- 1hive中行转列,列转行的各种情况及解决方法_hive 行转列几种方法
- 25-1对抗生成神经网络(GAN)--Keras实现_对抗神经网络python keras
- 3设计模式-解释器模式(Interpreter)_设计模式 解释器模式
- 4网络安全技术入门到项目实战_微职位 网络安全技术入门到项目实战视频教程解压密码
- 5burp2023专业版,配置上游代理太难找_burpsuite2023
- 6大数据处理实验(三)HDFS基本操作实验_hdfs的基本操作大学实验
- 7VS Code工具将json数据格式化_vscode json格式化
- 8关于YOLOv5_deepsort训练自己的数据集_deepsort训练自己的特征权重文件
- 9unity android录制视频教程,Unity移动端视频录制,Android和IOS都支持
- 10优雅停机方案
Dijkstra 算法求单源最短路径_基于dijsktra算法的最短路径求解
赞
踩
1.最短路径
在一个连通图中,从一个顶点到另一个顶点间可能存在多条路径,而每条路径的边数并不一定相同。如果是一个带权图,那么路径长度为路径上各边的权值的总和。两个顶点间路径长度最短的那条路径称为两个顶点间的最短路径,其路径长度称为最短路径长度。
最短路径在实际中有重要的应用价值。如用顶点表示城市,边表示两城市之间的道路,边上的权值表示两城市之间的距离。那么城市A到城市B连通的情况下,哪条路径距离最短呢,这样的问题可以归结为最短路径问题。
求最短路径常见的算法有Dijkstra算法和Floyd算法。本文将详细讲解Dijkstra算法的原理和实现。
2.Dijkstra 算法
2.1 简介
Dijkstra 算法是由 E.W.Dijkstra 于1959年提出,又叫迪科斯彻算法,它应用了贪心算法思想,是目前公认的最好的求解最短路径的方法。
算法解决的是有带权连通图(带权有向图也可以)中单个源点到其他顶点的最短路径问题,所以也叫作单源最短路径算法。其主要特点是每次迭代时选择的下一个顶点是标记点之外距离源点最近的顶点。可以求出源点到其他所有点的最短路径,当然也可以指定源点和目标点,求两点之间的最短路径。其做法是迭代至目标点被标记时结束。
2.2 算法思想
Dijkstra 算法的基本思路是先将与起点有边直接相连的节点到起点的距离记为对应的边的权重值,将与起点无边直接相连的节点到起点的距离记为无穷大。然后以起点为中心向外层层扩展,计算所有节点到起点的最短距离。每次新扩展到一个距离最短的点后,更新与它有边直接相邻的节点到起点的最短距离。当所有点都扩展进来后,所有节点到起点的最短距离将不会再被改变,因而保证了算法的正确性。
2.3 算法基本过程
Dijkstra 算法求解单源最短路径问题的基本步骤如下:
(1)设立U 和Y两个节点集合, Y用于保存所有未被访问的节点,U 记录所有已经访问过的节点。已经被访问指的是节点已经被纳入最短路径中。
(2)从Y中找出距离起点最近的节点,放入U中,并更新与这个节点有边直接相连的相邻节点到起始节点的最短距离。
(3)重复步骤(2)直到Y集合为空,即从起点出发可以到达的所有顶点都在集合U中为止。
Dijkstra 算法的基本思想和求解步骤决定了Dijkstra算法只能解决最基本的在起点和终点之间求最短路径的问题,无法解决添加了其他限制条件的,如要求经过指定中间节点集的最短路径问题,Dijkstra 算法是无法直接解决的。
2.4 算法实例过程描述
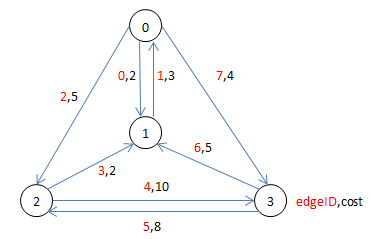
已经带权有向图G如下图所示,现求节点2到节点3的最短路径。这里要求节点ID从0开始并且连续编号,且边的权值大于0。后面的代码实现也是要遵循这两个前提条件的。
如果两个节点见未直接相连,则节点间的距离设为无穷大,可用一个很大的数表示。
图中红色数字表示边的ID,圆圈中的数字为节点ID,边旁边的黑色数字表示节点间边的权值。并且所有ID均不重复。
(1)初始时,标记起点2为已访问的节点,并置于集合U中,此时集合U={2},集合Y={0,1,3}。
且初始化其它节点到起点2的距离distance[N]数组,N表示图中节点数。distance[N]数组不仅需要保存其它节点到起点2的距离,也要保存起点2到达该节点的最短路径的最后一个中间节点,这里称为当前节点的前节点。如果没有前一个节点则设为-1。
此时,distance[N]数组初始化为 {distance[0]={∞,-1}, distance[1]={2,2}, distance[2]={0,-1}, distance[3]={10,2}}。标粗的表示该节点已经置于集合U中。
(2)在集合Y中找出距离起点2最短的节点,遍历数组distance[N]得节点1距离起点2最近,并将其加入集合U中。此时集合U={2,1},集合Y={0,3}。
(3)以新加入集合U的节点1为中间节点,更新起点2到其它节点之间的最短距离。
对节点0,因为节点2到节点0的距离为无穷大∞,大于起点2通过节点1到节点0的距离2+3=5,并且节点0的前屈节点变为1,所以更新distance[0]={5,1};
对节点3,同理,因为节点2到节点3的距离为10,小于节点2通过节点1到节点3的距离1+∞=∞,所以无需更新。
所以,更新完之后的distance[N]取值情况为:{distance[0]={5,1}, distance[1]={2,2}, distance[2]={0,-1}, distance[3]={10,2}}。
(4)重复步骤2,继续在集合Y中寻找距离起点2最短的节点,并访问它。遍历数组distance[N]知道节点0到起点2的距离最短为5,其节点0加入集合U中。此时集合U={2,1,0},集合Y={3}。
(5)重复步骤3,以节点0为中间节点更新集合Y中节点到起点2的距离。因为distance[0].first+matrix[0][3]=5+4=9,小于distance[3].first=10,所以更新distance[3]={9,0}。
此时distance[N]取值情况为:{distance[0]={5,1}, distance[1]={2,2}, distance[2]={0,-1}, distance[3]={9,0}}。
(6)重复步骤2,再集合Y中找出距离起点2最近的节点,遍历distance[N]可知节点3距离最近,并将其纳入集合U中。此时集合U={2,1,0,3},集合Y={}。
(7)重复步骤3,以节点3为中间节点更新集合Y中节点到起点2的距离,此时发现集合Y为空,过程结束。
最后我们获得了加入集合U的所有节点,因为没有节点都记录了自己的前驱节点,所以可以获得从起点到任意目的节点见的最短路径。
3.具体实现
以上面的描述为基础,编码实现Dijkstra算法。
3.1 输入
(1)图的信息
文件Graph(以逗号为分隔符的文本文件)给出图的数据,文件每行以换行符(ASCII’\n’即0x0a)为结尾。
图的数据中,每一行包含如下的信息:
EdgeID,SourceID,DestinationID,Cost
其中,EdgeID为该有向边的索引,SourceID为该有向边的起始顶点的索引,DestinationID为该有向边的终止顶点的索引,Cost为该有向边的权重。顶点与有向边的索引均从0开始编号,这里要求连续,且保证索引不重复。
(2)起点与终点
程序运行过程中,输入起点和终点。
3.2 输出
打印输出起点至终点间最短路径顺序经过的节点,并且输出最短路径的长度,即边的权值和。
3.3 相关数据结构
(1)图的存储结构
图采用邻接矩阵存储,由图的信息构造。
(2)集合U和Y
没有实际存储,逻辑的在图邻接矩阵对角线的bool值来表示在集合U还是在集合Y。比如邻接矩阵matrix[2][2]初始时为0,即自己到自己的距离是0。当被纳入集合U中,将其matrix[2][2]设置为1即可。
(3)distance[N]
distance[N]记录了未被纳入最短路径的集合Y中的节点距离起点的最短距离,以及它的前驱节点。因为是二元信息组,所以采用C++的STL标准模板库中的键值对容器pair。pair< int,int>第一个元素表示节点ID,第二元素表示该节点的前驱节点。
(4)起点到其它所有节点的最短路径
采用map< int,int>容器存储。如果再给定任意非起点的节点作为终点,即可从起点到其它所有节点的最短路径找出起点到终点的最短路径,并且根据关系矩阵求出最短路径的长度。
##3.4时间复杂度
算法中构造邻接矩阵的时间复杂度是
O
(
n
2
)
O(n^2)
O(n2),求最短路径部分又两层循环构成,外循环n-1次,内循环为n次,所以时间复杂度为
O
(
n
2
)
O(n^2)
O(n2),因此总的时间复杂度为
O
(
n
2
)
O(n^2)
O(n2)。这里的n表示图的节点数。
3.5 具体实现
Dijkstra算法核心代码:
/************************************************** func:求带权有向图的单源最短路径; para:matrix:图的邻接矩阵;nodeNum:图的节点数;startID:起始节点;shortestPath:最短路径; retu:0:成功;-1:失败,表明从起点出发有不可到达的节点 **************************************************/ int djkstra(int* (*matrix),int nodeNum,int startID,map<int,int>& shortestPath){ if(matrix==NULL||nodeNum<1||startID<0||startID>nodeNum-1) return -1; shortestPath.insert(make_pair(startID,-1));//startID为路径起点,进入容器 matrix[startID][startID]=1;//表示顶点startID在集合U中 pair<int,int>* distance=new pair<int,int>[nodeNum];//顶点startID到其它定点距离,后一个int表示当前节点的前一个节点 memset(distance,0,nodeNum*sizeof(pair<int,int>)); //初始化startID到集合Y中顶点的距离值 for(int i=0;i<nodeNum;++i){ if(i==startID) continue; distance[i]=make_pair(matrix[startID][i],-1); if(matrix[startID][i]!=INFINITY) distance[i].second=startID; } //循环的次数是Y集合中的定点数,去除起点,只有nodeNum-1个 for(int i=0;i<nodeNum-1;++i){ int minID=0,minWeight=INFINITY; for(int j=0;j<nodeNum;++j){ if(j==startID) continue; if(matrix[j][j]!=1&&distance[j].first<minWeight){ minWeight=distance[j].first; minID=j; } } if(minWeight==INFINITY) return -1; //从startID=0到集合V-U中没有路径 shortestPath.insert(make_pair(minID,distance[minID].second)); matrix[minID][minID]=1; //设置为已访问 //更新顶点startID通过顶点minID到集合V-U中的定点的最短距离 for(int j=0;j<nodeNum;++j){ if(matrix[j][j]!=1){ if(distance[j].first>distance[minID].first+matrix[minID][j]){ distance[j].first=distance[minID].first+matrix[minID][j]; distance[j].second=minID; } } } } delete[] distance; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
求给定终点的最短路径:
/************************************************** func:求给定终点的最短路径以及路径长度 para:matrix:图的邻接矩阵;startID:起点;endID:终点;shortestTwoNode:两点间的最短路径;shortestPath:起点到其它所有节点的最短路径;minWeight:两点间最短路径长度 retu:成功返回0,失败返回-1 **************************************************/ int getShortestPath(int* (*matrix),int startID,int endID,list<int>& shortestTwoNode,map<int,int>& shortestPath,int& minWeight){ if(startID==endID||startID<0||endID<0) return -1; std::stack<int> nodeS; map<int,int>::iterator it=shortestPath.find(endID); while(it!=shortestPath.end()){ nodeS.push((*it).first); if(it->first==startID) break; it=shortestPath.find(it->second); } while(!nodeS.empty()){ int topEle=nodeS.top(); nodeS.pop(); shortestTwoNode.push_back(topEle); if(!nodeS.empty()) minWeight+=matrix[topEle][nodeS.top()]; } return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
相关辅助函数:
//qsort函数需要的比较函数,按照升序排序 int comp(const void*a,const void*b) { return *(int*)a-*(int*)b; } //按指定分隔符分割字符串 //src:源字符串 delimiter:分隔符集合 vector<string> split(const string& src,const string& delimiter) { vector<string> strRes; if(src=="") return strRes; int maxSubstrNum=src.size(); int* pos=new int[maxSubstrNum]; memset(pos,NULL,maxSubstrNum*sizeof(int)); int j=0; for(int i=0;i<delimiter.size();++i) { string::size_type index=src.find(delimiter[i]); while(index!=string::npos) { pos[j++]=index; index=src.find(delimiter[i],index+1); } } //排序 qsort(pos,j,sizeof(int),comp); //取出第一个子串 string substrFir=src.substr(0,pos[0]); if(substrFir!="") strRes.push_back(substrFir); //取出中间j-1个子串 for(int i=0;i<j-1;++i) { string substr=src.substr(pos[i]+1,pos[i+1]-pos[i]-1); if(substr!="") strRes.push_back(substr); } //取出最后一个子串 string substrLast=src.substr(pos[j-1]+1,src.size()-pos[j-1]-1); if(substrLast!="") strRes.push_back(substrLast); delete[] pos; return strRes; } //根据输入文件读取图的边信息 int getEdge(char* filePath,vector<Edge>& edgeVec){ if(filePath==NULL||*filePath=='\0') return -1; char buffer[32]=""; Edge edgeTemp; memset(&edgeTemp,0,sizeof(Edge)); ifstream graph(filePath); if(graph.is_open()){ while(graph.peek()!=EOF){ graph.getline(buffer,32,'\n'); vector<string> edgeInfo=split(buffer,","); if(edgeInfo.size()!=4) return -1; edgeTemp.linkID=atoi(edgeInfo[0].c_str()); edgeTemp.start=atoi(edgeInfo[1].c_str()); edgeTemp.end=atoi(edgeInfo[2].c_str()); edgeTemp.cost=atoi(edgeInfo[3].c_str()); edgeVec.push_back(edgeTemp); } graph.close(); return 0; }else return -1; } //根据图的边信息构造邻接矩阵 int getMatrix(vector<Edge>& edgeVec,int* (*&matrix),int& nodeNum){ set<int> nodeSet; for(int i=0;i<edgeVec.size();++i){ nodeSet.insert(edgeVec[i].start); nodeSet.insert(edgeVec[i].end); } nodeNum=nodeSet.size(); matrix=new int*[nodeNum]; memset(matrix,0,nodeNum*sizeof(int*)); for(int i=0;i<nodeNum;++i){ matrix[i]=new int[nodeNum]; memset(matrix[i],0,sizeof(int)*nodeNum); } //为关系矩阵赋值 for(int row=0;row<nodeNum;++row){ for(int colum=0;colum<nodeNum;++colum){ if(row==colum) matrix[row][colum]=0; else{ vector<Edge>::iterator it=find(edgeVec.begin(),edgeVec.end(),Edge(0,row,colum,0)); if(it!=edgeVec.end()){ matrix[row][colum]=it->cost; }else{ matrix[row][colum]=INFINITY; } } } } return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
main函数
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> #include <list> #include <algorithm> #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <stack> using namespace std; #define INFINITY 0x0fffffff struct Edge{ int linkID; int start; int end; int cost; Edge(){ this->linkID=0; this->start=0; this->end=0; this->cost=0; } Edge(int linkID,int start,int end,int cost){ this->linkID=linkID; this->start=start; this->end=end; this->cost=cost; } bool operator==(const Edge& edge) const{ return edge.start==start && edge.end == end;//这里可以自定匹配个数 } }; vector<Edge> edgeVec; //带权有向图边的集合 int main(int argc,char* argv[]){ if(argc!=2) return -1; vector<Edge> edgeVec; getEdge(argv[1],edgeVec); int* (*matrix)=NULL; int nodeNum=0; getMatrix(edgeVec,matrix,nodeNum);//构造关系矩阵 map<int,int> shortestPath; //起点到所有其他节点的最短路径 list<int> shortestTwoNode; //起点到终点的最短路径 int shortestTwoNodeWeight=0; int startID=0,endID=0; cout<<"input startID endID"<<endl; cin>>startID>>endID; int res=djkstra(matrix,nodeNum,startID,shortestPath); if(res==-1) cout<<"get shortest path start from "<<startID<<" failed "<<endl; else getShortestPath(matrix,startID,endID,shortestTwoNode,shortestPath,shortestTwoNodeWeight); cout<<startID<<" to "<<endID<<":"; for(list<int>::iterator it=shortestTwoNode.begin();it!=shortestTwoNode.end();++it){ cout<<*it<<" "; } cout<<endl; cout<<"weight:"<<shortestTwoNodeWeight<<endl; getchar(); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
3.6 实验结果
以上面描述的图为例,输入图的信息文本文件如下:
0,0,1,2
1,1,0,3
2,0,2,5
3,2,1,2
4,2,3,10
5,3,2,8
6,3,1,5
7,0,3,4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
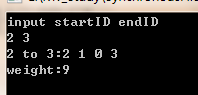
求节点2到节点3的最短路径,输出结果如下:
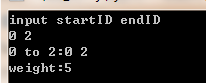
再求节点0到2的最短路径,输出结果如下:
4.小结
(1)本文实现的Djkstra求单源最短路径,在具体实现上采用邻接矩阵存储图的信息,所以要求节点索引均从0开始编号且连续。这一点需要改进,可采取邻接表存储图的信息。
(2)本文将图的信息单独存储在文本文件中,将程序的输入与代码分离,降低了耦合性,提升了程序的扩展性。
(3)本文的做法是将起点到其它所有节点的最短路径求出后再求给定的终点与起点之间的最短路径,其实可以不必如此。具体做法是在访问到给定的终点时,停止求起点到其它节点的最短路径,可提高算法性能。
(4)书写过程难免误笔,请网友留言指正。
参考文献
经过指定的中间节点集的最短路径算法[J].黄书力,胡大裟,蒋玉明.计算机工程与应用:2015,51(11).
算法与数据结构.C语言第二版.张乃孝.高等教育出版社.
Dijkstra算法详解 - CSDN