热门标签
热门文章
- 1【100个 Unity实用技能】☀️ | Unity读取本地文件(Json,txt等)的三种方法示例
- 2使用mpvue框架开发小程序入门系列_mpvue小程序可以用idea打开吗
- 3【鸿蒙开发】第九章 ArkTS语言UI范式-状态管理(一)_鸿蒙artts对象数组中数据怎么更新
- 4Juno markets:特斯拉FSD登陆中国市场,自动驾驶能否颠覆传统出行?
- 5ONLYOFFICE 桌面编辑器 8.1使用体验分享
- 6基于Flask的Web应用框架_flask 前端框架
- 75大技巧教你快速找到最感兴趣的文章
- 8ssh: command not found的解决办法_ssh报错command 'roslaunch' not found, but can be ins
- 9Elasticsearch 之 commit point | Segment | refresh | flush 索引分片内部原理_在 elasticsearch 中,commit 操作做了什么
- 10matlab读取cvs文件的几种方法_matla中怎么完整读入csv文件
当前位置: article > 正文
机器学习(四):决策树绘画(基础篇)_决策树绘图代码
作者:运维做开发 | 2024-06-29 06:46:13
赞
踩
决策树绘图代码
在前面的章节中,我们已经学过了ID3树,C4.5树和CART树的构造。如果还没有了解过这三棵决策树的话可以点击下方链接:
相关的决策树文章:
下面我们来看看在前面所生成的决策树的模样。
决策树的文字格式
决策树没有绘图之前是由一个多重字典组成,如图:
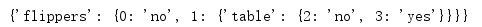
这是我们生成的决策树的文字格式,如今,我们要将其转到图像化。
决策树绘图代码
import matplotlib.pylab as plt #用来正常显示中文 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] #用来正常显示负号 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False def getNumLeafs(myTree): #初始化树的叶子节点的个数 numLeafs = 0 #myTree.keys()获取树的非叶子节点’no surfacing'和‘flippers’ #list(mytree.keys()[0]获取第一个键名‘no surfacing’ firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] #通过键名获取与之对应的值,即{0:'no',1:{'flippers':{0:'no,1:'yes'}}} secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #遍历树,secondDict.keys()获取所有的键 for key in secondDict.keys(): #判断键是否为字典,键名1和其值就组成了一个字典,如果是字典则通过递归继续遍历,寻找叶子节点 if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key]) #如果不是字典,则叶子节点的数目就加1 else: numLeafs += 1 #返回叶子节点的数目 return numLeafs def getTreeDepth(mytree): #初始化树的深度 maxDepth = 0 #获取树的第一个键名 firstStr = list(mytree.keys())[0] #获取键名所对应的值 secondDict = mytree[firstStr] #遍历树 for key in secondDict.keys(): #如果获取的键是字典,树的深度加一 if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': thisDepth = 1+ getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) else: thisDepth = 1 #去深度最大值 if thisDepth > maxDepth : maxDepth = thisDepth #返回树的深度 return maxDepth #设置画节点用的盒子的样式 decisionNode = dict(boxstyle = 'sawtooth', fc='0.8') leafNode = dict(boxstyle = 'round4', fc = '0.8') #设置画箭头的样式 arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-") #绘图相关参数的设置 def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType): #annotate函数是为绘制图上指定的数据点xy添加一个nodeTxt注释 #nodeTxt是给数据点xy添加一个注释,xy为数据点的开始绘制的坐标,位于节点的中间位置 #xycoords设置指定点xy的坐标类型,xytext为注释的中间点坐标,textcoords设置注释点坐标样式 #bbox设置装注释盒子的样式,arrowprops设置箭头的样式 ''' figure points:表示坐标原点在图的左下角的数据点 figure pixels:表示坐标原点在图的左下角的像素点 figure fraction:此时取值是小数,范围是([0,1],[0,1]),在图的左下角时xy是(0,0),最右上角是(1,1) 其他位置是按相对图的宽高的比例取最小值 axes points : 表示坐标原点在图中坐标的左下角的数据点 axes pixels : 表示坐标原点在图中坐标的左下角的像素点 axes fraction : 与figure fraction类似,只不过相对于图的位置改成是相对于坐标轴的位置 ''' createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction', xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction', va='center', ha='center', bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args) #绘制线中间的文字(0和1)的绘制 def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString): xMid = (parentPt[0] - cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0] yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1] createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString) #绘制树 def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt): #获取树的叶子节点 numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #获取树的深度 depth = getTreeDepth(myTree) #firstStr = mytree.keys()[0] #获取第一个键名 firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] # 计算子节点的坐标 cntrPt = (plotTree.xoff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs)) / 2.0 / plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yoff) # 绘制线上的文字 plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt) # 绘制节点 plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode) # 获取第一个键值 secondDict = myTree[firstStr] # 计算节点y方向上的偏移量,根据树的深度 plotTree.yoff = plotTree.yoff - 1.0 / plotTree.totalD for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': # 递归绘制树 plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key)) else: # 更新x的偏移量,每个叶子结点x轴方向上的距离为 1/plotTree.totalW plotTree.xoff = plotTree.xoff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalW # 绘制非叶子节点 plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xoff, plotTree.yoff), cntrPt, leafNode) # 绘制箭头上的标志 plotMidText((plotTree.xoff, plotTree.yoff), cntrPt, str(key)) plotTree.yoff = plotTree.yoff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalD #绘制决策树,inTree的格式为{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}}} def createPlot(inTree): #新建一个figure设置背景颜色为白色 fig = plt.figure(1,facecolor='white') #清除figure fig.clf() axprops = dict(xticks=[],yticks=[]) #创建一个1行1列1个figure,并把网格里面的第一个figure的Axes实例返回给ax1作为函数createPlot() #的属性,这个属性ax1相当于一个全局变量,可以给plotNode函数使用 createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111,frameon=False,**axprops) #获取树的叶子节点 plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree)) #获取树的深度 plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree)) #节点的x轴的偏移量为-1/plotTree.totlaW/2,1为x轴的长度,除以2保证每一个节点的x轴之间的距离为1/plotTree.totlaW*2 plotTree.xoff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW plotTree.yoff = 1.0 plotTree(inTree,(0.5,1.0),'') plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
绘图代码的使用
将绘图的代码的py文件放置于前面三个文件的同一文件目录下。只需要在三个决策树的代码文件中加入:
import plotTrees #加在代码头
plotTrees.createPlot(myTree) #加在代码的尾
- 1
- 2
- 3
结果1:ID3决策树

结果2:C4.5决策树

结果3:CART决策树

成功的画出了三个决策树的图解,是不是感觉自己很棒呢。哈哈。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/运维做开发/article/detail/768533
推荐阅读
相关标签



