- 12024年毕业设计 毕业论文 毕设选题 机器学习&深度学习实战案例,含有python代码和教程 (3月19日已更新700篇)_含python代码的论文
- 2【鸿蒙软件开发】ArkTS基础组件之Marquee(文字跑马灯)、QRCode(二维码生成)_arkts marquee
- 3一文让你更了解linux设备树_properties must precede subnodes
- 4Android 无线调试手机(WiFi 调试)_无线调试 手机自身
- 5.bat文件不能运行怎么办? bat文件不能运行解决方法。_自编的bat无法运行,在dos状态正常运行
- 6uniapp canvas文字和元素居中
- 7GCC的一些环境变量的配置_gcc配置变量
- 8android多个usb摄像头,Android中多USB摄像头解决方案——UVCCamera源码分析(四)
- 9javaCompileOptions { annotationProcessorOptions { includeCompileClasspath = true } }
- 10Python问题1:ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘numpy‘_modulenotfounderror: no module named 'numpy
OpenCV3之XML文件和YAML文件的文件读写_%yaml:1.0 opencv
赞
踩
一、XML文件和YAML文件
这两种文件可以作为参数配置文件。
这两种文件有着特定的格式,表示这是能被opencv读取的。你不要记住这格式怎么写,只需要大概了解样子就行,格式填充会由程序编译自动填写。
1.XML文件
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<opencv_storage>
<!--主体内容-->
</opencv_storage>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2.YAML文件
也叫xxx.yml文件
%YAML:1.0
---
- 1
- 2
如果你想了解这东西怎么手动写:配置文件 .yml 写法小结
3.指定文件
对于这两种文件,读写的函数操作都一样,只要你指定文件名的后缀xxx.xml还是xxx.yaml,就能输出读取相应格式的文件。
二、cv库函数
注意:不能用一个FileStorage句柄同时读写,也不能使用两个FileStorage句柄同时读写,必须一个执行完关闭后再打开另一个进行操作。
1.打开 FileStorage
我们使用FileStorage类作为文件的句柄,类似c的FILE
(1)带参构造函数
cv::FileStorage::FileStorage(
const String & filename,
int flags,
const String & encoding = String()
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
参数:
- filename:
xxx.xml是xml文件,xxx.yaml是yaml文件 - flags:操作类型。不能同时读写,可执行但无结果。
FileStorage::WRITE:写入FileStorage::READ:读取FileStorage::APPEND:附加
- encoding:编码格式UTF-8,不用管。
例如:
// 打开文件,写操作
string filename = "myXML.xml";
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
- 1
- 2
- 3
(2)无参构造+open()
virtual bool cv::FileStorage::open (
const String & filename,
int flags,
const String & encoding = String()
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
例如:
// 打开文件,写操作
string filename = "myXML.xml";
FileStorage fs;
fs.open(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2.是否打开成功 isOpened
virtual bool cv::FileStorage::isOpened() const
- 1
返回值:
- true:成功
- false:失败
3.关闭 release
virtual void cv::FileStorage::release()
- 1
虽然会自动关闭,但建议手动调用。
4.C++基本类型的读写
| 类型 | 写入 | xml中 | 读出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| int | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| double | 100.1 | 1.0009999999999999e+02 | 100.1 |
| bool | true | 1 | true |
| string | "hello" | hello | hello |
| string | "hello world" | "hello world" | "hello world" |
(1)写
使用操作符<<:fs_write << "xml中变量的名字" << 变量的值;
fs_write << "speed" << 100;
- 1
xml中:
<speed>100</speed>
- 1
(2)读
方式一:
使用操作符>>:先声明变量变量的类型 变量的名字;,再fs_read["xml中变量的名字"] >> 变量的名字;
int speed;
fs_read["speed"] >> speed;
- 1
- 2
方式二:
强制类型转化:(变量的类型)fs_read["xml中变量的名字"];。
int speed = (int)fs_read["speed"];
cout << (int)fs_write["speed"] << endl;
- 1
- 2
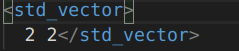
5.c++的STL
可以用vector的
// 读
vector<int> v1(2, 2);
fs_write << "std_vector" << v1;
// 写
vector<int> v2;
fs_read["std_vector"] >> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++)
{
cout << v2[i] << endl;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
6.OpenCV数据类型的读写
操作同上
| 类型 | 写入 | xml中 | 读出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mat | (Mat_<uchar>(2, 3) << 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6); | 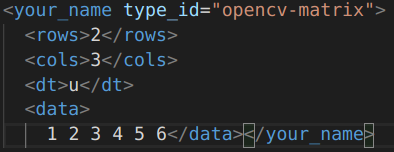 | 一样 |
| Size | Size(200,100); | 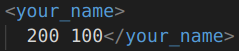 | 一样 |
| Vec3i | Vec3i(1,2,3); | 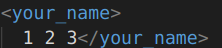 | 一样 |
后面就不试了
都只有第一种读法,比如Mat类型:
// 写
fs_write << "opencv_matrix" << (Mat_<uchar>(2, 3) << 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
// 读
Mat result;
fs_read["opencv_matrix"] >> result;
cout << result << endl;
// 报错
// cout << (Mat)fs_read["opencv_matrix"] << endl;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
7.sequence和mapping的读写
(1)介绍
sequence是处理类型STL的vector的xml和yaml的数据类型。
mapping是处理类型STL的map的xml和yaml的数据类型。
(2)实际意义
sequence模仿vector,而opencv的数据类型中也有模仿vector的Vec,而Vec中只能存数字类型。所以简单的数字类型直接用Vec就行,复杂的数据类型如string,我们再用sequence。
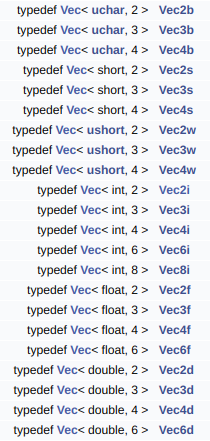
(3)sequence的读写
写:在数据前后加了个[和]表示sequence类型。
读:类似List链表遍历,先读取该链表块FileNode,再用迭代器FileNodeIterator遍历链表节点,每个节点的读的方式和上面一样有两种。
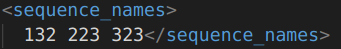
// 写 fs_write << "sequence_names" << "[" << 132 << 223 << 323 << "]"; // 读 FileNode fn_sequence_names = fs_read["sequence_names"]; if (fn_sequence_names.type() != FileNode::SEQ) { cout << "the type is not sequence!\n"; return 0; } int v[3]; int i = 0; for (FileNodeIterator fni = fn_sequence_names.begin(); fni != fn_sequence_names.end(); fni++) { *fni >> v[i++]; // 或者(int)*fni >> v[i++]; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
xml中:可以看到和opencv的存储样式一样。
(4)mappping的读写
写:在数据前后加了个{和}表示mappping类型,单个键值对是先键后值 << "键名" << 值
读:类似map根据键获得值,先读取该链表块FileNode,再用键获得值。每个键值对的读的方式和上面一样有两种。
PS:键必须字符串类型,键不能重复;同一个mapping中的值的类型可以不一样,值可以重复。
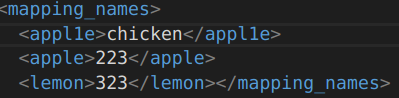
// 写 fs_write << "mapping_names" << "{" << "banana" << "chicken" << "apple" << 223 << "lemon" << 323 << "}"; // 读 FileNode fn_mapping_names = fs_read["mapping_names"]; if (fn_mapping_names.type() != FileNode::MAP) { cout << "the type is not mapping!\n"; return 0; } string banana; fn_mapping_names["banana"] >> banana; int apple = (int)fn_mapping_names["apple"];
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
三、例子
1.给定类型
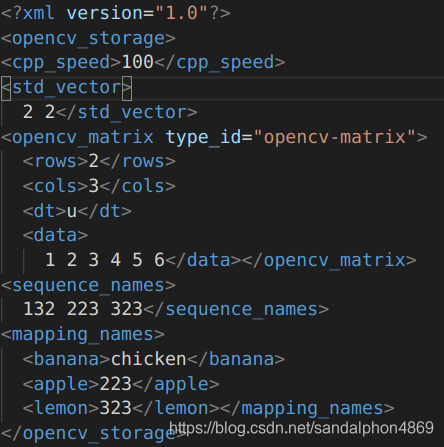
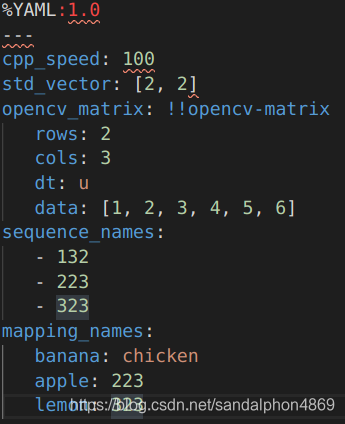
#include <iostream> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> using namespace cv; using namespace std; int main() { string filename = "myXML.xml"; /*********************************** 打开文件,写操作 ************************************/ FileStorage fs_write; fs_write.open(filename, FileStorage::WRITE); /* 写入 */ // c++ fs_write << "cpp_speed" << 100; // std::vector vector<int> v1(2, 2); fs_write << "std_vector" << v1; // Opencv fs_write << "opencv_matrix" << (Mat_<uchar>(2, 3) << 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6); // sequence fs_write << "sequence_names" << "[" << 132 << 223 << 323 << "]"; // mapping fs_write << "mapping_names" << "{" << "banana" << "chicken" << "apple" << 223 << "lemon" << 323 << "}"; fs_write.release(); /************************************* 打开文件,读操作 ************************************/ FileStorage fs_read; fs_read.open(filename, FileStorage::READ); /* 读取 */ // c++ cout << (int)fs_read["cpp_speed"] << endl; // std::vector vector<int> v2; fs_read["std_vector"] >> v2; for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++) { cout << v2[i] << endl; } // Opencv Mat result; fs_read["opencv_matrix"] >> result; cout << result << endl; // !cout << (Mat)fs_read["opencv_matrix"] << endl; // sequence FileNode fn_sequence_names = fs_read["sequence_names"]; if (fn_sequence_names.type() != FileNode::SEQ) { cout << "the type is not sequence!\n"; return 0; } for (FileNodeIterator fni = fn_sequence_names.begin(); fni != fn_sequence_names.end(); fni++) { cout << (int)*fni << endl; } // mapping FileNode fn_mapping_names = fs_read["mapping_names"]; if (fn_mapping_names.type() != FileNode::MAP) { cout << "the type is not mapping!\n"; return 0; } cout << (string)fn_mapping_names["banana"] << endl; cout << (int)(fn_mapping_names)["apple"] << endl; cout << (int)(fn_mapping_names)["lemon"] << endl; fs_read.release(); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
2.自定义类型
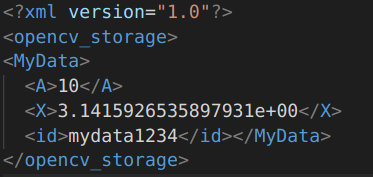
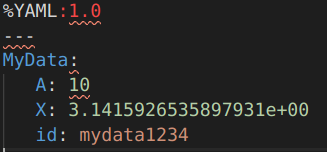
#include <iostream> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> using namespace cv; using namespace std; class MyData { public: MyData() : A(0), X(0), id() {} explicit MyData(int A) : A(A), X(CV_PI), id("mydata1234") {} public: int A; double X; string id; public: // inside of your class void write(FileStorage &fs) const //Write serialization for this class { fs << "{" << "A" << A << "X" << X << "id" << id << "}"; } void read(const FileNode &node) //Read serialization for this class { A = (int)node["A"]; X = (double)node["X"]; id = (string)node["id"]; } }; // outside of your class void write(FileStorage &fs, const std::string &, const MyData &x) { x.write(fs); } void read(const FileNode &node, MyData &x, const MyData &default_value = MyData()) { if (node.empty()) x = default_value; else x.read(node); } // 这个和主题无关,只是让其可以直接用cout输出MyData的值是什么而已 ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const MyData &m) { out << "id = " << m.id << ", " << "X = " << m.X << ", " << "A = " << m.A; return out; } int main() { string filename = "myXML.xml"; /*********************************** 打开文件,写操作 ************************************/ FileStorage fs_write; fs_write.open(filename, FileStorage::WRITE); MyData m1(1); fs_write << "MyData" << m1; fs_write.release(); /************************************* 打开文件,读操作 ************************************/ FileStorage fs_read; fs_read.open(filename, FileStorage::READ); MyData m2; fs_read["MyData"] >> m2; cout << m2 << endl; fs_read.release(); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
reference
opencv3.4.6官方文档:tutorial_file_input_output_with_xml_yml.html




