- 1mtk log系统详解_mtklog
- 2[400]anaconda详细安装使用教程_anaconda安装教程
- 3Unity3D实现UI的单击、双击、拖动状态判断_unity ui 按下
- 4NTP网络时间服务器(gps卫星同步时钟)的组网方法及步骤
- 5java @Test 使用不了_@test' not applicable to field
- 6『HarmonyOS』Ability基础(类比Android中Activity学习)_安卓fa pa
- 7centos7.1 inter 82599 万兆光网卡驱动安装心得_82599网卡驱动
- 8计算机专业英语_计算机专业英语转义词
- 9WEB三大组件之Filter
- 10vscode调试exe可执行文件出现的问题_vscode exe不存在
详细教程:c++ 如何操作yaml文件
赞
踩
创作背景
使用python来对yolov8的模型进行推理速度有些慢,准备做一个c++版本的POC。POC会使用opencv dnn或者openvino来进行推理,其中涉及到需要读取coco.yaml文件,但是发现C++本身并没有提供读取YAML文件的API,但是可以使用第三方库来实现。
其中比较流行的是yaml-cpp库,它是一个纯C++实现的YAML解析器,支持C++11标准。
安装yaml-cpp库
安装环境: Windows10 + CMake + VS 2022
从Git Hub下载源代码
Git Hub地址:
jbeder/yaml-cpp: A YAML parser and emitter in C++ (github.com)
Release 版本:
Releases · jbeder/yaml-cpp (github.com)
我下载的是最新版本:yaml-cpp-0.8.0。

使用CMake生成VS 2022解决方案
解压下载回来的源代码包到 `D:/cxx_3_parties/yaml-cpp-0.8.0`,使用CMake-GUI来生成项目对应的VS 2022解决方案。
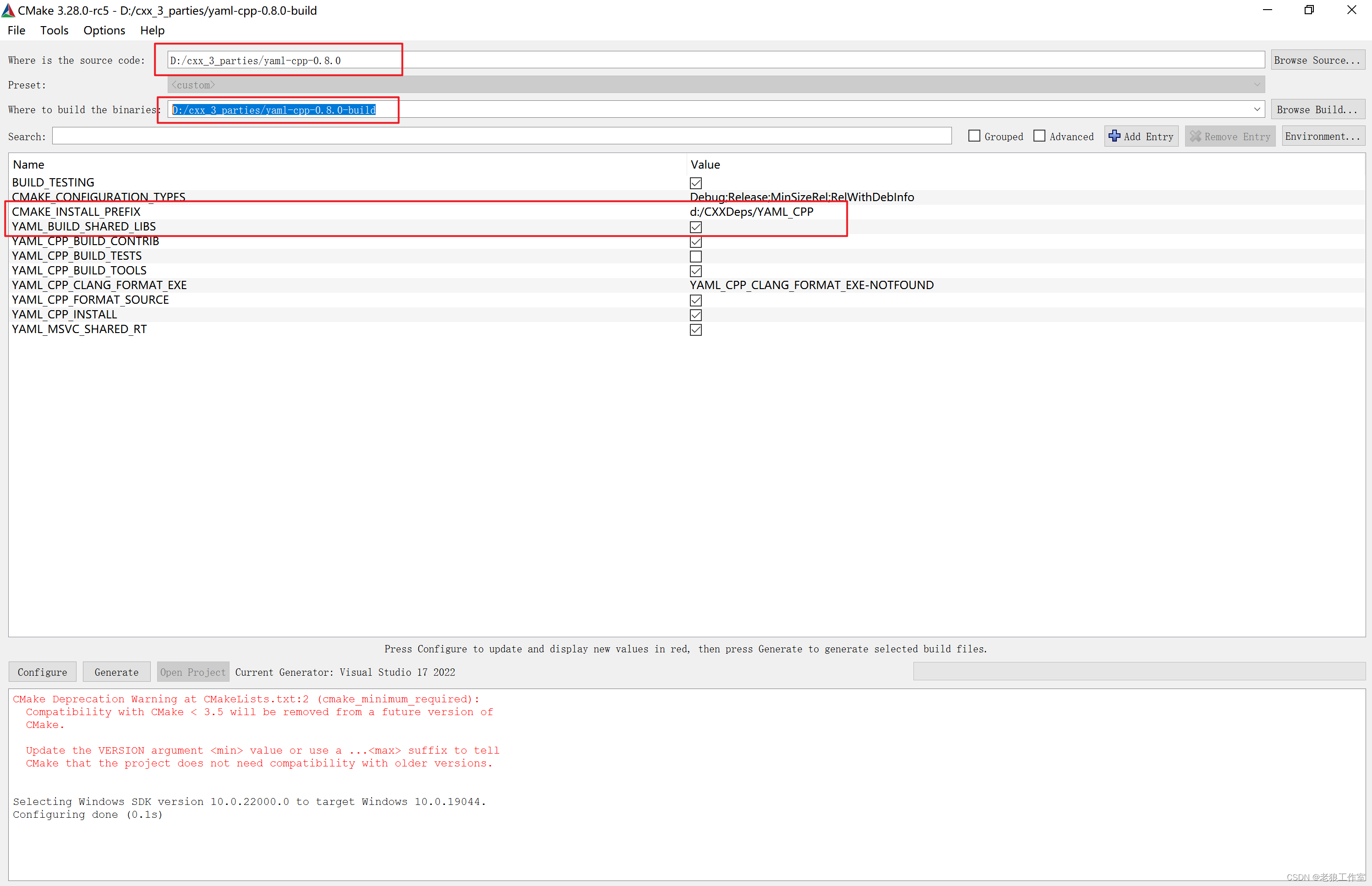
其中 “Where is the source code” 为源代码的目录,“Where to build the binaries”为VS解决方案保存的目录。
修改“CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX”库安装的目录为“d:/CXXDeps/YAML_CPP”,
修改“YAML_BUILD_SHARED_LIBS”为选中状态,其他保持默认值。
点击“Configure”进行配置,然后点击“Generate” 生成VS 2022解决方案。

生成成功之后,通过点击“Open Project”打开解决方案。
使用VS 2022构建并安装库
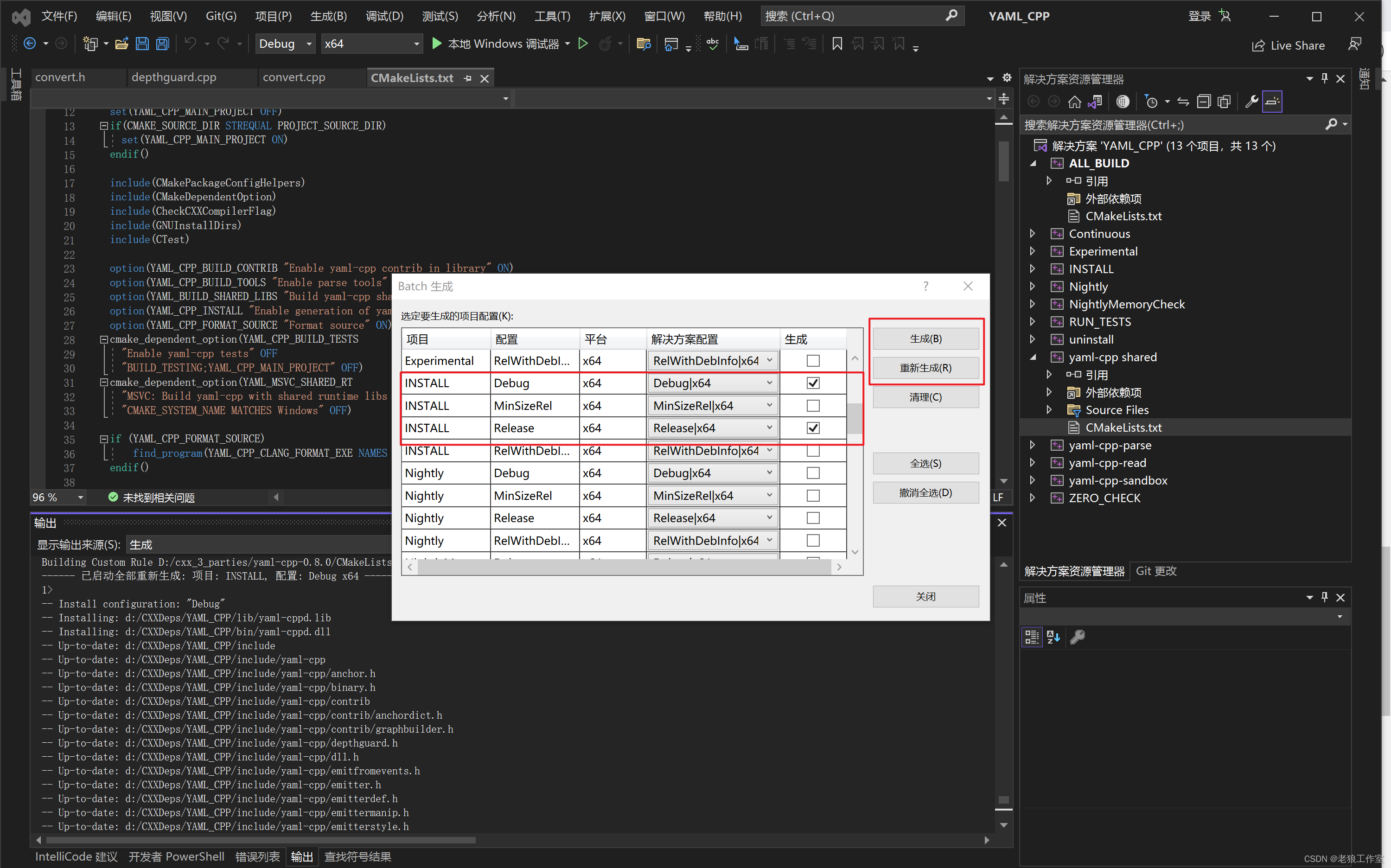
通过“生成 -> 批生成...”打开Batch生成窗口,选中ALL_BUILD和INSTALL的Debug和Release版本,点击“生成”或者“重新生成”同时构建和安装Debug和Release的x64的版本。

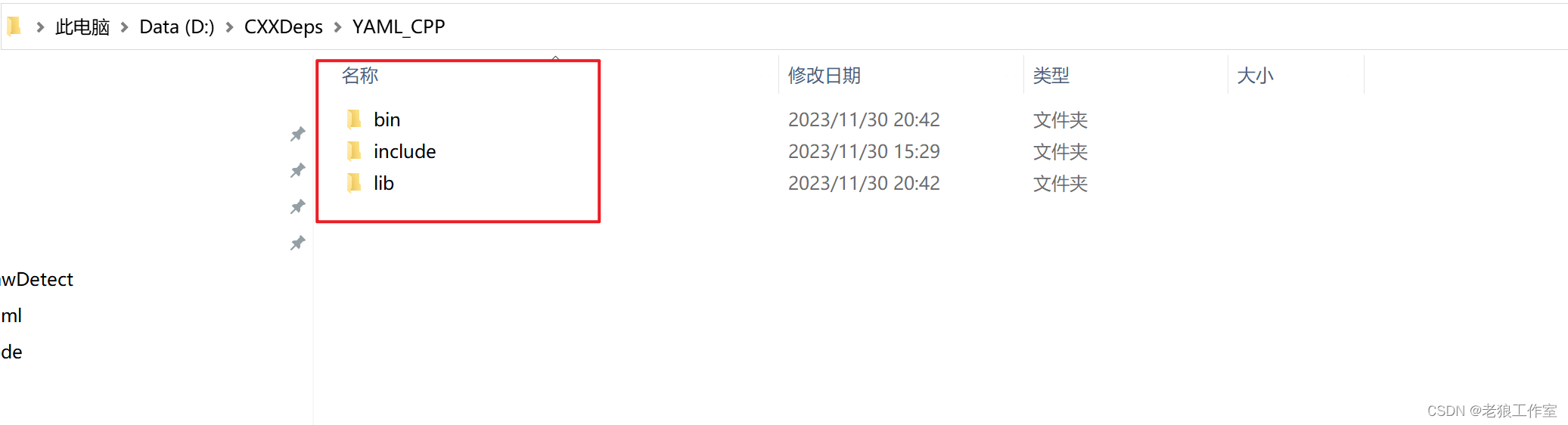
点击“生成”按钮,进行库构建和安装,构建完成之后,可以在“D:\CXXDeps\YAML_CPP”目录下看到生成的头文件目录(include), 库目录(lib),动态链接库目录(bin)。
使用案例
读取coco.yaml文件
- // 使用yaml-cpp库提供的API读取YAML文件
- void read_coco_yaml()
- {
- std::cout << "read_coco_yaml --------------------" << std::endl;
- // 加载YAML文件
- YAML::Node config = YAML::LoadFile("coco.yaml");
-
- // 获取指定路径下的值
- std::string path = config["path"].as<std::string>();
- std::cout << "path: " << path << std::endl;
- std::map<int, std::string> names = config["names"].as<std::map<int, std::string>>();
- std::cout << "names: " << std::endl;
- for (const auto& node : names) {
- std::cout << node.first << ": " << node.second << std::endl;
- }
-
- // 或者直接遍历YAML节点
- for (const auto& node : config["names"]) {
- std::cout << node.first << ": " << node.second << std::endl;
- }
- }
修改coco.yaml并另存为new_coco.yaml
- // 使用yaml-cpp库提供的API读取和修改YAML文件
- void modify_coco_yaml()
- {
- std::cout << "modify_coco_yaml --------------------" << std::endl;
- // 加载YAML文件
- YAML::Node config = YAML::LoadFile("coco.yaml");
-
- // 获取指定路径下的值
- std::string path = config["path"].as<std::string>();
- std::cout << "path: " << path << std::endl;
- config["path"] = "./newdataset/coco";
- std::map<int, std::string> names = config["names"].as<std::map<int, std::string>>();
- std::cout << "names: " << std::endl;
- names[80] = "test";
- config["names"] = names;
-
- YAML::Emitter out;
- out << YAML::BeginMap;
- out << config;
- out << YAML::EndMap;
-
- std::ofstream outFile("new_coco.yaml");
- outFile << out.c_str();
- outFile.close();
- }
创建新的yaml文件
- // 使用yaml-cpp库提供的API创建YAML文件
- void create_new_yaml_file()
- {
- std::cout << "create_new_yaml_file --------------------" << std::endl;
-
- YAML::Emitter out;
-
- out << "test yaml!";
-
- /* A simple list. produce as:
-
- - eggs
- - bread
- - milk
- */
- out << YAML::BeginSeq;
- out << "eggs";
- out << "bread";
- out << "milk";
- out << YAML::EndSeq;
-
- /* A simple map. produce as:
-
- name: Ryan Braun
- position: LF
-
- */
- out << YAML::BeginMap;
- out << YAML::Key << "name";
- out << YAML::Value << "Ryan Braun";
- out << YAML::Key << "position";
- out << YAML::Value << "LF";
- out << YAML::EndMap;
-
- /* These elements can, of course, be nested. produce as:
-
- name1: Barack Obama
- children1:
- - Sasha
- - Malia
- */
- out << YAML::BeginMap;
- out << YAML::Key << "name1";
- out << YAML::Value << "Barack Obama";
- out << YAML::Key << "children1";
- out << YAML::Value << YAML::BeginSeq << "Sasha" << "Malia" << YAML::EndSeq;
- out << YAML::EndMap;
-
- /* STL Containers. produce as:
-
- - [1, 4, 9, 16]
- -
- Daniel: 26
- Jesse: 24
- */
- std::vector <int> squares;
- squares.push_back(1);
- squares.push_back(4);
- squares.push_back(9);
- squares.push_back(16);
-
- std::map <std::string, int> ages;
- ages["Daniel"] = 26;
- ages["Jesse"] = 24;
-
- out << YAML::BeginSeq;
- out << YAML::Flow << squares;
- out << ages;
- out << YAML::EndSeq;
-
-
- std::cout << "yaml str: \n" << out.c_str() << std::endl;
-
- std::ofstream fileOut("yaml_test.yaml");
- fileOut << out.c_str();
- fileOut.close();
- }
VSCode项目文件
CMakeLists.txt
- # 设置yaml-cpp所在的目录
- set(YAML_CPP_DIR D:/CXXDeps/YAML_CPP)
- set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Debug")
- # 使用c++ iso 17(保持vs 2022解决方案使用的c++版本保持一致)
- set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
- set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
-
- add_executable(cpp_yaml_demo main.cpp)
- target_include_directories(cpp_yaml_demo PRIVATE ${YAML_CPP_DIR}/include)
- target_link_libraries(cpp_yaml_demo ${YAML_CPP_DIR}/lib/yaml-cppd.lib)
- file(COPY ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/coco.yaml DESTINATION ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}/)
- file(COPY ${YAML_CPP_DIR}/bin/yaml-cppd.dll DESTINATION ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}/)
main.cpp
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream>
- // 包含yaml-cpp头文件
- #include <yaml-cpp/yaml.h>
-
- // 使用yaml-cpp库提供的API读取YAML文件
- void read_coco_yaml()
- {
- std::cout << "read_coco_yaml --------------------" << std::endl;
- // 加载YAML文件
- YAML::Node config = YAML::LoadFile("coco.yaml");
-
- // 获取指定路径下的值
- std::string path = config["path"].as<std::string>();
- std::cout << "path: " << path << std::endl;
- std::map<int, std::string> names = config["names"].as<std::map<int, std::string>>();
- std::cout << "names: " << std::endl;
- for (const auto& node : names) {
- std::cout << node.first << ": " << node.second << std::endl;
- }
-
- // 或者直接遍历YAML节点
- for (const auto& node : config["names"]) {
- std::cout << node.first << ": " << node.second << std::endl;
- }
- }
-
-
- // 使用yaml-cpp库提供的API读取和修改YAML文件
- void modify_coco_yaml()
- {
- std::cout << "modify_coco_yaml --------------------" << std::endl;
- // 加载YAML文件
- YAML::Node config = YAML::LoadFile("coco.yaml");
-
- // 获取指定路径下的值
- std::string path = config["path"].as<std::string>();
- std::cout << "path: " << path << std::endl;
- config["path"] = "./newdataset/coco";
- std::map<int, std::string> names = config["names"].as<std::map<int, std::string>>();
- std::cout << "names: " << std::endl;
- names[80] = "test";
- config["names"] = names;
-
- YAML::Emitter out;
- out << YAML::BeginMap;
- out << config;
- out << YAML::EndMap;
-
- std::ofstream outFile("new_coco.yaml");
- outFile << out.c_str();
- outFile.close();
- }
-
- // 使用yaml-cpp库提供的API创建YAML文件
- void create_new_yaml_file()
- {
- std::cout << "create_new_yaml_file --------------------" << std::endl;
-
- YAML::Emitter out;
-
- out << "test yaml!";
-
- /* A simple list. produce as:
-
- - eggs
- - bread
- - milk
- */
- out << YAML::BeginSeq;
- out << "eggs";
- out << "bread";
- out << "milk";
- out << YAML::EndSeq;
-
- /* A simple map. produce as:
-
- name: Ryan Braun
- position: LF
-
- */
- out << YAML::BeginMap;
- out << YAML::Key << "name";
- out << YAML::Value << "Ryan Braun";
- out << YAML::Key << "position";
- out << YAML::Value << "LF";
- out << YAML::EndMap;
-
- /* These elements can, of course, be nested. produce as:
-
- name1: Barack Obama
- children1:
- - Sasha
- - Malia
- */
- out << YAML::BeginMap;
- out << YAML::Key << "name1";
- out << YAML::Value << "Barack Obama";
- out << YAML::Key << "children1";
- out << YAML::Value << YAML::BeginSeq << "Sasha" << "Malia" << YAML::EndSeq;
- out << YAML::EndMap;
-
- /* STL Containers. produce as:
-
- - [1, 4, 9, 16]
- -
- Daniel: 26
- Jesse: 24
- */
- std::vector <int> squares;
- squares.push_back(1);
- squares.push_back(4);
- squares.push_back(9);
- squares.push_back(16);
-
- std::map <std::string, int> ages;
- ages["Daniel"] = 26;
- ages["Jesse"] = 24;
-
- out << YAML::BeginSeq;
- out << YAML::Flow << squares;
- out << ages;
- out << YAML::EndSeq;
-
-
- std::cout << "yaml str: \n" << out.c_str() << std::endl;
-
- std::ofstream fileOut("yaml_test.yaml");
- fileOut << out.c_str();
- fileOut.close();
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- read_coco_yaml();
- modify_coco_yaml();
- create_new_yaml_file();
- return 0;
- }
coco.yaml
- # Ultralytics YOLO 声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/你好赵伟/article/detail/274699推荐阅读
相关标签
Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。