- 1基于深度学习的轮廓匹配
- 2python开发抢票软件_12306抢票软件run python版
- 3Ipython和Jupyter Notebook介绍_ipython notebook
- 4用Python 来做Cluster Analysis_python中cluster analysis 的源代码
- 5使用Visual Studio Code调试Unity_vscode调试unity
- 6基于FPGA的简单数字钟设计VHDL代码Quartus仿真_24进制计数器vhdl代码
- 7【机器学习】预测宽带客户流失(决策树、随机森林 )_一种博弈论辅助的机器学习算法检测用户流失行为
- 8RecyclerView 水平滚动+自动循环轮播_recuclerview循环轮播
- 9大数据学习(6)-hive底层原理Mapreduce_hive mapreduce原理
- 10VMware下安装的Mac OS X如何修改显示分辨率_vmware安装osx,分辨率1024*768
C++14新特性总结
赞
踩
一、语言特性
1.1 函数返回类型推导
如下,声明一个返回类型为auto的函数,让它依据函数调用时传入的参数进行推导,指定C++11标准进行编译,我用的是clang编译器,编译命令为:clang++ -std=c++11 1.1.cpp,发现会有编译错误,并且报告说这是C++14的新特性,如下:
/**
* @file 1.1.cpp
* @brief
* @author YongDu
* @date 2021-07-18
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
auto func(int i) { return i; }
int main() {
cout << func(4) << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

用C++14编译:clang++ -std=c++14 1.1.cpp,发现没有问题,程序也正常执行。
同时,返回值类型也可以用在模板中,不像C++11需要使用尾置返回类型:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T1, typename T2> auto Sum(T1 t1, T2 t2) { return t1 + t2; } int main() { cout << Sum(2, 3) << endl; cout << Sum(1.1, 2.2) << endl; return 0; } // 5 // 3.3
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
注意:
- 函数内如果有多个返回语句,它们必须返回相同的类型,否则编译失败
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
auto func(bool flag) {
if (flag)
return 1;
else
return 2.2;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

- 如果return语句返回初始化列表,返回值类型推导也会失败
auto func() { return {1, 2, 3}; }
// error: cannot deduce return type from initializer list
- 1
- 2
- 虚函数不能使用返回值类型推导
struct A {
virtual auto func() {}
};
// error: function with deduced return type cannot be virtual
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
返回类型声明可以用在前向声明,但是在使用它们之前,翻译单元中必须能够得到函数定义
-
返回类型推导可以用在递归函数中,但是递归调用必须至少以一个返回语句作为先导,以便编译器推导出返回类型
auto fib(int n) {
if (0 == n || 1 == n) {
return n;
}
return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
1.2 变量模板
C++14支持变量模板,如下:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template <class T> constexpr T pi = T(3.1415926535897932385L); // 变量模板 template <class T> T circular_area(T r) { // 函数模板 return pi<T> * r * r; // pi<T> 是变量模板实例化 } int main() { cout << circular_area(2) << endl; // 12 cout << circular_area(2.0) << endl; // 12.5664 return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
1.3 别名模板
template <typename T, typename U> struct A { T t; U u; }; template <typename T> using B = A<T, int>; int main() { B<double> b; b.t = 10; b.u = 20; cout << b.t << ", " << b.u << endl; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
1.4 泛型lambda和lambda初始化捕获
在C++11中,lambda表达式参数需要使用具体的类型说明:
auto f = [] (int a) { return a; };
- 1
在C++14中,对此进行优化,lambda表达式参数可以为auto类型,类似于函数模板:
auto f = [](auto a) { return a; };
cout << f(1) << endl;
cout << f(1.1) << endl;
- 1
- 2
- 3
在C++14中,我们可以对捕获列表的捕获变量“赋值”。如下代码:
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 2;
[a = sin(a)]() {
cout << a << endl; // 0.909297
cout << cos(a) << endl; // 0.6143
}();
cout << a << endl; // 2
cout << cos(a) << endl; // -0.416147
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
C++14中的这个新特性允许了在捕获列表中定义前面没有出现过的变量,但必须赋予一个值,并且不使用类型说明符和auto,类型由编译器自动推断。
1.5 constexpr函数
C++11中的常量表达式函数:

如下代码:
constexpr int factorial(int n) { // 在C++11或者C++14中均可以编译通过
return n <= 1 ? 1 : (n * factorial(n - 1));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
constexpr int factorial(int n) { // 只有在C++14中可以编译通过
int ret = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
ret *= i;
}
return ret;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
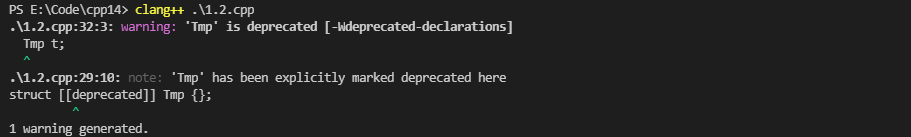
1.6 [[deprecated]]标记
C++14中增加了[[deprecated]]标记,可以修饰类、函数、变量等,当程序中使用了被其修饰的模块时,编译器会产生告警,提示用户该标记标记的内容将来可能会被废弃,尽量不要使用。
struct [[deprecated]] Tmp {};
- 1
1.7 二进制字面量和数位分隔符
int a = 0b0001'0011'1010;
double b = 3.14'1234'1234'1234;
- 1
- 2
二、库相关
2.1 std::make_unique
C++11中没有std::make_unique,在C++14中实现了这个方法。
struct A {};
std::unique_ptr<A> ptr = std::make_unique<A>();
- 1
- 2
2.2 std::shared_timed_mutex和std::shared_lock
C++14中通过std::shared_timed_mutex和std::shared_lock实现读写锁,保证多个线程可以同时读,但是写线程必须独立运行,写操作不能和读操作同时进行。
struct ThreadSafe { mutable std::shared_timed_mutex _mutex; int _value; ThreadSafe() { _value = 0; } int get() const { std::shared_lock<std::shared_timed_mutex> loc(_mutex); return _value; } void increase() { std::unique_lock<std::shared_timed_mutex> lock(_mutex); _value += 1; } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
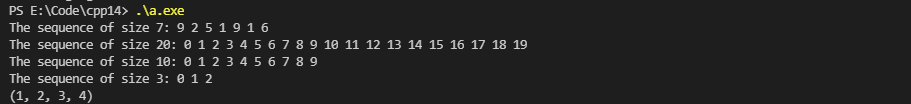
2.3 std::integer_sequence
#include <array> #include <iostream> #include <tuple> #include <utility> template <typename T, T... ints> void print_sequence(std::integer_sequence<T, ints...> int_seq) { std::cout << "The sequence of size " << int_seq.size() << ": "; ((std::cout << ints << ' '), ...); std::cout << '\n'; } // 转换数组为 tuple template <typename Array, std::size_t... I> auto a2t_impl(const Array &a, std::index_sequence<I...>) { return std::make_tuple(a[I]...); } template <typename T, std::size_t N, typename Indices = std::make_index_sequence<N>> auto a2t(const std::array<T, N> &a) { return a2t_impl(a, Indices{}); } // 漂亮地打印 tuple template <class Ch, class Tr, class Tuple, std::size_t... Is> void print_tuple_impl(std::basic_ostream<Ch, Tr> &os, const Tuple &t, std::index_sequence<Is...>) { ((os << (Is == 0 ? "" : ", ") << std::get<Is>(t)), ...); } template <class Ch, class Tr, class... Args> auto &operator<<(std::basic_ostream<Ch, Tr> &os, const std::tuple<Args...> &t) { os << "("; print_tuple_impl(os, t, std::index_sequence_for<Args...>{}); return os << ")"; } int main() { print_sequence(std::integer_sequence<unsigned, 9, 2, 5, 1, 9, 1, 6>{}); print_sequence(std::make_integer_sequence<int, 20>{}); print_sequence(std::make_index_sequence<10>{}); print_sequence(std::index_sequence_for<float, std::iostream, char>{}); std::array<int, 4> array = {1, 2, 3, 4}; // 转换 array 为 tuple auto tuple = a2t(array); static_assert(std::is_same<decltype(tuple), std::tuple<int, int, int, int>>::value, ""); // 打印到 cout std::cout << tuple << '\n'; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
2.4 std::exchange
#include <iostream> #include <utility> #include <vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int> vec1{1, 2, 3, 4}; vector<int> vec2{5, 6, 7, 8}; cout << "exchange before: " << endl; cout << "vec1: " << endl; copy(vec1.begin(), vec1.end(), ostream_iterator<int>{cout, " "}); cout << endl << "vec2: " << endl; copy(vec2.begin(), vec2.end(), ostream_iterator<int>{cout, " "}); exchange(vec1, vec2); cout << endl << "exchange after: " << endl; cout << "vec1: " << endl; copy(vec1.begin(), vec1.end(), ostream_iterator<int>{cout, " "}); cout << endl << "vec2: " << endl; copy(vec2.begin(), vec2.end(), ostream_iterator<int>{cout, " "}); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26

MSVC编译器的实现:
// FUNCTION TEMPLATE exchange
template <class _Ty, class _Other = _Ty>
_CONSTEXPR20 _Ty exchange(_Ty& _Val, _Other&& _New_val) noexcept(
conjunction_v<is_nothrow_move_constructible<_Ty>, is_nothrow_assignable<_Ty&, _Other>>) /* strengthened */ {
// assign _New_val to _Val, return previous _Val
_Ty _Old_val = static_cast<_Ty&&>(_Val);
_Val = static_cast<_Other&&>(_New_val);
return _Old_val;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
2.5 std::quoted
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string str{"hello world"};
std::cout << str << std::endl; // hello world
std::cout << std::quoted(str) << std::endl; // "hello world"
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11



