- 1CentOS 6.6 升级GCC G++ (当前最新版本为v6.1.0) (完整)_g++最新版本
- 2PyQt5初学试验记录(三):Pyinstaller打包小结_pyinstaller pyqt5 no such file or directory: qcand
- 3记一次oracle分组后再分页查询_oracle分组后分页查询
- 4Spark Core(十五)Executor执行Task的原理与源码分析(一)_spark executor 进程 task 线程
- 5(四)Resquest 知识点总结 (来自那些年的笔记)_restquest
- 6MobileNet系列(4):MobileNetv3网络详解
- 7The hvigorVersion version (2.1.1) is not within theexpected range 3.x.x (3.x.x >= 3.0.9)._cause: the @ohos/hvigor-ohos-plugin version () is
- 8用python编写两个正整数的最大公约数和最小公倍数的小程序_python任务描述 本关任务:编写一个能求两个正整数的最大公约数和最小公倍数的小程
- 9【Ubuntu-20.04】OpenCV-3.4.16的安装并对图片与视频处理
- 10win10下在虚拟机中下载安装ubuntu16、下载安装Anaconda以及apt/pip/conda换源等系列操作_apt anaconda
鸿蒙Harmony-PersistentStorage--持久化存储UI状态储详解_鸿蒙 持久化保存
赞
踩
用简单的心境,对待复杂的人生,方能看淡得失,从容入世,潇洒自如,心变得简单了,世界也就简单了
目录
一,定义
LocalStorage和AppStorage都是运行时的内存,但是在应用退出再次启动后,依然能保存选定的结果,是应用开发中十分常见的现象,这就需要用到PersistentStorage。
PersistentStorage是应用程序中的可选单例对象。此对象的作用是持久化存储选定的AppStorage属性,以确保这些属性在应用程序重新启动时的值与应用程序关闭时的值相同。
PersistentStorage将选定的AppStorage属性保留在设备磁盘上。应用程序通过API,以决定哪些AppStorage属性应借助PersistentStorage持久化。UI和业务逻辑不直接访问PersistentStorage中的属性,所有属性访问都是对AppStorage的访问,AppStorage中的更改会自动同步到PersistentStorage。
PersistentStorage和AppStorage中的属性建立双向同步。应用开发通常通过AppStorage访问PersistentStorage,另外还有一些接口可以用于管理持久化属性,但是业务逻辑始终是通过AppStorage获取和设置属性的。
二,限制条件
PersistentStorage允许的类型和值有:
number, string, boolean, enum等简单类型。- 可以被
JSON.stringify()和JSON.parse()重构的对象。例如Date, Map, Set等内置类型则不支持,以及对象的属性方法不支持持久化。
PersistentStorage不允许的类型和值有:
- 不支持嵌套对象(对象数组,对象的属性是对象等)。因为目前框架无法检测AppStorage中嵌套对象(包括数组)值的变化,所以无法写回到PersistentStorage中。
- 不支持
undefined和null。
持久化数据是一个相对缓慢的操作,应用程序应避免以下情况:
-
持久化大型数据集。
-
持久化经常变化的变量。
PersistentStorage的持久化变量最好是小于2kb的数据,不要大量的数据持久化,因为PersistentStorage写入磁盘的操作是同步的,大量的数据本地化读写会同步在UI线程中执行,影响UI渲染性能。如果开发者需要存储大量的数据,建议使用数据库api。
PersistentStorage和UIContext相关联,需要在UIContext明确的时候才可以调用,如果没有在UIContext明确的地方调用,将导致无法持久化数据。
三,使用
父组件
- import ProvideTest from './ProvideTest';
-
- PersistentStorage.PersistProp('yuanzhen', 100);
-
- @Entry()
- @Component
- struct Index {
- @StorageLink("yuanzhen") yuanzhen:number =888
-
- build() {
- Column(){
- Text("父name:" + this.yuanzhen)
- .fontSize(50)
- .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.yuanzhen=999
- })
- ProvideTest()
- }
- }
- }
子组件
- @Component
- export default struct ProvideTest {
-
- @StorageLink("yuanzhen")yuanZhen:number =1000
-
- build() {
- Row() {
- Column() {
- Text("子name:"+this.yuanZhen)
- .fontSize(50)
- .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
- .onClick(() => {
- this.yuanZhen=123456
- })
- }.width('100%')
- }.height('100%')
- }
- }
运行
 点击父
点击父 点击子
点击子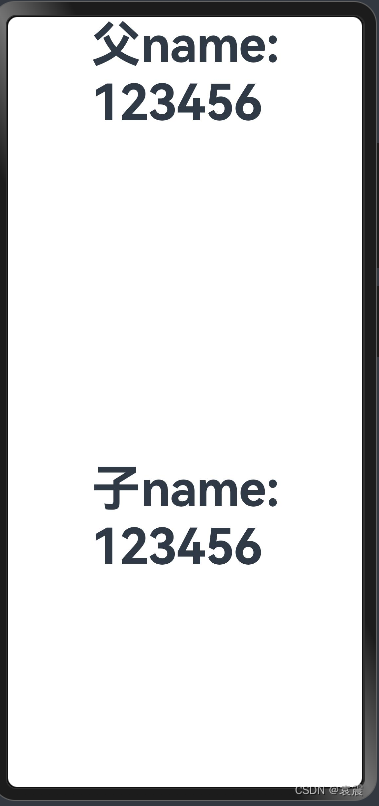
新应用安装后首次启动运行:
- 调用persistProp初始化PersistentStorage,首先查询在PersistentStorage本地文件中是否存在“yuanzhen”,查询结果为不存在,因为应用是第一次安装。
- 接着查询属性“yuanzhen”在AppStorage中是否存在,依旧不存在。
- 在AppStorge中创建名为“yuanzhen”的number类型属性,属性初始值是定义的默认值100。
- PersistentStorage将属性“yuanzhen”和值100写入磁盘,AppStorage中“yuanzhen”对应的值和其后续的更改将被持久化。
- 在Index组件中创建状态变量@StorageLink(‘yuanzhen’) yuanzhen,和AppStorage中“yuanzhen”双向绑定,在创建的过程中会在AppStorage中查找,成功找到“yuanzhen”,所以使用其在AppStorage找到的值47。


