- 1Rancher创建arm架构的下游k8s集群_arm版本rancher部署
- 2网络攻防原理(更新中)_常见网络攻防方法原理与实践选题的意义
- 3IntelliJ IDEA 2022.3.1 (Ultimate Edition) 配置教程_intellij idea ultimate
- 42021年九月上旬文章推荐_围绕hugetlb的极致优化
- 5fpga开发过程中遇到的一些小问题_labtools 27-3312
- 6MYSQL 查找单个字段或者多个字段重复数据,清除重复数据,保留一条_mysql查询重复数据保留一条
- 7【MYSQL】—— MySQL 在 Centos 7环境安装_centos7 mysql
- 82024年最新超全Python图像处理讲解(多图预警)_return im1,2024年最新涨姿势了
- 951单片机学习笔记16 小型直流电机和五线四相电机控制_51单片机 步进电机
- 10移植 u-boot-2020.07 到 iTOP-4412(四)重定位、UART_emmc4.4
数据结构-链表基础详解(超详细代码)_链表代码
赞
踩
目录
一、线性表
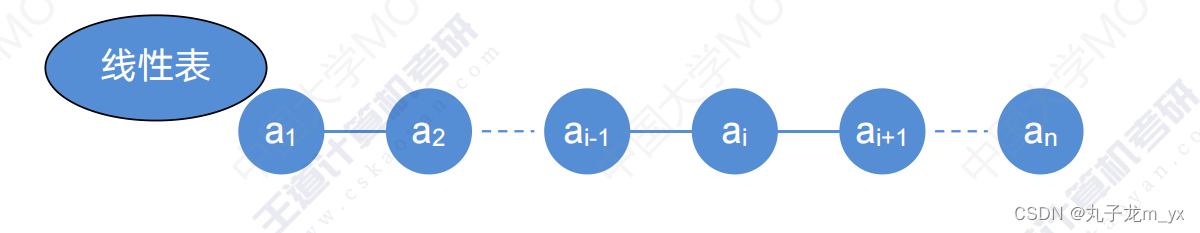
1.线性表定义
有n(n>=0)个相同类型的元素组成的有序集合。
L=(a1,a2,......,a(i-1),ai,a(i+1),......,an)
2.线性表特点
二、线性表的顺序表示(顺序表)

顺序表的定义 :
- #define MaxSize 50 //定义线性表的长度
- typedef struct{
- ElemType data[MaxSize]; //顺序表的元素
- int len; //顺序表的当前长度
- }SqList; //顺序表的类型定义
1、顺序表的优缺点
1.优点:
2.插入操作
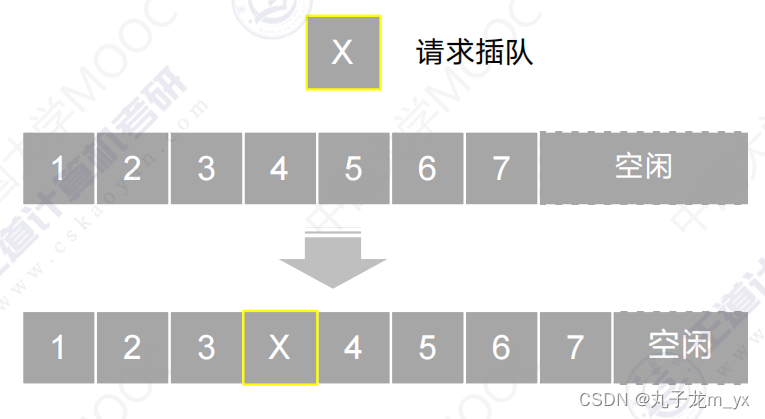 最好情况:在表尾插入元素,不需要移动元素,时间复杂度为O(1)。
最好情况:在表尾插入元素,不需要移动元素,时间复杂度为O(1)。
复杂度为O(n)。
代码片段:
- //判断插入位置i是否合法(满足1≤i≤len+1)
- //判断存储空间是否已满(即插入x后是否会超出数组长度)
- for(int j=L.len;j>=i;j--) //将最后一个元素到第i个元素依次后移一位
- L.data[j]=L.data[j-1];
- L.data[i-1]=x; //空出的位置i处放入x
- L.len++; //线性表长度加1
注意:线性表第一个元素的数组下标是0;
3.删除操作
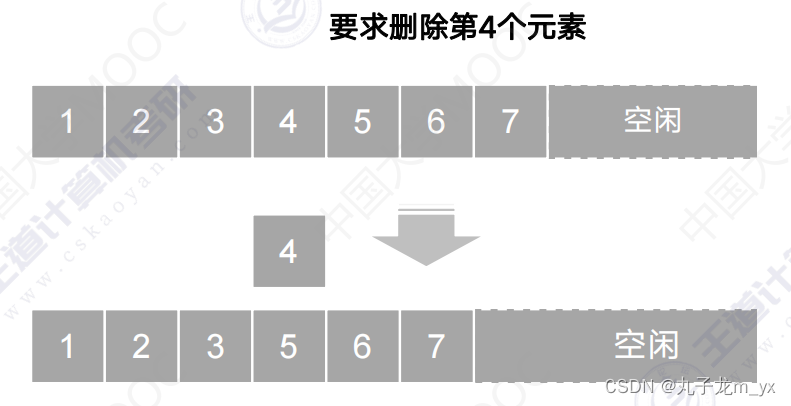
最好情况:删除表尾元素,不需要移动元素,时间复杂度为O(1)。
- //判断删除位置i是否合法(满足1≤i≤len)
- e=L.data[i-1]; //将被删除的元素赋值给e
- for(int j=i;j<L.len;j++) //将删除位置后的元素依次前移
- L.data[j-1]=L.data[j];
- L.len--;
4.顺序表完整代码
- #include <stdio.h>
-
- #define MaxSize 50
- typedef int ElemType;//让顺序表存储其他类型元素时,可以快速完成代码修改
- typedef struct{
- ElemType data[MaxSize];
- int length;//顺序表长度
- }SqList;
- //顺序表的插入,因为L会改变,因此我们这里要用引用,i是插入的位置
- bool ListInsert(SqList &L,int i,ElemType element)
- {
- //判断i是否合法
- if(i<1 || i>L.length+1)
- {
- return false;
- }
- //如果存储空间满了,不能插入
- if(L.length==MaxSize)
- {
- return false;//未插入返回false
- }
- //把后面的元素依次往后移动,空出位置,来放要插入的元素
- for(int j=L.length;j>=i;j--)
- {
- L.data[j]=L.data[j-1];
- }
- L.data[i-1]=element;//放入要插入的元素
- L.length++;//顺序表长度要加1
- return true;//插入成功返回true
- }
-
- //打印顺序表
- void PrintList(SqList L)
- {
- int i;
- for(i=0;i<L.length;i++)
- {
- printf("%3d",L.data[i]);//为了打印到同一行
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- //删除顺序表中的元素,i是要删除的元素的位置,e是为了获取被删除的元素的值
- bool ListDelete(SqList &L,int i,ElemType &e)
- {
- //判断删除的元素的位置是否合法
- if(i<1 || i>L.length)
- {
- return false;//一旦走到return函数就结束了
- }
- e=L.data[i-1];//首先保存要删除元素的值
- int j;
- for(j=i;j<L.length;j++)//往前移动元素
- {
- L.data[j-1]=L.data[j];
- }
- L.length--;//顺序表长度减1
- return true;
- }
- //查找某个元素的位置,找到了就会对应位置,没找到就返回0
- int LocateElem(SqList L,ElemType element)
- {
- int i;
- for(i=0;i<L.length;i++)
- {
- if(element==L.data[i])
- {
- return i+1;//因为i是数组的下标,加1以后才是顺序表的下标
- }
- }
- return 0;//循环结束没找到
- }
-
- //顺序表的初始化及插入操作实战
- int main() {
- SqList L;//定义一个顺序表,变量L
- bool ret;//ret用来装函数的返回值
- L.data[0]=1;//放置元素
- L.data[1]=2;
- L.data[2]=3;
- L.length=3;//设置长度
- ret=ListInsert(L,2,60);
- if(ret)
- {
- printf("insert sqlist success\n");
- PrintList(L);
- }else{
- printf("insert sqlist failed\n");
- }
- printf("----------------------\n");
- ElemType del;//删除的元素存入del中
- ret=ListDelete(L,1,del);
- if(ret)
- {
- printf("delete sqlist success\n");
- printf("del element=%d\n",del);
- PrintList(L);//顺序表打印
- }else{
- printf("delete sqlist failed\n");
- }
- int pos;//存储元素位置
- pos=LocateElem(L,60);
- if(pos)
- {
- printf("find this element\n");
- printf("element pos=%d\n",pos);
- }else{
- printf("don't find this element\n");
- }
- return 0;
- }

5.练习
初始化顺序表(顺序表中元素为整型),里边的元素是1,2,3,然后通过scanf读取一个元素(假如插入的是6),插入到第2个位置,打印输出顺序表,每个元素占3个空格,格式为1 6 2 3,然后scanf读取一个整型数,是删除的位置(假如输入为1),然后输出顺序表 6 2 3,假如输入的位置不合法,输出false字符串。
Input
第一次输入插入的元素值,第二次输入删除的位置
Output
假如插入的元素为6,那么输出为
1 6 2 3
假如删除的位置为1,那么输出为
6 2 3
Sample Input 1
6 1
Sample Output 1
1 6 2 3 6 2 3
Sample Input 2
9 3
Sample Output 2
1 9 2 3 1 9 3
Sample Input 3
9 6
Sample Output 3
1 9 2 3 false
代码:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- #define MaxSize 50
- typedef int ElemType;
- typedef struct {
- ElemType data[MaxSize];
- int length;
- }SqList;
-
- //链表插入
- bool ListInsert(SqList &L,int i, ElemType ist)
- {
- if(i < 1 || i > L.length + 1)
- return false;
- if (L.length >= MaxSize)
- return false;
- for (int j = L.length; j >= i; --j) {
- L.data[j] = L.data[j - 1];
- }
- L.data[i - 1] = ist;
- L.length++;
- return true;
- }
-
- //链表删除
- bool ListDelete(SqList &L,int pos)
- {
- if(pos < 1 || pos > L.length)
- return false;
- if(L.length >= MaxSize)
- return false;
- for(int i = pos - 1; i <= L.length - 1; i++)
- {
- L.data[i] = L.data[i + 1];
- }
- L.length--;
- return true;
- }
- int main() {
- SqList L;
- L.data[0] = 1;
- L.data[1] = 2;
- L.data[2] = 3;
- L.length = 3;
- ElemType ist;
- scanf("%d",&ist);
- bool ret = ListInsert(L,2,ist);
- if(ret){
- for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++)
- {
- printf("%3d",L.data[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- else
- printf("false\n");
- ElemType pos;
- scanf("%d",&pos);
- ret = ListDelete(L,pos);
- if (ret){
- for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++)
- {
- printf("%3d",L.data[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- else
- printf("false\n");
- return 0;
- }

三、线性表的链式表示(单链表)
1.单链表定义
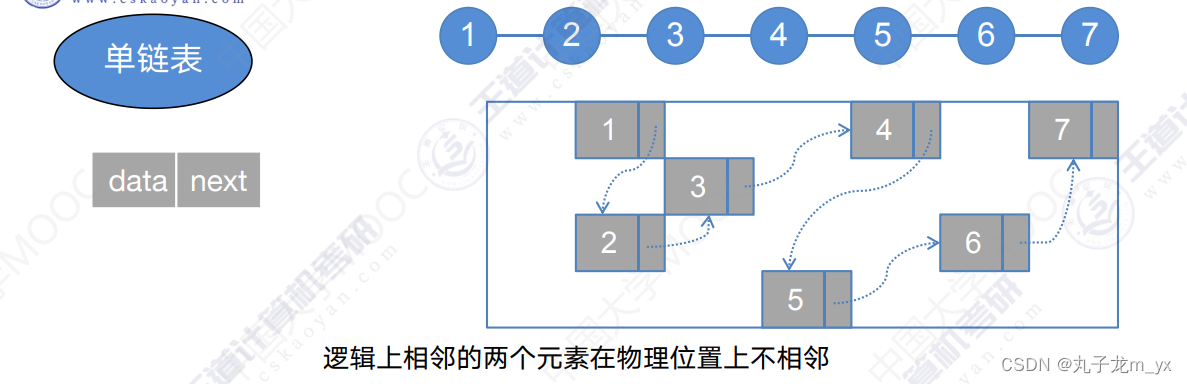
单链表结点的定义:
- typedef struct LNode{ //单链表结点类型
- ElemType data; //数据域
- struct LNode *next; //指针域
- }LNode, *LinkList;

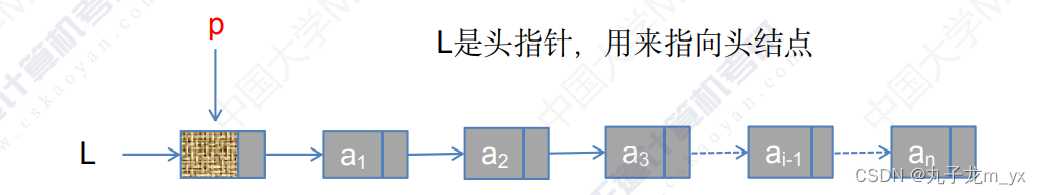
头指针:链表中第一个结点的存储位置,用来标识单链表。 头结点:在单链表第一个结点之前附加的一个结点,为了操作上的方便。
若链表有头结点,则头指针永远指向头结点,不论链表是否为空,头指针均不为 空,头指针是链表的必须元素,他标识一个链表。 头结点是为了操作的方便而设立的,其数据域一般为空,或者存放链表的长度。 有头结点后,对在第一结点前插入和删除第一结点的操作就统一了,不需要频繁 重置头指针。但头结点不是必须的。
2.单链表优缺点
1、优点:
1.1 插入和删除操作不需要移动元 素,只需要修改指针。
1.2 不需要大量的连续存储空间。
2、缺点
2.1 单链表附加指针域,也存在浪 费存储空间的缺点。
2.2 查找操作时需要从表头开始遍历,依次查找,不能随机存取。
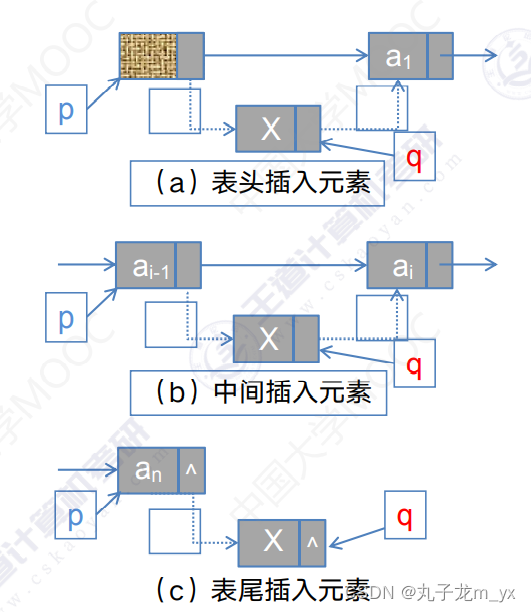
3.插入操作
创建新结点代码:
- q=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode))
- q->data=x;
(a) (b)操作的代码:
- q->next=p->next;
- p->next=q;
(c)操作的代码:
- p->next=q;
- q->next=NULL;
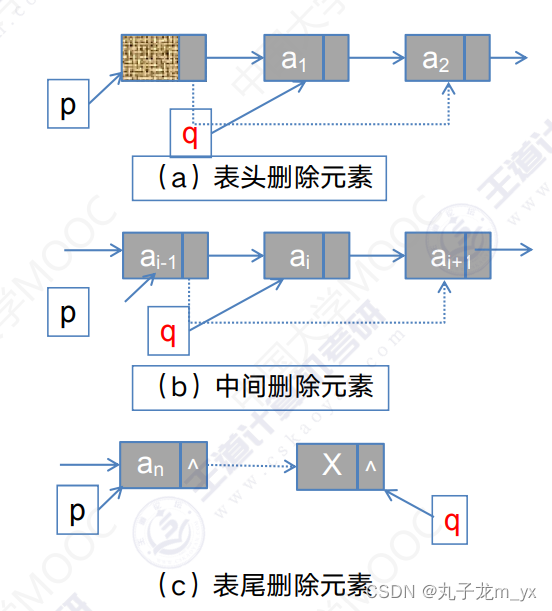
4.删除操作
(a)(b)(c)操作的代码:
- p=GetElem(L,i-1);//查找删除位置的前驱节点
- q=p->next;
- p->next=q->next;
- free(q);
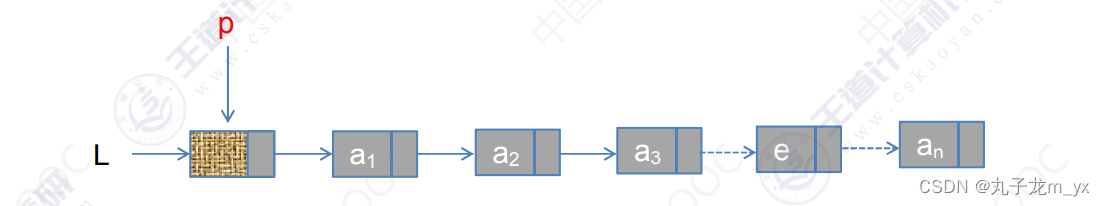
5.查找操作
5.1按序号查找结点
代码:
- LNode *p = L->next;
- int j = 1;
- while(p && j<i){
- p = p->next;
- j++;
- }
- retrun p;
5.2按值查找结点
代码:
- LNode *p = L->next;
- while(p!=NULL && p->date!=e){
- p = p->next;
- }
- return p;
6.链表完整代码
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- typedef int ElemType;
- typedef struct LNode{
- ElemType data;//数据域
- struct LNode *next;
- }LNode,*LinkList;
- //LNode*是结构体指针,和LinkList完全等价的
- //输入3,4,5,6,7,9999
- void list_head_insert(LNode* &L)
- {
- L= (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));//申请头结点空间,头指针指向头结点
- L->next=NULL;
- ElemType x;
- scanf("%d",&x);
- LNode *s;//用来指向申请的新结点
- while(x!=9999)
- {
- s=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
- s->data=x;
- s->next=L->next;//s的next指向原本链表的第一个结点
- L->next=s;//头结点的next,指向新结点
- scanf("%d",&x);
- }
- }
- //尾插法新建链表
- void list_tail_insert(LNode* &L)
- {
- L= (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));//申请头结点空间,头指针指向头结点
- L->next=NULL;
- ElemType x;
- scanf("%d",&x);
- LNode *s,*r=L;//s是用来指向申请的新结点,r始终指向链表尾部
- while(x!=9999)
- {
- s=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));//为新结点申请空间
- s->data=x;
- r->next=s;//新结点给尾结点的next指针
- r=s;//r要指向新的尾部
- scanf("%d",&x);
- }
- r->next=NULL;//让尾结点的next为NULL
- }
-
- void print_list(LinkList L)
- {
- L=L->next;
- while(L!=NULL)
- {
- printf("%3d",L->data);
- L=L->next;
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- //按位置查找
- LinkList GetElem(LinkList L,int SearchPos)
- {
- int j=0;
- if(SearchPos<0)
- {
- return NULL;
- }
- while(L&&j<SearchPos)
- {
- L=L->next;
- j++;
- }
- return L;
- }
- //按值查找
- LinkList LocateElem(LinkList L,ElemType SearchVal)
- {
- while(L)
- {
- if(L->data==SearchVal)//如果找到对应的值,就返回那个结点的地址
- {
- return L;
- }
- L=L->next;
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- //i代表插入到第几个位置
- bool ListFrontInsert(LinkList L,int i,ElemType InsertVal)
- {
- LinkList p= GetElem(L,i-1);
- if(NULL==p)
- {
- return false;
- }
- LinkList q;
- q=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));//为新结点申请空间
- q->data=InsertVal;
- q->next=p->next;
- p->next=q;
- return true;
- }
-
- //删除第i个位置的元素
- //删除时L是不会变的,所以不需要加引用
- bool ListDelete(LinkList L,int i)
- {
- LinkList p= GetElem(L,i-1);//拿到要删除结点的前一个结点
- if(NULL==p)
- {
- return false;
- }
- LinkList q=p->next;//拿到要删除的结点指针
- p->next=q->next;//断链
- free(q);//释放被删除结点的空间
- return true;
- }
-
- //头插法,尾插法来新建链表
- int main() {
- LinkList L,search;//L是链表头指针,是结构体指针类型
- // list_head_insert(L);//输入数据可以为3 4 5 6 7 9999,头插法新建链表
- list_tail_insert(L);
- print_list(L);//链表打印
- // //按位置查找
- // search=GetElem(L,2);
- // if(search!=NULL)
- // {
- // printf("Succeeded in searching by serial number\n");
- // printf("%d\n",search->data);
- // }
- // search=LocateElem(L,6);//按值查询
- // if(search!=NULL)
- // {
- // printf("Search by value succeeded\n");
- // printf("%d\n",search->data);
- // }
- // bool ret;
- // ret=ListFrontInsert(L,2,99);//新结点插入第i个位置
- // print_list(L);
- ListDelete(L,5);//删除第4个位置
- print_list(L);
- return 0;
- }

7.练习
输入3 4 5 6 7 9999一串整数,9999代表结束,通过头插法新建链表,并输出,通过尾插法新建链表并输出。
注意输出要采用如下代码
- //打印链表中每个结点的值
- void PrintList(LinkList L)
- {
- L=L->next;
- while(L!=NULL)
- {
- printf("%d",L->data);//打印当前结点数据
- L=L->next;//指向下一个结点
- if(L!=NULL)
- {
- printf(" ");
- }
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
Input
3 4 5 6 7 9999,第二行也是3 4 5 6 7 9999,数据需要输入两次
Output
如果输入是3 4 5 6 7 9999,那么输出是7 6 5 4 3,数之间空格隔开,尾插法的输出是3 4 5 6 7
Sample Input 1
3 4 5 6 7 9999 3 4 5 6 7 9999
Sample Output 1
7 6 5 4 3 3 4 5 6 7
Sample Input 2
1 3 5 7 9 9999 1 3 5 7 9 9999
Sample Output 2
9 7 5 3 1 1 3 5 7 9
答案:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- typedef int ElemType;
-
- typedef struct LNode{
- ElemType data;
- struct LNode *next;
- }LNode,*LinkList;
-
- //头插法
- void List_head_insert(LNode* &L)
- {
- L = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
- L->next = NULL;
- ElemType x;
- scanf("%d",&x);
- LinkList q;
- while (x != 9999)
- {
- q = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
- q->data = x;
- q->next = L->next;
- L->next = q;
- scanf("%d",&x);
- }
- }
-
- //尾插法
- void List_tail_insert(LinkList &L)
- {
- L = (LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
- //L->next = NULL;
- ElemType x;
- scanf("%d",&x);
- LinkList p = L,q;
- while (x != 9999)
- {
- q = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
- q->data = x;
- p->next = q;
- p = q;
- scanf("%d",&x);
- }
- q->next = NULL;
- }
-
- //链表打印
- void print_List(LNode* L)
- {
- L=L->next;
- while(L!=NULL)
- {
- printf("%d",L->data);//打印当前结点数据
- L=L->next;//指向下一个结点
- if(L!=NULL)
- {
- printf(" ");
- }
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- //按值查询
- LinkList GetElem(LNode* L,int i)
- {
- if(i < 0)
- return NULL;
- while(i-- && L)
- {
- L = L->next;
- }
- return L;
- }
-
- //按位置查询
- LinkList LocateElem(LinkList L,int key)
- {
- L = L->next;
- while(L)
- {
- if(L->data == key)
- return L;
- L = L->next;
- }
- return NULL;
- }
-
- //中间插入
- bool ListFrontInsert(LinkList L,int pos,ElemType key) //中间插入不会改变头指针
- {
- LinkList p,q;
- p = GetElem(L,pos - 1);
- if(p)
- {
- q = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
- q->data = key;
- q->next = p->next;
- p->next = q;
- return true;
- }
- return false;
-
- }
-
- int main() {
- LinkList L1,L2,search; //链表头指针
- ElemType key;
- List_head_insert(L1);
- List_tail_insert(L2);
- print_List(L1);
- print_List(L2);
- return 0;
- }



