- 1搭建新零售订单中台
- 2python装饰器_python 装饰器 (func)
- 3Django博客实战T10-CSS框架协助前端布局
- 4链表内指定区间反转
- 5python 自定义异常/raise关键字抛出异常_python抛出异常的关键字
- 6银河麒麟本地软件源配置方法_麒麟软件商店软件源配置
- 7最炙手可热的行业——大数据就业方向和学习路线图详解!_数据科学与大数据技术 就业拓扑图
- 8解决在VMware里Ubuntu无法自动生成/dev/ttyUSB0_ubuntu ttyusb没有找到
- 9CVPR 2023 ,只需简单的几步,2D视频变3D?最新视频创作AI模型!_2d转3d整合包
- 10uos桌面专业版arm64_关于UOS生态建设的一些解释
Flutter | 常用组件_flutter characters
赞
踩

文本
-
常用的配置
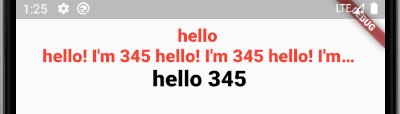
class TextTest extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( body: Padding( padding: EdgeInsets.all(30), child: Column( children: <Widget>[ Text("hello "), //最大行数为一 ,TextOverflow.ellipsis :省略号代替 Text( "hello! I'm 345 " * 5, maxLines: 1, overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis, ), //文本缩放因子 Text("hello 345", textScaleFactor: 2), // Text("hello 345", style: TextStyle( //颜色 color: Colors.red, //字号,默认 14 fontSize: 18, //粗细 fontWeight: FontWeight.w800, //斜体 fontStyle: FontStyle.italic, //underline:下划线,overline:上划线,lineThrough:删除线 decoration: TextDecoration.underline, decorationColor: Colors.black, //solid:实线,double:双线,dotted:点虚线,dashed:横虚线,wavy:波浪线 decorationStyle: TextDecorationStyle.wavy)) ], ), )); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38

textAlign:文本的对齐方式;可以选择左对齐、右对齐还是居中。注意,对齐的参考系是Text widget本身
-
DefaultTextStyle
在 widget 树中,文本的样式默认是可以继承的,因此,如果在 widget 树中的某一个节点设置一个默认的样式,那么该接口的子树中所有文本都会默认使用这个样式
Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( body: Padding( padding: EdgeInsets.all(30), child: DefaultTextStyle( style: TextStyle( //颜色 color: Colors.red, //字号,默认 14 fontSize: 20, //粗细 fontWeight: FontWeight.w900, ), child: Column( children: [ Text("hello "), Text("hello! I'm 345 " * 5, maxLines: 1,overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,), //替换默认文本 Text("hello 345",style: TextStyle(fontSize: 25, color: Colors.black)) ], )))); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
-
TextSpan
如果需要对一个 Text 按照不同部分进行不同的显示,这个时候就可以使用 TextSpan,他代表文本中的一个片段
const TextSpan({
TextStyle style,
Sting text,
List children,
GestureRecognizer recognizer,
});
style 和 text 表示样式和内容,children 是一个数组,也就是说 TextSpan 可以包含其他的 TextSpan,recognizer 用于对该文本片段上用手势进行识别处理
```dart
Widget _richText() {
var textSpan = TextSpan(text: "hello", children: [
TextSpan(text: "3", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.blueAccent)),
TextSpan(text: "4", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black)),
TextSpan(text: "5", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.green))
]);
return Text.rich(textSpan);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
上面使用 Text.rich 方法将 TextSpan 添加到 Text 中,之所以这样做,就是应为 Text 本身就是 RichText 的一个包装,而 RichText 是可以显示多种样式(富文本)的 widget,样式如下:

-
字体
在 flutter 中使用字体需要两个步骤,首先是在
pubspec.yaml文件中声明,然后通过 textStyle 属性使用字体flutter: fonts: - family: Raleway fonts: - asset: assets/fonts/Raleway-Regular.ttf - asset: assets/fonts/Raleway-Medium.ttf weight: 500 - asset: assets/fonts/Raleway-SemiBold.ttf weight: 600 - family: AbrilFatface fonts: - asset: assets/fonts/abrilfatface/AbrilFatface-Regular.ttf- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
使用字体
// 声明文本样式 const textStyle = const TextStyle( fontFamily: 'Raleway', ); // 使用文本样式 var buttonText = const Text( "Use the font for this text", style: textStyle, );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
按钮
Material 组件库中提供了很多按钮组件,如 RaisedButton,FlatButton,OutlineButton,等,他们都是间接或者直接对 RawMaterialButton 组件的包装定制,所以他们大多是属性都和 RawMaterialButton 一样
另外,所有的 Material 库中的按钮都有如下的相同点:
1,按下都会有 “水波纹动画”
2,都有一个 onPressed 属性来设置点击事件的回调,若没有该回调则按钮会处于禁用状态,禁用状态不响应用户点击
各种常见的按钮
class Button extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( body: Padding( padding: EdgeInsets.all(20), child: Column( children: [ //漂浮按钮,默认有阴影和灰色背景 RaisedButton( child: Text("RaisedButton"), onPressed: () => print('RaisedButton'), ), //扁平按钮,默认背景透明不带阴影 FlatButton( child: Text("flatButton"), onPressed: () => print('flatButton'), ), //默认有一个边框,不带阴影且背景透明 OutlineButton( child: Text("OutlineButton"), onPressed: () => print('OutlineButton'), ), //可点击的 Icon IconButton( icon: Icon(Icons.thumb_up_alt), onPressed: () => print('点赞'), ), //带图标的按钮,通过 icon 构造函数创建带图标的按钮 RaisedButton.icon( icon: Icon(Icons.send), label: Text("发送"), onPressed: () => print('发送'), ), FlatButton.icon( icon: Icon(Icons.live_help), label: Text("疑问"), onPressed: () => print('疑问'), ) ], ), )); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44

有些按钮默认是由 icon 这个构造函数的,同个这个构造可以轻松创建出带图标的按钮,如 RaisedButton 等
自定义按钮外观
按钮的外观可以通过属性来定义,不同的按钮属性都大同小异,以 FlatButton 为例,看一下常用的按钮属性,详细的可以查看 api
const FlatButton({
...
@required this.onPressed, //按钮点击回调
this.textColor, //按钮文字颜色
this.disabledTextColor, //按钮禁用时的文字颜色
this.color, //按钮背景颜色
this.disabledColor,//按钮禁用时的背景颜色
this.highlightColor, //按钮按下时的背景颜色
this.splashColor, //点击时,水波动画中水波的颜色
this.colorBrightness,//按钮主题,默认是浅色主题
this.padding, //按钮的填充
this.shape, //外形
@required this.child, //按钮的内容
})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
栗子:定义一个提交按钮
FlatButton(
color: Colors.blue,
child: Text("提交"),
splashColor: Colors.grey,
highlightColor: Colors.red,
shape:
RoundedRectangleBorder(borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(20)),
onPressed: () => print('提交'),
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Flutter 中 没有提供去除背景的设置,如果需要去除背景,可通过将背景颜色设置为透明来实现,将 color: Colors.blue 替换为 color: Color(0x000000) 即可
FlatButton 是没有 阴影的,这样总会感觉差了点啥,如果需要阴影,可直接使用 RaisedButton 即可
const RaisedButton({
...
this.elevation = 2.0, //正常状态下的阴影
this.highlightElevation = 8.0,//按下时的阴影
this.disabledElevation = 0.0,// 禁用时的阴影
...
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
通过设置以上属性即可设置阴影,elevation 这个属性会在很多组件中见到,都是用来控制阴影的
图片
在 Flutter 中,我们可以通过 Image 组件来加载并显示图片,Image 的加载源可能是 asset,文件,内存,以及网络
-
ImageProvider
ImageProvider 是一个抽象类,主要定义了图片获取的接口
load, 从不同的数据源获取图片需要实现不同的ImageProvider,如 AssetImage 就是实现了 Asset 中加载图片的ImageProvider,而NetWorkImages实现了从网络加载图片的ImageProvider。 -
Image
Imagewidget 有一个必选的参数,对应一个 ImageProvider -
加载图片
1,加载 assets 中图片
Image( image: AssetImage("images/avatar.png"), width: 100.0 ); Image.asset("images/avatar.png", width: 100.0, )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2,加载网络图片
Image( image: NetworkImage( "https://avatars2.githubusercontent.com/u/20411648?s=460&v=4"), width: 100.0, ) Image.network( "https://avatars2.githubusercontent.com/u/20411648?s=460&v=4", width: 100.0, )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
3,加载本地图片文件
Image.file- 1
4,加载内存图片
Image.memory- 1
-
参数
const Image({ ... this.width, //图片的宽 this.height, //图片高度 this.color, //图片的混合色值 this.colorBlendMode, //混合模式 this.fit,//缩放模式 this.alignment = Alignment.center, //对齐方式 this.repeat = ImageRepeat.noRepeat, //重复方式 ... })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
-
width ,height :设置图片的宽高,若不指定,图片图片会根据当前父容器的限制,尽可能的显示其原始大小,如果只设置了其中的一个,则另一个则会按比例缩放,但是可通过
fit属性来适应规则 -
fit:用于在图片的显示空间和图片本身大小不同的时候指定图片的适应模式
fit 本质 BoxFit.fill 填充,忽略原来的宽高比,填满为止 BoxFit.contain 包含,不改变原有比例让容器包含整个图片,容器多余部分填充背景 BoxFit.cover 覆盖,不改变原有比例,让图片充满整个容器,图片多余部分裁剪 BoxFit.fitWidth 图片横向填充 BoxFit.fitHeight 图片纵向填充 BoxFit.none 无样式,原始大小居中,如果图片比显示空间大,则只会显示图片中间的部分 BoxFit.scaleDown 图片大小小于容器事相当于none,图片大小大于容器时缩小图片大小实现contain -
color和colorBlendMode:在图片绘制时可以对每一个像素的颜色进行混合处理,color指定混合色,colorBlenMode指定混合模式Image( image:NetworkImage("https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fimg.houpao.com%2Fdy%2Fdyrs%2F20200711%2F94fb713a5985aa0c0c6f29a20357880f.jpeg&refer=http%3A%2F%2Fimg.houpao.com&app=2002&size=f9999,10000&q=a80&n=0&g=0n&fmt=jpeg?sec=1614828035&t=cf5430f8cc9a51b7000cde9c9cc30b5a"), width: 500, height: 300, fit: BoxFit.cover, color: Colors.red, colorBlendMode: BlendMode.difference, )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8


-
repeat:当图片本身大小小于显示空间时,指定图片的重复规则
-
Image 缓存
Flutter 框架对加载获得图片是有缓存的(内存),默认最大缓存数量是 1000,最大缓存空间为 100M
-
常用的图片组件
-
CircleAvatar
CircleAvatar( backgroundImage:NetworkImage("https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fimg.houpao.com%2Fdy%2Fdyrs%2F20200711%2F94fb713a5985aa0c0c6f29a20357880f.jpeg&refer=http%3A%2F%2Fimg.houpao.com&app=2002&size=f9999,10000&q=a80&n=0&g=0n&fmt=jpeg?sec=1614828035&t=cf5430f8cc9a51b7000cde9c9cc30b5a"), radius: 50, ),- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
圆形图片
-
FadeInImage
FadeInImage( image: NetworkImage("https://gimg2.baidu.com/i......."), placeholder: AssetImage("images/icon.png"), )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如果直接从网络加载图片然后在显示会有些突兀,使用
FadeInImage之后会在图片的加载过程中显示一个占位符,在图片加载完成之后显示淡入
-
ICON
在 Flutter 中,可以直接使用 字体图标,它是将图标做成字体文件,然后通过指定不同的字符而现实不同的图片
在字体文件中,每个字符都对应一个码,每个码对应一个显示字形,不同的字体就是指字形不同,及字符对应的字形是不同的。而在 iconfont 中,只是将位码对应的字形做成了图标,所以不同的字符最终就会渲染成不同的图标
在 Flutter 中,iconfont 和图片相比有如下优势
1,体积小
2,矢量的图标,放大不会影响清晰度
3,可以应用文本样式,可以像文本一样改变字体图标颜色,大小对齐等
4,可以通过 TextSpan 和文本混用
使用 Material Design 字体图标
Flutter 默认包含了一套 Material Design 的字体图标库,在 pubspec.yaml 文件中配置如下
flutter:
uses-material-design: true
- 1
- 2
看一个简单栗子
String icons = "";
icons += "\uE814";
icons += " \uE200";
icons += " \uE80D";
Text(
icons,
style: TextStyle(
fontFamily: "MaterialIcons", fontSize: 40, color: Colors.green),
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

通过上面可以看到,使用图标就像使用文本一样,但这种需要提供每个图标的码点,这点对开发者并不友好,所以 Flutter 封装了 IconData 和 Icon 来专门显示字体图标,上面栗子可使用如下方式实现
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Icon(Icons.accessible, color: Colors.green),
Icon(Icons.error, color: Colors.green),
Icon(Icons.fingerprint, color: Colors.green)
],
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
使用自定义图标库
1,导入 ttf 文件
fonts:
- family: myIcon #指定一个字体名
fonts:
- asset: fonts/iconfont.ttf
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2,自定义 icon 类,功能和上面的 Icons 一样,将字体文件中的所有文件都定义为静态变量
class MyIcons{
static const IconData book = const IconData(
0xe614,
fontFamily: 'myIcon',
matchTextDirection: true
);
static const IconData wechat = const IconData(
0xec7d,
fontFamily: 'myIcon',
matchTextDirection: true
);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
3,使用
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(MyIcons.book,color: Colors.purple,),
Icon(MyIcons.wechat,color: Colors.green,),
],
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
单选按钮和复选框
Material 组件库中提供了单选开关 Switch 和 复选框 Checkbox,他们本身都是继承自 StatefulWidget ,他们本身不会保存当前选择状态,选中状态都是由父组件来管理的。
当 Switch 或者 CheckBox 被点击时,会触发 onChanged 回调,我们可以回调中改变逻辑
class SwitchAndCheckboxTest extends StatefulWidget { @override State<StatefulWidget> createState() { return _SwitchAndCheckboxTest(); } } class _SwitchAndCheckboxTest extends State<SwitchAndCheckboxTest> { bool _switchSelected = true; //单选状态 bool _checkboxSelected = true; //复选框状态 var groupValue = 0; //单选框,默认选中的值 @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("单选开关和复选框"), ), body: Column( children: [ Switch( value: _switchSelected, activeColor: Colors.red, onChanged: (value) { setState(() { _switchSelected = value; }); }, ), Checkbox( value: _checkboxSelected, activeColor: Colors.red, onChanged: (value) => setState(() => _checkboxSelected = value), ), Row( children: [ Radio( activeColor: Colors.red, //此单选框绑定的值 value: 0, //点击状态改变的回调 onChanged: (value) => setState(() => this.groupValue = value), //当前组件中选定的值 groupValue: groupValue, ), Radio( //此单选框绑定的值 activeColor: Colors.red, value: 1, //点击状态改变的回调 onChanged: (value) => setState(() => this.groupValue = value), //当前组件中选定的值 groupValue: groupValue, ), Radio( activeColor: Colors.red, //此单选框绑定的值 value: 2, //点击状态改变的回调 onChanged: (value) => setState(() => this.groupValue = value), //当前组件中选定的值 groupValue: groupValue, ) ], ) ], ), ); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
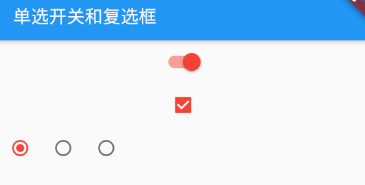
上面代码中,都行需要维护组件的状态,所以继承自 StatefulWidget ,在 build 中,构建了 checkBox 和 Switch 和 Radio,在点击的时候修改状态,然后重新构建 UI
属性
- 共有属性 activeColor,设置激活状态的颜色
- 宽高:Checkbox 无法自定义,Switch 只能定义宽度
- Checkbox 有一个属性 tristate,表示是否为三态,默认值为false,如果为true 时,valude 的值会自动增加一个状态 null
总结
Switch , Checkbox 和 Radio 本身不会维护状态,而是需要父组件来管理状态,当用户点击时,通过事件将状态通知到父组件,因此是否选中就会和用户数据发生关联,而这些用户数据也不是他们的私有状态。因此,我们在自定义组件是应该思考一下那种方式最为合理
输入框和表单
Material 组件库中提供了输入框组件 TextField 和表单组件 From ,下面来具体看一下
TextField
用于文本输入,它提供了很多属性,首先简单看一下关键的属性作用
const TextField({ ... TextEditingController controller, FocusNode focusNode, InputDecoration decoration = const InputDecoration(), TextInputType keyboardType, TextInputAction textInputAction, TextStyle style, TextAlign textAlign = TextAlign.start, bool autofocus = false, bool obscureText = false, int maxLines = 1, int maxLength, bool maxLengthEnforced = true, ValueChanged<String> onChanged, VoidCallback onEditingComplete, ValueChanged<String> onSubmitted, List<TextInputFormatter> inputFormatters, bool enabled, this.cursorWidth = 2.0, this.cursorRadius, this.cursorColor, ... })
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
-
controller:编辑框的控制器,可以通过它设置/获取编辑框的内容,选择编辑框的内容,监听编辑框文本改变事件。大多数情况下我们都需要显示的提供一个controller来与文本框交互,如果没有提供,则TextField会自动创建一个 -
focusNode:用于控制 TextField 是否占有当前键盘输入的焦点、他是我们和键盘交互的一个句柄(handler)。 -
InputDecoration:用于控制TextField的外观显示,如提示文本,背景颜色,边框等 -
keyboardType:用于设置该输入框的键盘输入类型,取值如下:TextInputType枚举值 含义 text 文本输入键盘 multiline 多行文本,需和maxLines配合使用(设为null或大于1) number 数字;会弹出数字键盘 phone 优化后的电话号码输入键盘;会弹出数字键盘并显示“* #” datetime 优化后的日期输入键盘;Android上会显示“: -” emailAddress 优化后的电子邮件地址;会显示“@ .” url 优化后的url输入键盘; 会显示“/ .” -
textInputAction:键盘动作按钮图标,他是一个枚举值,有多个可选值,具体的可查看 api -
style:正在编辑的文本样式 -
textAlign:输入框内编辑文本在水平方向的对齐方式 -
autofocus:是否自动获取焦点. -
obscureText:是否隐藏正在编辑的文本,如输入密码等。 -
maxLines:输入最大行数,默认为 1,如果为 null,则为无限制maxLength和maxLengthEnforced:前者代表输入文本的最大长度,设置后输入框右下角会显示输入的文本计数。后者决定输入长度超过maxLength后是否阻止 -
onChange:输入框内容改变的回调,也可通过controller来监听 -
onEditingComplete和onSubmitted:这两者都是在输入完成时触发,例如点击键盘的完成,或者搜索等。不同的是后者的回调是ValueChanged<String>,前者不接受参数 -
inputFormatters:用于指定输入格式,当输入内容改变时,会根据指定格式来校验 -
enable:若为 false,则输入框被禁用 -
cursorWidth,cursorRadius和cursorColor:定义光标的宽度,圆角和颜色
栗子
class InputText extends StatefulWidget { @override State<StatefulWidget> createState() { return _InputText(); } } class _InputText extends State<InputText> { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("输入框"), ), body: Column( children: [ TextField( autocorrect: true, decoration: InputDecoration( labelText: "用户名", hintText: "用户名或邮箱", prefixIcon: Icon(Icons.person)), ), TextField( decoration: InputDecoration( labelText: "密码", hintText: "您的登录密码", prefixIcon: Icon(Icons.lock)), obscureText: true, ) ], ), ); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35

-
获取输入内容
1,定义两个变量,则 onChange 触发的时候保存即可
2,通过 controler 直接获取
//定义一个controller TextEditingController _nameController = TextEditingController();- 1
- 2
TextField( autofocus: true, controller: _nameController, //设置controller ... )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
//直接输出即可 print(_nameController.text)- 1
- 2
controller 还可以用来设置默认值,选择文本等
_nameController.text="hello world!"; _nameController.selection=TextSelection( baseOffset: 2, extentOffset: _nameController.text.length ); TextField( controller: _nameController, )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
-
控制焦点
焦点可以通过
FocusNode和FocusScopeNode来控制,默认情况下,焦点由FocusScope来管理,它代表焦点控制范围,可以在这个范围内可以通过FocusScopeNode在输入框之间移动焦点、设置默认焦点等。我们可以通过FocusScope.of(context)来获取Widget树中默认的FocusScopeNode。 -
简单焦点状态改变事件
// 创建 focusNode FocusNode focusNode = new FocusNode(); ... // focusNode绑定输入框 TextField(focusNode: focusNode); ... // 监听焦点变化 focusNode.addListener((){ print(focusNode.hasFocus); });- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
-
自定义样式
-
隐藏文本
TextField( obscureText: true, )- 1
- 2
- 3
隐藏后输入的内容将不可见,变成密码类型了
-
键盘类型
TextField( keyboardType: TextInputType.number, ),- 1
- 2
- 3
例如,number 就只能输入数字,还有很多的值,如下,可以自行查看

-
键盘按钮
即键盘右下角的按钮,常见的例如完成,是一个对号的按钮等

-
大小写
控制英文字母的大小写,比如但是首字母大写等
TextField( textCapitalization: TextCapitalization.words, ),- 1
- 2
- 3
textCapitalization 的选项
1,words:单词首字母大写
2,sentences:句子首字母大写
3,characters:所有字母大写
4,none:默认无
-
光标
TextField( cursorColor: Colors.orange,//颜色 cursorWidth: 15,//宽度 cursorRadius: Radius.circular(15),//圆角 ),- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
-
计数器
TextField( maxLength: 11, ),- 1
- 2
- 3
设置最大长度计数器就可显示出来

自定义计数器/图标
TextField( autocorrect: true, maxLength: 11, controller: _nameController, decoration: InputDecoration( labelText: "用户名", hintText: "用户名或邮箱", counter: Text("计数器 0/100"), prefixIcon: Icon(Icons.person)), ),- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
通过 counter 来实现 自定义计数器
并且通过 prefixIcon 可以设置左侧内图标,通过 icon 可设置左侧外图标
decoration: InputDecoration( suffixIcon: IconButton( icon: Icon(Icons.close), onPressed: () { controller.clear(); }, ),- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
通过 suffixIcon 可以设置右侧内图标,并且可以设置点击事件
-
错误文字提示
TextField( controller: controller, decoration: InputDecoration( errorText: "请输入内容", ), ),- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
-
去除下划线
decoration: InputDecoration.collapsed(hintText: "用户名或邮箱")),- 1
-
边框
decoration: InputDecoration( border: OutlineInputBorder( borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(15)),//圆角 borderSide: BorderSide(color: Colors.red, width: 2.0)),//颜色,宽度 ),- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
颜色使用的是主题颜色,//TODO 这里设置的不生效,日后解决
-
表单 Form
在实际开发中,在请求接口之前会对输入框中的数据进行校验,如果对每个 TextField 都进行校验会非常麻烦,为此,Flutter 提供了一个 Form 组件,他可以对 输入框进行分组,然后统一进行一些操作,如内容校验,重置,保存等
Form 继承自 StatefulWidget 类,对应的状态为 FormState,定义如下:
Form({
@required Widget child,
bool autovalidate = false,
WillPopCallback onWillPop,
VoidCallback onChanged,
})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- autovalidate:是否自动校验输入内容,当 为 true 时,每一个自 FormField 都会自动校验合法性,并直接显示错误信息。否则,需要通过
FormState.validate()来手动校验 - onWillPop:决定
Form所在的路由是否可以直接返回(如点击返回按钮),该回调返回一个 Future 对象,若 Future 结果为 false,则当前路由不会返回,若为 true,则会返回到上一个路由,此属性通常用于拦截按钮 - onChange:Form 的任意一个字
FormField内容变化时都会触发此回调
FormField
Form 的子孙元素必须是 FormField 类型,FormField 是一个抽象类,有几个属性,FormState 通过他们来完成操作,FormField 部分定义如下:
const FormField({
...
FormFieldSetter<T> onSaved, //保存回调
FormFieldValidator<T> validator, //验证回调
T initialValue, //初始值
bool autovalidate = false, //是否自动校验。
})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
为了方便使用,Flutter 提供了一个 TextFormField 组件,他继承自 FormField 类,也是一个包装类,所以除了 FormField 之后,它还包括 TextField 的属性
FormState
FormState 为 Form 的 State 类,可以通过 Form.of() 或者 Globalkey 获得,我们可以通过他来对 Form 的子孙 FormField 进行统一的操作。
- FormState.validate():此方法会调用 Form 子孙 FormFile 的1 validate 回调,如果有一个校验失败,则返回 false,所有校验失败的都会返回错误提示
- FormState.save():此方法会调用 Form 子孙 FormField 的 save 回调,用于保存表单内容
- FormSata.reset():调用此方法后,会将子孙 FormField 的内容清空
栗子
class InputText extends StatefulWidget { @override State<StatefulWidget> createState() { return _InputText(); } } class _InputText extends State<InputText> { //定义一个controller TextEditingController _nameController = TextEditingController(); GlobalKey _formKey = new GlobalKey<FormState>(); @override void initState() { super.initState(); _nameController.addListener(() => print("账号:" + _nameController.text)); } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text("输入框"), ), body: Padding( padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 16, horizontal: 24), child: Form( key: _formKey,//设置globalKey,用于后面获取FormState autovalidate: true,//开启自动校验 child: Column( children: [ TextFormField( autocorrect: true, maxLength: 11, controller: _nameController, decoration: InputDecoration.collapsed(hintText: "用户名或邮箱"), validator: (v) { return v.trim().length > 0 ? null : "用户名不能为空"; }, ), TextFormField( decoration: InputDecoration.collapsed(hintText: "您的登录密码"), validator: (v) { return v.trim().length > 5 ? null : "密码不能少于6位"; }, ), Padding( padding: const EdgeInsets.only(top: 28), child: Row( children: [ Expanded( child: RaisedButton( padding: EdgeInsets.all(15), child: Text("登录"), color: Theme.of(context).primaryColor, textColor: Colors.white, onPressed: () { //获取 formState ,调用 validate 验证合法性, if ((_formKey.currentState as FormState) .validate()) { print('验证成功'); } }, ), ) ], ), ) ], ), ), )); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75

在登录按钮的 onPressed 方法中不能通过 Form.of(context ) 来获取,原因是,此处的 context 为 InputText 的 context**,而 Form.of(context) 是根据所指定 context 向根去查找,而 FormState 是在 InputText 的子树中,所以不行。**
正确的做法是通过 Builder 来构建登录按钮,Builder 会将 widget 节点的 context 作为回调参数:
Expanded( child: Builder(builder: (context) { return RaisedButton( padding: EdgeInsets.all(15), child: Text("登录"), color: Theme.of(context).primaryColor, textColor: Colors.white, onPressed: () { //获取 formState ,调用 validate 验证合法性, if ((Form.of(context)).validate()) { print('验证成功'); } }, ); }), )
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
使用这种方式即可
参考自 Flutter 实战


