使用机器学习进行疾病预测 -- 机器学习项目基础篇(3)_机器学习疾病预测
赞
踩
本文旨在实现一个强大的机器学习模型,可以根据他/她所拥有的症状有效地预测人类的疾病。让我们看看如何解决这个机器学习问题:
方法:
- 收集数据:数据准备是任何机器学习问题的主要步骤。我们将使用来自Kaggle的数据集来解决这个问题。该数据集由两个CSV文件组成,一个用于训练,一个用于测试。数据集中总共有133列,其中132列表示症状,最后一列是预后。
- 清理数据:清理是机器学习项目中最重要的一步。数据的质量决定了机器学习模型的质量。因此,在将数据馈送到模型进行训练之前,总是需要清理数据。在我们的数据集中,所有列都是数字列,目标列即预后是字符串类型并且使用标签编码器被编码为数字形式。
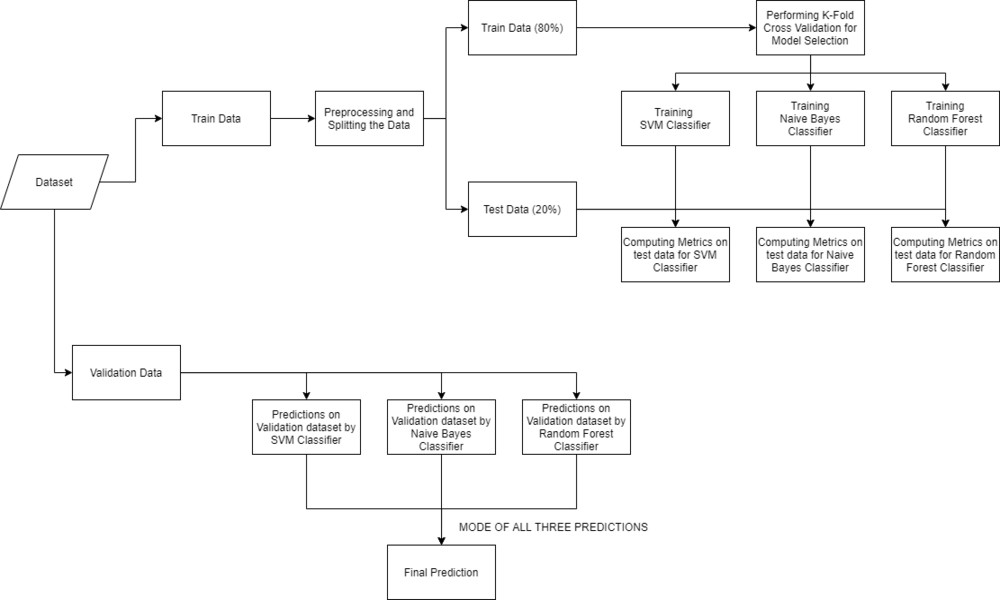
- 模型构建:在收集和清理数据之后,数据就准备好了,可以用来训练机器学习模型。我们将使用这些经过清理的数据来训练支持向量分类器,朴素贝叶斯分类器和随机森林分类器。我们将使用混淆矩阵来确定模型的质量。
- 推断:在训练三个模型之后,我们将通过结合所有三个模型的预测来预测输入症状的疾病。这使得我们的整体预测更加稳健和准确。
最后,我们将定义一个函数,该函数以逗号分隔的症状作为输入,通过使用训练的模型根据症状预测疾病,并以JSON格式返回预测结果。
具体操作
确保下载了Training和Testing,并将train.csv和test.csv放入数据集文件夹中。打开jupyter notebook并单独运行代码以更好地理解。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from scipy.stats import mode
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix
%matplotlib inline
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
阅读数据集
首先,我们将使用pandas库从文件夹中加载数据集。在阅读数据集时,我们将删除null列。此数据集是一个干净的数据集,没有空值,所有特征都由0和1组成。每当我们解决分类任务时,有必要检查目标列是否平衡。我们将使用条形图来检查数据集是否平衡。
# Reading the train.csv by removing the # last column since it's an empty column DATA_PATH = "dataset/Training.csv" data = pd.read_csv(DATA_PATH).dropna(axis = 1) # Checking whether the dataset is balanced or not disease_counts = data["prognosis"].value_counts() temp_df = pd.DataFrame({ "Disease": disease_counts.index, "Counts": disease_counts.values }) plt.figure(figsize = (18,8)) sns.barplot(x = "Disease", y = "Counts", data = temp_df) plt.xticks(rotation=90) plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
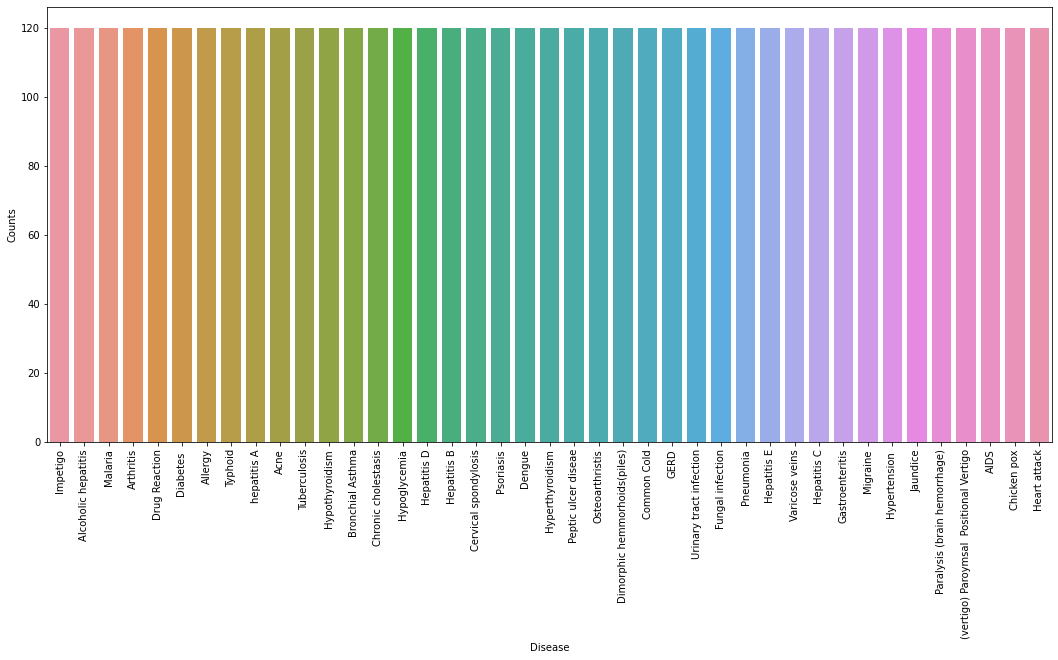
从上面的图中,我们可以观察到数据集是平衡的数据集,即每种疾病正好有120个样本,不需要进一步的平衡。我们可以注意到我们的目标列,即预测列是对象数据类型,这种格式不适合训练机器学习模型。因此,我们将使用标签编码器将预测列转换为数值数据类型。标签编码器通过为标签分配唯一索引来将标签转换为数字形式。如果标签的总数是n,则分配给每个标签的数字将在0到n-1之间。
# Encoding the target value into numerical
# value using LabelEncoder
encoder = LabelEncoder()
data["prognosis"] = encoder.fit_transform(data["prognosis"])
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
划分数据以训练和测试模型
现在,我们已经通过删除Null值并将标签转换为数字格式来清理数据,现在是时候拆分数据以训练和测试模型了。我们将数据分割为80:20格式,即80%的数据集将用于训练模型,20%的数据将用于评估模型的性能。
X = data.iloc[:,:-1]
y = data.iloc[:, -1]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test =train_test_split(
X, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 24)
print(f"Train: {X_train.shape}, {y_train.shape}")
print(f"Test: {X_test.shape}, {y_test.shape}")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
输出:
Train: (3936, 132), (3936,)
Test: (984, 132), (984,)
- 1
- 2
模型建立
分割数据后,我们现在将处理建模部分。我们将使用K-Fold交叉验证来评估机器学习模型。我们将使用支持向量分类器,高斯朴素贝叶斯分类器和随机森林分类器进行交叉验证。在进入实现部分之前,让我们熟悉一下k折交叉验证和机器学习模型。
- K折交叉验证:K-Fold交叉验证是交叉验证技术之一,其中整个数据集被分成k个子集,也称为折叠,然后在k-1个子集上执行模型的训练,剩余的一个子集用于评估模型性能。
- 支持向量分类器:支持向量分类器是一种判别式分类器,即当给定一个标记的训练数据时,该算法试图找到一个最佳的超平面,该超平面准确地将样本分成超空间中的不同类别。
- 高斯朴素贝叶斯分类器:它是一种概率机器学习算法,内部使用贝叶斯定理对数据点进行分类。
- 随机森林分类器:随机森林是一种基于集成学习的监督机器学习分类算法,它在内部使用多个决策树来进行分类。在随机森林分类器中,所有的内部决策树都是弱学习器,并且这些弱决策树的输出被组合,即所有预测的模式作为最终预测。
使用K折交叉验证进行模型选择
# Defining scoring metric for k-fold cross validation def cv_scoring(estimator, X, y): return accuracy_score(y, estimator.predict(X)) # Initializing Models models = { "SVC":SVC(), "Gaussian NB":GaussianNB(), "Random Forest":RandomForestClassifier(random_state=18) } # Producing cross validation score for the models for model_name in models: model = models[model_name] scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, cv = 10, n_jobs = -1, scoring = cv_scoring) print("=="*30) print(model_name) print(f"Scores: {scores}") print(f"Mean Score: {np.mean(scores)}")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
输出:
============================================================ SVC Scores: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] Mean Score: 1.0 ============================================================ Gaussian NB Scores: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] Mean Score: 1.0 ============================================================ Random Forest Scores: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] Mean Score: 1.0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
从上面的输出中,我们可以注意到,我们所有的机器学习算法都表现得非常好,k折交叉验证后的平均分数也非常高。为了建立一个强大的模型,我们可以联合采用所有三个模型的预测模式,使得即使其中一个模型做出错误的预测,而另外两个模型做出正确的预测,那么最终的输出将是正确的。这种方法将帮助我们在完全看不见的数据上保持预测更加准确。在下面的代码中,我们将在训练数据上训练所有三个模型,使用混淆矩阵检查模型的质量,然后联合所有三个模型的预测。
通过组合所有模型构建鲁棒分类器:
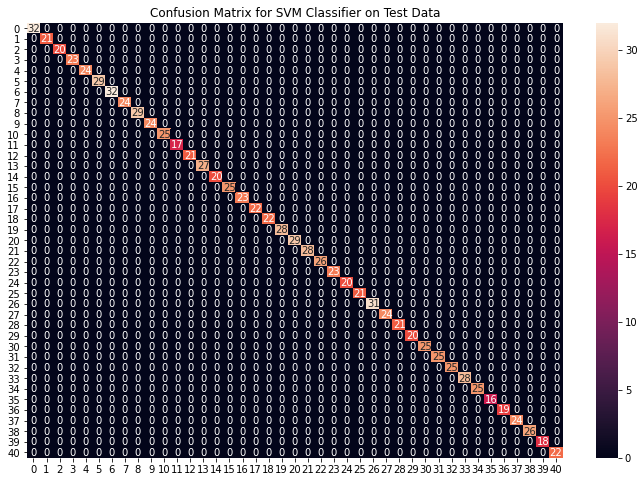
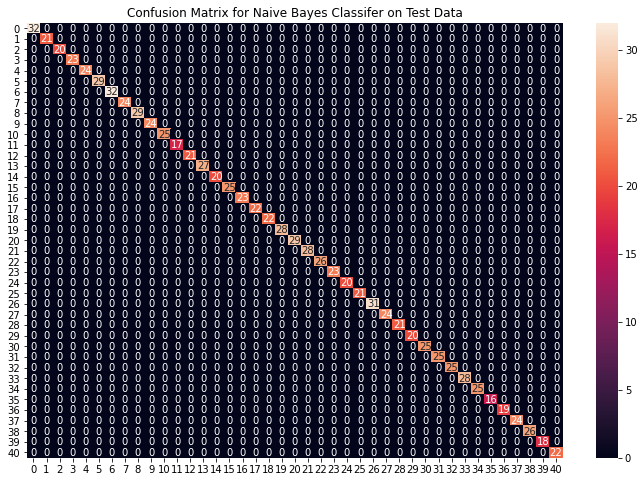
# Training and testing SVM Classifier svm_model = SVC() svm_model.fit(X_train, y_train) preds = svm_model.predict(X_test) print(f"Accuracy on train data by SVM Classifier\ : {accuracy_score(y_train, svm_model.predict(X_train))*100}") print(f"Accuracy on test data by SVM Classifier\ : {accuracy_score(y_test, preds)*100}") cf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, preds) plt.figure(figsize=(12,8)) sns.heatmap(cf_matrix, annot=True) plt.title("Confusion Matrix for SVM Classifier on Test Data") plt.show() # Training and testing Naive Bayes Classifier nb_model = GaussianNB() nb_model.fit(X_train, y_train) preds = nb_model.predict(X_test) print(f"Accuracy on train data by Naive Bayes Classifier\ : {accuracy_score(y_train, nb_model.predict(X_train))*100}") print(f"Accuracy on test data by Naive Bayes Classifier\ : {accuracy_score(y_test, preds)*100}") cf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, preds) plt.figure(figsize=(12,8)) sns.heatmap(cf_matrix, annot=True) plt.title("Confusion Matrix for Naive Bayes Classifier on Test Data") plt.show() # Training and testing Random Forest Classifier rf_model = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=18) rf_model.fit(X_train, y_train) preds = rf_model.predict(X_test) print(f"Accuracy on train data by Random Forest Classifier\ : {accuracy_score(y_train, rf_model.predict(X_train))*100}") print(f"Accuracy on test data by Random Forest Classifier\ : {accuracy_score(y_test, preds)*100}") cf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, preds) plt.figure(figsize=(12,8)) sns.heatmap(cf_matrix, annot=True) plt.title("Confusion Matrix for Random Forest Classifier on Test Data") plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
输出:
Accuracy on train data by SVM Classifier: 100.0
Accuracy on test data by SVM Classifier: 100.0
- 1
- 2
Accuracy on train data by Naive Bayes Classifier: 100.0
Accuracy on test data by Naive Bayes Classifier: 100.0
- 1
- 2
Accuracy on train data by Random Forest Classifier: 100.0
Accuracy on test data by Random Forest Classifier: 100.0
- 1
- 2
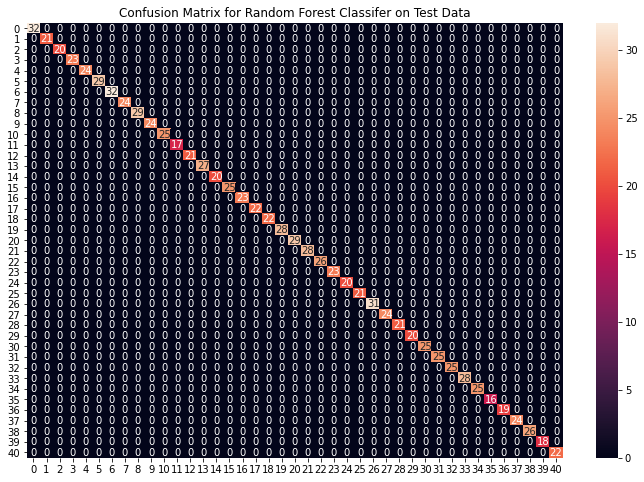
从上面的混淆矩阵,我们可以看到模型在看不见的数据上表现得非常好。现在,我们将在我们下载的数据集中的整个训练数据上训练模型,然后在数据集中的测试数据上测试我们的组合模型。
在整个数据上拟合模型并在测试数据集上验证:
# Training the models on whole data final_svm_model = SVC() final_nb_model = GaussianNB() final_rf_model = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=18) final_svm_model.fit(X, y) final_nb_model.fit(X, y) final_rf_model.fit(X, y) # Reading the test data test_data = pd.read_csv("./dataset/Testing.csv").dropna(axis=1) test_X = test_data.iloc[:, :-1] test_Y = encoder.transform(test_data.iloc[:, -1]) # Making prediction by take mode of predictions # made by all the classifiers svm_preds = final_svm_model.predict(test_X) nb_preds = final_nb_model.predict(test_X) rf_preds = final_rf_model.predict(test_X) final_preds = [mode([i,j,k])[0][0] for i,j, k in zip(svm_preds, nb_preds, rf_preds)] print(f"Accuracy on Test dataset by the combined model\ : {accuracy_score(test_Y, final_preds)*100}") cf_matrix = confusion_matrix(test_Y, final_preds) plt.figure(figsize=(12,8)) sns.heatmap(cf_matrix, annot = True) plt.title("Confusion Matrix for Combined Model on Test Dataset") plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
输出:
Accuracy on Test dataset by the combined model: 100.0
- 1
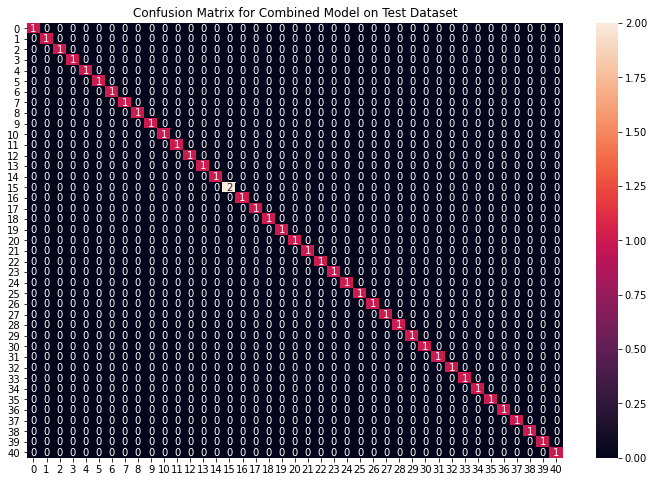
我们可以看到,我们的组合模型准确地分类了所有数据点。我们已经到了整个实现的最后一部分,我们将创建一个函数,该函数将逗号分隔的症状作为输入,并使用基于输入症状的组合模型输出预测的疾病。
创建一个可以将症状作为输入并生成疾病预测的函数
symptoms = X.columns.values # Creating a symptom index dictionary to encode the # input symptoms into numerical form symptom_index = {} for index, value in enumerate(symptoms): symptom = " ".join([i.capitalize() for i in value.split("_")]) symptom_index[symptom] = index data_dict = { "symptom_index":symptom_index, "predictions_classes":encoder.classes_ } # Defining the Function # Input: string containing symptoms separated by commas # Output: Generated predictions by models def predictDisease(symptoms): symptoms = symptoms.split(",") # creating input data for the models input_data = [0] * len(data_dict["symptom_index"]) for symptom in symptoms: index = data_dict["symptom_index"][symptom] input_data[index] = 1 # reshaping the input data and converting it # into suitable format for model predictions input_data = np.array(input_data).reshape(1,-1) # generating individual outputs rf_prediction = data_dict["predictions_classes"][final_rf_model.predict(input_data)[0]] nb_prediction = data_dict["predictions_classes"][final_nb_model.predict(input_data)[0]] svm_prediction = data_dict["predictions_classes"][final_svm_model.predict(input_data)[0]] # making final prediction by taking mode of all predictions final_prediction = mode([rf_prediction, nb_prediction, svm_prediction])[0][0] predictions = { "rf_model_prediction": rf_prediction, "naive_bayes_prediction": nb_prediction, "svm_model_prediction": svm_prediction, "final_prediction":final_prediction } return predictions # Testing the function print(predictDisease("Itching,Skin Rash,Nodal Skin Eruptions"))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
输出:
{
'rf_model_prediction': 'Fungal infection',
'naive_bayes_prediction': 'Fungal infection',
'svm_model_prediction': 'Fungal infection',
'final_prediction': 'Fungal infection'
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
注:作为函数输入的症状在数据集中的132个症状中应该完全相同。



