- 1词性标注教程_propn
- 2Android使用Tesseract-ocr进行文字识别_android tesseract
- 3基于神经网络的依存句法分析_神经网络 依存句法分析
- 4跟着Kimi Chat学习提示工程Prompt Engineering!让AI更高效地给你打工!
- 5区别探索:掩码语言模型 (MLM) 和因果语言模型 (CLM)的区别
- 6UEditor富文本编辑器
- 7人工智能原理(学习笔记)_生理学派起源于仿生学
- 8知识图谱基础知识(一): 概念和构建_本体作为知识图谱的模式层,在约束概念关系、明确概念属性上起到了重要 作用。
- 9TCP系列教程—SIM7000X TCP 通信猫之旅_tcp 猫
- 10【NLP】第15章 从 NLP 到与任务无关的 Transformer 模型_google/reformer-crime-and-punishment
【图像分类案例】(1) ResNeXt 交通标志四分类,附Tensorflow完整代码_resnext 模型架构
赞
踩
各位同学好,今天和大家分享一下如何使用 Tensorflow 构建 ResNeXt 神经网络模型,通过案例实战 ResNeXt 的训练以及预测过程。每个小节的末尾有网络、训练、预测的完整代码。想要数据集的私聊我就行。
ResNeXt 是 ResNet 的改进版,在 bottleneck卷积块 结构上进行了较小的改动,其他都和 ResNet 模块相近,如下图所示,ResNeXt 比 ResNet 的精度更好。
本节只介绍 ResNeXt 的改进部分,想了解 ResNet 网络的,可以看我的这篇文章:https://blog.csdn.net/dgvv4/article/details/122396424

1. ResNeXt 模型结构
1.1 分组卷积
(1)在标准卷积中,输入有多少个通道,卷积核就有多少个通道。
举个例子:若输入的图像shape为5x5x6,一个卷积核的shape为3x3x6,使用3个卷积核,得到的特征图shape为3x3x3。参数量 = 5x5x6x3 = 450
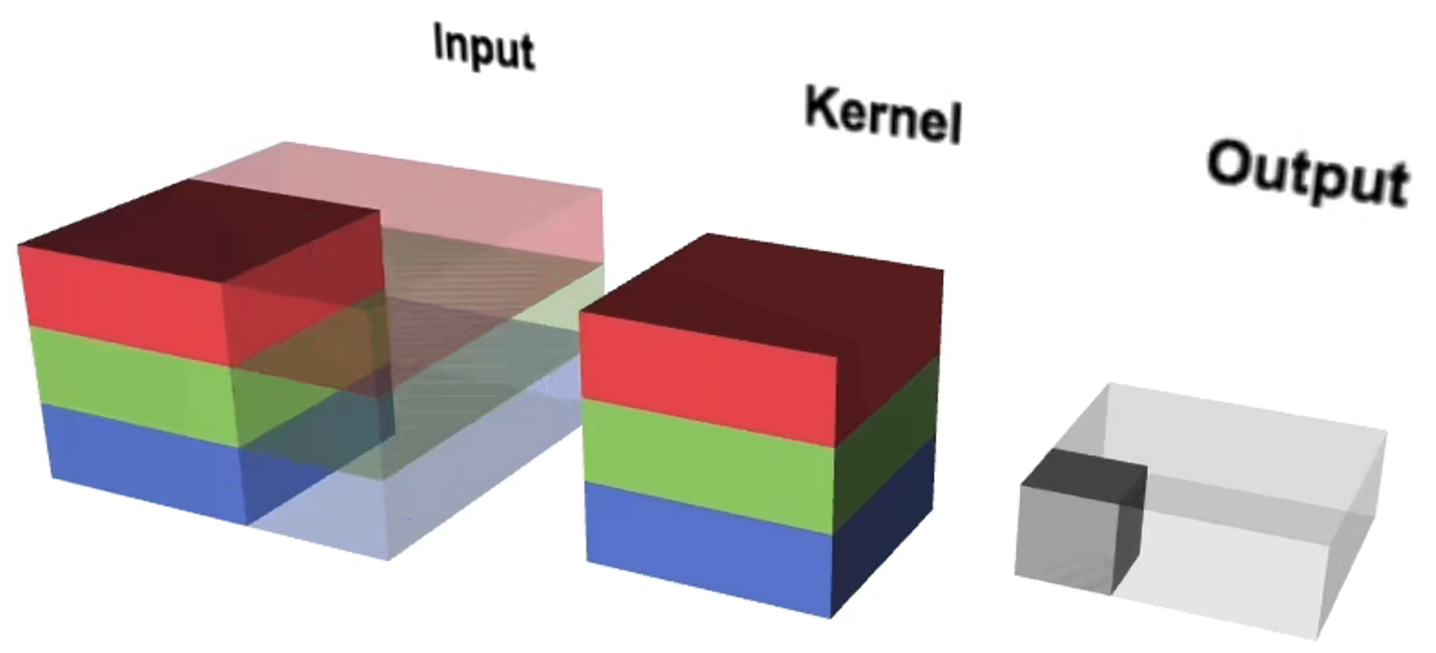
(2)在分组卷积中,每个卷积核只处理部分通道。如下图,红色的卷积核只处理输入图像中红色的两个通道,绿色的卷积核只处理输入图像中间的两个绿色的通道,第三个卷积核只处理黄色的两个通道。此时,每个卷积核有两个通道,每个卷积核生成一个特征图。
举个例子:若输入的图像shape为5x5x6,一个分组卷积核的shape为3x3x2,使用3个分组卷积核,得到的特征图shape为3x3x3。参数量 = 5x5x(6/3)x(3/3)x3 = 5x5x2x1x3 = 150 。可见,分成三组,参数量为原来的三分之一。
因此,分组卷积能够有效地降低参数量和计算量。

代码实现:
- #(1)分组卷积块
- def group_conv(inputs, filters, stride, num_groups):
- '''
- inputs为输入特征图
- filters为每个分组卷积的输出通道数
- stride为分组卷积的步长
- num_groups为分几组
- '''
- # 用来保存每个分组卷积的输出特征图
- groupList = []
-
- for i in range(num_groups): # 遍历每一组
- # 均匀取出需要卷积的特征图inputs.shape=[b,h,w,c]
- x = inputs[:, :, :, i*filters: (i+1)*filters]
- # 分别对每一组卷积使用3*3卷积
- x = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=3, strides=stride, padding='same', use_bias=False)(x)
- # 将每个分组卷积结果保存起来
- groupList.append(x)
-
- # 将每个分组卷积的输出特征图在通道维度上堆叠
- x = layers.Concatenate()(groupList)
-
- x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x) # 批标准化
-
- x = layers.Activation('relu')(x) # 激活函数
-
- return x
1.2 残差结构单元
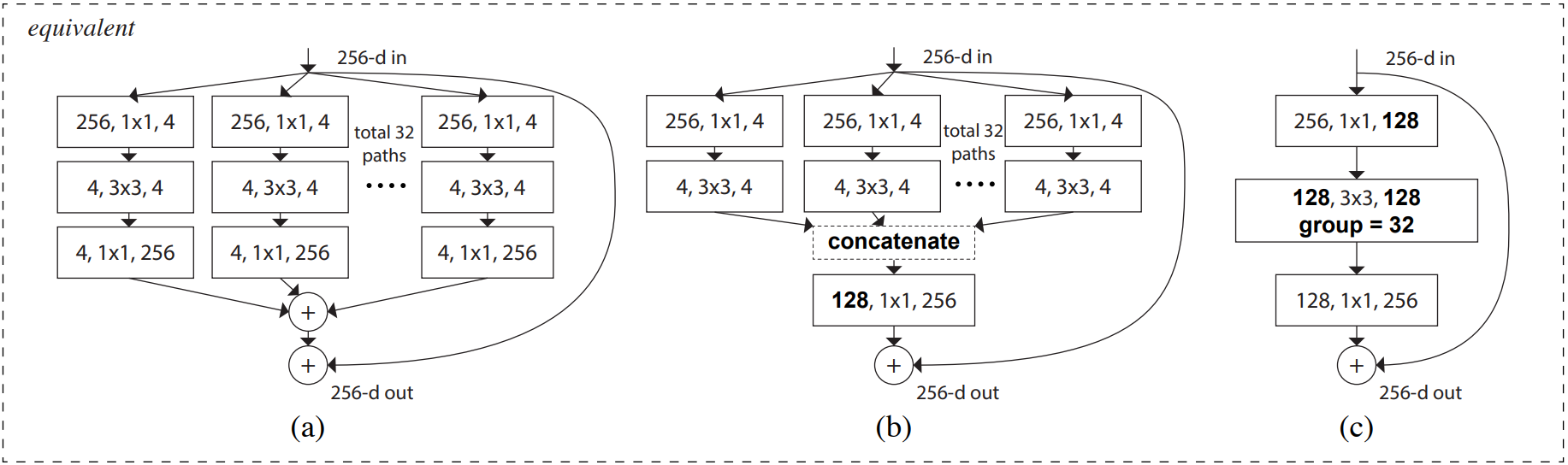
论文中的残差单元结构图如下,它们在数学计算上完全等价。
如图c,首先经过1x1卷积下降通道数 [h,w,256]==>[h,w,128];然后经过3x3分组卷积提取特征;再经过1x1卷积上升通道数 [h,w,128]==>[h,w,256];最后,如果输入和输出的shape相同,通过残差连接输入和输出。
如图b,可以理解为,第一层的32个1x1卷积相当于图c的第一个1x1卷积;第二三层的将分组卷积的结果在通道上堆叠,就是图c的3x3分组卷积
代码实现
- #(2)一个残差单元
- def res_block(inputs, out_channel, stride, shortcut, num_groups=32):
- '''
- inputs输入特征图
- out_channel最后一个1*1卷积的输出通道数
- stride=2下采样, 图像长宽减半, 残差边对输入卷积后再连接输出
- stride=1基本模块, size不变, 残差连接输入和输出
- num_groups代表3*3分组卷积分了几组
- shortcut判断是否要调整通道数
- '''
- # 残差边
- if shortcut is False: # 直接使用参加连接输入和输出
- residual = inputs
-
- elif shortcut is True: # 调整通道数
- # 1*1卷积调整通道数,使输入输出的size和通道数相同
- residual = layers.Conv2D(out_channel, kernel_size=1, strides=stride, padding='same', use_bias=False)(inputs)
- # 有BN层就不需要偏置
- residual = layers.BatchNormalization()(residual)
-
- # 1*1卷积,输出通道数是最后一个1*1卷积层输出通道数的一半
- x = layers.Conv2D(filters = out_channel//2, kernel_size=1, strides=1,
- padding = 'same', use_bias = False)(inputs)
-
- x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
- x = layers.Activation('relu')(x)
-
- # 3*3分组卷积
- group_filters = (out_channel//2) // num_groups # 每一组卷积的输出通道数
- x = group_conv(x, filters = group_filters, stride = stride, num_groups = num_groups)
-
- # 1*1卷积上升通道
- x = layers.Conv2D(filters = out_channel, kernel_size = 1, strides = 1,
- padding = 'same', use_bias = False)(x)
-
- x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
-
- # 残差连接,保证x和残差边的shape相同
- x = layers.Add()([x, residual])
- x = layers.Activation('relu')(x)
-
- return x
1.3 网络结构
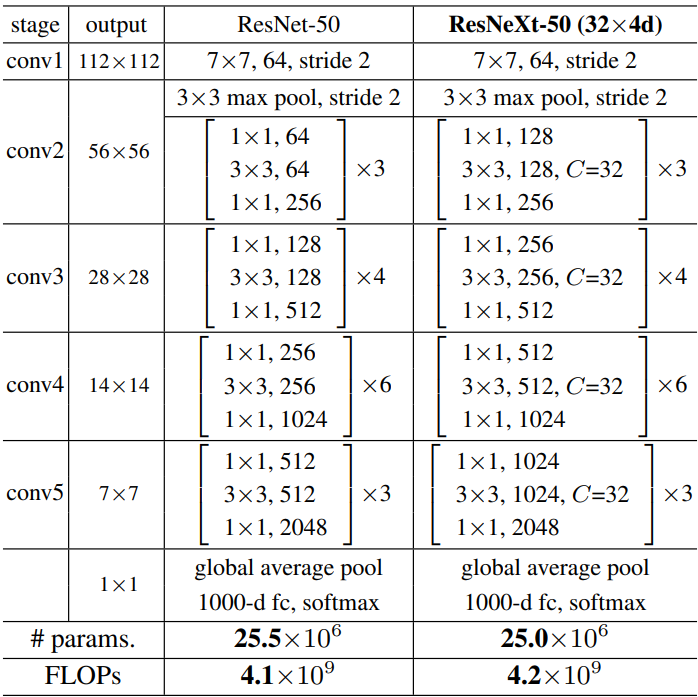
下图是 ResNet 和 ResNeXt 网络结构对比图,接下来就一层一层堆叠网络就可以了
完整代码展示:
- import tensorflow as tf
- from tensorflow import keras
- from tensorflow.keras import layers, Model
-
- #(1)分组卷积块
- def group_conv(inputs, filters, stride, num_groups):
- '''
- inputs为输入特征图
- filters为每个分组卷积的输出通道数
- stride为分组卷积的步长
- num_groups为分几组
- '''
- # 用来保存每个分组卷积的输出特征图
- groupList = []
-
- for i in range(num_groups): # 遍历每一组
- # 均匀取出需要卷积的特征图inputs.shape=[b,h,w,c]
- x = inputs[:, :, :, i*filters: (i+1)*filters]
- # 分别对每一组卷积使用3*3卷积
- x = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=3, strides=stride, padding='same', use_bias=False)(x)
- # 将每个分组卷积结果保存起来
- groupList.append(x)
-
- # 将每个分组卷积的输出特征图在通道维度上堆叠
- x = layers.Concatenate()(groupList)
-
- x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x) # 批标准化
-
- x = layers.Activation('relu')(x) # 激活函数
-
- return x
-
- #(2)一个残差单元
- def res_block(inputs, out_channel, stride, shortcut, num_groups=32):
- '''
- inputs输入特征图
- out_channel最后一个1*1卷积的输出通道数
- stride=2下采样, 图像长宽减半, 残差边对输入卷积后再连接输出
- stride=1基本模块, size不变, 残差连接输入和输出
- num_groups代表3*3分组卷积分了几组
- shortcut判断是否要调整通道数
- '''
- # 残差边
- if shortcut is False: # 直接使用参加连接输入和输出
- residual = inputs
-
- elif shortcut is True: # 调整通道数
- # 1*1卷积调整通道数,使输入输出的size和通道数相同
- residual = layers.Conv2D(out_channel, kernel_size=1, strides=stride, padding='same', use_bias=False)(inputs)
- # 有BN层就不需要偏置
- residual = layers.BatchNormalization()(residual)
-
- # 1*1卷积,输出通道数是最后一个1*1卷积层输出通道数的一半
- x = layers.Conv2D(filters = out_channel//2, kernel_size=1, strides=1,
- padding = 'same', use_bias = False)(inputs)
-
- x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
- x = layers.Activation('relu')(x)
-
- # 3*3分组卷积
- group_filters = (out_channel//2) // num_groups # 每一组卷积的输出通道数
- x = group_conv(x, filters = group_filters, stride = stride, num_groups = num_groups)
-
- # 1*1卷积上升通道
- x = layers.Conv2D(filters = out_channel, kernel_size = 1, strides = 1,
- padding = 'same', use_bias = False)(x)
-
- x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
-
- # 残差连接,保证x和残差边的shape相同
- x = layers.Add()([x, residual])
- x = layers.Activation('relu')(x)
-
- return x
-
- #(3)一个残差块
- def stage(x, num, out_channel, first_stride):
-
- # 第一个残差单元下采样步长可能是1也可能是2,第一个残差单元需要调整残差边通道数
- x = res_block(x, out_channel, stride=first_stride, shortcut=True)
-
- # 其他的都是基本模块strides=1
- for _ in range(num-1):
- x = res_block(x, out_channel, stride=1, shortcut=False)
-
- # 残差块输出结果
- return x
-
- #(4)网络骨架
- def resnext(input_shape, classes):
- '''
- input_shape代表输入图像的shape
- classes代表分类类别的数量
- '''
- # 构造输入层
- inputs = keras.Input(shape=input_shape)
-
- # 7*7标准卷积[224,224,3]==>[112,112,64]
- x = layers.Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=7, strides=2,
- padding='same', use_bias=False)(inputs)
-
- x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
- x = layers.Activation('relu')(x)
-
- # 最大池化[112,112,64]==>[56,56,64]
- x = layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(3,3), strides=2, padding='same')(x)
-
- # [56,56,64]==>[56,56,256]
- x = stage(x, num=3, out_channel=256, first_stride=1)
-
- # [56,56,256]==>[28,28,512]
- x = stage(x, num=4, out_channel=512, first_stride=2)
-
- # [28,28,512]==>[14,14,1024]
- x = stage(x, num=6, out_channel=1024, first_stride=2)
-
- # [14,14,1024]==>[7,7,2048]
- x = stage(x, num=3, out_channel=2048, first_stride=2)
-
- # [7,7,2048]==>[None,2048]
- x = layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
-
- # [None,2048]==>[None,classes]
- logits = layers.Dense(classes)(x) # 输出不经过softmax激活函数
-
- # 构建模型
- model = Model(inputs, logits)
-
- # 返回模型
- return model
-
- #(5)接收网络模型
- if __name__ == '__main__':
-
- model = resnext(input_shape = [224,224,3], # 输入图像shape
- classes = 1000) # 分类数
-
- model.summary() # 查看网络架构
通过model.summary()查看网络参数量
- ==================================================================================================
- Total params: 25,097,128
- Trainable params: 25,028,904
- Non-trainable params: 68,224
- __________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. 模型训练
我是用的GPU训练网络,先将各种包导入进来,并设置GPU内存占用,防止内存爆炸。
- from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator # 预处理
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import tensorflow as tf
- from tensorflow import keras
- from ResNeXt import resnext # 网络模型
- import json
- import os
-
- os.environ['CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER'] = 'PCI_BUS_ID' # 调用GPU训练
- os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '0' # 使用当前设备的第一块GPU
-
- gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices("GPU")
-
- # 设置GPU内存占用,根据网络模型大小占用相应的内存
- if gpus:
- try:
- for gpu in gpus:
- tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu, True)
- except RuntimeError as e:
- print(e)
- exit(-1)
2.1 数据集加载
接下来,在文件夹中图片数据以测试集、验证集、测试集分类。
函数 tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory() 构造数据集,
分批次读取图片数据,参数 img_size 会对读进来的图片resize成指定大小;参数 label_mode 中,'int'代表目标值y是数值类型索引,即0, 1, 2, 3等;'categorical'代表onehot类型,对应正确类别的索引的值为1,如图像属于第二类则表示为0,1,0,0,0;'binary'代表二分类。
- #(1)加载数据集
- def get_data(height, width, batchsz):
-
- # 训练集数据
- train_ds = keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
- directory = filepath + 'train', # 训练集图片所在文件夹
- label_mode = 'categorical', # onehot编码
- image_size = (height, width), # 输入图象的size
- batch_size = batchsz) # 每批次训练32张图片
-
- # 验证集数据
- val_ds = keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
- directory = filepath + 'val',
- label_mode = 'categorical',
- image_size = (height, width),
- batch_size = batchsz)
-
-
- # 返回划分好的数据集
- return train_ds, val_ds
-
- # 读取数据集
- train_ds, val_ds = get_data(height, width, batchsz)
2.2 显示图像信息
接下来绘图查看图像信息,iter()生成迭代器,配合next()每次运行取出训练集中的一个batch数据。
- def plot_show(train_ds):
-
- # 生成迭代器,每次取出一个batch的数据
- sample = next(iter(train_ds)) # sample[0]图像信息, sample[1]标签信息
- # 显示前5张图
- for i in range(5):
- plt.subplot(1,5,i+1) # 在一块画板的子画板上绘制1行5列
- plt.imshow(sample[0][i]/255.0) # 图像的像素值压缩到0-1
- plt.xticks([]) # 不显示xy坐标刻度
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.show()
-
- # 是否展示图像信息
- if plotShow is True:
- plot_show(train_ds)
显示图像如下:

2.3 数据预处理
使用.map()函数转换数据集中所有x和y的类型,并将每张图象的像素值映射到[0,1]之间,打乱训练集数据的顺序.shuffle()
- def processing(x,y): # 定义预处理函数
- x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.0 # 图片转换为tensor类型,并归一化
- y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32) # 分类标签转换成tensor类型
- return x,y
-
- # 对所有数据预处理
- train_ds = train_ds.map(processing).shuffle(10000) # map调用自定义预处理函数, shuffle打乱数据集
- val_ds = val_ds.map(processing)
2.4 网络训练
在网络编译.compile(),指定损失loss采用交叉熵损失。设置参数from_logits=True,由于网络的输出层没有使用softmax函数将输出的实数转为概率,参数设置为True时,会自动将logits的实数转为概率值,再和真实值计算损失,这里的真实值y是经过onehot编码之后的结果。
- #(7)保存权重文件
- if not os.path.exists(weights_dir): # 判断当前文件夹下有没有一个叫save_weights的文件夹
- os.makedirs(weights_dir) # 如果没有就创建一个
-
- #(8)模型编译
- opt = optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate) # 设置Adam优化器
-
- model.compile(optimizer=opt, #学习率
- loss=keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True), # 交叉熵损失,logits层先经过softmax
- metrics=['accuracy']) #评价指标
-
- #(9)定义回调函数,一个列表
- # 保存模型参数
- callbacks = [keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath = 'save_weights/resnext.h5', # 参数保存的位置
- save_best_only = True, # 保存最佳参数
- save_weights_only = True, # 只保存权重文件
- monitor = 'val_loss')] # 通过验证集损失判断是否是最佳参数
-
- #(10)模型训练,history保存训练信息
- history = model.fit(x = train_ds, # 训练集
- validation_data = val_ds, # 验证集
- epochs = epochs, #迭代30次
- callbacks = callbacks)
训练过程中的损失值和准确率如下:
- Epoch 1/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 247s 370ms/step - loss: 1.3545 - accuracy: 0.5662 - val_loss: 0.1252 - val_accuracy: 0.9664
- Epoch 2/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 175s 305ms/step - loss: 0.1186 - accuracy: 0.9622 - val_loss: 0.1337 - val_accuracy: 0.9724
- Epoch 3/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 176s 307ms/step - loss: 0.0499 - accuracy: 0.9859 - val_loss: 3.8282 - val_accuracy: 0.6735
- Epoch 4/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 176s 305ms/step - loss: 0.0697 - accuracy: 0.9816 - val_loss: 0.0783 - val_accuracy: 0.9796
- Epoch 5/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 176s 306ms/step - loss: 0.1167 - accuracy: 0.9661 - val_loss: 0.0843 - val_accuracy: 0.9844
- Epoch 6/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 177s 308ms/step - loss: 0.0703 - accuracy: 0.9841 - val_loss: 0.0096 - val_accuracy: 0.9964
- Epoch 7/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 176s 306ms/step - loss: 0.0267 - accuracy: 0.9920 - val_loss: 0.0295 - val_accuracy: 0.9940
- Epoch 8/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 176s 306ms/step - loss: 0.0339 - accuracy: 0.9925 - val_loss: 0.0870 - val_accuracy: 0.9712
- Epoch 9/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 174s 302ms/step - loss: 0.0622 - accuracy: 0.9851 - val_loss: 0.0588 - val_accuracy: 0.9904
- Epoch 10/10
- 556/556 [==============================] - 176s 306ms/step - loss: 0.0384 - accuracy: 0.9889 - val_loss: 3.3135 - val_accuracy: 0.6591
2.5 绘制训练曲线
history 中保存了本轮训练的信息,由于没有使用预训练权重,模型的训练损失和准确率波动比较大,但准确率还是可以的。并且训练时设置了回调函数callbacks,只保存验证集损失最小时的权重参数。
- #(11)获取训练信息
- history_dict = history.history # 获取训练的数据字典
- train_loss = history_dict['loss'] # 训练集损失
- train_accuracy = history_dict['accuracy'] # 训练集准确率
- val_loss = history_dict['val_loss'] # 验证集损失
- val_accuracy = history_dict['val_accuracy'] # 验证集准确率
-
- #(12)绘制训练损失和验证损失
- plt.figure()
- plt.plot(range(epochs), train_loss, label='train_loss') # 训练集损失
- plt.plot(range(epochs), val_loss, label='val_loss') # 验证集损失
- plt.legend() # 显示标签
- plt.xlabel('epochs')
- plt.ylabel('loss')
-
- #(13)绘制训练集和验证集准确率
- plt.figure()
- plt.plot(range(epochs), train_accuracy, label='train_accuracy') # 训练集准确率
- plt.plot(range(epochs), val_accuracy, label='val_accuracy') # 验证集准确率
- plt.legend()
- plt.xlabel('epochs')
- plt.ylabel('accuracy')
绘制损失曲线和准确率曲线

2.6 训练过程完整代码
训练阶段一定要注意 batch_size 的大小,batch_size 设置的越大,越容易导致显存爆炸,要改的话最好设置2的n次方
- import tensorflow as tf
- from tensorflow import keras
- from tensorflow.keras import optimizers
- from ResNeXt import resnext # 导入模型
- import os
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
- os.environ['CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER'] = 'PCI_BUS_ID' # 调用GPU训练
- os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '0' # 使用当前设备的第一块GPU
-
- gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices("GPU")
-
- # 设置GPU内存占用,根据网络模型大小占用相应的内存
- if gpus:
- try:
- for gpu in gpus:
- tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu, True)
- except RuntimeError as e:
- print(e)
- exit(-1)
-
- # ------------------------------------- #
- # 加载数据集,batchsz太大会导致显存爆炸
- # ------------------------------------- #
- filepath = 'D:/deeplearning/test/数据集/交通标志/new_data/' # 数据集所在文件夹
- height = 224 # 输入图象的高
- width = 224 # 输入图象的宽
- batchsz = 8 # 每个batch处理32张图片
- checkData = False # 查看数据集划分的信息
- plotShow = True # 绘制图像
- checkDataAgain = False # 预处理之后是否再次查看数据集信息
- # ------------------------------------- #
- # 网络模型结构
- # ------------------------------------- #
- input_shape = (224,224,3) # 输入图象的shape
- classes = 4 # 图像分类的类别数
- checkNet = False # 是否查看网络架构
- # ------------------------------------- #
- # 网络训练
- # ------------------------------------- #
- weights_dir = 'save_weights' # 权重文件保存的文件夹路径
- learning_rate = 0.0005 # adam优化器的学习率
- epochs = 10 # 训练迭代次数
-
-
- #(1)加载数据集
- def get_data(height, width, batchsz):
-
- # 训练集数据
- train_ds = keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
- directory = filepath + 'train', # 训练集图片所在文件夹
- label_mode = 'categorical', # onehot编码
- image_size = (height, width), # 输入图象的size
- batch_size = batchsz) # 每批次训练32张图片
-
- # 验证集数据
- val_ds = keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
- directory = filepath + 'val',
- label_mode = 'categorical',
- image_size = (height, width),
- batch_size = batchsz)
-
-
- # 返回划分好的数据集
- return train_ds, val_ds
-
- # 读取数据集
- train_ds, val_ds = get_data(height, width, batchsz)
-
- #(2)查看数据集信息
- def check_data(train_ds): # 传入训练集数据集
-
- # 查看数据集有几个分类类别
- class_names = train_ds.class_names
- print('classNames:', class_names)
-
- # 查看数据集的shape, x代表图片数据, y代表分类类别数据
- sample = next(iter(train_ds)) # 生成迭代器,每次取出一个batch的数据
- print('x_batch.shape:', sample[0].shape, 'y_batch.shape:', sample[1].shape)
- print('前五个目标值:', sample[1][:5])
-
- # 是否查看数据集信息
- if checkData is True:
- check_data(train_ds)
-
-
- #(3)查看图像
- def plot_show(train_ds):
-
- # 生成迭代器,每次取出一个batch的数据
- sample = next(iter(train_ds)) # sample[0]图像信息, sample[1]标签信息
- # 显示前5张图
- for i in range(5):
- plt.subplot(1,5,i+1) # 在一块画板的子画板上绘制1行5列
- plt.imshow(sample[0][i]) # 图像的像素值压缩到0-1
- plt.xticks([]) # 不显示xy坐标刻度
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.show()
-
- # 是否展示图像信息
- if plotShow is True:
- plot_show(train_ds)
-
-
- #(4)数据预处理
- def processing(x,y): # 定义预处理函数
- x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.0 # 图片转换为tensor类型,并归一化
- y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32) # 分类标签转换成tensor类型
- return x,y
-
- # 对所有数据预处理
- train_ds = train_ds.map(processing).shuffle(10000) # map调用自定义预处理函数, shuffle打乱数据集
- val_ds = val_ds.map(processing)
-
-
- #(5)查看预处理后的数据是否正确
- def check_data_again(train_ds): # 传入训练集数据集
-
- sample = next(iter(train_ds)) # 生成迭代器,每次取出一个batch的数据
- print('-------after preprocessing-------')
- print('x_batch.shape:', sample[0].shape, 'y_batch.shape:', sample[1].shape)
- print('前五个目标值:', sample[1][:5])
-
- # 是否查看数据集信息
- if checkDataAgain is True:
- check_data_again(train_ds)
-
-
- #(6)导入网络模型
- model = resnext(input_shape=input_shape, # 网络的输入图像的size
- classes=classes) # 分类数
-
- # 查看网络构架
- if checkNet is True:
- model.summary()
-
-
- #(7)保存权重文件
- if not os.path.exists(weights_dir): # 判断当前文件夹下有没有一个叫save_weights的文件夹
- os.makedirs(weights_dir) # 如果没有就创建一个
-
-
- #(8)模型编译
- opt = optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate) # 设置Adam优化器
-
- model.compile(optimizer=opt, #学习率
- loss=keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True), # 交叉熵损失,logits层先经过softmax
- metrics=['accuracy']) #评价指标
-
-
- #(9)定义回调函数,一个列表
- # 保存模型参数
- callbacks = [keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath = 'save_weights/resnext.h5', # 参数保存的位置
- save_best_only = True, # 保存最佳参数
- save_weights_only = True, # 只保存权重文件
- monitor = 'val_loss')] # 通过验证集损失判断是否是最佳参数
-
-
- #(10)模型训练,history保存训练信息
- history = model.fit(x = train_ds, # 训练集
- validation_data = val_ds, # 验证集
- epochs = epochs, #迭代30次
- callbacks = callbacks)
-
-
- #(11)获取训练信息
- history_dict = history.history # 获取训练的数据字典
- train_loss = history_dict['loss'] # 训练集损失
- train_accuracy = history_dict['accuracy'] # 训练集准确率
- val_loss = history_dict['val_loss'] # 验证集损失
- val_accuracy = history_dict['val_accuracy'] # 验证集准确率
-
- #(12)绘制训练损失和验证损失
- plt.figure()
- plt.plot(range(epochs), train_loss, label='train_loss') # 训练集损失
- plt.plot(range(epochs), val_loss, label='val_loss') # 验证集损失
- plt.legend() # 显示标签
- plt.xlabel('epochs')
- plt.ylabel('loss')
-
- #(13)绘制训练集和验证集准确率
- plt.figure()
- plt.plot(range(epochs), train_accuracy, label='train_accuracy') # 训练集准确率
- plt.plot(range(epochs), val_accuracy, label='val_accuracy') # 验证集准确率
- plt.legend()
- plt.xlabel('epochs')
- plt.ylabel('accuracy')
3. 预测阶段
以对整个测试集的图片预测为例,test_ds 存放测试集的图片和类别标签,对测试集进行和训练集相同的预处理方法,将像素值映射到0-1之间。
model.predict(img) 返回的是每张图片属于每个类别的概率,需要找到概率最大值所对应的索引 np.argmax(result),该索引对应的分类名称就是最终预测结果。
打印前10组预测结果
- 真实值: ['forbiden', 'forbiden', 'slow', 'forbiden', 'goahead', 'slow', 'goahead', 'slow', 'slow', 'forbiden']
- 预测值: ['forbiden', 'forbiden', 'slow', 'forbiden', 'goahead', 'slow', 'goahead', 'slow', 'slow', 'forbiden']
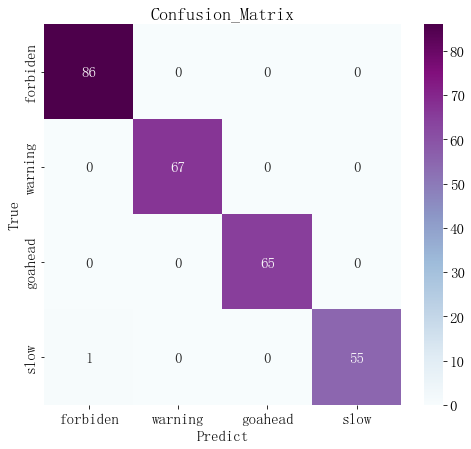
生成真实值和预测值的对比热力图可以观察整个测试集的预测情况
完整代码如下:
- import tensorflow as tf
- from tensorflow import keras
- from ResNeXt import resnext
- from PIL import Image
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
- # 报错解决:NotFoundError: No algorithm worked! when using Conv2D
- from tensorflow.compat.v1 import ConfigProto
- from tensorflow.compat.v1 import InteractiveSession
- config = ConfigProto()
- config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
- session = InteractiveSession(config=config)
-
-
- # ------------------------------------ #
- # 预测参数设置
- # ------------------------------------ #
- im_height = 224 # 输入图像的高
- im_width = 224 # 输入图像的高
- # 分类名称
- class_names = ['forbiden', 'warning', 'goahead', 'slow']
- # 权重路径
- weight_dir = 'save_weights/resnext.h5'
-
- # ------------------------------------ #
- # 单张图片预测
- # ------------------------------------ #
- # 是否只预测一张图
- single_pic = False
- # 图像所在文件夹的路径
- single_filepath = 'D:/deeplearning/test/数据集/交通标志/new_data/test/禁令标志/'
- # 指定某张图片
- picture = single_filepath + '010_0001.png'
-
- # ------------------------------------ #
- # 对测试集图片预测
- # ------------------------------------ #
- test_pack = True
- # 验证集文件夹路径
- test_filepath = 'D:/deeplearning/test/数据集/交通标志/new_data/test/'
-
-
- #(1)载入模型
- model = resnext(input_shape=[224,224,3], classes=4) # 模型的输入shape和输出分类数
- print('model is loaded')
-
- #(2)载入权重.h文件
- model.load_weights(weight_dir)
- print('weights is loaded')
-
- #(3)只对单张图像预测
- if single_pic is True:
-
- # 加载图片
- img = Image.open(picture)
- # 改变图片size
- img = img.resize((im_height, im_width))
- # 展示图像
- plt.figure()
- plt.imshow(img)
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
-
- # 图像像素值归一化处理
- img = np.array(img) / 255.0
-
- # 输入网络的要求,给图像增加一个batch维度, [h,w,c]==>[b,h,w,c]
- img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
-
- # 预测图片,返回结果包含batch维度[b,n]
- result = model.predict(img)
- # 转换成一维,挤压掉batch维度
- result = np.squeeze(result)
-
- # 找到概率最大值对应的索引
- predict_class = np.argmax(result)
-
- # 打印预测类别及概率
- print('class:', class_names[predict_class],
- 'prob:', result[predict_class])
-
- plt.title(f'{class_names[predict_class]}')
- plt.show()
-
- #(4)对测试集图像预测
- if test_pack is True:
-
- # 载入测试集
- test_ds = keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
- directory = test_filepath,
- label_mode = 'int', # 不经过ont编码, 1、2、3、4、、、
- image_size = (im_height, im_width), # 测试集的图像resize
- batch_size = 32) # 每批次32张图
-
- # 测试机预处理
- #(2)数据预处理
- def processing(image, label):
- image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32) / 255.0 #[0,1]之间
- label = tf.cast(label, tf.int32) # 修改数据类型
- return (image, label)
-
- test_ds = test_ds.map(processing) # 预处理
-
-
- test_true = [] # 存放真实值
- test_pred = [] # 存放预测值
-
- # 遍历测试集所有的batch
- for imgs, labels in test_ds:
- # 每次每次取出一个batch的一张图像和一个标签
- for img, label in zip(imgs, labels):
-
- # 网络输入的要求,给图像增加一个维度[h,w,c]==>[b,h,w,c]
- image_array = tf.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
- # 预测某一张图片,返回图片属于许多类别的概率
- prediction = model.predict(image_array)
-
- # 找到预测概率最大的索引对应的类别
- test_pred.append(class_names[np.argmax(prediction)])
- # label是真实标签索引
- test_true.append(class_names[label])
-
- # 展示结果
- print('真实值: ', test_true[:10])
- print('预测值: ', test_pred[:10])
-
- # 绘制混淆矩阵
- from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
- import seaborn as sns
- import pandas as pd
- plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimSun'] #宋体
- plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 15 #设置字体大小
-
- # 生成混淆矩阵
- conf_numpy = confusion_matrix(test_true, test_pred)
- # 转换成DataFrame表格类型,设置行列标签
- conf_df = pd.DataFrame(conf_numpy, index=class_names, columns=class_names)
-
- # 创建绘图区
- plt.figure(figsize=(8,7))
-
- # 生成热力图
- sns.heatmap(conf_df, annot=True, fmt="d", cmap="BuPu")
-
- # 设置标签
- plt.title('Confusion_Matrix')
- plt.xlabel('Predict')
- plt.ylabel('True')


