热门标签
热门文章
- 1Python 爬虫 requests 库教程(附案例)
- 2鸿蒙-arkTs:开发工具安装_arkts怎么打包安装到手机
- 3win10中搭建并配置ftp服务器的方法(实现多用户登录整合版)_win10添加ftp网络存储设备
- 4Oracle19C图形界面安装教程
- 5uniCloud 微信小程序登陆全流程demo
- 6Android Studio 连接真机调试
- 7Flutter 输入框(TextField)被键盘遮挡两种解决方案_flutter 键盘遮挡输入框问题
- 8ConstraintLayout基本使用之toLeftOf 、toTopOf、toRightOf、toBottomOf_layout_constraintleft_toleftof
- 9COMP9315 week07课堂笔记_bit-sliced index
- 10写代码常用英文及缩写_代码里的英文缩写
当前位置: article > 正文
【OpenCV 图像基础】2.2图像基本处理:图像几何变换_img.shape[:2]
作者:花生_TL007 | 2024-03-14 13:22:25
赞
踩
img.shape[:2]
目录
1.图像平移
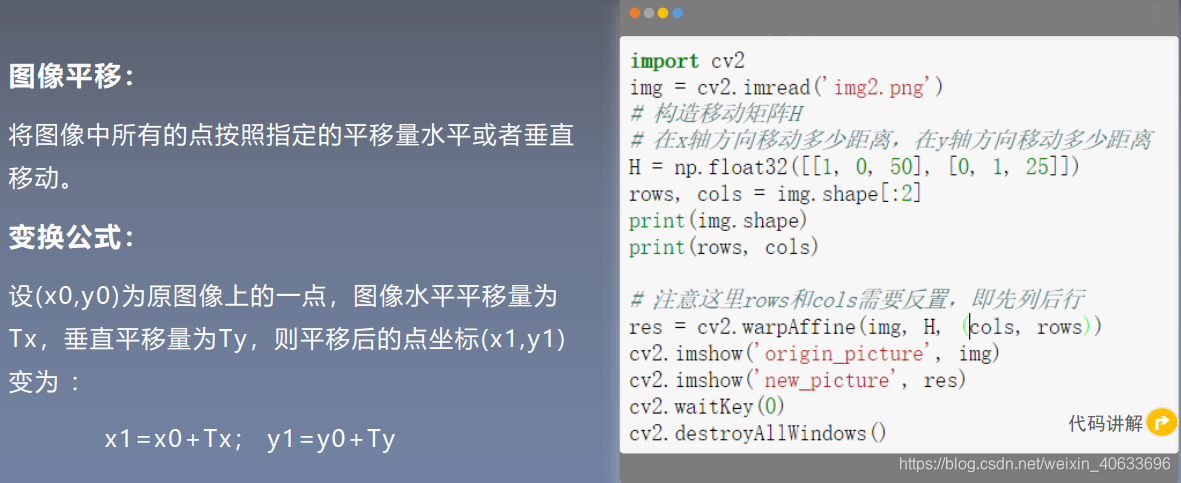
 代码:
代码:
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- img = cv2.imread('img2.png')
- # 构造移动矩阵H
- # 在x轴方向移动多少距离,在y轴方向移动多少距离
- H = np.float32([[1, 0, 50], [0, 1, 25]])
- rows, cols = img.shape[:2]
- print(img.shape)
- print(rows, cols)
-
- # 注意这里rows和cols需要反置,即先列后行
- res = cv2.warpAffine(img, H, (cols, rows))
- cv2.imshow('origin_picture', img)
- cv2.imshow('new_picture', res)
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()

输出:
- (297, 221, 3)
- 297 221
 平移后:
平移后: 
2.图像缩放
2.1上采样和下采样
 2.2插值法
2.2插值法
图像放缩
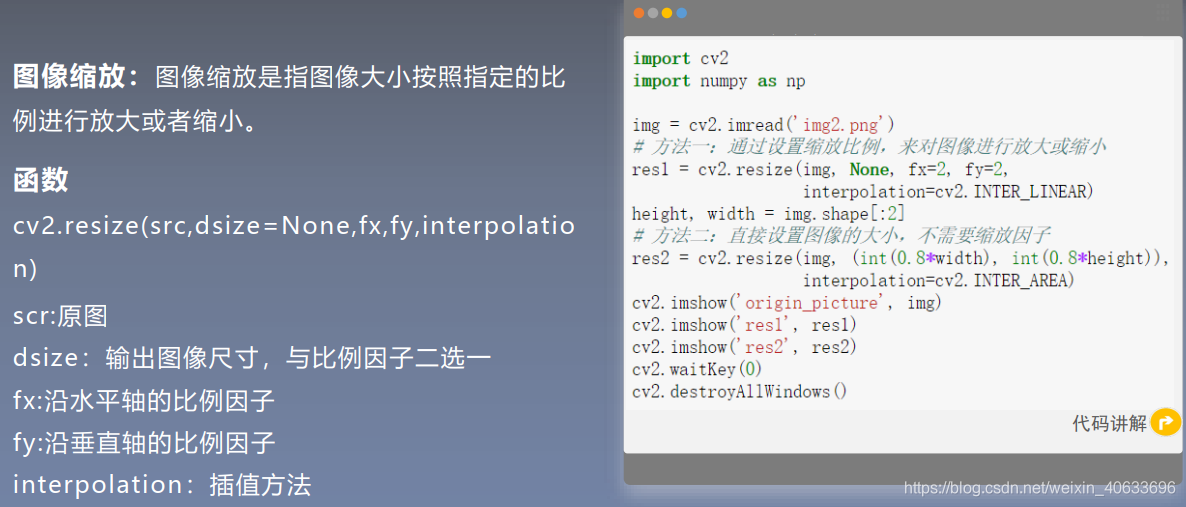
插值法
2.2.1最近邻插值

举个栗子:

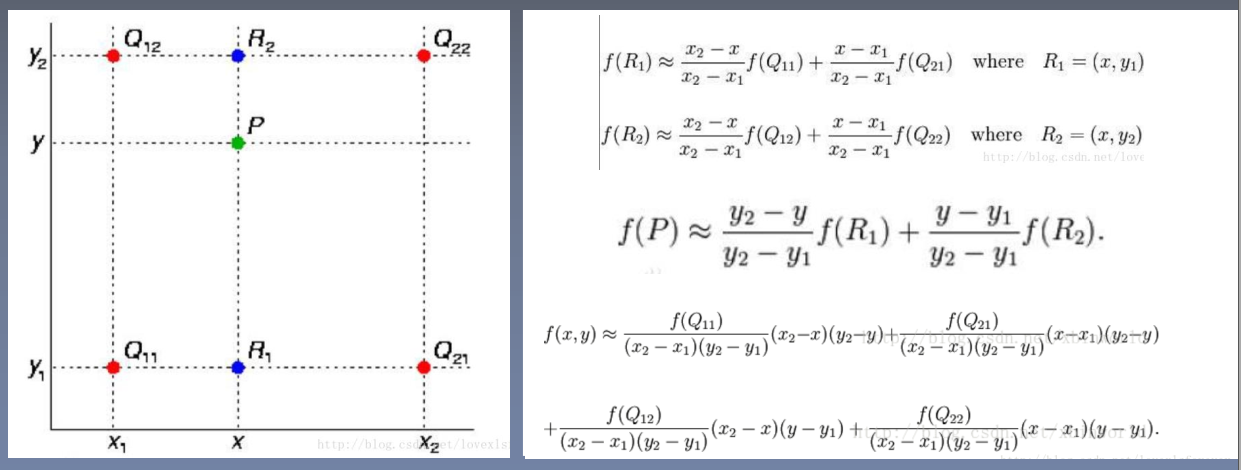
2.2.2双线性插值

举个栗子:
2.3代码实现
 代码:
代码:
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
-
- img = cv2.imread('img2.png')
- # 方法一:通过设置缩放比例,来对图像进行放大或缩小
- res1 = cv2.resize(img, None, fx=2, fy=2,
- interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
- height, width = img.shape[:2]
- # 方法二:直接设置图像的大小,不需要缩放因子
- #cv2.INTER_NEAREST(最近邻插值) cv2.INTER_AREA (区域插值) cv2.INTER_CUBIC(三次样条插值) cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4(Lanczos插值)
-
- res2 = cv2.resize(img, (int(0.8*width), int(0.8*height)),interpolation=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
- cv2.imshow('origin_picture', img)
- cv2.imshow('res1', res1)
- # cv2.imshow('res2', res2)
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()

方法一输出:
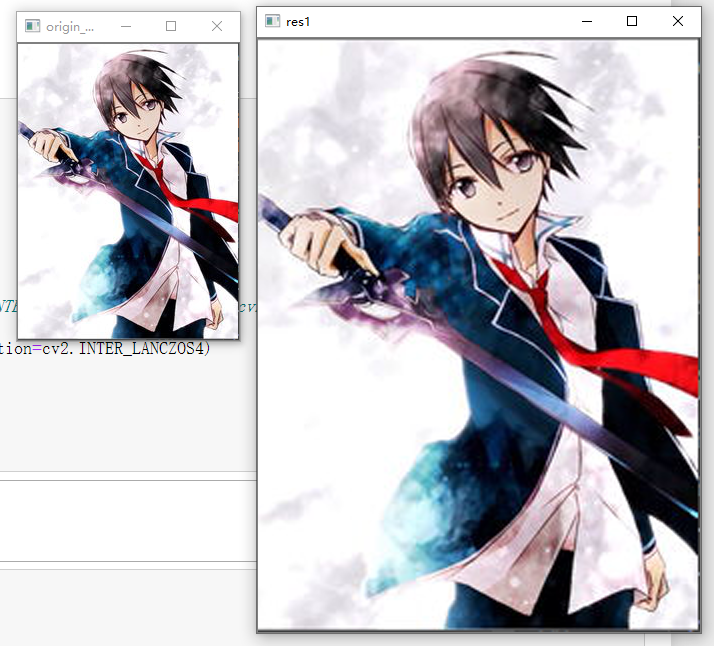
方法二输出:
3.图像旋转

 代码:
代码:
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- img=cv2.imread('img2.png',1)
- rows,cols=img.shape[:2]
- #参数1:旋转中心,参数2:旋转角度,参数3:旋转因子,正为逆时针,负值为顺时针
- M=cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cols/2,rows/2),45,-1,)
- print(M)
- #第三个参数是输出图像的尺寸中心
- dst=cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(cols,rows))
- #dst=cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(cols,rows),borderValue=(255,255,255))
- while(1):
- cv2.imshow('img', img)
- cv2.imshow('img1',dst)
- #0xFF==27 ESC
- if cv2.waitKey(1)&0xFF==27:
- break
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()

输出:
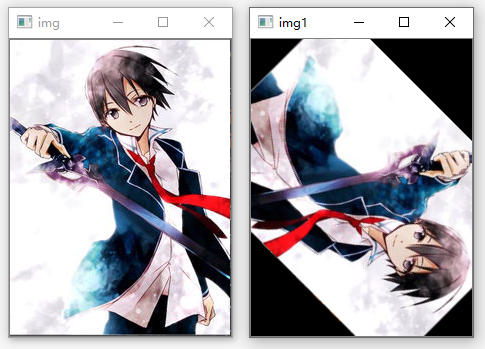
4.仿射变换
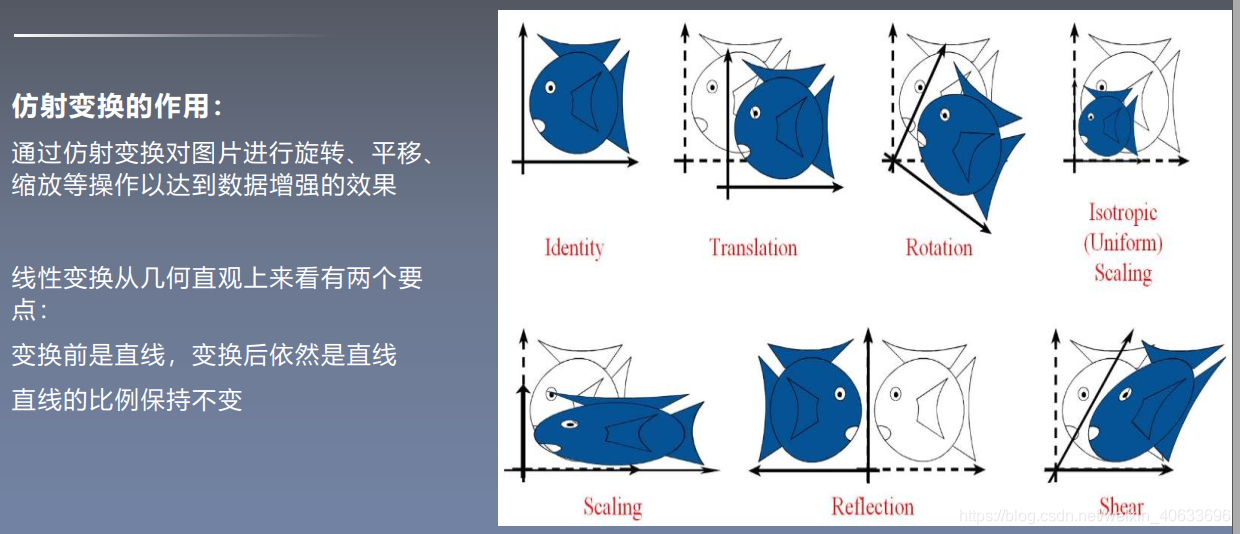
 代码:
代码:
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- #读取图片
- src = cv2.imread('bird.png')
- #获取图像大小
- rows, cols = src.shape[:2]
- #设置图像仿射变换矩阵
- pos1 = np.float32([[50,50], [200,50], [50,200]])
- pos2 = np.float32([[10,100], [200,50], [100,250]])
- M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pos1, pos2)
- print(M)
- #图像仿射变换
- result = cv2.warpAffine(src, M, (2*cols, 2*rows))
- #显示图像
- cv2.imshow("original", src)
-
- cv2.imshow("result", result)
- #等待显示
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()

输出:
- [[ 1.26666667 0.6 -83.33333333]
- [ -0.33333333 1. 66.66666667]]
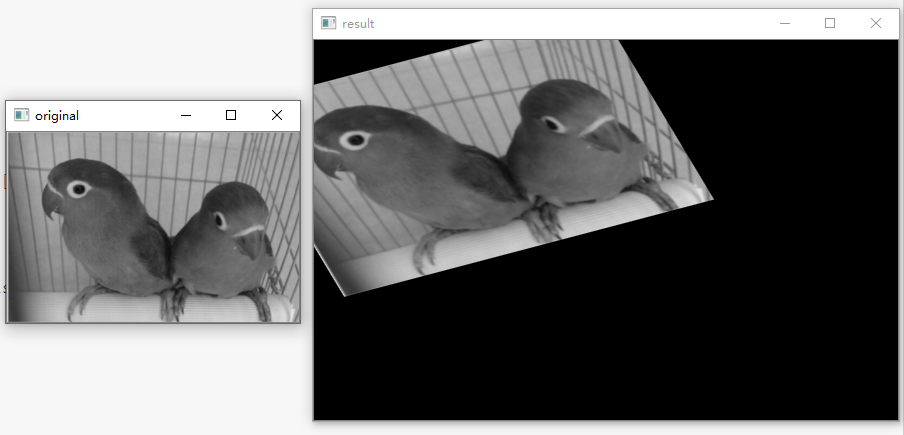
5.透视变换
 代码:
代码:
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- #读取图片
- src = cv2.imread('bird.png')
- #获取图像大小
- rows, cols = src.shape[:2]
- #设置图像透视变换矩阵
- pos1 = np.float32([[114, 82], [287, 156],
- [8, 100], [143, 177]])
- pos2 = np.float32([[0, 0], [188, 0],
- [0, 262], [188, 262]])
- M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pos1, pos2)
- #图像透视变换
- result = cv2.warpPerspective(src, M, (2*cols,2*rows))
- #显示图像
- cv2.imshow("original", src)
- cv2.imshow("result", result)
- #等待显示
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()

输出:

6.几何变换小结

6.1例1:文档矫正
代码:
- #encoding:utf-8
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
- #读取图片
- src = cv2.imread('paper.png')
-
- #获取图像大小
- rows, cols = src.shape[:2]
-
- #将源图像高斯模糊,去除图像中的噪声
- img = cv2.GaussianBlur(src, (3,3), 0)
- #进行灰度化处理
- gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
-
- #边缘检测(检测出图像的边缘信息)
- edges = cv2.Canny(gray,50,250,apertureSize = 3)
- cv2.imwrite("canny.jpg", edges)
- cv2.imshow("canny", edges)
- #通过霍夫变换得到A4纸边缘
- lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(edges,1,np.pi/180,50,minLineLength=90,maxLineGap=10)
- print(lines)
- #下面输出的四个点分别为四个顶点
- for x1,y1,x2,y2 in lines[0]:
- print(x1,y1)
- print(x2,y2)
- for x3,y3,x4,y4 in lines[1]:
- print(x3,y3)
- print(x4,y4)
-
- #绘制边缘
- for x1,y1,x2,y2 in lines[0]:
- cv2.line(gray, (x1,y1), (x2,y2), (0,0,255), 1)
-
- #根据四个顶点设置图像透视变换矩阵
- pos1 = np.float32([[114, 82], [287, 156], [8, 322], [216, 333]])
- pos2 = np.float32([[0, 0], [188, 0], [0, 262], [188, 262]])
- M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pos1, pos2)
- # pos1 = np.float32([[114, 82], [287, 156], [8, 322]])
- # pos2 = np.float32([[0, 0], [188, 0], [0, 262]])
- # M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pos1,pos2)
- print(M)
- #图像仿射变换
- #result = cv2.warpAffine(src, M, (2*cols, 2*rows))
-
- #图像透视变换
- result = cv2.warpPerspective(src, M, (190, 272))
-
- #显示图像
- cv2.imshow("original", src)
- cv2.imshow("result", result)
-
- cv2.imshow("gray", gray)
- #等待显示
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()

输出:
- [[[ 8 332 114 82]]
-
- [[217 330 287 155]]
-
- [[ 8 333 160 392]]
-
- [[116 83 286 155]]
-
- [[255 20 294 136]]
-
- [[ 9 331 84 154]]]
- 8 332
- 114 82
- 217 330
- 287 155
- [[ 5.66589226e-01 2.50243575e-01 -8.51111449e+01]
- [-3.46690724e-01 8.10506692e-01 -2.69388062e+01]
- [-1.14188388e-03 -3.35875357e-04 1.00000000e+00]]


6.2例2:图像几何变化
代码:
- #encoding:utf-8
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
- #读取图片
- img = cv2.imread('test2.png')
- image = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
-
- #图像平移矩阵
- M = np.float32([[1, 0, 80], [0, 1, 30]])
- rows, cols = image.shape[:2]
- img1 = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (cols, rows))
-
- #图像缩小
- img2 = cv2.resize(image, (200,100))
-
- #图像放大
- img3 = cv2.resize(image, None, fx=1.1, fy=1.1)
-
- #绕图像的中心旋转
- #源图像的高、宽 以及通道数
- rows, cols, channel = image.shape
- #函数参数:旋转中心 旋转度数 scale
- M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cols/2, rows/2), 30, 1)
- #函数参数:原始图像 旋转参数 元素图像宽高
- img4 = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (cols, rows))
-
- #图像翻转
- img5 = cv2.flip(image, 0) #参数=0以X轴为对称轴翻转
- img6 = cv2.flip(image, 1) #参数>0以Y轴为对称轴翻转
-
- #图像的仿射
- pts1 = np.float32([[50,50],[200,50],[50,200]])
- pts2 = np.float32([[10,100],[200,50],[100,250]])
- M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1,pts2)
- img7 = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (rows,cols))
-
- #图像的透射
- pts1 = np.float32([[56,65],[238,52],[28,237],[239,240]])
- pts2 = np.float32([[0,0],[200,0],[0,200],[200,200]])
- M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1,pts2)
- img8 = cv2.warpPerspective(image,M,(200,200))
-
-
- #循环显示图形
- titles = [ 'source', 'shift', 'reduction', 'enlarge', 'rotation', 'flipX', 'flipY', 'affine', 'transmission']
- images = [image, img1, img2, img3, img4, img5, img6, img7, img8]
- for i in range(9):
- plt.subplot(3, 3, i+1), plt.imshow(images[i], 'gray')
- plt.title(titles[i])
- plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
- plt.show()

输出:

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/花生_TL007/article/detail/234763
推荐阅读
Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。


