热门标签
热门文章
- 1深入了解AI大模型在语音识别领域的挑战
- 2EncryptUtil加密解密工具类,实测可以,复制粘贴皆可。全套代码加使用案例方法。
- 3为了避免内存攻击,美国国家安全局提倡Rust、C#、Go、Java、Ruby 和 Swift,但将 C 和 C++ 置于一边...
- 4redux的基础学习使用
- 5pytorch,torchvision与python版本对应关系_torch1.10.1对应的torchvision
- 6JavaScript基础(一)_js根据条件显示
- 7多种方式实现Android页面布局的切换_安卓 切换布局文件
- 8主题模型LDA教程:主题数选取 困惑度perplexing_lda困惑度
- 9自然语言处理之准确率、召回率、F1理解_nlp f1
- 10机器学习的入门教学-scikit-learn_scikit-learn教程
当前位置: article > 正文
Python机器学习库sklearn几种分类算法建模可视化(实验)_python机器学习分类模型可视化
作者:菜鸟追梦旅行 | 2024-04-04 13:26:09
赞
踩
python机器学习分类模型可视化
sklearn官网API查询http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/classes.html
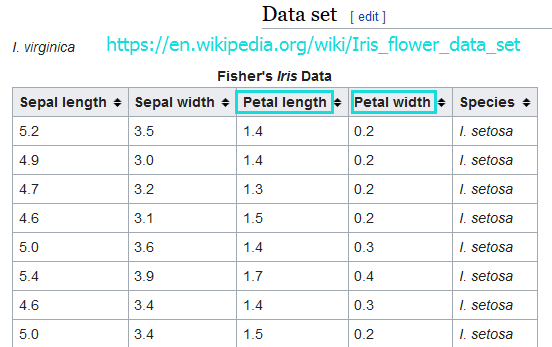
scikit-learn中自带了一些数据集,比如说最著名的Iris数据集。
数据集中第3列和第4列数据表示花瓣的长度和宽度,类别标签列已经转成了数字,比如0=Iris-Setosa,1=Iris-Versicolor,2=Iris-Virginica.
一、导入python库和实验数据集
- from IPython.display import Image
- %matplotlib inline
- # Added version check for recent scikit-learn 0.18 checks
- from distutils.version import LooseVersion as Version
- from sklearn import __version__ as sklearn_version
-
- from sklearn import datasets
- import numpy as np
- iris = datasets.load_iris()
- #http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/datasets/plot_iris_dataset.html
- X = iris.data[:, [2, 3]]
- y = iris.target #取species列,类别
- print('Class labels:', np.unique(y))
- #Output:Class labels: [0 1 2]
二、数据集切分
把数据集切分成训练集和测试集,这里70%的训练集,30%的测试集
- if Version(sklearn_version) < '0.18':
- from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
- else:
- from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
-
- X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
- X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0) #train_test_split方法分割数据集
-
- X_train.shape
- #Output:(105, 2)
- X_test.shape
- #Output:(45, 2)
- X.shape
- #Output:(150, 2)
- y_train.shape
- #Output: (105,)
- y_test.shape
- #Output: (45,)

三、对特征做标准化
非树形模型一般都要对特征数据进行标准化处理,避免数据波动的影响。处理后各维特征有0均值,单位方差。也叫z-score规范化(零均值规范化)。计算方式是将特征值减去均值,除以标准差。
- #scaler = sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit(train)
- #scaler.transform(train);scaler.transform(test)
- #fit()方法建模,transform()方法转换
- from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
- sc = StandardScaler() #初始化一个对象sc去对数据集作变换
- sc.fit(X_train) #用对象去拟合数据集X_train,并且存下来拟合参数
- #Output:StandardScaler(copy=True, with_mean=True, with_std=True)
- #type(sc.fit(X_train))
- #Output:sklearn.preprocessing.data.StandardScaler
- sc.scale_ #sc.std_同样输出结果
- #Output:array([ 1.79595918, 0.77769705])
- sc.mean_
- #Output:array([ 3.82857143, 1.22666667])
-
- import numpy as np
- X_train_std = sc.transform(X_train)
- X_test_std = sc.transform(X_test)
- #test标准化原理
- at=X_train_std[:5]*sc.scale_+sc.mean_
- a=X_train[:5]
- at==a
- #Output:
- #array([[ True, True],
- # [ True, True],
- # [ True, True],
- # [ True, True],
- # [ True, True]], dtype=bool)

四、各种算法分类及可视化
下面各算法中,通过plot_decision_region函数可视化,方便直观看分类结果
- from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import warnings
- def versiontuple(v):#Numpy版本检测函数
- return tuple(map(int, (v.split("."))))
- def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, test_idx=None, resolution=0.02):
- #画决策边界,X是特征,y是标签,classifier是分类器,test_idx是测试集序号
- # setup marker generator and color map
- markers = ('s', 'x', 'o', '^', 'v')
- colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')
- cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
-
- # plot the decision surface
- x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1 #第一个特征取值范围作为横轴
- x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1 #第二个特征取值范围作为纵轴
- xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution),
- np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution)) #reolution是网格剖分粒度,xx1和xx2数组维度一样
- Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T)
- #classifier指定分类器,ravel是数组展平;Z的作用是对组合的二种特征进行预测
- Z = Z.reshape(xx1.shape) #Z是列向量
- plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap=cmap)
- #contourf(x,y,z)其中x和y为两个等长一维数组,z为二维数组,指定每一对xy所对应的z值。
- #对等高线间的区域进行填充(使用不同的颜色)
- plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max())
- plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max())
-
- for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
- plt.scatter(x=X[y == cl, 0], y=X[y == cl, 1],
- alpha=0.8, c=cmap(idx),
- marker=markers[idx], label=cl) #全数据集,不同类别样本点的特征作为坐标(x,y),用不同颜色画散点图
-
- # highlight test samples
- if test_idx:
- # plot all samples
- if not versiontuple(np.__version__) >= versiontuple('1.9.0'):
- X_test, y_test = X[list(test_idx), :], y[list(test_idx)]
- warnings.warn('Please update to NumPy 1.9.0 or newer')
- else:
- X_test, y_test = X[test_idx, :], y[test_idx] #X_test取测试集样本两列特征,y_test取测试集标签
-
- plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0],
- X_test[:, 1],
- c='',
- alpha=1.0,
- linewidths=1,
- marker='o',
- s=55, label='test set') #c设置颜色,测试集不同类别的实例点画图不区别颜色

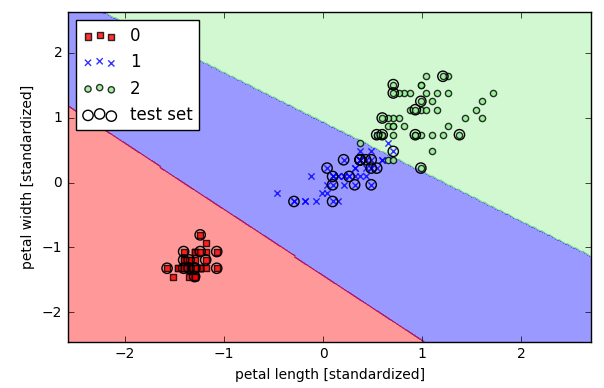
用scikit-learn中的感知器做分类(三类分类)
- from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
- #http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.Perceptron.html#sklearn.linear_model.Perceptron
- #ppn = Perceptron(n_iter=40, eta0=0.1, random_state=0)
- ppn = Perceptron() #y=w.x+b
- ppn.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
- #Output:Perceptron(alpha=0.0001, class_weight=None, eta0=1.0, fit_intercept=True,
- # n_iter=5, n_jobs=1, penalty=None, random_state=0, shuffle=True,
- # verbose=0, warm_start=False)
- ppn.coef_ #分类决策函数中的特征系数w
- #Output:array([[-1.48746619, -1.1229737 ],
- # [ 3.0624304 , -2.18594118],
- # [ 2.9272062 , 2.64027405]])
- ppn.intercept_ #分类决策函数中的偏置项b
- #Output:array([-1., 0., -2.])
- y_pred = ppn.predict(X_test_std) #对测试集做类别预测
- y_pred
- #Output:array([2, 1, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0,
- # 0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 2, 2, 1, 0, 2, 1, 1, 2, 0, 2, 0, 0])
- y_test
- #Output:array([2, 1, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0,
- # 0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 2, 2, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 2, 0, 0])
- y_pred == y_test
- #Output:array([ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
- # True, False, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
- # True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
- # True, False, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
- # True, False, True, True, True, True, True, True, True], dtype=bool)
- print('Misclassified samples: %d' % (y_test != y_pred).sum())
- #Output:Misclassified samples: 3
- from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
- print('Accuracy: %.2f' % accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)) #预测准确度,(len(y_test)-3)/len(y_test):0.9333333333333333
- #Output:Accuracy: 0.93

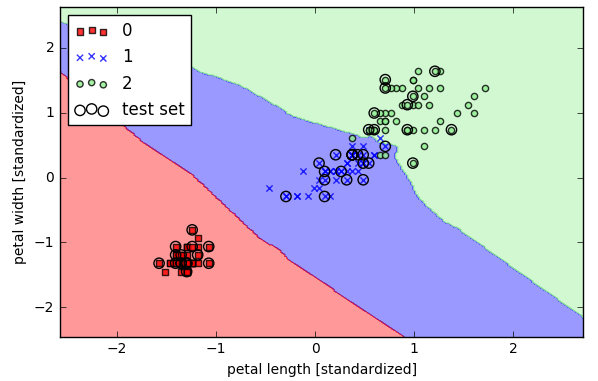
用标准化的数据做一个感知器分类器
- %matplotlib inline
- X_combined_std = np.vstack((X_train_std, X_test_std)) #shape是(150,2)
- y_combined = np.hstack((y_train, y_test)) #shape是(150,)
-
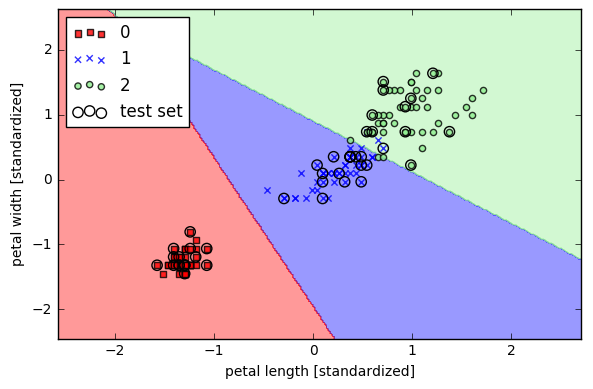
- plot_decision_regions(X=X_combined_std, y=y_combined,
- classifier=ppn, test_idx=range(105, 150))
- plt.xlabel('petal length [standardized]')
- plt.ylabel('petal width [standardized]')
- plt.legend(loc='upper left')
-
- plt.tight_layout() #紧凑显示图片,居中显示;避免出现叠影
- # plt.savefig('./figures/iris_perceptron_scikit.png', dpi=300)
- plt.show()
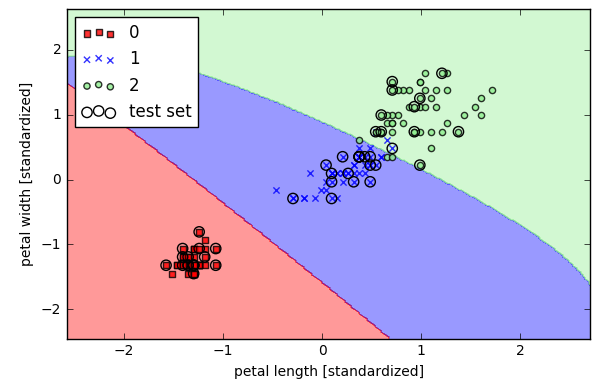
用scikit-learn中的LR预测属于每个类别的概率(三类分类)
- from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
- lr = LogisticRegression(C=1000.0, random_state=0)
- #http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression.html#sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression
- lr.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
- plot_decision_regions(X_combined_std, y_combined, classifier=lr, test_idx=range(105, 150))
- plt.xlabel('petal length [standardized]')
- plt.ylabel('petal width [standardized]')
- plt.legend(loc='upper left')
- plt.tight_layout()
- # plt.savefig('./figures/logistic_regression.png', dpi=300)
- plt.show()
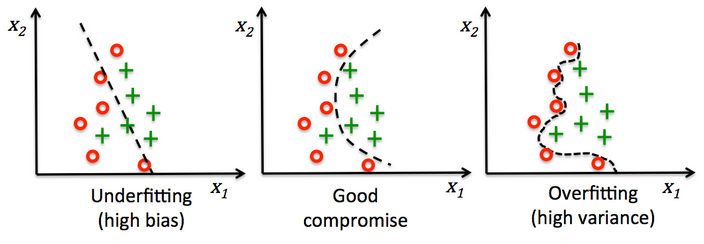
过拟合/overfitting 与 正则化/regularization
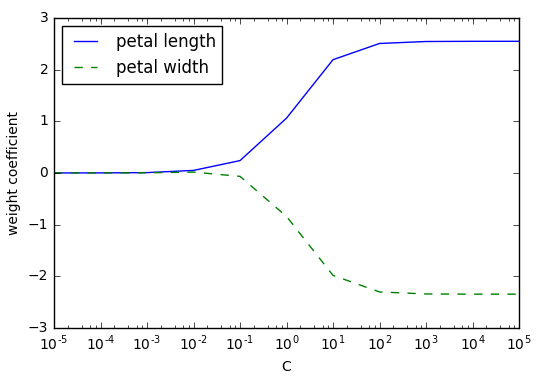
- weights, params = [], []
-
- for c in range(-5,6):
- lr = LogisticRegression(C=10**c, random_state=0) #默认L2正则,C是正则化系数的倒数(C越小,特征权重越小)
- lr.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
- weights.append(lr.coef_[1]) ##############################lr.coef_[1]
- params.append(10**c)
-
- weights = np.array(weights)
- plt.plot(params,weights[:, 0],label='petal length')
- plt.plot(params,weights[:, 1],linestyle='--',label='petal width')
- plt.ylabel('weight coefficient')
- plt.xlabel('C')
- plt.legend(loc='upper left')
- plt.xscale('log') #在x轴上画对数坐标轴
- # plt.savefig('./figures/regression_path.png', dpi=300)
- plt.show()

用scikit-learn中的SVM做分类(三类分类)
- from sklearn.svm import SVC
- #http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.svm.SVC.html#sklearn.svm.SVC
- svm = SVC(kernel='linear', C=1.0, random_state=0)
- svm.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
-
- plot_decision_regions(X_combined_std, y_combined, classifier=svm, test_idx=range(105, 150))
- plt.xlabel('petal length [standardized]')
- plt.ylabel('petal width [standardized]')
- plt.legend(loc='upper left')
- plt.tight_layout()
- # plt.savefig('./figures/support_vector_machine_linear.png', dpi=300)
- plt.show()
上图利用的是线性SVM分类,但是从上图可见有些点被分错类了,进一步,考虑利用核函数进行非线性分类
- from sklearn.svm import SVC
- svm = SVC(kernel='rbf',random_state=0,gamma=0.2,C=1.0)
- svm.fit(X_train_std,y_train)
- plot_decision_regions(X_combined_std, y_combined, classifier=svm, test_idx=range(105, 150))
- plt.xlabel('petal length [standardized]')
- plt.ylabel('petal width [standardized]')
- plt.legend(loc='upper left')
- plt.tight_layout()
- # plt.savefig('./figures/support_vector_machine_rbf_iris_1.png', dpi=300)
- plt.show()
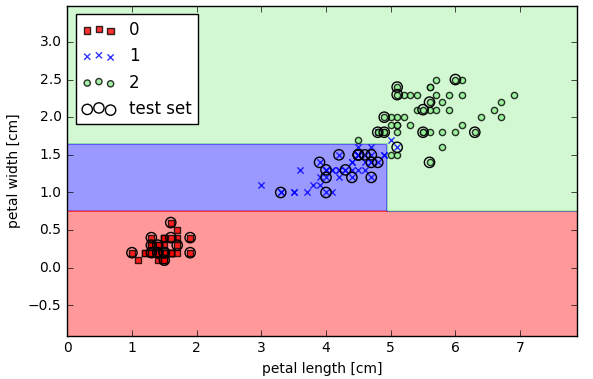
用scikit-learn中的决策树做分类(三类分类)
- from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
- #http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier.html#sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier
- tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy', max_depth=3, random_state=0)
- #特征选择的度量,entropy是信息增益;max_depth参数是数的最大深度
- tree.fit(X_train, y_train)
- X_combined = np.vstack((X_train, X_test))
- y_combined = np.hstack((y_train, y_test))
- plot_decision_regions(X_combined, y_combined, classifier=tree, test_idx=range(105, 150))
- plt.xlabel('petal length [cm]')
- plt.ylabel('petal width [cm]')
- plt.legend(loc='upper left')
- plt.tight_layout()
- # plt.savefig('./figures/decision_tree_decision.png', dpi=300)
- plt.show()
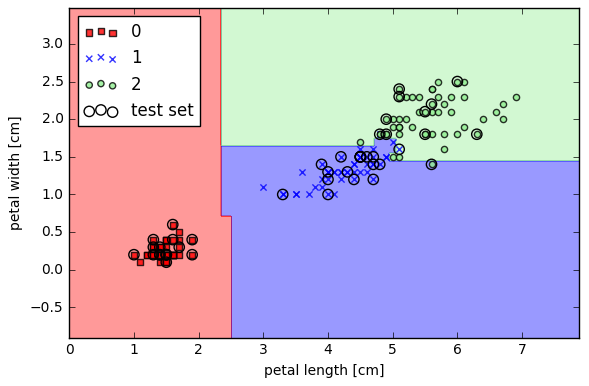
用scikit-learn中的随机森林做分类(三类分类)
- from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
- forest = RandomForestClassifier(criterion='entropy', n_estimators=10, random_state=1, n_jobs=2)
- #http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier.html#sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier
- #criterion特征选择度量,n_estimators随机森林中单棵树数目,n_jobs设置并行生成树模型得数目
- forest.fit(X_train, y_train)
- plot_decision_regions(X_combined, y_combined, classifier=forest, test_idx=range(105, 150))
- plt.xlabel('petal length [cm]')
- plt.ylabel('petal width [cm]')
- plt.legend(loc='upper left')
- plt.tight_layout()
- # plt.savefig('./figures/random_forest.png', dpi=300)
- plt.show()
用scikit-learn中的k-近邻做分类(三类分类)
- from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
- knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5, p=2, metric='minkowski')
- #http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier.html#sklearn.neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier
- #p是度量范数,metric='minkowski'距离度量标准2范数
- knn.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
- plot_decision_regions(X_combined_std, y_combined, classifier=knn, test_idx=range(105, 150))
- plt.xlabel('petal length [standardized]')
- plt.ylabel('petal width [standardized]')
- plt.legend(loc='upper left')
- plt.tight_layout()
- # plt.savefig('./figures/k_nearest_neighbors.png', dpi=300)
- plt.show()
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/菜鸟追梦旅行/article/detail/358893
推荐阅读
相关标签