- 1Window系统下安装python并运行hello world_python releases for windows
- 2Gradle 设置代理及不代理_gradle 配置代理
- 3slowfast实现行为识别_slowfast行为
- 4FreeCAD傻瓜式教程之约束设定、构建实体、开孔、调整颜色、透明度、参考距离、任意修改尺寸、保持开孔居中、外部图形、基准平面等_freecad 教程
- 5【0002day】citespace知网教程_citespace知网文献导出
- 6测试必备技能:如何才能正确解读并发数?
- 7神器级别的BT磁力搜索网站_btdigg
- 82024(20届)数据科学与大数据专业毕业设计选题合集_数据科学与大数据技术 专业 本科论文选题方向_数据科学与大数据技术专业毕业论文题目,论文题目
- 9使用FastAPI同时搭建WebSocket服务端和HTTP服务端
- 10创建一个简单的区块链,并使用 Flask 框架提供一个简单的 Web 接口来与区块链交互。(持续更新)_区块链接口
Android Studio的笔记--SerialPort串口通讯学习和使用_android serialport
赞
踩
摘要:本篇介绍android中SerialPort串口通讯学习和使用。主要用到android-serialport-api。
SerialPort
几个工程参考学习使用
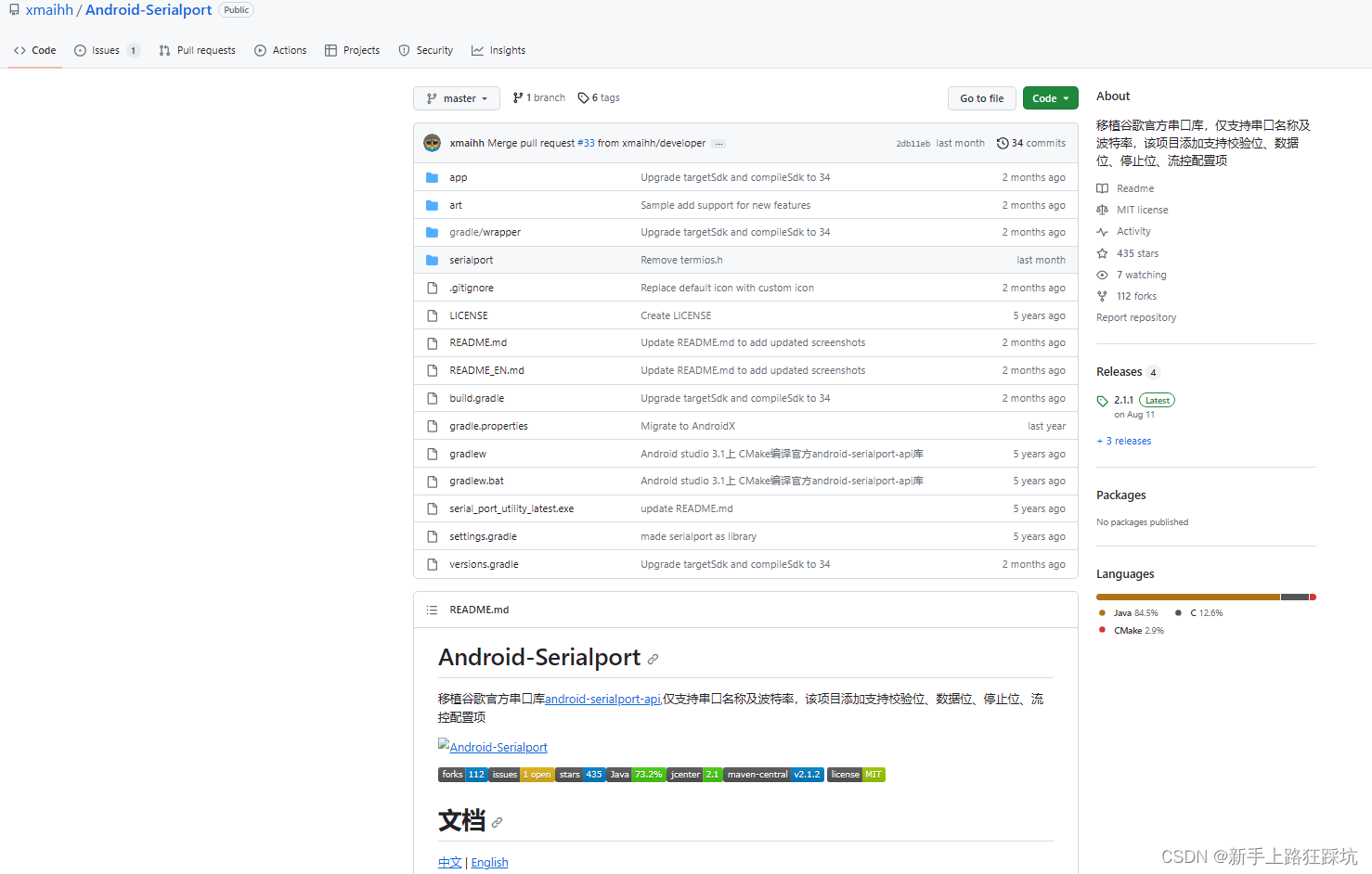
android-serialport-api
Google开源的Android串口通信Demo android-serialport-api
源码下载
cepr/android-serialport-api
SerialPort获取串口输入输出流
SerialPortFinder获取硬件地址
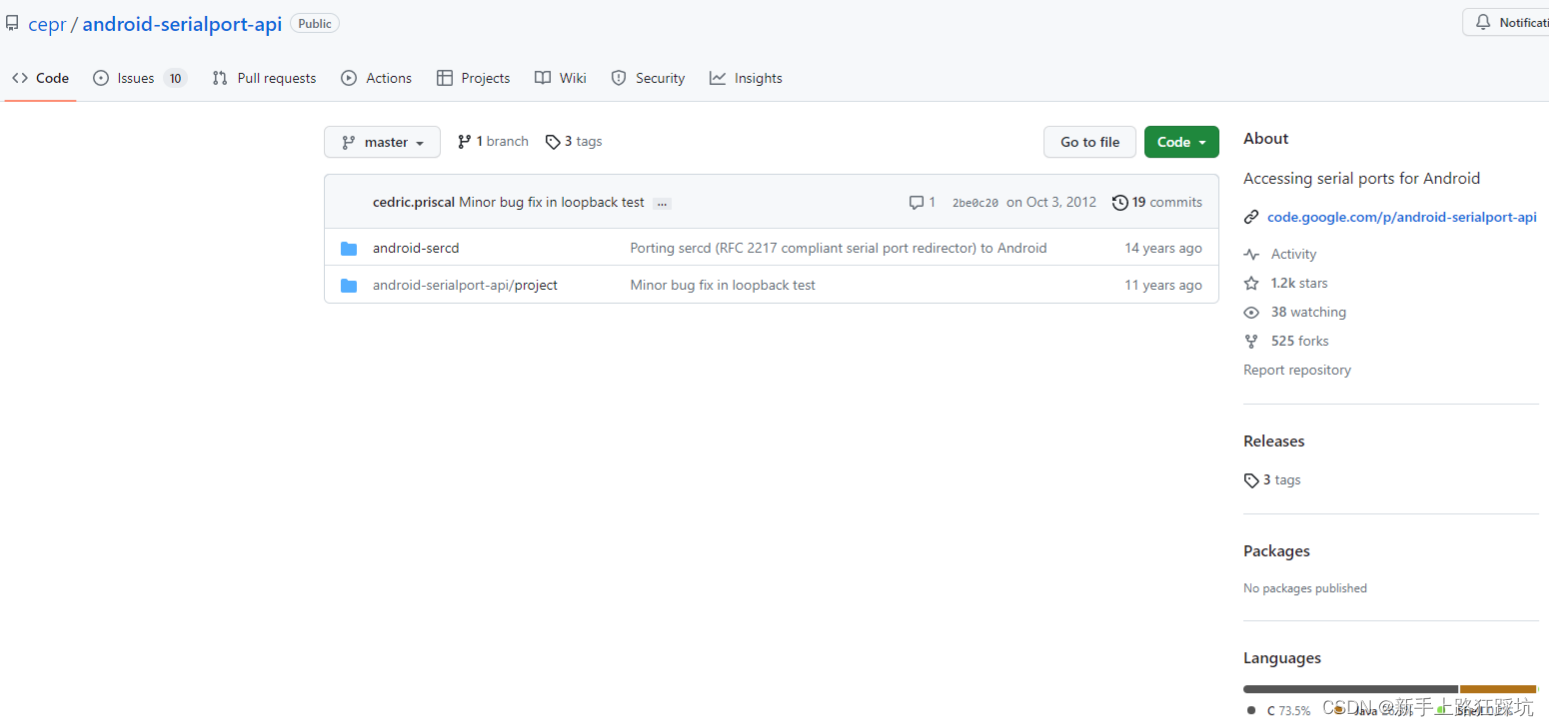
可以推荐看android串口通信——android-serialport-api 源
Android-SerialPort-API
源码下载
licheedev/Android-SerialPort-API
readme
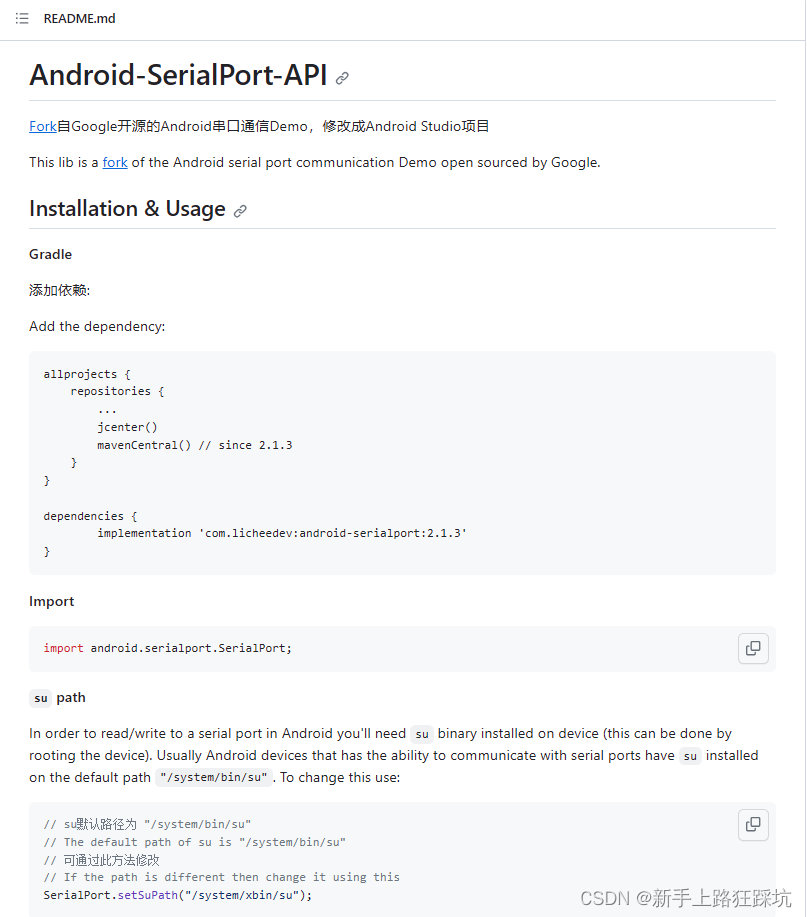

版本
添加依赖:implementation ‘com.licheedev:android-serialport:2.1.3’
allprojects {
repositories {
...
jcenter()
mavenCentral() // since 2.1.3
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
dependencies {
implementation 'com.licheedev:android-serialport:2.1.3'
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
除了选择2.1.3版本,还可以看 releases 选择其他版本。
Android-SerialPort-Tool
源码下载
licheedev/Android-SerialPort-Tool
Android-Serialport
源码下载
使用方法
Android移植谷歌官方串口库支持校验位、数据位、停止位、流控配置
1. 检验参数合法性 /* Check arguments */ { speed = getBaudrate(baudrate); if (speed == -1) { /* TODO: throw an exception */ LOGE("Invalid baudrate"); return NULL; } } 2. 打开串口 /* Opening device */ { jboolean iscopy; const char *path_utf = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, path, &iscopy); LOGD("Opening serial port %s with flags 0x%x", path_utf, O_RDWR | flags); fd = open(path_utf, O_RDWR | flags); LOGD("open() fd = %d", fd); (*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env, path, path_utf); if (fd == -1) { /* Throw an exception */ LOGE("Cannot open port"); /* TODO: throw an exception */ return NULL; } } 3.配置波特率 /* Configure device */ { struct termios cfg; LOGD("Configuring serial port"); if (tcgetattr(fd, &cfg)) { LOGE("tcgetattr() failed"); close(fd); /* TODO: throw an exception */ return NULL; } cfmakeraw(&cfg); cfsetispeed(&cfg, speed); cfsetospeed(&cfg, speed); 4.配置数据位 cfg.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; switch (dataBits) { case 5: cfg.c_cflag |= CS5; //使用5位数据位 break; case 6: cfg.c_cflag |= CS6; //使用6位数据位 break; case 7: cfg.c_cflag |= CS7; //使用7位数据位 break; case 8: cfg.c_cflag |= CS8; //使用8位数据位 break; default: cfg.c_cflag |= CS8; break; } 5.配置校验位 switch (parity) { case 0: cfg.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; //无奇偶校验 break; case 1: cfg.c_cflag |= (PARODD | PARENB); //奇校验 break; case 2: cfg.c_iflag &= ~(IGNPAR | PARMRK); // 偶校验 cfg.c_iflag |= INPCK; cfg.c_cflag |= PARENB; cfg.c_cflag &= ~PARODD; break; default: cfg.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; break; } 6.配置停止位 switch (stopBits) { case 1: cfg.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; //1位停止位 break; case 2: cfg.c_cflag |= CSTOPB; //2位停止位 break; default: break; } 7.配置流控 switch (flowCon) { case 0: cfg.c_cflag &= ~CRTSCTS; //不使用流控 break; case 1: cfg.c_cflag |= CRTSCTS; //硬件流控 break; case 2: cfg.c_cflag |= IXON | IXOFF | IXANY; //软件流控 break; default: cfg.c_cflag &= ~CRTSCTS; break; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
readme
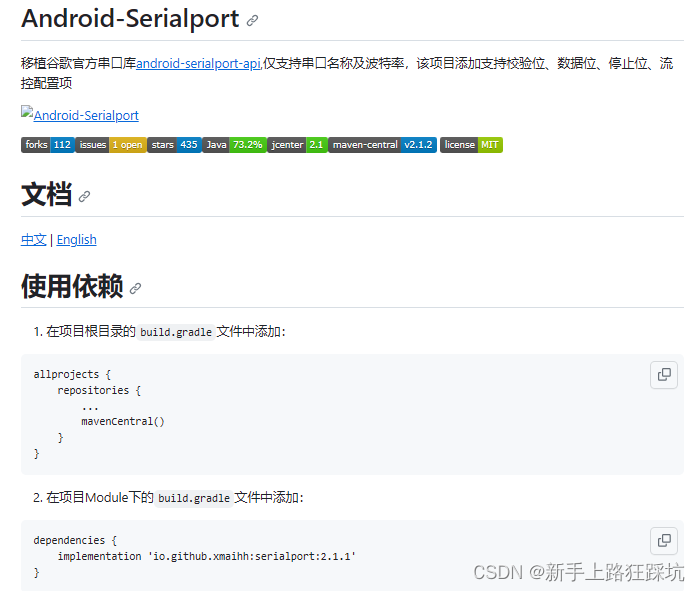
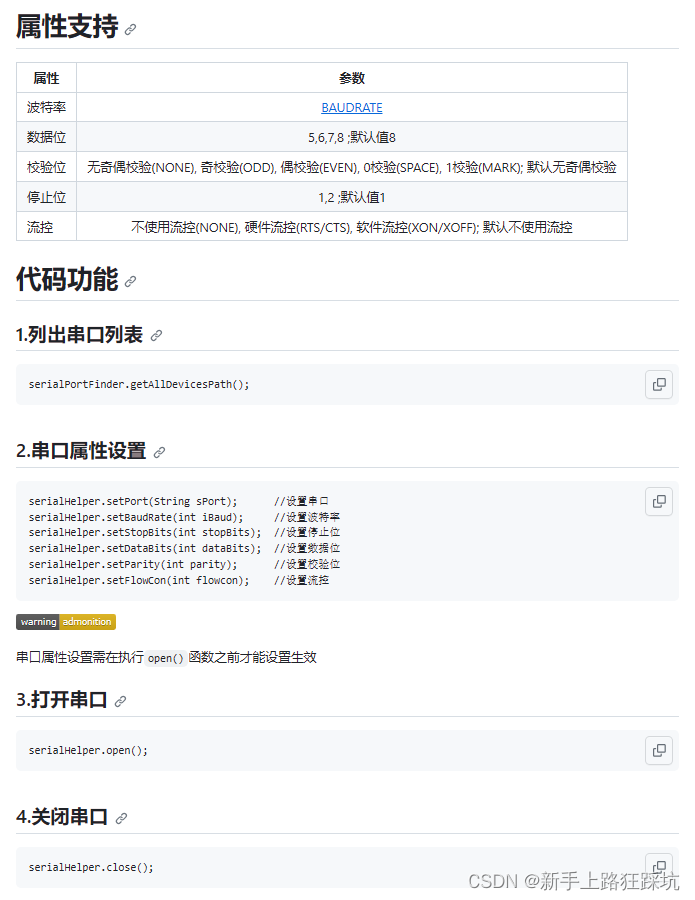
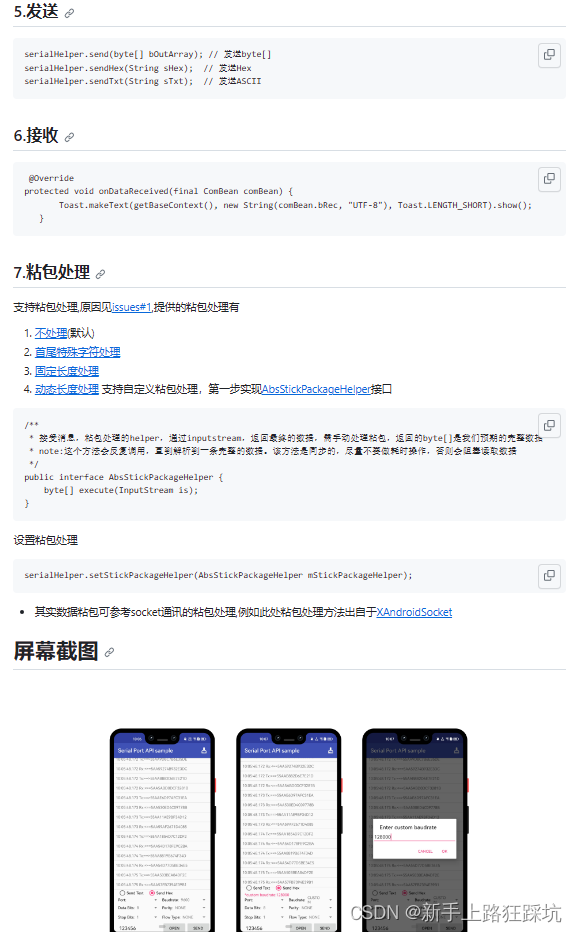
android中使用串口通信
使用android-serialport-api方式
import android.serialport.SerialPort;
- 1
第1种 链接
在gradle/build.gradle中添加
maven { url "https://jitpack.io" }
- 1
在app/build.gradle文件配置中的dependencies,加上
implementation 'com.github.licheedev.Android-SerialPort-API:serialport:1.0.1'
- 1
第2种 导入SerialPort库
1、将android-serialport-api中的libs的so库资源放到项目libs中
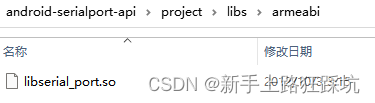
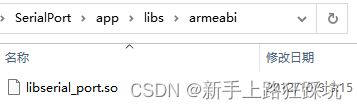
2、将Android-SerialPort-API中的java下的文件复制到项目中java
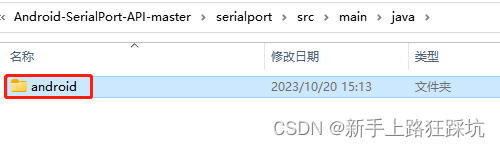
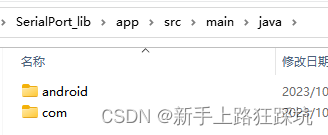
3、修改app的build.gradle文件,在android {}里添加支持的cpu架构
defaultConfig {
ndk {
abiFilters "armeabi","armeabi-v7a" // "x86", "arm64-v8a"
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
第3种 编译SerialPort模块
1、将Android-SerialPort-API中的serialport模块复制到工程中,目录与app文件同级
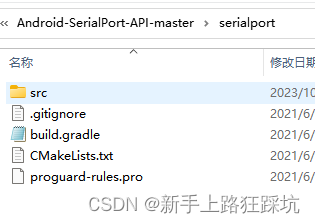
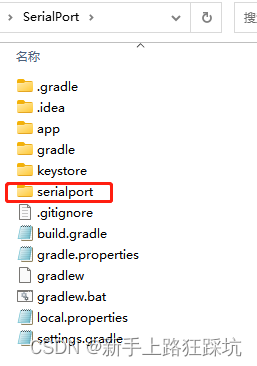
2、修改settings.gradle,将改成如下,即增加serialport模块
rootProject.name = "SerialPort"
include ':app',':serialport'
- 1
- 2
3、修改app的build.gradle文件,在dependencies{}中添加project
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
implementation project(':serialport')
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
串口通信部分代码
待续
好的文章推荐参考
Android串口通讯SerialPort(使用篇)
与君共勉!待续
欢迎指错,一起学习