- 12023,九章云极DataCanvas的澎湃时刻
- 2一个比较完善的httpWebRequest 封装,适合网络爬取及暴力破解
- 3rsync—远程同步_rsync远程拷贝文件
- 4首先是java接口代码写了四个让前端请求的接口,以下为代码_java后端api接口供前端调用代码
- 5卸载WPS但电脑设备和驱动还显示WPS网盘图标,右击删除却是灰色_wps删除后留了一个网盘
- 6开窗函数 OVER(PARTITION BY)函数介绍_开窗函数partition by
- 7构造方法以及构造方法的重载
- 8【AI绘画】Stable Diffusion 提示词——时尚日志封面_stable diffustion 照片质量正向通用提示词
- 9看了同事用AI做项目管理,我人都傻了!
- 10微软 AR 眼镜新专利:包含热拔插电池_ar新专利
注意力机制(一)SE模块(Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks)论文总结和代码实现
赞
踩
Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks(压缩和激励网络)
论文地址:Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
论文中文版:Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks_中文版
代码地址:GitHub - hujie-frank/SENet: Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
一、论文出发点
为了提高网络的表示能力,许多现有的工作已经显示出增强空间编码的好处。而作者专注于通道,希望能够提出了一种新的架构单元,通过显式地建模出卷积特征通道之间的相互依赖性来提高网络的表示能力。
这里引用“博文:Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks解读”中的总结:核心思想是不同通道的权重应该自适应分配,由网络自己学习出来的,而不是像Inception net一样留下过多人工干预的痕迹。
二、论文的主要工作
1.提出了一种新的架构单元Squeeze-and-Excitation模块,该模块可以显式地建模卷积特征通道之间的相互依赖性来提高网络的表示能力。
2.提出了一种机制,使网络能够执行特征重新校准,通过这种机制可以学习使用全局信息来选择性地强调信息特征并抑制不太有用的特征。
三、Squeeze-and-Excitation模块
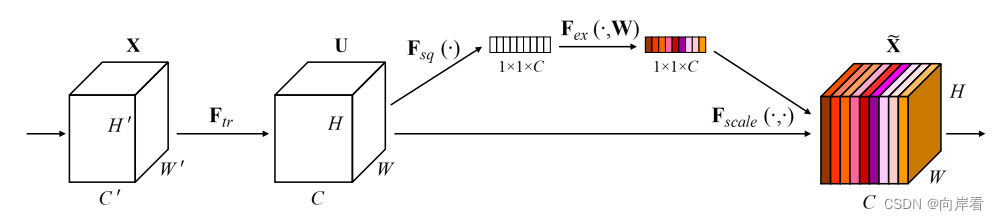
3.1 Transformation(Ftr)(转型)
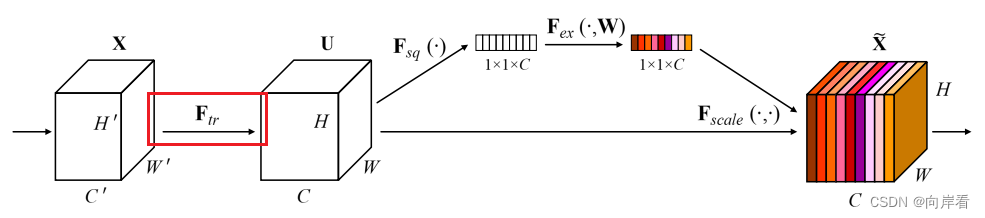
:
,经过F_{tr}特征图X变为特征图U。
可以看作一个标准的卷积算子。公式定义如下:
其中,X∈R^(H′×W′×C′)为输入特征图U∈R^(H×W×C):输出特征图,V:表示学习到的一组滤波器核,Vc:指的是第c个滤波器的参数,V_{c}^{s}表示一个2D的空间核,*表示卷积操作。
该卷积算子公式表示,输入特征图X的每一层都经过一个2D空间核的卷积最终得到C个输出的feature map,组成特征图U。
3.2 Squeeze(全局信息嵌入)
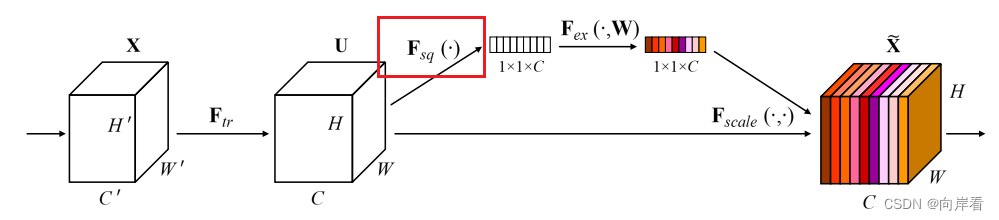
Fsq就是使用通道的全局平均池化。
原文中为了解决利用通道依赖性的问题,选择将全局空间信息压缩到一个信道描述符中,即使用通道的全局平均池化,将包含全局信息的W×H×C 的特征图直接压缩成一个1×1×C的特征向量Z,C个feature map的通道特征都被压缩成了一个数值,这样使得生成的通道级统计数据Z就包含了上下文信息,缓解了通道依赖性的问题。定义如下:
![]()
其中,Zc为Z的第c个元素。
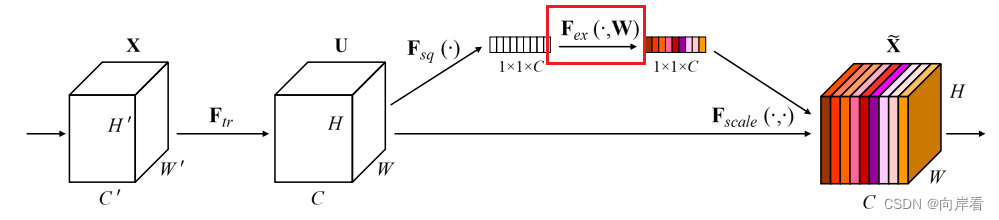
3.3 Excitation(自适应重新校正)
![]()
为什么这里要有两个FC,并且通道先缩小,再放大?
因为一个全连接层无法同时应用relu和sigmoid两个非线性函数,但是两者又缺一不可。为了减少参数,所以设置了r比率。
3.4 Scale(重新加权)
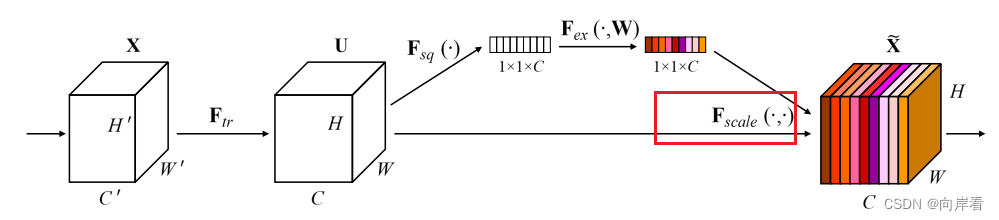
目的:最后是Scale操作,将前面得到的注意力权重加权到每个通道的特征上。
![]()
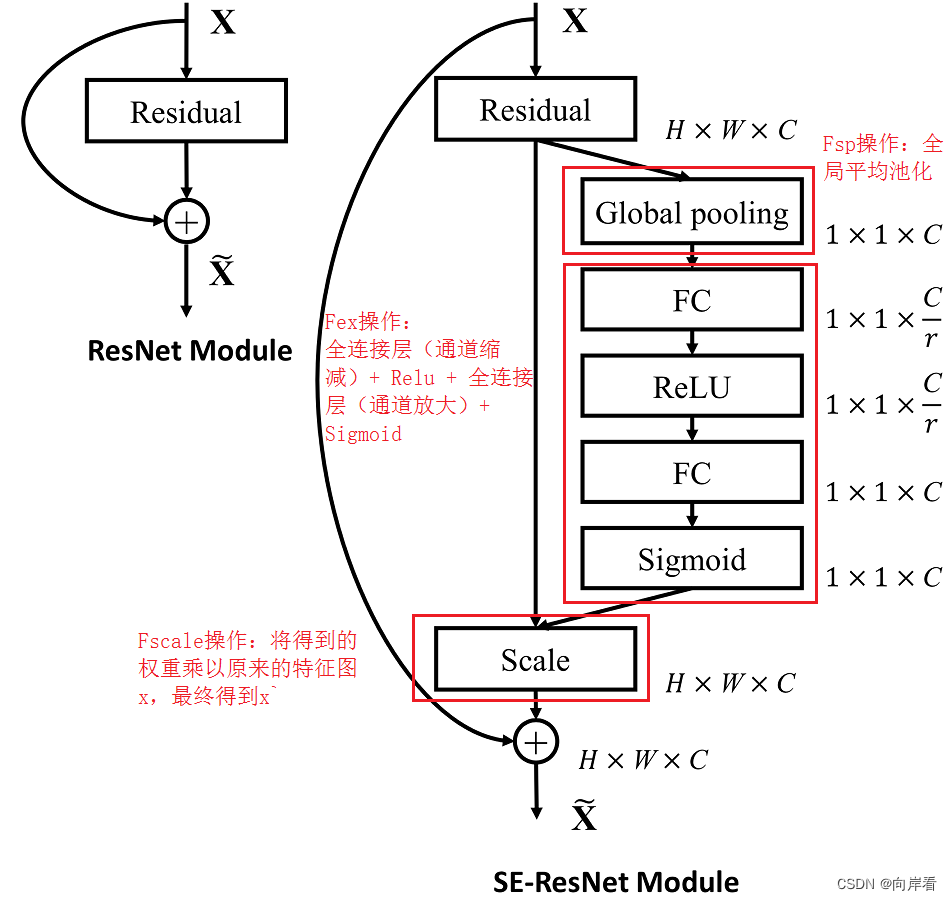
四、模型:SE-Inception和SE-ResNet
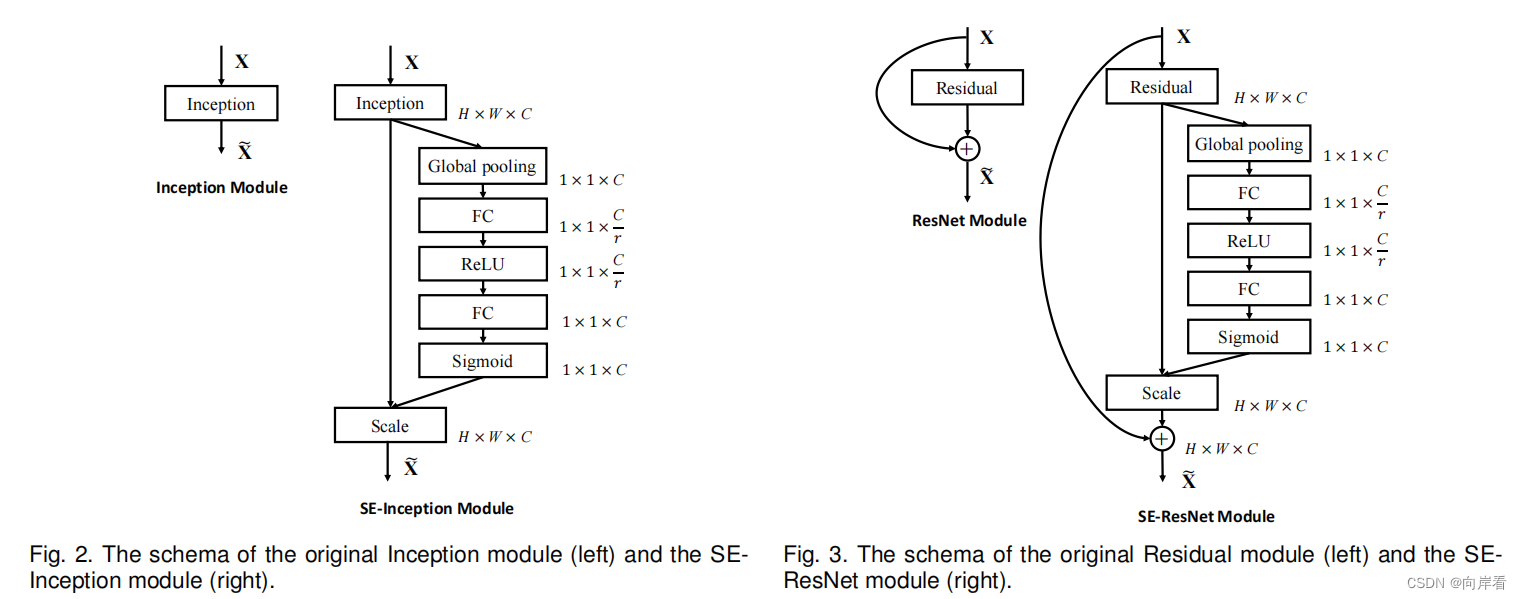
通过将一个整体的Inception模块看作SE模块中,为Inception网络构建SE模块。
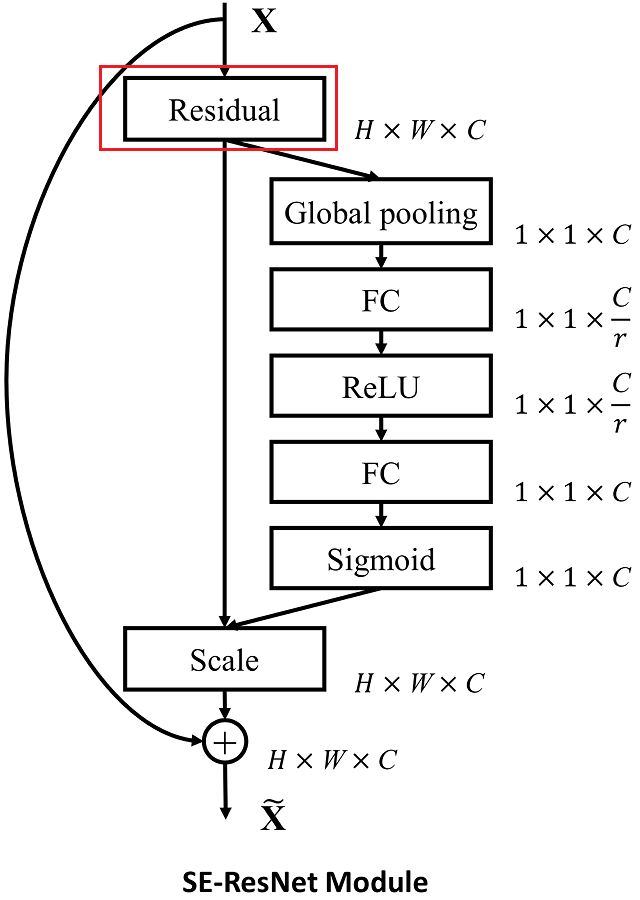
同理, 将一个整体的Residual模块看作SE模块中,为ResNet网络构建SE模块。
五、实验
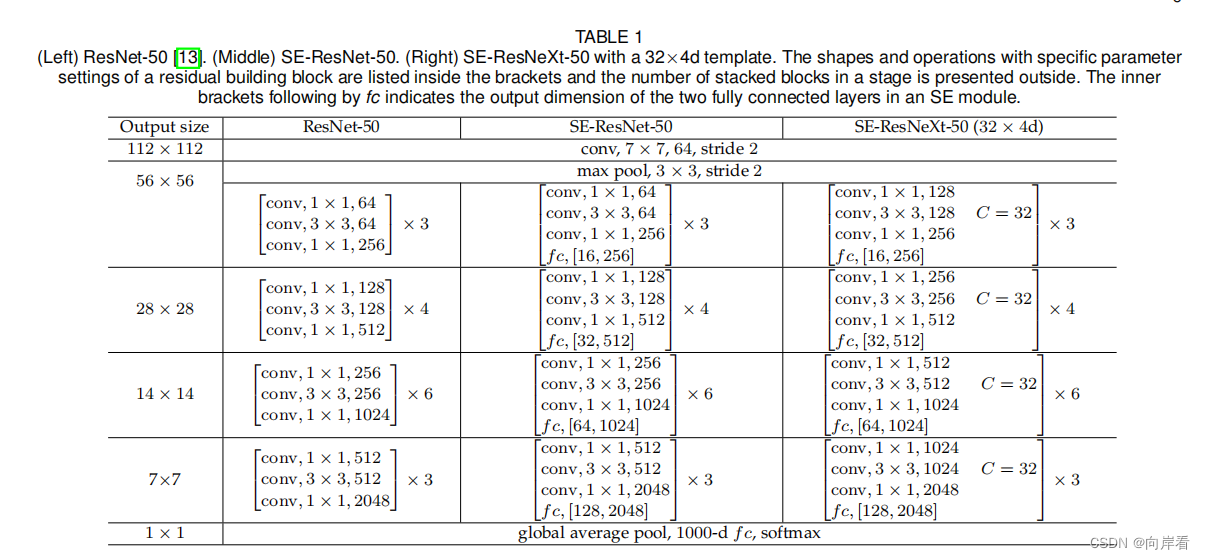
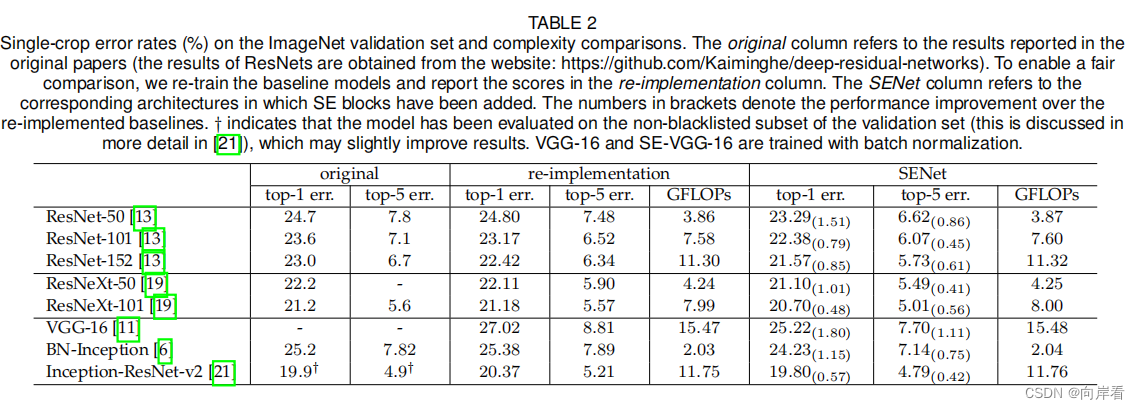
六、结论
本文提出的SE模块,这是一种新颖的架构单元,旨在通过使网络能够执行动态通道特征重新校准来提高网络的表示能力。大量实验证明了SENets的有效性,其在多个数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
七、源码分析
将SEblock嵌入ResNet的残差模块中。
7.1 SE模块
- '''-------------一、SE模块-----------------------------'''
- #全局平均池化+1*1卷积核+ReLu+1*1卷积核+Sigmoid
- class SE_Block(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, inchannel, ratio=16):
- super(SE_Block, self).__init__()
- # 全局平均池化(Fsq操作)
- self.gap = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
- # 两个全连接层(Fex操作)
- self.fc = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Linear(inchannel, inchannel // ratio, bias=False), # 从 c -> c/r
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Linear(inchannel // ratio, inchannel, bias=False), # 从 c/r -> c
- nn.Sigmoid()
- )
-
- def forward(self, x):
- # 读取批数据图片数量及通道数
- b, c, h, w = x.size()
- # Fsq操作:经池化后输出b*c的矩阵
- y = self.gap(x).view(b, c)
- # Fex操作:经全连接层输出(b,c,1,1)矩阵
- y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
- # Fscale操作:将得到的权重乘以原来的特征图x
- return x * y.expand_as(x)

7.2 SE-ResNet完整代码
不同版本的ResNet各层主要是由BasicBlock模块(18-layer、34-layer)或Bottleneck模块(50-layer、101-layer、152-layer)构成的。
添加SE模块位置:在BasicBlock模块或Bottleneck模块尾部添加,但是要注意放在shortcut之前。
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- from torchsummary import summary
-
- '''-------------SE模块-----------------------------'''
- #全局平均池化+1*1卷积核+ReLu+1*1卷积核+Sigmoid
- class SE_Block(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, inchannel, ratio=16):
- super(SE_Block, self).__init__()
- # 全局平均池化(Fsq操作)
- self.gap = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
- # 两个全连接层(Fex操作)
- self.fc = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Linear(inchannel, inchannel // ratio, bias=False), # 从 c -> c/r
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Linear(inchannel // ratio, inchannel, bias=False), # 从 c/r -> c
- nn.Sigmoid()
- )
-
- def forward(self, x):
- # 读取批数据图片数量及通道数
- b, c, h, w = x.size()
- # Fsq操作:经池化后输出b*c的矩阵
- y = self.gap(x).view(b, c)
- # Fex操作:经全连接层输出(b,c,1,1)矩阵
- y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
- # Fscale操作:将得到的权重乘以原来的特征图x
- return x * y.expand_as(x)
-
- '''-------------(18-layer、34-layer)BasicBlock模块-----------------------------'''
- # residual block 结构
- class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
- expansion = 1
-
- def __init__(self, inchannel, outchannel, stride=1):
- super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
- self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=3,
- stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
- self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel)
- self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(outchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=3,
- stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
- self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel)
- # SE_Block放在BN之后,shortcut之前
- self.SE = SE_Block(outchannel)
-
- self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
- if stride != 1 or inchannel != self.expansion*outchannel:
- self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(inchannel, self.expansion*outchannel,
- kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
- nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion*outchannel)
- )
-
- def forward(self, x):
- out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
- out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out))
- SE_out = self.SE(out)
- out = out * SE_out
- out += self.shortcut(x)
- out = F.relu(out)
- return out
-
- '''-------------(50-layer、101-layer、152-layer)Bottleneck模块-----------------------------'''
- # residual block 结构
- class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
- expansion = 4
-
- def __init__(self, inchannel, outchannel, stride=1):
- super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
- self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
- self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel)
- self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(outchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=3,
- stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
- self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel)
- self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(outchannel, self.expansion*outchannel,
- kernel_size=1, bias=False)
- self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion*outchannel)
- # SE_Block放在BN之后,shortcut之前
- self.SE = SE_Block(self.expansion*outchannel)
-
- self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
- if stride != 1 or inchannel != self.expansion*outchannel:
- self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
- nn.Conv2d(inchannel, self.expansion*outchannel,
- kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
- nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion*outchannel)
- )
-
- def forward(self, x):
- out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
- out = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(out)))
- out = self.bn3(self.conv3(out))
- SE_out = self.SE(out)
- out = out * SE_out
- out += self.shortcut(x)
- out = F.relu(out)
- return out
-
- '''-------------搭建SE_ResNet结构-----------------------------'''
- class SE_ResNet(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, num_classes=10):
- super(SE_ResNet, self).__init__()
- self.in_planes = 64
-
- self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3,
- stride=1, padding=1, bias=False) # conv1
- self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
- self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_blocks[0], stride=1) # conv2_x
- self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, num_blocks[1], stride=2) # conv3_x
- self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, num_blocks[2], stride=2) # conv4_x
- self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, num_blocks[3], stride=2) # conv5_x
- self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
- self.linear = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
-
- def _make_layer(self, block, planes, num_blocks, stride):
- strides = [stride] + [1]*(num_blocks-1)
- layers = []
- for stride in strides:
- layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, stride))
- self.in_planes = planes * block.expansion
- return nn.Sequential(*layers)
-
- def forward(self, x):
- x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
- x = self.layer1(x)
- x = self.layer2(x)
- x = self.layer3(x)
- x = self.layer4(x)
- x = self.avgpool(x)
- x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
- out = self.linear(x)
- return out
-
-
- def SE_ResNet18():
- return SE_ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2])
-
-
- def SE_ResNet34():
- return SE_ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3])
-
-
- def SE_ResNet50():
- return SE_ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3])
-
-
- def SE_ResNet101():
- return SE_ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3])
-
-
- def SE_ResNet152():
- return SE_ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3])
-
-
- '''
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- model = SE_ResNet50()
- print(model)
- input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
- out = model(input)
- print(out.shape)
- # test()
- '''
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
- net = SE_ResNet50().to(device)
- # 打印网络结构和参数
- summary(net, (3, 224, 224))



