize=True)
- elif args.position_embedding in ('v3', 'learned'):
- position_embedding = PositionEmbeddingLearned(N_steps)
- else:
- raise ValueError(f"not supported {args.position_embedding}")
-
- return position_embedding

为了使得网络感知到不同输入的位置信息,最直观的方式就是给第一个Feature赋值1 ,第二个Feature赋值2 ,但是这种赋值方式对于较大的输入是不友好的,因此有人提出使用正弦函数将值控制在−1和1 之间,但是正弦函数又具备周期性,可能会造成不同位置值相同的情况。因此作者将正弦函数扩展到d维向量,不同通道具备不同的波长.如上文公式。
换句话来说,pos是词向量在序列中的位置,而 i 是channel的index。对照代码,可以看出DETR是为二维特征图的 x 和 y 方向各自计算了一个位置编码,每个维度的位置编码长度为num_pos_feats(该数值实际上为hidden_dim的一半),对x或y,计算奇数位置的正弦,计算偶数位置的余弦,然后将pos_x和pos_y拼接起来得到一个NHWD的数组,再经过permute(0,3,1,2),形状变为NDHW,其中D等于hidden_dim。这个hidden_dim是Transformer输入向量的维度,在实现上,要等于CNN backbone输出的特征图的维度。所以pos code和CNN输出特征的形状是完全一样的。
其中的细节代码
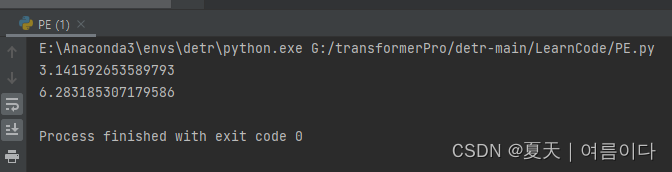
- math.pi:是 python 中 math 函数库里的一个内建函数,主要表示圆周率。
- #1:math.pi
- import math
- print(math.pi)
- scale = 2 * math.pi
- print(scale)
结果:
- NestedTensor 嵌套张量
嵌套张量与常规张量非常相似,除了形状:
-
对于正则张量,每个维度都有一个大小
-
对于嵌套张量,并非所有维度都有规则大小;其中一些是锯齿状的
嵌套张量是表示各个域中顺序数据的自然解决方案:
-
在 NLP 中,句子可以有可变长度,因此一批句子形成一个嵌套张量
-
在 CV 中,图像可以具有可变的形状,因此一批图像形成一个嵌套张量
实例:嵌套张量在transformer中
- #Transformers中使用的多头注意力组件
- import math
- import torch
- import torch.nn.functional as F
-
- device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
- #嵌套张量初始化
- nt = torch.nested_tensor([torch.randn((2, 6)), torch.randn((3, 6))], device=device)
- print(nt)
- #通过将每个底层张量填充为相同的形状,嵌套张量可以转换为常规张量。
- pt = torch.nested.to_padded_tensor(nt, padding=0.0)
- print(pt)
- """
- Args参数:
- query: query of shape 形状的查询 (N, L_t, E_q)
- key: key of shape key的形状 (N, L_s, E_k)
- value: value of shape value的形状(N, L_s, E_v)
- nheads: number of heads in multi-head attention多头注意力中的头数
- W_q: Weight for query input projection of shape (E_total, E_q)形状的查询输入投影的权重
- W_k: Weight for key input projection of shape (E_total, E_k)形状的关键输入投影的权重
- W_v: Weight for value input projection of shape (E_total, E_v)形状的价值输入投影的权重
- W_out: Weight for output projection of shape (E_out, E_total)形状的输出投影的权重
- b_q (optional): Bias for query input projection of shape E_total. Default: None b_q(可选)。形状E_total的查询输入投影的偏置。默认值。无
- b_k (optional): Bias for key input projection of shape E_total. Default: None b_k (可选): 形状E_total的关键输入投影的偏置。默认值。无
- b_v (optional): Bias for value input projection of shape E_total. Default: None b_v (可选): 形状E_total的值输入投影的偏置。默认值。无
- b_out (optional): Bias for output projection of shape E_out. Default: None b_out(可选)。形状E_out的输出投影的偏置。默认值。无
- dropout_p: dropout probability. Default: 0.0 dropout_p: dropout概率。默认值:0.0
- where:
- N is the batch size N是批次大小
- L_t is the target sequence length (jagged) L_t是目标序列的长度(锯齿状)
- L_s is the source sequence length (jagged) L_s是源序列的长度(锯齿状)
- E_q is the embedding size for query E_q是查询的嵌入大小
- E_k is the embedding size for key E_k是键的嵌入大小
- E_v is the embedding size for value E_v是值的嵌入大小
- E_total is the embedding size for all heads combined E_total is the embedding size for all heads
- E_out is the output embedding size E_out是输出嵌入的大小
- Returns返回:
- attn_output: Output of shape (N, L_t, E_out) attn_output: 形状的输出(N, L_t, E_out)
- """
- def mha_nested(query, key, value, nheads,
- W_q, W_k, W_v, W_out,
- b_q=None, b_k=None, b_v=None, b_out=None,
- dropout_p=0.0):
- N = query.size(0)
- E_total = W_q.size(0)
- assert E_total % nheads == 0, "Embedding dim is not divisible by nheads"#嵌入的dim不能被nheads分割,必须是8的倍数
- E_head = E_total // nheads
-
- # apply input projection
- # (N, L_t, E_q) -> (N, L_t, E_total)
- query = F.linear(query, W_q, b_q)
- # (N, L_s, E_k) -> (N, L_s, E_total)
- key = F.linear(key, W_k, b_k)
- # (N, L_s, E_v) -> (N, L_s, E_total)
- value = F.linear(value, W_v, b_v)
-
- # reshape query, key, value to separate by head
- # (N, L_t, E_total) -> (N, L_t, nheads, E_head) -> (N, nheads, L_t, E_head)
- query = query.reshape(-1, -1, nheads, E_head).transpose(1, 2)
- # (N, L_s, E_total) -> (N, L_s, nheads, E_head) -> (N, nheads, L_s, E_head)
- key = key.reshape(-1, -1, nheads, E_head).transpose(1, 2)
- # (N, L_s, E_total) -> (N, L_s, nheads, E_head) -> (N, nheads, L_s, E_head)
- value = value.reshape(-1, -1, nheads, E_head).transpose(1, 2)
-
- # query matmul key^T
- # (N, nheads, L_t, E_head) x (N, nheads, L_s, E_head)^T -> (N, nheads, L_t, L_s)
- keyT = key.transpose(-1, -2)
- attn_weights = torch.matmul(query, keyT)
-
- # scale down
- attn_weights = attn_weights * (1.0 / math.sqrt(E_head))
-
- # softmax
- attn_weights = F.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1)
-
- # dropout
- if dropout_p > 0.0:
- attn_weights = F.dropout(attn_weights, p=dropout_p)
-
- # attention_weights matmul value
- # (N, nheads, L_t, L_s) x (N, nheads, L_s, E_head) -> (N, nheads, L_t, E_head)
- attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, value)
-
- # merge heads
- # (N, nheads, L_t, E_head) -> (N, L_t, nheads, E_head) -> (N, L_t, E_total)
- attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2).reshape(N, -1, E_total)
-
- # apply output projection
- # (N, L_t, E_total) -> (N, L_t, E_out)
- attn_output = F.linear(attn_output, W_out, b_out)
-
- return attn_output

- mask是一个位置掩码数组,对于一个没有经过zero_pad的图像,它的mask是一个全为0的数组。
参考文献
【1】2017-Attention Is All You Need-https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf
【2】1) 트랜스포머(Transformer) - 딥 러닝을 이용한 자연어 처리 입문
【3】 理解DETR - 知乎


