- 1干货|AI辅助完成论文的正确打开方式!_使用任意的ai文献工具辅助完成一个文献综述文档,文档内容必须包含截图,适当的说明
- 2botzone snake代码思路整理_提交到botzone上面的代码
- 3如何高效学习Python?Python(入门 、教程、电子书 、学习路线)全都在这啦_如何快速有效学习python
- 4Python 更换源的方法_python从文件里替换源
- 5adb常用指令(集合)_adb查看pid
- 6Mysql set字段类型剖析_mysql set类型的字段
- 7路由器重温——OSPF路由(很重要的协议)-2_type area interarea
- 8工业互联网-企业数据打通解决方案_各系统进行打通
- 9Android 传感器开发详解_传感系统的开发工具csdn
- 10用python编写用户登录界面,用python做登录界面_使用python中的qt库实现用户登陆注册界面
用java写区块链_java中实现一个区块链的基本功能
赞
踩
区块链就好比多个区块连接起来。其中每一块都将拥有自己的签名,签名由其前面的块签名、当前块的一些数据(例如交易信息)生成。
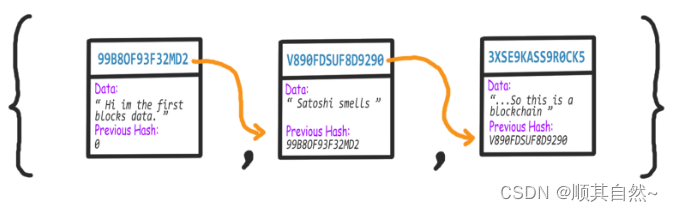
每个块不仅仅包含它之前的块信息,同时也包含自身。如果前面一块内容改变了,其 hash 值也会改变,将会导致其后面所有的块发生变化。通过计算和比较所得的 hash 值,我们可以判断区块链是否合法。换句话说,改变区块链中的任意内容,将会改变整个区块链的签名。区块链就是区块+链,首先创建区块,然后把区块串起来,就像串珠子一样。每个区块可以存储各种数据或数据的摘要。区块链是一个数据库,区块就是数据库的一条记录。
根据上面的分析,我们先创建一个 Block 类。
- import java.util.Date;
-
- public class Block {
- public String hash; //本区块的数字签名
- public String preHash; //前面区块的数字签名
- private String data;//本区块存放的数据
- private long timeStamp;//本区块产生的时间
-
- public Block(String data, String preHash) {
- this.data = data;
- this.preHash = preHash;
- this.timeStamp = new Date().getTime();
- }
- }
接下来,我们需要一个生成签名的方法。有很多加密算法可供选择,这里使用 SHA256。
- import java.security.MessageDigest;
-
- public class StringUtil {
- public static String applySha256(String input) {
- try {
- MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
-
- byte[] hash = digest.digest(input.getBytes("UTF-8"));
- StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
- for (int i = 0; i < hash.length; i++) {
- String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & hash[i]);
- if (hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
- hexString.append(hex);
- }
- return hexString.toString();
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- }

现在,我们向 Block 类中添加计算数字签名的方法,并修改一下其构造方法。
- public Block(String data, String preHash) {
- this.data = data;
- this.preHash = preHash;
- this.timeStamp = new Date().getTime();
- this.hash = calculateHash();
- }
-
- public String calculateHash() {
- String calculatedhash = StringUtil.applySha256(preHash + Long.toString(timeStamp) + data);
- return calculatedhash;
- }
到这里,可以写个 Main 方法看一下效果。
- public class Main {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Block first = new Block("Hi i am the first block", "0");
- System.out.println("Hash for block 1 : " + first.hash);
- Block second = new Block("Hi i am the second block", first.hash);
- System.out.println("Hash for block 2 : " + second.hash);
- Block third = new Block("Hi i am the third block", second.hash);
- System.out.println("Hash for block 3 : " + third.hash);
- }
- }
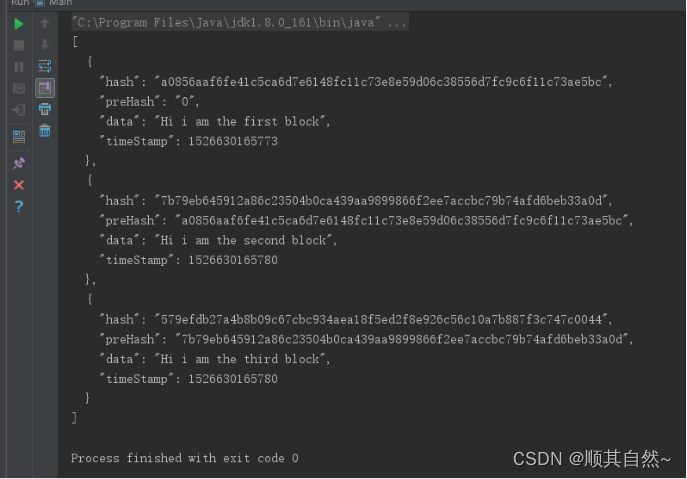
可以看见每个 Block 都有自己唯一的 数字签名,当然,现在还没有构成一个区块链,将这些块存放到一个 ArrayList 中吧。修改 Main 类后再次运行。
- import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
-
- import java.util.ArrayList;
-
- public class Main {
-
- public static ArrayList<Block> blockchain = new ArrayList<Block>();
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- blockchain.add(new Block("Hi i am the first block", "0"));
- blockchain.add(new Block("Hi i am the second block", blockchain.get(blockchain.size() - 1).hash));
- blockchain.add(new Block("Hi i am the third block", blockchain.get(blockchain.size() - 1).hash));
-
- String blockchainJson = new GsonBuilder().setPrettyPrinting().create().toJson(blockchain);
- System.out.println(blockchainJson);
- }
- }

现在,需要一种方法去验证创建的区块链。编写一段 isChainValid() 方法。任何块的改变将会导致这个方法失效。
- public static Boolean isChainValid() {
- Block currentBlock;
- Block previousBlock;
-
- for (int i = 1; i < blockchain.size(); i++) {
- currentBlock = blockchain.get(i);
- previousBlock = blockchain.get(i - 1);
-
- if (!currentBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.calculateHash())) {
- //当前区块不能由上一区块计算出来,说明上一区块改变了
- System.out.println("Current Hashes not equal!");
- return false;
- }
-
- if (!previousBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.preHash)) {
- //当前区块中保持的上一区块hash不等于上一区块hash,说明上一区块改变了
- System.out.println("Previous Hashes not equal!");
- return false
- }
- }
- return true;
- }

接下来,尝试一下挖矿!
在 Block 类中,新增一个变量 nonce(随机数),并且添加到 calculateHash() 这个方法中,同时需要 mineBlock() 这个方法。这个方法中的 difficulty 变量就是用来控制计算量的。当设置的值较低时,大部分计算机很快就能算出来。
- import java.util.Date;
-
- public class Block {
- public String hash; //本区块的数字签名
- public String preHash; //前面区块的数字签名
- private String data;//本区块存放的数据
- private long timeStamp;//本区块产生的时间
- private int nonce;//随机数
-
- public Block(String data, String preHash) {
- this.data = data;
- this.preHash = preHash;
- this.timeStamp = new Date().getTime();
- this.hash = calculateHash();
- }
- /**
- * 根据前面区块前面+本区块产生时间+本区块数据生成本区块签名
- * @return
- */
- public String calculateHash() {
- String calculatedhash = StringUtil.applySha256(preHash + Long.toString(timeStamp) + Integer.toString(nonce) +
- data);
- return calculatedhash;
- }
- //挖矿
- public void mineBlock(int difficulty) {
- String target = new String(new char[difficulty]).replace('\0', '0');
- while (!hash.substring(0, difficulty).equals(target)) {//找到符合难度的hash
- nonce++;
- hash = calculateHash();
- }
- System.out.println("Block Mined!!!" + hash);
- }
- }

我们可以在 Main 类中定义个静态变量。尝试在每次创建新块去调用 mineBlock() 方法。
- import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
-
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Date;
-
- public class Main {
-
- public static ArrayList<Block> blockchain = new ArrayList<Block>();
- public static int difficulty = 5;
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- long beginTime1 = new Date().getTime();
- blockchain.add(new Block("Hi i am the first block", "0"));
- System.out.println("Trying to mine block 1...");
- blockchain.get(0).mineBlock(difficulty);
- long endTime1 = new Date().getTime();
- System.out.println("Mining block 1 cost " + (endTime1 - beginTime1));
-
-
- long beginTime2 = new Date().getTime();
- blockchain.add(new Block("Hi i am the second block", blockchain.get(blockchain.size() - 1).hash));
- System.out.println("Trying to mine block 2...");
- blockchain.get(1).mineBlock(difficulty);
- long endTime2 = new Date().getTime();
- System.out.println("Mining block 1 cost " + (endTime2 - beginTime2));
-
- long beginTime3 = new Date().getTime();
- blockchain.add(new Block("Hi i am the third block", blockchain.get(blockchain.size() - 1).hash));
- System.out.println("Trying to mine block 3...");
- blockchain.get(2).mineBlock(difficulty);
- long endTime3 = new Date().getTime();
- System.out.println("Mining block 1 cost " + (endTime3 - beginTime3));
-
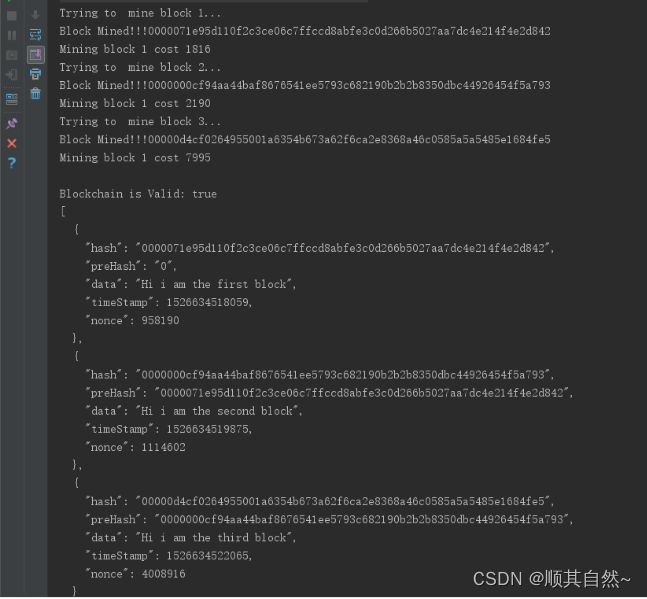
- System.out.println("\nBlockchain is Valid: " + isChainValid());
-
- String blockchainJson = new GsonBuilder().setPrettyPrinting().create().toJson(blockchain);
- System.out.println(blockchainJson);
- }
-
- public static Boolean isChainValid() {
- Block currentBlock;
- Block previousBlock;
- String hashTarget = new String(new char[difficulty]).replace('\0', '0');
-
- for (int i = 1; i < blockchain.size(); i++) {
- currentBlock = blockchain.get(i);
- previousBlock = blockchain.get(i - 1);
-
- if (!currentBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.calculateHash())) {
- System.out.println("Current Hashes not equal!");
- return false;
- }
-
- if (!previousBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.preHash)) {
- System.out.println("Previous Hashes not equal!");
- return false;
- }
-
- if (!currentBlock.hash.substring(0, difficulty).equals(hashTarget)) {
- System.out.println("This block hasn't been mined");
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- }

运行发现,挖矿过程还是很费时间的。把计算量改成7,差不多每挖一个需要一分钟。。。
如果在此过程中,有人篡改了数据,将会导致:
1)区块链将会无效
2)不能够创建一个更长的区块链
3)网络中的诚实链将会比较长的区块链有时间上的优势
不过如果篡改数据拥有更强的运算速度,可能成功篡改。
这样,基本上简单实现了一个区块链了。


