热门标签
当前位置: article > 正文
TensorFlow 实现车牌识别_tensorflow训练车牌识别模型
作者:繁依Fanyi0 | 2024-07-19 12:09:08
赞
踩
tensorflow训练车牌识别模型
1:生成训练数据集
#pip install pillow -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple #pip install opencv-python -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple import PIL from PIL import ImageFont from PIL import Image from PIL import ImageDraw import cv2; import numpy as np; import os; from math import * import matplotlib.pyplot as plt index = {"京": 0, "沪": 1, "津": 2, "渝": 3, "冀": 4, "晋": 5, "蒙": 6, "辽": 7, "吉": 8, "黑": 9, "苏": 10, "浙": 11, "皖": 12, "闽": 13, "赣": 14, "鲁": 15, "豫": 16, "鄂": 17, "湘": 18, "粤": 19, "桂": 20, "琼": 21, "川": 22, "贵": 23, "云": 24, "藏": 25, "陕": 26, "甘": 27, "青": 28, "宁": 29, "新": 30, "0": 31, "1": 32, "2": 33, "3": 34, "4": 35, "5": 36, "6": 37, "7": 38, "8": 39, "9": 40, "A": 41, "B": 42, "C": 43, "D": 44, "E": 45, "F": 46, "G": 47, "H": 48, "J": 49, "K": 50, "L": 51, "M": 52, "N": 53, "P": 54, "Q": 55, "R": 56, "S": 57, "T": 58, "U": 59, "V": 60, "W": 61, "X": 62, "Y": 63, "Z": 64}; chars = ["京", "沪", "津", "渝", "冀", "晋", "蒙", "辽", "吉", "黑", "苏", "浙", "皖", "闽", "赣", "鲁", "豫", "鄂", "湘", "粤", "桂", "琼", "川", "贵", "云", "藏", "陕", "甘", "青", "宁", "新", "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z" ]; def GenCh(f,val): # 生成中文字符 img=Image.new("RGB", (45,70),(255,255,255)) draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img) draw.text((0, 3),val,(0,0,0),font=f) img = img.resize((23,70)) A = np.array(img) return A def GenCh1(f,val): # 生成英文字符 img=Image.new("RGB", (23,70),(255,255,255)) draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img) draw.text((0, 2),val.encode('utf-8').decode('unicode_escape'),(0,0,0),font=f) A = np.array(img) return A def AddSmudginess(img, Smu): rows = r(Smu.shape[0] - 50) cols = r(Smu.shape[1] - 50) adder = Smu[rows:rows + 50, cols:cols + 50]; adder = cv2.resize(adder, (50, 50)); img = cv2.resize(img,(50,50)) img = cv2.bitwise_not(img) img = cv2.bitwise_and(adder, img) img = cv2.bitwise_not(img) return img def rot(img,angel,shape,max_angel): # 添加仿射变。img表示输入图像,factor表示畸变的参数,size表示图片的目标尺寸。 size_o = [shape[1],shape[0]] size = (shape[1]+ int(shape[0]*cos((float(max_angel )/180) * 3.14)),shape[0]) interval = abs( int( sin((float(angel) /180) * 3.14)* shape[0])); pts1 = np.float32([[0,0],[0,size_o[1]],[size_o[0],0],[size_o[0],size_o[1]]]) if(angel>0): pts2 = np.float32([[interval,0],[0,size[1] ],[size[0],0 ],[size[0]-interval,size_o[1]]]) else: pts2 = np.float32([[0,0],[interval,size[1] ],[size[0]-interval,0 ],[size[0],size_o[1]]]) M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1,pts2); dst = cv2.warpPerspective(img,M,size); return dst def rotRandrom(img, factor, size): # 添加透视变换 shape = size; pts1 = np.float32([[0, 0], [0, shape[0]], [shape[1], 0], [shape[1], shape[0]]]) pts2 = np.float32([[r(factor), r(factor)], [ r(factor), shape[0] - r(factor)], [shape[1] - r(factor), r(factor)], [shape[1] - r(factor), shape[0] - r(factor)]]) M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1, pts2); dst = cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, size); return dst def tfactor(img): # 添加饱和度光照的噪声 hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV); hsv[:,:,0] = hsv[:,:,0]*(0.8+ np.random.random()*0.2); hsv[:,:,1] = hsv[:,:,1]*(0.3+ np.random.random()*0.7); hsv[:,:,2] = hsv[:,:,2]*(0.2+ np.random.random()*0.8); img = cv2.cvtColor(hsv,cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR); return img def random_envirment(img,data_set): # 添加自然环境的噪声 index=r(len(data_set)) env = cv2.imread(data_set[index]) env = cv2.resize(env,(img.shape[1],img.shape[0])) bak = (img==0); bak = bak.astype(np.uint8)*255; inv = cv2.bitwise_and(bak,env) img = cv2.bitwise_or(inv,img) return img def AddGauss(img, level): # 添加高斯模糊 return cv2.blur(img, (level * 2 + 1, level * 2 + 1)); def r(val): return int(np.random.random() * val) def AddNoiseSingleChannel(single): # 添加高斯噪声 diff = 255-single.max(); noise = np.random.normal(0,1+r(6),single.shape); noise = (noise - noise.min())/(noise.max()-noise.min()) noise= diff*noise; noise= noise.astype(np.uint8) dst = single + noise return dst def addNoise(img,sdev = 0.5,avg=10): img[:,:,0] = AddNoiseSingleChannel(img[:,:,0]); img[:,:,1] = AddNoiseSingleChannel(img[:,:,1]); img[:,:,2] = AddNoiseSingleChannel(img[:,:,2]); return img class GenPlate: def __init__(self,fontCh,fontEng,NoPlates): self.fontC = ImageFont.truetype(fontCh,43,0); self.fontE = ImageFont.truetype(fontEng,60,0); self.img=np.array(Image.new("RGB", (226,70),(255,255,255))) self.bg = cv2.resize(cv2.imread("./images/template.bmp"),(226,70)); self.smu = cv2.imread("./images/smu2.jpg"); self.noplates_path = []; for parent,parent_folder,filenames in os.walk(NoPlates): for filename in filenames: path = parent+"/"+filename; self.noplates_path.append(path); def draw(self,val): offset= 2 ; self.img[0:70,offset+8:offset+8+23]= GenCh(self.fontC,val[0]); self.img[0:70,offset+8+23+6:offset+8+23+6+23]= GenCh1(self.fontE,val[1]); for i in range(5): base = offset+8+23+6+23+17 +i*23 + i*6 ; self.img[0:70, base : base+23]= GenCh1(self.fontE,val[i+2]); return self.img def generate(self,text): if len(text) == 7: fg = self.draw(text.encode('utf-8').decode(encoding="utf-8")); fg = cv2.bitwise_not(fg); com = cv2.bitwise_or(fg,self.bg); com = rot(com,r(60)-30,com.shape,30); com = rotRandrom(com,10,(com.shape[1],com.shape[0])); com = tfactor(com) com = random_envirment(com,self.noplates_path); com = AddGauss(com, 1+r(4)); com = addNoise(com); return com def genPlateString(self,pos,val): # 生成车牌string,将其以图片形式保存 plateStr = ""; box = [0,0,0,0,0,0,0]; if(pos!=-1): box[pos]=1; for unit,cpos in zip(box,range(len(box))): if unit == 1: plateStr += val else: if cpos == 0: plateStr += chars[r(31)] elif cpos == 1: plateStr += chars[41+r(24)] else: plateStr += chars[31 + r(34)] return plateStr; # 将生成的车牌图片写入文件夹 def genBatch(self, batchSize,pos,charRange, outputPath,size): if (not os.path.exists(outputPath)): os.mkdir(outputPath) for i in range(batchSize): plateStr = G.genPlateString(-1,-1) img = G.generate(plateStr); img = cv2.resize(img,size); plt.imshow(img) cv2.imwrite(outputPath + "/" + str(i).zfill(2) + ".jpg", img); G = GenPlate("./font/platech.ttf",'./font/platechar.ttf',"./NoPlates") G.genBatch(15,2,range(31,65),"./plate",(272,72)) #在每次其他模块运行时,若导入该库,则刷新该函数
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184



2:数据读取
import numpy as np import cv2 from genplate import * #产生用于训练的数据 class OCRIter(): def __init__(self,batch_size,height,width): super(OCRIter, self).__init__() self.genplate = GenPlate("./font/platech.ttf",'./font/platechar.ttf','./NoPlates') self.batch_size = batch_size self.height = height self.width = width #print("make plate data") # def iter(self): # for k in range((int)(self.count / self.batch_size)): # data = [] # label = [] # for i in range(self.batch_size): # num, img = gen_sample(self.genplate, self.width, self.height) # data.append(img) # label.append(num) # data_all = data # label_all = label # return data_all,label_all def iter(self): data = [] label = [] for i in range(self.batch_size): num, img = gen_sample(self.genplate, self.width, self.height) data.append(img) label.append(num) data_all = data label_all = label return data_all,label_all def rand_range(lo,hi): return lo+r(hi-lo); def gen_rand(): name = "" label=[] label.append(rand_range(0,31)) #产生车牌开头32个省的标签 label.append(rand_range(41,65)) #产生车牌第二个字母的标签 for i in range(5): label.append(rand_range(31,65)) #产生车牌后续5个字母的标签 name+=chars[label[0]] name+=chars[label[1]] for i in range(5): name+=chars[label[i+2]] return name,label def gen_sample(genplate, width, height): num,label =gen_rand() img = genplate.generate(num) img = cv2.resize(img,(width,height)) img = np.multiply(img,1/255.0) #[height,width,channel] #img = img.transpose(2,0,1) #img = img.transpose(1,0,2) return label,img #返回的label为标签,img为深度为3的图像像素
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
3:构建神经网络模型
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np def inference (images,keep_prob): # 第1层卷积层 with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape = [3,3,3,32], dtype = tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images,weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID') biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[32], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases) conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation,name= scope.name) # 第2层卷积层 with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights',shape=[3,3,32,32],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv1,weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID') biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[32], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases) conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation,name= scope.name) # 池化层1,进行最大池化操作 with tf.variable_scope('max_pooling1') as scope: pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2,ksize = [1,2,2,1],strides= [1,2,2,1],padding='VALID',name='pooling1') # 第3层卷积层 with tf.variable_scope('conv3') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights',shape=[3,3,32,64],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID') biases = tf.get_variable('biases',shape=[64],dtype = tf.float32,initializer= tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases) conv3 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation,name=scope.name) # 第4层卷积层 with tf.variable_scope('conv4') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights',shape=[3,3,64,64],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) conv =tf.nn.conv2d(conv3,weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID') biases = tf.get_variable('biases',shape=[64],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases) conv4 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation,name=scope.name) # 池化层2,进行最大池化操作 with tf.variable_scope('max_pooling2') as scope: pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv4,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='VALID',name='pooling2') # 第5层卷积层 with tf.variable_scope('conv5') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights',shape=[3,3,64,128],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) conv =tf.nn.conv2d(pool2,weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID') biases = tf.get_variable('biases',shape=[128],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases) conv5 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation,name=scope.name) # 第6层卷积层 with tf.variable_scope('conv6') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights',shape=[3,3,128,128],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) conv =tf.nn.conv2d(conv5,weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='VALID') biases = tf.get_variable('biases',shape=[128],dtype=tf.float32,initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases) conv6 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation,name=scope.name) # 池化层3,进行最大池化操作 with tf.variable_scope('max_pool3') as scope: pool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv6,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='VALID',name='pool3') with tf.variable_scope('fc1') as scope: shp = pool3.get_shape() flattened_shape =shp[1].value*shp[2].value*shp[3].value reshape = tf.reshape(pool3,[-1,flattened_shape]) fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(reshape,keep_prob,name='fc1_dropdot') with tf.variable_scope('fc21') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[flattened_shape,65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.1) ) fc21 = tf.matmul(fc1,weights)+biases with tf.variable_scope('fc22') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[flattened_shape,65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.1) ) fc22 = tf.matmul(fc1,weights)+biases with tf.variable_scope('fc23') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[flattened_shape,65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.1) ) fc23= tf.matmul(fc1,weights)+biases with tf.variable_scope('fc24') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[flattened_shape,65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.1) ) fc24 = tf.matmul(fc1,weights)+biases with tf.variable_scope('fc25') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[flattened_shape,65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.1) ) fc25 = tf.matmul(fc1,weights)+biases with tf.variable_scope('fc26') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[flattened_shape,65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.1) ) fc26 = tf.matmul(fc1,weights)+biases with tf.variable_scope('fc27') as scope: weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[flattened_shape,65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32)) biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[65], dtype=tf.float32, initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.1) ) fc27 = tf.matmul(fc1,weights)+biases return fc21,fc22,fc23,fc24,fc25,fc26,fc27 def losses(logits1,logits2,logits3,logits4,logits5,logits6,logits7,labels): '''Compute loss from logits and labels Args: logits: logits tensor, float, [7*batch_size, 65] labels: label tensor, tf.int32, [7*batch_size] Returns: loss tensor of float type ''' labels = tf.convert_to_tensor(labels,tf.int32) with tf.variable_scope('loss1') as scope: cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits1, labels=labels[:,0], name='xentropy_per_example') #cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=labels,name='xentropy_per_example') loss1 = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss1') tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/loss1', loss1) with tf.variable_scope('loss2') as scope: cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits2, labels=labels[:,1], name='xentropy_per_example') #cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=labels,name='xentropy_per_example') loss2 = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss2') tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/loss2', loss2) with tf.variable_scope('loss3') as scope: cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits3, labels=labels[:,2], name='xentropy_per_example') #cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=labels,name='xentropy_per_example') loss3 = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss3') tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/loss3', loss3) with tf.variable_scope('loss4') as scope: cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits4, labels=labels[:,3], name='xentropy_per_example') #cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=labels,name='xentropy_per_example') loss4 = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss4') tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/loss4', loss4) with tf.variable_scope('loss5') as scope: cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits5, labels=labels[:,4], name='xentropy_per_example') #cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=labels,name='xentropy_per_example') loss5 = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss5') tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/loss5', loss5) with tf.variable_scope('loss6') as scope: cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits6, labels=labels[:,5], name='xentropy_per_example') #cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=labels,name='xentropy_per_example') loss6 = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss6') tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/loss6', loss6) with tf.variable_scope('loss7') as scope: cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits7, labels=labels[:,6], name='xentropy_per_example') #cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=labels,name='xentropy_per_example') loss7 = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss7') tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/loss7', loss7) return loss1,loss2,loss3,loss4,loss5,loss6,loss7 def trainning( loss1,loss2,loss3,loss4,loss5,loss6,loss7, learning_rate): '''Training ops, the Op returned by this function is what must be passed to 'sess.run()' call to cause the model to train. Args: loss: loss tensor, from losses() Returns: train_op: The op for trainning ''' with tf.name_scope('optimizer1'): optimizer1 = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op1 = optimizer1.minimize(loss1, global_step= global_step) with tf.name_scope('optimizer2'): optimizer2 = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op2 = optimizer2.minimize(loss2, global_step= global_step) with tf.name_scope('optimizer3'): optimizer3 = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op3 = optimizer3.minimize(loss3, global_step= global_step) with tf.name_scope('optimizer4'): optimizer4 = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op4 = optimizer4.minimize(loss4, global_step= global_step) with tf.name_scope('optimizer5'): optimizer5 = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op5 = optimizer5.minimize(loss5, global_step= global_step) with tf.name_scope('optimizer6'): optimizer6 = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op6 = optimizer6.minimize(loss6, global_step= global_step) with tf.name_scope('optimizer7'): optimizer7 = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate) global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False) train_op7 = optimizer7.minimize(loss7, global_step= global_step) return train_op1,train_op2,train_op3,train_op4,train_op5,train_op6,train_op7 def evaluation(logits1,logits2,logits3,logits4,logits5,logits6,logits7,labels): """Evaluate the quality of the logits at predicting the label. Args: logits: Logits tensor, float - [batch_size, NUM_CLASSES]. labels: Labels tensor, int32 - [batch_size], with values in the range [0, NUM_CLASSES). Returns: A scalar int32 tensor with the number of examples (out of batch_size) that were predicted correctly. """ logits_all = tf.concat([logits1,logits2,logits3,logits4,logits5,logits6,logits7],0) labels = tf.convert_to_tensor(labels,tf.int32) labels_all = tf.reshape(tf.transpose(labels),[-1]) with tf.variable_scope('accuracy') as scope: correct = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits_all, labels_all, 1) correct = tf.cast(correct, tf.float16) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(correct) tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/accuracy', accuracy) return accuracy
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
4:开始训练模型
#%% import os import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from input_data import OCRIter import model import time import datetime tf.reset_default_graph() img_w = 272 img_h = 72 num_label=7 batch_size = 8 count = 30000 learning_rate = 0.0001 #默认参数[N,H,W,C] image_holder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[batch_size,img_h,img_w,3]) label_holder = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,[batch_size,7]) keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) logs_train_dir = (r'.\train_result') def get_batch(): data_batch = OCRIter(batch_size,img_h,img_w) image_batch,label_batch = data_batch.iter() image_batch1 = np.array(image_batch) label_batch1 = np.array(label_batch) return image_batch1,label_batch1 train_logits1,train_logits2,train_logits3,train_logits4,train_logits5,train_logits6,train_logits7= model.inference(image_holder,keep_prob) train_loss1,train_loss2,train_loss3,train_loss4,train_loss5,train_loss6,train_loss7 = model.losses(train_logits1,train_logits2,train_logits3,train_logits4,train_logits5,train_logits6,train_logits7,label_holder) train_op1,train_op2,train_op3,train_op4,train_op5,train_op6,train_op7 = model.trainning(train_loss1,train_loss2,train_loss3,train_loss4,train_loss5,train_loss6,train_loss7,learning_rate) train_acc = model.evaluation(train_logits1,train_logits2,train_logits3,train_logits4,train_logits5,train_logits6,train_logits7,label_holder) input_image=tf.summary.image('input',image_holder) #tf.summary.histogram('label',label_holder) #label的histogram,测试训练代码时用,参考:http://geek.csdn.net/news/detail/197155 summary_op = tf.summary.merge(tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.SUMMARIES)) #sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True)) #运行日志 sess = tf.Session() train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logs_train_dir,sess.graph) saver = tf.train.Saver() sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) start_time1 = time.time() for step in range(count): x_batch,y_batch = get_batch() start_time2 = time.time() time_str = datetime.datetime.now().isoformat() feed_dict = {image_holder:x_batch,label_holder:y_batch,keep_prob:0.5} _,_,_,_,_,_,_,tra_loss1,tra_loss2,tra_loss3,tra_loss4,tra_loss5,tra_loss6,tra_loss7,acc,summary_str= sess.run([train_op1,train_op2,train_op3,train_op4,train_op5,train_op6,train_op7,train_loss1,train_loss2,train_loss3,train_loss4,train_loss5,train_loss6,train_loss7,train_acc,summary_op],feed_dict) train_writer.add_summary(summary_str,step) duration = time.time()-start_time2 tra_all_loss =tra_loss1+tra_loss2+tra_loss3+tra_loss4+tra_loss5+tra_loss6+tra_loss7 #print(y_batch) #仅测试代码训练实际样本与标签是否一致 if step % 10== 0: sec_per_batch = float(duration) print('%s : Step %d,train_loss = %.2f,acc= %.2f,sec/batch=%.3f' %(time_str,step,tra_all_loss,acc,sec_per_batch)) if step % 10000==0 or (step+1) == count: checkpoint_path = os.path.join(logs_train_dir,'model.ckpt') saver = tf.train.Saver() saver.save(sess,checkpoint_path,global_step=step) sess.close() print(time.time()-start_time1)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
因为测试数据过大,所以运行了一整天才出结果,调试可以把数据量改为30
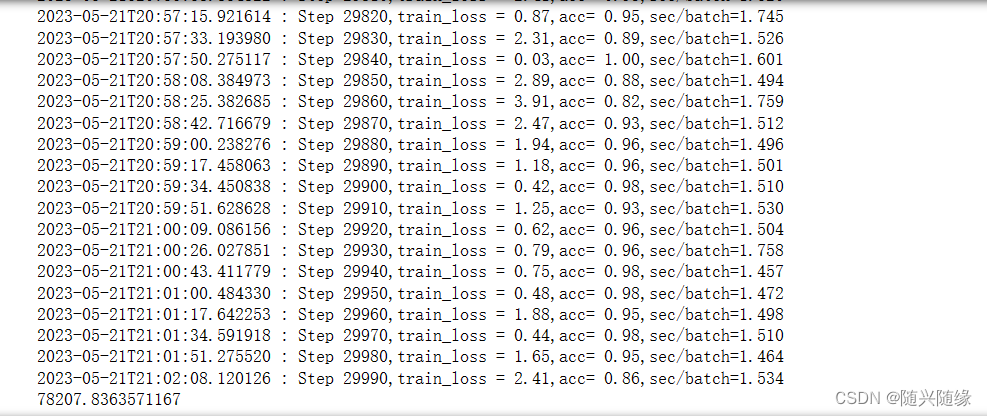
5:测试模型准确度
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import os from PIL import Image import cv2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import model import genplate tf.reset_default_graph() index = {"京": 0, "沪": 1, "津": 2, "渝": 3, "冀": 4, "晋": 5, "蒙": 6, "辽": 7, "吉": 8, "黑": 9, "苏": 10, "浙": 11, "皖": 12, "闽": 13, "赣": 14, "鲁": 15, "豫": 16, "鄂": 17, "湘": 18, "粤": 19, "桂": 20, "琼": 21, "川": 22, "贵": 23, "云": 24, "藏": 25, "陕": 26, "甘": 27, "青": 28, "宁": 29, "新": 30, "0": 31, "1": 32, "2": 33, "3": 34, "4": 35, "5": 36, "6": 37, "7": 38, "8": 39, "9": 40, "A": 41, "B": 42, "C": 43, "D": 44, "E": 45, "F": 46, "G": 47, "H": 48, "J": 49, "K": 50, "L": 51, "M": 52, "N": 53, "P": 54, "Q": 55, "R": 56, "S": 57, "T": 58, "U": 59, "V": 60, "W": 61, "X": 62, "Y": 63, "Z": 64}; chars = ["京", "沪", "津", "渝", "冀", "晋", "蒙", "辽", "吉", "黑", "苏", "浙", "皖", "闽", "赣", "鲁", "豫", "鄂", "湘", "粤", "桂", "琼", "川", "贵", "云", "藏", "陕", "甘", "青", "宁", "新", "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z" ]; ''' Test one image against the saved models and parameters ''' global pic def get_one_image(test): ''' Randomly pick one image from training data Return: ndarry ''' G = genplate.GenPlate("./font/platech.ttf", './font/platechar.ttf', "./NoPlates") G.genBatch(15, 2, range(31, 65), "./plate", (272, 72)) # 注释原因为每次其他模块运行,若导入该库,都会刷性该函数 n = len(test) ind =np.random.randint(0,n) img_dir = test[ind] image_show = Image.open(img_dir) plt.imshow(image_show) #image = image.resize([120,30]) image = cv2.imread(img_dir) global pic pic = image # cv2.imshow('image', image) # cv2.waitKey(0) img = np.multiply(image,1/255.0) #image = np.array(img) #image = img.transpose(1,0,2) image = np.array([img]) print(image.shape) return image batch_size = 1 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[batch_size,72,272,3]) keep_prob =tf.placeholder(tf.float32) test_dir = (r'.\plate/') test_image = [] for file in os.listdir(test_dir): test_image.append(test_dir + file) test_image = list(test_image) image_array = get_one_image(test_image) #logit = model.inference(x,keep_prob) logit1,logit2,logit3,logit4,logit5,logit6,logit7 = model.inference(x,keep_prob) #logit1 = tf.nn.softmax(logit1) #logit2 = tf.nn.softmax(logit2) #logit3 = tf.nn.softmax(logit3) #logit4 = tf.nn.softmax(logit4) #logit5 = tf.nn.softmax(logit5) #logit6 = tf.nn.softmax(logit6) #logit7 = tf.nn.softmax(logit7) # logs_train_dir = '/home/llc/TF_test/Chinese_plate_recognition/Plate_recognition/train_logs_50000/' logs_train_dir = (r'.\train_result/') saver = tf.train.Saver() with tf.Session() as sess: tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables() print ("Reading checkpoint...") ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(logs_train_dir) if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path: global_step = ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].split('-')[-1] saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path) print('Loading success, global_step is %s' % global_step) else: print('No checkpoint file found') pre1,pre2,pre3,pre4,pre5,pre6,pre7 = sess.run([logit1,logit2,logit3,logit4,logit5,logit6,logit7], feed_dict={x: image_array,keep_prob:1.0}) prediction = np.reshape(np.array([pre1,pre2,pre3,pre4,pre5,pre6,pre7]),[-1,65]) #prediction = np.array([[pre1],[pre2],[pre3],[pre4],[pre5],[pre6],[pre7]]) #print(prediction) max_index = np.argmax(prediction,axis=1) print(max_index) line = '' for i in range(prediction.shape[0]): if i == 0: result = np.argmax(prediction[i][0:31]) if i == 1: result = np.argmax(prediction[i][41:65])+41 if i > 1: result = np.argmax(prediction[i][31:65])+31 line += chars[result]+" " print ('predicted: ' + line) cv2.imshow('pic',pic) cv2.waitKeyEx(0)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112


声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/繁依Fanyi0/article/detail/851405
推荐阅读
相关标签



