- 1【 香橙派 AIpro评测】烧系统运行部署LLMS大模型跑开源yolov5物体检测并体验Jupyter Lab AI 应用样例(新手入门)
- 2linux的重要知识点_linux中的重要知识点
- 3深度学习:05 卷积神经网络介绍(CNN)_tride 池化
- 4sequoiadb java使用_Java开发基础_Java驱动_开发_JSON实例_文档中心_SequoiaDB巨杉数据库...
- 5AI时代,人工智能是开发者的助手还是替代者?
- 6大模型之SORA技术学习_sora模型csdn
- 7风险评估:IIS的安全配置,IIS安全基线检查加固
- 8pytorch之torch基础学习_torch 学习
- 9heic图片转换_heic-convert
- 10SpringCloud实战【九】: SpringCloud服务间调用_springcloud服务与服务之间的调用
大模型ReAct:思考与工具协同完成复杂任务推理_大模型 react
赞
踩
ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models

Github:https://github.com/ysymyth/ReAct
一、动机
人类的认知通常具备一定的自我调节(self-regulation)和策略制定(strategization)的能力,对于解决一个复杂问题时,可以很自然地运用工作记忆(working memory)将任务相关的决策动作(actions)与思考推理(reasoning)相结合。
- 相邻的两个具体action之间,能够以自然语言的形式进行推理和进度追踪;
- 能够根据当前的状态及时调整策略;
- 能够自如地运用外部的工具;
- 能够根据推理的结果完成一些QA等;
This tight synergy between “acting” and “reasoning” allows humans to learn new tasks quickly and perform robust decision making or reasoning, even under previously unseen circumstances or facing information uncertainties.
虽然现如今诸如Chain-of-Thought(CoT)通过上下文提示的形式可以提高大语言模型step-by-step的推理能力,但是其依然属于静态的黑盒子,依靠其推理的结果很难与真实知识保持一致,且限制了推理过程中及时反应和知识更新的能力。从而可能引发推理过程中的幻觉问题。
虽然目前有一些工作在研究嵌入式reasoning,但还没有研究如何将推理和行动以协同的方式结合起来解决通用任务,以及这种结合是否比单独的推理或行动带来系统性的好处。
二、方法——ReAct
2.1 ReAct思想
本文提出ReAct,旨在通过提示的方式来让大语言模型能够协同Action和Reasoning。下图展示了ReAct的工作机制,挑选了两个例子(HotpotQA和AlfWold)并对比了其他三个Baseline(ICL、CoT、Act-only):

可发现,传统的ICL、CoT方法都不能够给出正确的答案,因为其没有运用Action来获得环境给予的反馈;Act-only则没有真正地将Action和Reasoning结合。
回顾一下Act-only的定义(类似强化学习中的过程),第
t
t
t时刻,Agent观察到当前的环境给予的反馈记作
o
t
∈
O
o_t\in\mathcal{O}
ot∈O(其中
O
\mathcal{O}
O表示整个环境)后,做出一个动作记作
a
t
∈
A
a_t\in\mathcal{A}
at∈A(
A
\mathcal{A}
A表示动作空间),因此,Agent需要学习一个策略
π
(
a
t
∣
c
t
)
\pi(a_t|c_t)
π(at∣ct),使得其能够在基于当前状态和历史行为序列
c
t
=
(
o
1
,
a
1
,
⋯
,
o
t
−
1
,
a
t
−
1
,
o
t
)
c_t=(o_1, a_1, \cdots, o_{t-1}, a_{t-1}, o_t)
ct=(o1,a1,⋯,ot−1,at−1,ot)的基础上给出合适的动作
a
t
a_t
at。
ReAct的创新点在于,在动作空间中新增了一个基于自然语言的推理动作空间
L
\mathcal{L}
L,即
A
^
=
A
∪
L
\hat{\mathcal{A}}=\mathcal{A}\cup\mathcal{L}
A^=A∪L。换句话说,Agent在某时刻除了可以直接执行一个实质性的Action
a
t
a_t
at以外,也可以触发Reasoning
a
^
t
\hat{a}_t
a^t。而触发Reasoning其实不会影响到环境。
a thought a ^ t \hat{a}_t a^t aims to compose useful information by reasoning over the current context c t c_t ct, and update the context c t + 1 = ( c t , a ^ t ) c_{t+1} = (c_t, \hat{a}_t) ct+1=(ct,a^t) to support future reasoning or acting.
换句话说,ReAct是将Act-only额外扩展了Reasoning的动作。大语言模型在执行动作与外部环境进行交互的同时,能够及时的进行推理和思考,并基于这些思考及时地调整后续的Action。相比Act-only,这些Reasoning可以约束并优化可能存在错误或无法执行的Action。
如下图所示:


- 给定一个HotpotQA问题之后,大模型首先进行Thought1动作,即先进行思考和规划;
- 根据思考结果,执行Act1动作(搜索),并根据搜索结果获得反馈Obs1;
- 大模型即第二次触发思考动作Thought2,即根据搜索的结果进行分析和思考;
- 根据Thought2思考的结果,执行Act2,并获得Obs2反馈;
- 紧接着,大模型触发第三次思考Thought3;
- 基于Thought3,执行Act3并获得反馈Obs3;
- 最后,大模型触发第四次思考Thought4,并分析发现可以获得最终答案。
在这个例子中,Thought1的思考相当于规划,Thought2相当于抽取Obs1中的有价值信息;Thought3相当于调整Action,Thought4相当于总结并得出结论。试想一下,如果没有这些Reasoning的介入,可能执行道Act3就无法继续执行下去,从而引发幻觉。
2.2 ReAct Prompt
ReAct在具体实现时需要注意下面的一些情况。
(1)基于自然语言的推理动作空间
L
\mathcal{L}
L**通常是无限的,所以需要通过prompt进行一些约束。**即通过上下文提示来告诉大模型当前任务有哪些动作空间。
在ReAct中,针对不同的domain,设置了人工编写的In-Context Examplar。每个样本都是action-thought-observation序列。
以HotpotQA为例:
- 标准的ICL模式的prompt(6-shot)

- 只有Action(Act-only)的prompt(prompt过长,只展示1-shot)

- CoT的prompt(6-shot)

- ReAct的prompt(prompt过长,只展示1-shot)


因此,ReAct的运作本质上还是和CoT一样,只是以插入的形式交叉地添加了Act和Reasoning。
(2)Reasoning与Action的稀疏性
- 对于一些reasoning为主的任务(例如HotpotQA、数学运算等),Reasoning与Action是交替进行的;
- 对于一些决策类(Decision-making)任务,则还是以Action为主,不间断地插入少量的Reasoning Thought。
以上都是通过ICL exemplar来实现的。
2.3 ReAct应用在知识密集推理任务
包含两个任务:
- HotpotQA:基于wikipedia的多跳QA;
- FEVER:事实性验证,判断描述的事实是否符合真实性,包含SUPPORTS, REFUTES, or NOT ENOUGH INFO三个结果;
动作空间:
- search[entity]:调用wikipedia搜索引擎返回top-5个实体结果页面,或者返回与entity相关的top5个句子;
- lookup[string]:搜索包含当前string的页面的下一个句子;
- finish[answer]:结束推理并返回answer;
prompt如下所示:


prompt包含若干个thought-action-observation序列,且都是人工标注,每个序列都是按照预先设定的模式编写的:
- 规划类Thought固定格式为:“I need to search x, find y, then find z”;
- 从Obs中抽取信息的Thought:例如“x was started in 1844”, “The paragraph does not tell x”;
- 常识或数学推理的Thought:例如“x is not y, so z must instead be…”、“1844 < 1989”
- 指导进行搜索重构的Thought:“maybe I can search/look up x instead”;
- 得出最终结论的Thought:“…so the answer is x”
参数内知识与外部知识的结合
- 当ReAct超过一定步骤依然无法获得结果时,则退化为CoT+SC(Self-Consistency),利用参数内知识并进行投票来获得答案;
- 当Self-Consistency投票最多的答案依然没有过半数的,说明参数内知识不足与准确回答此问题,则升级为ReAct(涉及调用外部搜索知识)
ReAct与CoT在HotpotQA任务上执行情况如下表:

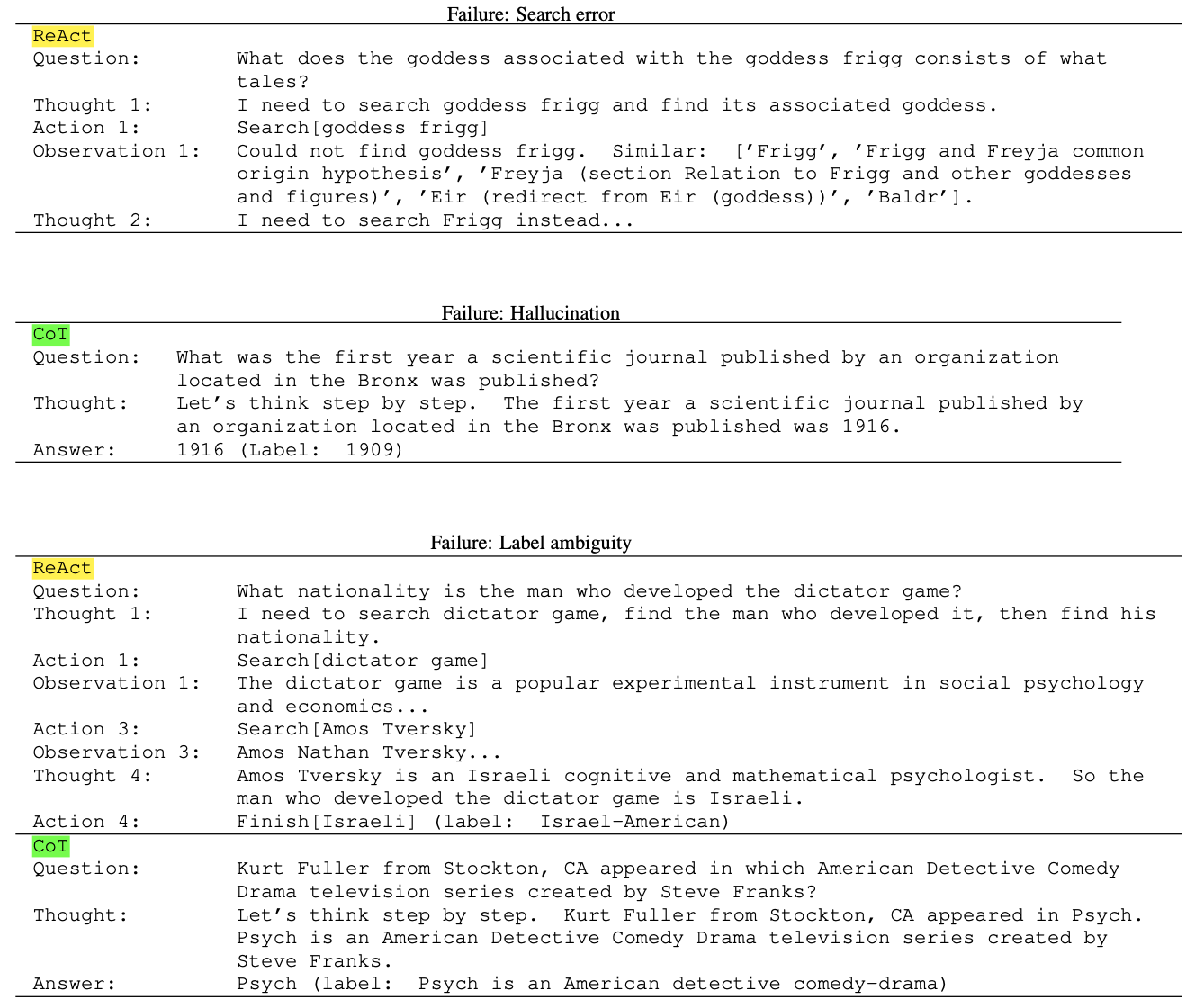
执行成功的所有任务中,ReAct达到94%的精度。
也有部分任务执行失败,其中大多数来自于推理错误、搜索结果错误或失败。也有一部分实质上预测的结果正确,但没有匹配到标签上。

2.4 Decision-making任务
挑选了ALFWorld和WebShop两个任务。prompt如下所示:

三、复现
以HotpotQA任务为例,测试样本如下所示:
{
"question": "What government position was held by the woman who portrayed Corliss Archer in the film Kiss and Tell?",
"answer": "Chief of Protocol",
"type": "bridge"
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
因为HotpotQA需要涉及到搜索Wikipedia的环境,因此先定义WikiEnv。
import ast import json import time import gym # reinforcement learning toolkit,用于与环境做交互的python工具包 import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # 访问http # import wikipedia def clean_str(p): return p.encode().decode("unicode-escape").encode("latin1").decode("utf-8") class textSpace(gym.spaces.Space): def contains(self, x) -> bool: """Return boolean specifying if x is a valid member of this space.""" return isinstance(x, str) class WikiEnv(gym.Env): def __init__(self): """ 定义环境类 Initialize the environment. """ super().__init__() self.page = None # current Wikipedia page self.obs = None # current observation self.lookup_keyword = None # current lookup keyword self.lookup_list = None # list of paragraphs containing current lookup keyword self.lookup_cnt = None # current lookup index self.steps = 0 # current number of steps self.answer = None # current answer from the agent self.observation_space = self.action_space = textSpace() self.search_time = 0 self.num_searches = 0 def _get_obs(self): return self.obs def _get_info(self): return {"steps": self.steps, "answer": self.answer} def reset(self, seed=None, return_info=False, options=None): # We need the following line to seed self.np_random # super().reset(seed=seed) self.obs = ("Interact with Wikipedia using search[], lookup[], and " "finish[].\n") self.page = None self.lookup_keyword = None self.lookup_list = None self.lookup_cnt = None self.steps = 0 self.answer = None observation = self._get_obs() info = self._get_info() return (observation, info) if return_info else observation def construct_lookup_list(self, keyword): # lookup action:用于寻找符合keyword的next sentence # find all paragraphs if self.page is None: return [] paragraphs = self.page.split("\n") paragraphs = [p.strip() for p in paragraphs if p.strip()] # find all sentence sentences = [] for p in paragraphs: sentences += p.split('. ') sentences = [s.strip() + '.' for s in sentences if s.strip()] parts = sentences parts = [p for p in parts if keyword.lower() in p.lower()] return parts @staticmethod def get_page_obs(page): # find all paragraphs paragraphs = page.split("\n") paragraphs = [p.strip() for p in paragraphs if p.strip()] # find all sentence sentences = [] for p in paragraphs: sentences += p.split('. ') sentences = [s.strip() + '.' for s in sentences if s.strip()] return ' '.join(sentences[:5]) # ps = page.split("\n") # ret = ps[0] # for i in range(1, len(ps)): # if len((ret + ps[i]).split(" ")) <= 50: # ret += ps[i] # else: # break # return ret def search_step(self, entity): # search action:执行搜索entity的动作 # 解析wikipedia页面 entity_ = entity.replace(" ", "+") search_url = f"https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?search={entity_}" old_time = time.time() response_text = requests.get(search_url).text self.search_time += time.time() - old_time self.num_searches += 1 soup = BeautifulSoup(response_text, features="html.parser") result_divs = soup.find_all("div", {"class": "mw-search-result-heading"}) if result_divs: # mismatch self.result_titles = [clean_str(div.get_text().strip()) for div in result_divs] self.obs = f"Could not find {entity}. Similar: {self.result_titles[:5]}." else: page = [p.get_text().strip() for p in soup.find_all("p") + soup.find_all("ul")] if any("may refer to:" in p for p in page): self.search_step("[" + entity + "]") else: self.page = "" for p in page: if len(p.split(" ")) > 2: self.page += clean_str(p) if not p.endswith("\n"): self.page += "\n" self.obs = self.get_page_obs(self.page) self.lookup_keyword = self.lookup_list = self.lookup_cnt = None def step(self, action): # 调用此方法,根据action的类别,选择执行相应的动作 # search entity,则调用self.search_step # lookup,则调用self.construct_lookup_list、 reward = 0 done = False action = action.strip() if self.answer is not None: # already finished done = True return self.obs, reward, done, self._get_info() if action.startswith("search[") and action.endswith("]"): entity = action[len("search["):-1] # entity_ = entity.replace(" ", "_") # search_url = f"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/{entity_}" self.search_step(entity) elif action.startswith("lookup[") and action.endswith("]"): keyword = action[len("lookup["):-1] if self.lookup_keyword != keyword: # reset lookup self.lookup_keyword = keyword self.lookup_list = self.construct_lookup_list(keyword) self.lookup_cnt = 0 if self.lookup_cnt >= len(self.lookup_list): self.obs = "No more results.\n" else: self.obs = f"(Result {self.lookup_cnt + 1} / {len(self.lookup_list)}) " + self.lookup_list[self.lookup_cnt] self.lookup_cnt += 1 elif action.startswith("finish[") and action.endswith("]"): answer = action[len("finish["):-1] self.answer = answer done = True self.obs = f"Episode finished, reward = {reward}\n" elif action.startswith("think[") and action.endswith("]"): self.obs = "Nice thought." else: self.obs = "Invalid action: {}".format(action) self.steps += 1 return self.obs, reward, done, self._get_info() def get_time_info(self): speed = self.search_time / self.num_searches if self.num_searches else 0 return { "call_speed": speed, "call_time": self.search_time, "num_calls": self.num_searches, }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
定义一个Wrapper,将与HotpotQa相关的信息进行封装,包括环境等。
class HotPotQAWrapper(gym.Wrapper): def __init__(self, env, split): super().__init__(env) data_file = f"{DATA_DIR}/{HOTPOTQA_SPLIT_FILE[split]}" self.data = json.load(open(data_file)) self.data = [(d['question'], d['answer']) for d in self.data] self.data_idx = 0 self.split = split def reset(self, seed=None, return_info=False, options=None, idx=None): self.env.reset(seed=seed, return_info=return_info, options=options) try: self.env.step('') except: pass self.env.reset(seed=seed, return_info=return_info, options=options) self.data_idx = int(np.random.randint(len(self.data))) if idx is None else idx observation = f"Question: {self.data[self.data_idx][0]}" info = self._get_info() return (observation, info) if return_info else observation def _get_info(self): return { "steps": self.steps, "answer": self.answer, "question": self.data[self.data_idx][0], "hotpot_split": self.split } def get_reward(self, info): if info['answer'] is not None: pred = normalize_answer(self.data[self.data_idx][1]) gt = normalize_answer(info['answer']) score = (pred == gt) return int(score) return 0 def get_metrics(self, info): if info['answer'] is not None: pred = normalize_answer(self.data[self.data_idx][1]) gt = normalize_answer(info['answer']) em = (pred == gt) f1 = f1_score(pred, gt)[0] return {'reward': em, 'em': em, 'f1': f1} return {'reward': 0, 'em': 0, 'f1': 0} def step(self, action): # TODO: first step obs does not have question. obs, _, done, info = self.env.step(action) reward = self.get_reward(info) # 这里的reward认为是适配gym框架所需,实际上可以直接用evaluation(例如acc等)做代替 if done: obs = f"Episode finished, reward = {reward}\n" info.update({"gt_answer": self.data[self.data_idx][1], "question_idx": self.data_idx}) info.update(self.get_metrics(info)) return obs, reward, done, info def __len__(self): return len(self.data)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
定义好了Wrapper和Env,下面进行ReAct的调用
- 配置好LLM、env和wrapper:
import os import openai import wikienv, wrappers env = wikienv.WikiEnv() env = wrappers.HotPotQAWrapper(env, split="dev") env = wrappers.LoggingWrapper(env) openai.api_key = os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] def llm(prompt, stop=["\n"]): response = openai.Completion.create( model="text-davinci-002", prompt=prompt, temperature=0, max_tokens=100, top_p=1, frequency_penalty=0.0, presence_penalty=0.0, stop=stop ) return response["choices"][0]["text"] def step(env, action): attempts = 0 while attempts < 10: try: return env.step(action) except requests.exceptions.Timeout: attempts += 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- ReAct核心代码
import json import sys import random import time idxs = list(range(7405)) # 所有任务 random.Random(233).shuffle(idxs) # 打乱顺序 # 先获得In-Context Exemplar,构建prompt folder = './prompts/' prompt_file = 'prompts_naive.json' with open(folder + prompt_file, 'r') as f: prompt_dict = json.load(f) webthink_examples = prompt_dict['webthink_simple6'] instruction = """Solve a question answering task with interleaving Thought, Action, Observation steps. Thought can reason about the current situation, and Action can be three types: (1) Search[entity], which searches the exact entity on Wikipedia and returns the first paragraph if it exists. If not, it will return some similar entities to search. (2) Lookup[keyword], which returns the next sentence containing keyword in the current passage. (3) Finish[answer], which returns the answer and finishes the task. Here are some examples. """ # Instruction+In-Context Exemplar webthink_prompt = instruction + webthink_examples def webthink(idx=None, prompt=webthink_prompt, to_print=True): # 给定一个编号为idx的的question,重置当前的环境 question = env.reset(idx=idx) if to_print: print(idx, question) prompt += question + "\n" # 设置好prompt n_calls, n_badcalls = 0, 0 # 一个任务,最多调用LLM8次。 for i in range(1, 8): n_calls += 1 # 根据当前的prompt(这个prompt可以是最开始的ICL+指令,也可以是经过几轮之后的动作序列)进行思考(reasoning thought),大模型生成一些action thought_action = llm(prompt + f"Thought {i}:", stop=[f"\nObservation {i}:"]) try: thought, action = thought_action.strip().split(f"\nAction {i}: ") except: print('ohh...', thought_action) n_badcalls += 1 n_calls += 1 thought = thought_action.strip().split('\n')[0] action = llm(prompt + f"Thought {i}: {thought}\nAction {i}:", stop=[f"\n"]).strip() # 根据action,在环境中执行一个动作,并获得observation # 这里的step()会根据action的类型,执行包括search、lookup等调用外部工具的动作。 obs, r, done, info = step(env, action[0].lower() + action[1:]) obs = obs.replace('\\n', '') # 将Thought、Action和Obs重新规约到一个prompt里,并与之前的prompt进行拼接 step_str = f"Thought {i}: {thought}\nAction {i}: {action}\nObservation {i}: {obs}\n" prompt += step_str if to_print: print(step_str) if done: break if not done: obs, r, done, info = step(env, "finish[]") if to_print: print(info, '\n') info.update({'n_calls': n_calls, 'n_badcalls': n_badcalls, 'traj': prompt}) return r, info rs = [] infos = [] old_time = time.time() for i in idxs[:500]: # 对当前第idx个任务进行推理 r, info = webthink(i, to_print=True) rs.append(info['em']) infos.append(info) print(sum(rs), len(rs), sum(rs) / len(rs), (time.time() - old_time) / len(rs)) print('-----------') print()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
分析
- ReAct是比较早期的让大模型完成Agent的工作,即Action与Reasoning相结合。但不同于现如今的LLMAgent,即需要有一个明显的pipeline。ReAct只是通过一个任务相关的静态的ICL prompt来引导大模型完成Agent的工作,并没有设置非常详细且明显的流程,例如planning、retrieving from memory、tool use、self-correction等;
- 动作空间是有限的,外部工具的调用也是有限的,当外部工具或者可执行的动作非常多的时候,可能不太适用;
- 启发:可通过prompt来实现定义好这个任务需要结合reasoning和action(工具调用);在具体的推理过程中,如果涉及到工具的调用,可以通过tool retriever的形式来选择合适的工具,而不是ReAct中为每个工具单独写死了逻辑实现。
- 外部工具的调用目前可以抽象为两种,一种是先planing,再根据planing的每个step action决定是reasoning还是检索并使用工具;另一种是以Tree-of-thought、ToolLLM为代表的直接列出所有可能的reasoning和工具列表,通过树搜索的形式选择一个路径。本文的ReAct属于第一种,只不过planing的过程不是单独的pipeline,而是统一到prompt中并以类似多轮对话的形式实现,其次planing的结果很固定,形如“I need to search x, find y, then find z”的格式。



