热门标签
热门文章
- 12024中国AI Agent行业研究报告
- 2在 Android 上恢复已删除文件的 5 种简单方法_安卓文件恢复
- 3springboot项目 Spring Security 302 问题 loginProcessingUrl 无效
- 4安卓期末课程设计、一款刷小视频的App 包含源代码、使用手册和心得体会_android结课作业开发一个简易app
- 5thinkphp框架源码交易系统资源网站源码_tp开发源码交易系统 网站交易
- 6导出数据提示--secure-file-priv选项问题的解决方法
- 7【Flink 面试指南】Flink 详解(一):基础篇(架构、并行度、算子)_flink 架构
- 8【MySQL】mysql访问
- 9腾讯云部署SD_sd不用web ui如何部署
- 10自然语言处理技术(Natural Language Processing)知识点_基于自然语言处理的数据加工
当前位置: article > 正文
springboot项目管理双数据库_springboot支持多数据库
作者:weixin_40725706 | 2024-07-20 13:51:24
赞
踩
springboot支持多数据库
提示:使用springboot项目管理双数据库操作说明来咯
前言
最新公司需要弄个数据库同步的项目,但是又要保护目标数据库的用户相关数据,所以不能用mysql工具直接同步,只能写一个项目来进行指定数据的同步,这样就涉及到一个项目需要访问两个数据库的问题,这里做个记录。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面可供参考
一、如何构建springboot项目?
1.新建项目
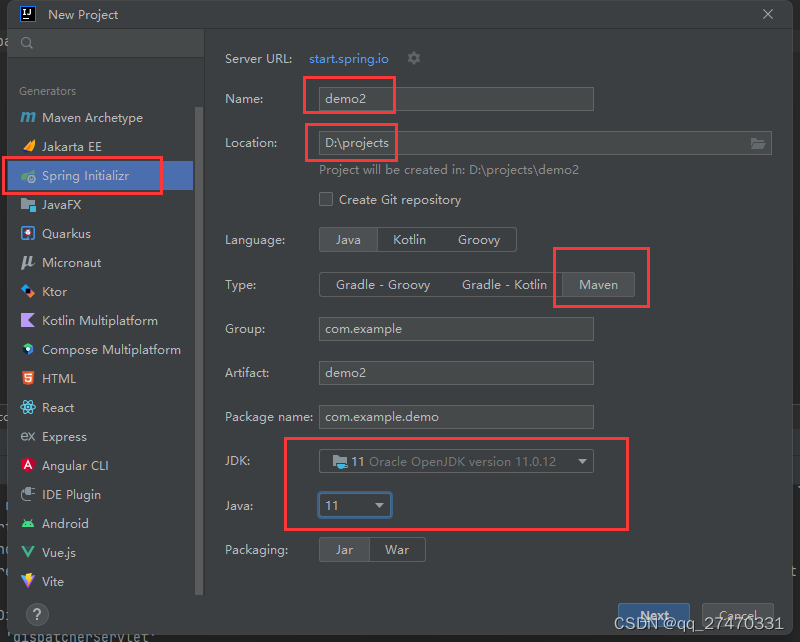
2.设置项目基础配置
这里我需要用maven,所以选的maven。下面的jdk和java最好配置一样,不然可能会报错。
3.配置项目框架支持
这里可以根据自己需要的选择。我这里选择了这些
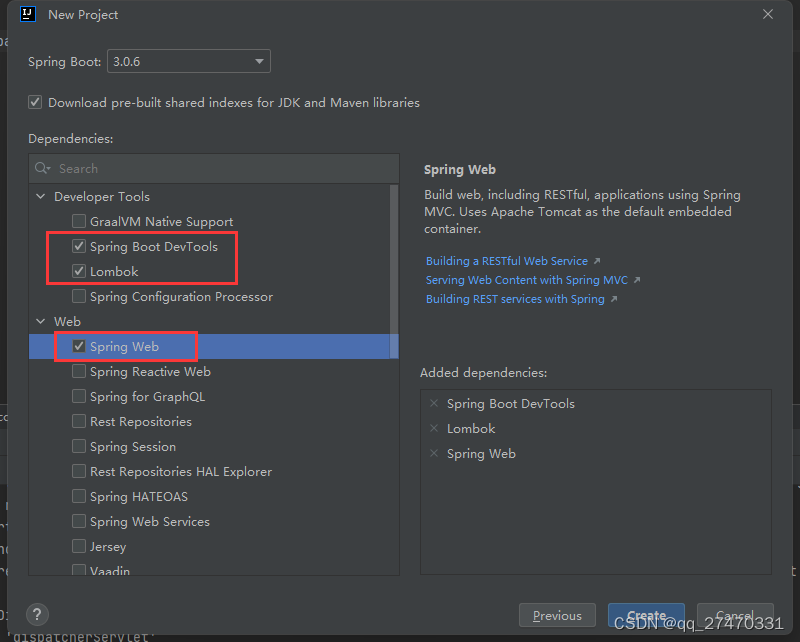
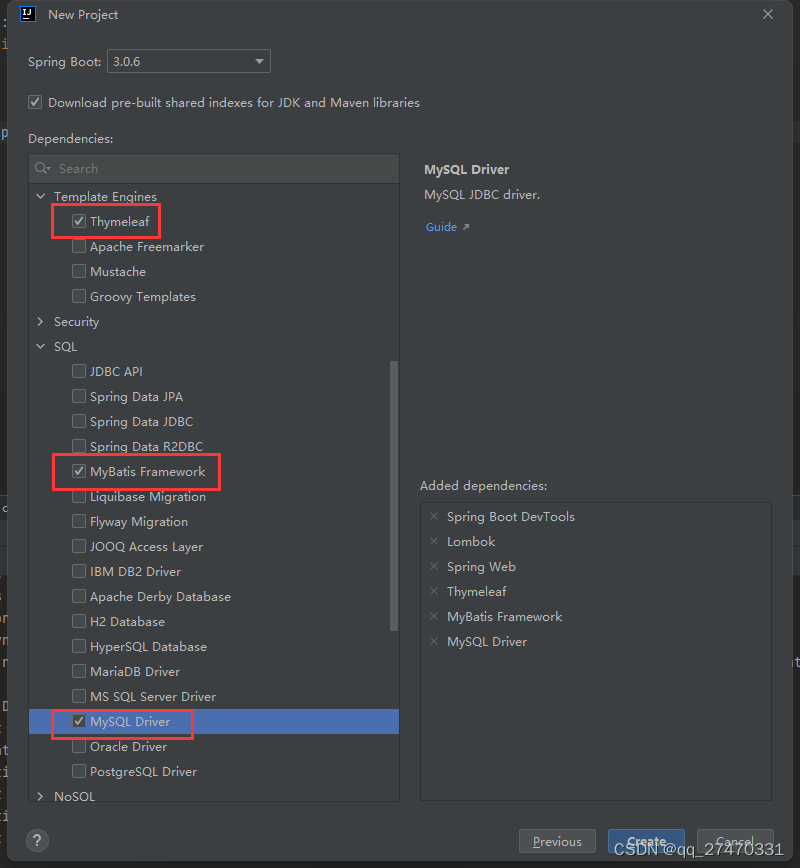
然后点击create进行创建。等待项目进行加载pom文件里面的依赖完成后即可。
4.修改配置文件为yml文件
这里为了方便配置管理,改成了yml文件
二、配置双数据库所需文件
1.编写配置文件
代码如下(示例):
server:
port: 8991
db1:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
user: root
password: xxx
db2:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
user: root
password: xxx
spring:
datasource:
db01:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc-url: ${db1.url}
username: ${db1.user}
password: ${db1.password}
db02:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc-url: ${db2.url}
username: ${db2.user}
password: ${db2.password}
servlet:
multipart:
max-file-size: -1
max-request-size: -1
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
timing-task:
glossary:
batch: 100000
logging:
level:
root: INFO
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
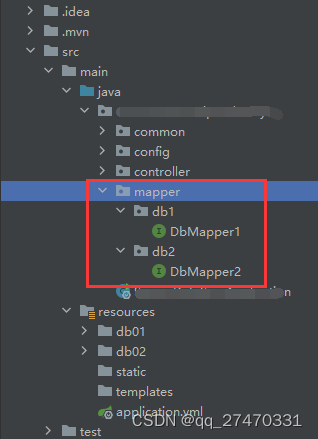
2.使用代码进行数据源注入,和扫描mapper层路径
这里添加了两个数据配置类

(1) 第一个数据库作为主数据库,项目启动默认连接此数据库:
提示:主数据库都有 @Primary注解,从数据库都没有
package com.demo.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.demo.mapper.db1", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "test1SqlSessionTemplate")
public class DataSource1Config {
@Bean("db01DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.db01")
@Primary
public DataSource db01DataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "test1SqlSessionFactory")
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory testSqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db01DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:db01/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean(name = "test1TransactionManager")
@Primary
public DataSourceTransactionManager testTransactionManager(@Qualifier("db01DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "test1SqlSessionTemplate")
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate testSqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("test1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
(2) 第二个数据库作为从数据库。
package com.demo.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.demo.mapper.db2", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "test2SqlSessionTemplate")
public class DataSource2Config {
@Bean("db02DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.db02")
public DataSource db02DataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "test2SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory testSqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db02DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:db02/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean(name = "test2TransactionManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager testTransactionManager(@Qualifier("db02DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "test2SqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate testSqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("test2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
3.设置mapper
package com.demo.mapper.db1;
public interface DbMapper1 {
Integer getMaterialCount();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
package com.demo.mapper.db2;
public interface DbMapper2 {
Integer getMaterialCount();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
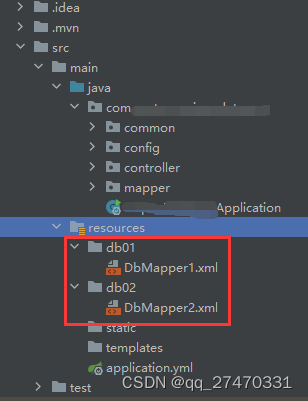
4.设置Mapper对应的sql执行语句
提示:这里的xml的文件名要和上面的mapper的类名一样
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.demo.mapper.db1.DbMapper1">
<select id="getTestCount" resultType="Integer">
SELECT count(*) FROM t_v_test
</select>
</mapper>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.demo.mapper.db2.DbMapper2">
<select id="getTestCount" resultType="Integer">
SELECT count(*) FROM t_v_test
</select>
</mapper>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
5.控制器
这里举例分别访问不同的数据库的控制器方法
package com.demo.controller;
import com.demo.common.ResponseWrapper;
import com.demo.mapper.db1.DbMapper1;
import com.demo.mapper.db2.DbMapper2;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class TestController{
@Autowired
private DbMapper1 testDao1;
@Autowired
private DbMapper2 testDao2;
@GetMapping("/test1")
public ResponseWrapper getTestCount1() {
return ResponseWrapper.wrapperData(tmId -> testDao1.getTestCount(), null);
}
@GetMapping("/test2")
public ResponseWrapper getTestCount2() {
return ResponseWrapper.wrapperData(tmId -> testDao2.getTestCount(), null);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
6.访问地址测试
http://localhost:8991/test1
http://localhost:8991/test2
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文介绍了使用springboot+Mybatis项目管理双数据库的操作。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/weixin_40725706/article/detail/857138
推荐阅读
相关标签



