热门标签
热门文章
- 1探索前沿技术:FastGPT - 高效、灵活的预训练语言模型工具
- 2从零开始开发自己的类keras深度学习框架7:简易版word2vec_keras work2vec
- 3快到飞起!不用代码,一分钟体验二十个开源模型_菜品识别 开源
- 4python安装pip_解决Python安装下载及Python环境的配置(pip,flake8,yapf)
- 5基于STM32的多功能智能手环设计(可以当做毕设与简历项目)_智能手环系统作为毕业设计够么?
- 6Python爬取旅游网站数据机票酒店价格对比分析_python爬取携程酒店数据
- 7双重差分法(DID):算法策略效果评估的利器
- 8python进行中文文本聚类实例(TFIDF计算、词袋构建)_中文文本聚类分析实例
- 9JavaScript基础(一)_js根据条件显示
- 10遥感测深方法综述(三)机载雷达测深系统关键参数_最大水深4/kd是什么意思
当前位置: article > 正文
文本分类-Word2vec+LSTM_word2vec lstm
作者:AllinToyou | 2024-04-02 19:16:51
赞
踩
word2vec lstm
目录
LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory)是一种特殊的循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network,RNN),用于处理序列数据和时间序列数据的建模和预测。相比于传统的RNN结构,LSTM引入了门控机制,能够更好地捕捉和记忆长期依赖关系。
LSTM的关键思想是通过控制信息的流动和遗忘来实现长期记忆。它由一系列称为"记忆单元"的单元组成,每个记忆单元都具有一个内部状态(cell state)和三个门(gate):输入门(input gate)、遗忘门(forget gate)和输出门(output gate)。
一、LSTM文本分类实战
1、数据读取及预处理
- # 导包
- import re
- import os
- from sqlalchemy import create_engine
- import pandas as pd
- import numpy as np
- import warnings
- warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
- import sklearn
- from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
- from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve,roc_auc_score
- import xgboost as xgb
- from xgboost.sklearn import XGBClassifier
- import lightgbm as lgb
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import gc
-
- from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
- from tensorflow.keras import models
- from tensorflow.keras import layers
- from tensorflow.keras import optimizers
-
- # 2、数据读取+预处理
- data=pd.read_excel('Inshorts Cleaned Data.xlsx')
-
- def data_preprocess(data):
- df=data.drop(['Publish Date','Time ','Headline'],axis=1).copy()
- df.rename(columns={'Source ':'Source'},inplace=True)
- df=df[df.Source.isin(['YouTube','India Today'])].reset_index(drop=True)
- df['y']=np.where(df.Source=='YouTube',1,0)
- df=df.drop(['Source'],axis=1)
- return df
-
- df=data.pipe(data_preprocess)
- print(df.shape)
- df.head()
-
- # 导入英文停用词
- from nltk.corpus import stopwords
- from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize
- stop_english=stopwords.words('english')
- stop_spanish=stopwords.words('spanish')
- stop_english
-
- # 4、文本预处理:处理简写、小写化、去除停用词、词性还原
- from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
- from nltk.corpus import stopwords
- from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize
- import nltk
-
- def replace_abbreviation(text):
-
- rep_list=[
- ("it's", "it is"),
- ("i'm", "i am"),
- ("he's", "he is"),
- ("she's", "she is"),
- ("we're", "we are"),
- ("they're", "they are"),
- ("you're", "you are"),
- ("that's", "that is"),
- ("this's", "this is"),
- ("can't", "can not"),
- ("don't", "do not"),
- ("doesn't", "does not"),
- ("we've", "we have"),
- ("i've", " i have"),
- ("isn't", "is not"),
- ("won't", "will not"),
- ("hasn't", "has not"),
- ("wasn't", "was not"),
- ("weren't", "were not"),
- ("let's", "let us"),
- ("didn't", "did not"),
- ("hadn't", "had not"),
- ("waht's", "what is"),
- ("couldn't", "could not"),
- ("you'll", "you will"),
- ("i'll", "i will"),
- ("you've", "you have")
- ]
- result = text.lower()
- for word_replace in rep_list:
- result=result.replace(word_replace[0],word_replace[1])
- # result = result.replace("'s", "")
-
- return result
-
- def drop_char(text):
- result=text.lower()
- result=re.sub('[^\w\s]',' ',result) # 去掉标点符号、特殊字符
- result=re.sub('\s+',' ',result) # 多空格处理为单空格
- return result
-
- def stemed_words(text,stop_words,lemma):
-
- word_list = [lemma.lemmatize(word, pos='v') for word in text.split() if word not in stop_words]
- result=" ".join(word_list)
- return result
-
- def text_preprocess(text_seq):
- stop_words = stopwords.words("english")
- lemma = WordNetLemmatizer()
-
- result=[]
- for text in text_seq:
- if pd.isnull(text):
- result.append(None)
- continue
- text=replace_abbreviation(text)
- text=drop_char(text)
- text=stemed_words(text,stop_words,lemma)
- result.append(text)
- return result
-
- df['short']=text_preprocess(df.Short)
- df[['Short','short']]
-
- # 5、划分训练、测试集
- test_index=list(df.sample(2000).index)
- df['label']=np.where(df.index.isin(test_index),'test','train')
- df['label'].value_counts()

2、文本序列编码
按照词频排序,创建长度为6000的高频词词典、来对文本进行序列化编码。
- from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
- def word_dict_fit(train_text_list,num_words):
- '''
- train_text_list: ['some thing today ','some thing today2']
- '''
- tok_params={
- 'num_words':num_words, # 词典的长度,仅保留词频top的num_words个词
- 'filters':'!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~\t\n',
- 'lower':True,
- 'split':' ',
- 'char_level':False,
- 'oov_token':None, # 设定词典外的词编码
- }
- tok = Tokenizer(**tok_params) # 分词
- tok.fit_on_texts(train_text_list)
-
- return tok
-
- def word_dict_apply_sequences(tok_model,text_list,len_vec):
- '''
- text_list: ['some thing today ','some thing today2']
- '''
- list_tok = tok_model.texts_to_sequences(text_list) # 编码映射
-
- pad_params={
- 'sequences':list_tok,
- 'maxlen':len_vec, # 补全后向量长度
- 'padding':'pre', # 'pre' or 'post',在前、在后补全
- 'truncating':'pre', # 'pre' or 'post',在前、在后删除长度多余的部分
- 'value':0, # 补全0
- }
- seq_tok = pad_sequences(**pad_params) # 补全编码向量,返回二维array
- return seq_tok
-
- num_words,len_vec = 6000,40
- tok_model= word_dict_fit(df[df.label=='train'].short,num_words)
- tok_train = word_dict_apply_sequences(tok_model,df[df.label=='train'].short,len_vec)
- tok_test = word_dict_apply_sequences(tok_model,df[df.label=='test'].short,len_vec)
- tok_test


3、Embedding+LSTM(含LSTM参数介绍)
LSTM层的输入是三维张量(batch_size, timesteps, input_dim),所以使用的数据可以是时间序列、也可以是文本数据的embedding;输出设置return_sequences为False,返回尺寸为 (batch_size, units) 的 2D 张量。
- '''
- LSTM层核心参数
- units:输出维度
- activation:激活函数
- recurrent_activation: RNN循环激活函数
- use_bias: 布尔值,是否使用偏置项
- dropout:0~1之间的浮点数,神经元失活比例
- recurrent_dropout:0~1之间的浮点数,循环状态的神经元失活比例
- return_sequences: True时返回RNN全部输出序列(3D),False时输出序列的最后一个输出(2D)
- '''
- def init_lstm_model(max_features, embed_size):
- model = Sequential()
- model.add(Embedding(input_dim=max_features, output_dim=embed_size))
- model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(units=32,activation='relu', recurrent_dropout=0.1)))
- model.add(Dropout(0.25,seed=1))
- model.add(Dense(64))
- model.add(Dropout(0.3,seed=1))
- model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
-
- model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
-
- return model
-
- def model_fit(model, x, y,test_x,test_y):
- return model.fit(x, y, batch_size=100, epochs=2, validation_data=(test_x,test_y))
-
- embed_size = 128
- lstm_model=init_lstm_model(num_words, embed_size)
- model_train=model_fit(lstm_model,tok_train,np.array(df[df.label=='train'].y),tok_test,np.array(df[df.label=='test'].y))
- lstm_model.summary()

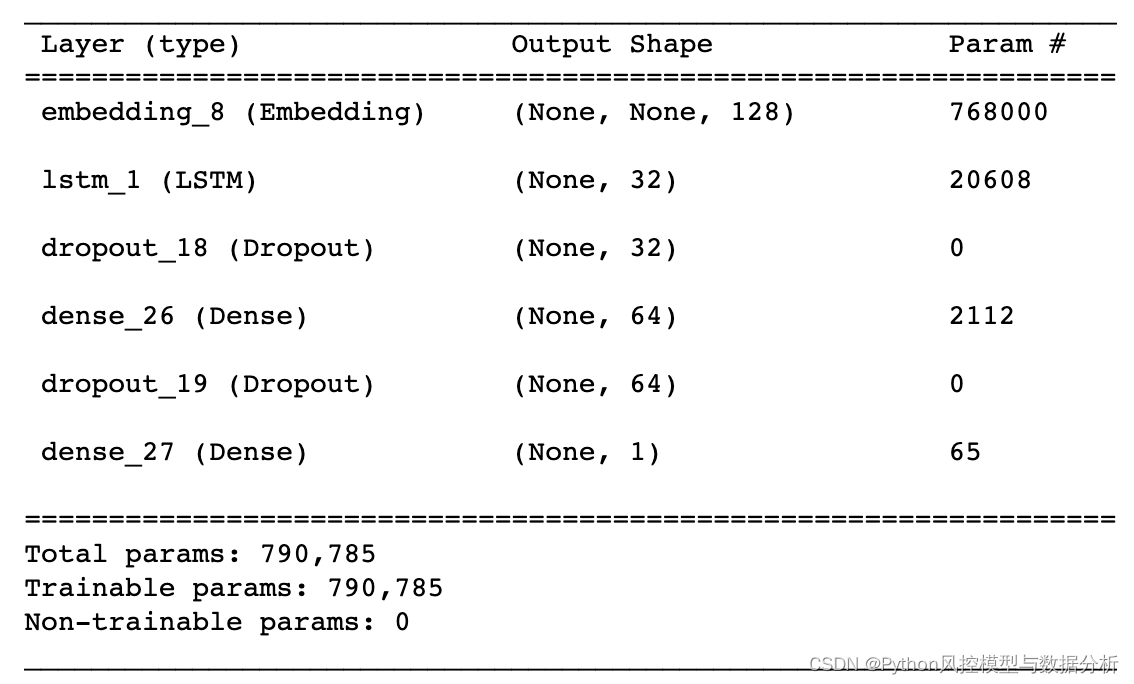
- def ks_auc_value(y_value,df,model):
- y_pred=model.predict(df)
- fpr,tpr,thresholds= roc_curve(list(y_value),list(y_pred))
- ks=max(tpr-fpr)
- auc= roc_auc_score(list(y_value),list(y_pred))
- return ks,auc
-
- ks_auc_value(df[df.label=='train'].y,tok_train,model)
- '''
- output:
- (0.8611593007957995, 0.9749818730610305)
- '''
-
- ks_auc_value(df[df.label=='test'].y,tok_test,model)
- '''
- output:
- (0.7191120926957301, 0.9123405591831509)
- '''

4、Word2vec+双向LSTM
双向LSTM是两个单向LSTM拼接而成,分别为按照序列从前往后、从后往前训练得到。前面可以看到由于数据量小,Embedding+LSTM的结果存在一定过拟合问题,因此使用Word2vec预训练模型+双向LSTM来训练评估,最终评估结果训练集、测试集差异明显缩小。
- def init_lstm_model(max_features, embed_size ,embedding_matrix):
-
- model = Sequential()
- model.add(Embedding(input_dim=max_features, output_dim=embed_size,weights=[embedding_matrix],trainable=False))
- model.add(Bidirectional(layers.LSTM(units=32,activation='relu', recurrent_dropout=0.1)))
- model.add(Dropout(0.3,seed=1))
- model.add(Dense(64,activation='relu'))
- model.add(Dropout(0.3,seed=1))
- model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
-
- model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
-
- return model
-
- def model_fit(model, x, y,test_x,test_y):
- return model.fit(x, y, batch_size=100, epochs=5, validation_data=(test_x,test_y))
-
- num_words,embed_size = 6000,128
- lstm_model=init_lstm_model(num_words, embed_size ,embedding_matrix)
- model_train=model_fit(lstm_model,tok_train,np.array(df[df.label=='train'].y),tok_test,np.array(df[df.label=='test'].y))
-

- ks_auc_value(df[df.label=='train'].y,tok_train,model)
- '''
- output:
- (0.7223217797649937, 0.922939132379851)
- '''
-
- ks_auc_value(df[df.label=='test'].y,tok_test,model)
- '''
- output:
- (0.7046603930606234, 0.9140880065296716)
- '''
二、划重点
少走10年弯路
关注威信公众号Python风控模型与数据分析,回复 文本分类4 获取本篇数据及代码
还有更多理论、代码分享等你来拿
本文内容由网友自发贡献,转载请注明出处:【wpsshop博客】
推荐阅读
相关标签


