热门标签
热门文章
- 1Seata事务管理---Seata简介
- 2C语言强化-1.数据结构概述
- 3lora训练调参
- 4百度智能云千帆 ModelBuilder 技术实践系列:通过 SDK 快速构建并发布垂域模型_百度智能云千帆modelbuilder 最丰富的大模型,全流程工具链
- 5Qt(C++) | QPropertyAnimation动画(移动、缩放、透明)篇_qt 动画放大
- 6windows的svn_windows svn
- 7YOLOv8的代码如何升级到YOLOv10_yolov10 attributeerror: can't get attribute 'scdow
- 8分布式锁3: zk实现分布式锁3 使用临时顺序节点+watch监听实现阻塞锁_zk watch 与监听事件
- 9(五)阿里云ECS服务器的基本管理与磁盘扩容_阿里云ecs磁盘扩容
- 10【饭谈】面试官让你来个“自我介绍”,你准备怎么说?_自我介绍 需要说 技术栈
当前位置: article > 正文
rrt* 算法_rrt*算法
作者:笔触狂放9 | 2024-07-25 17:04:01
赞
踩
rrt*算法
rrt算法由于没有考虑cost值,使得最终规划的路径质量很差。rrt*算法在此基础上,引入贪心思想,使得规划路径可以随着采样次数增多逐步优化。
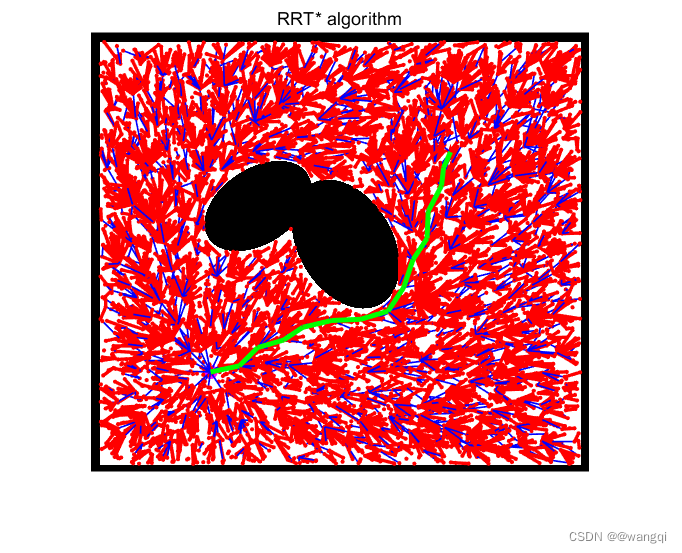
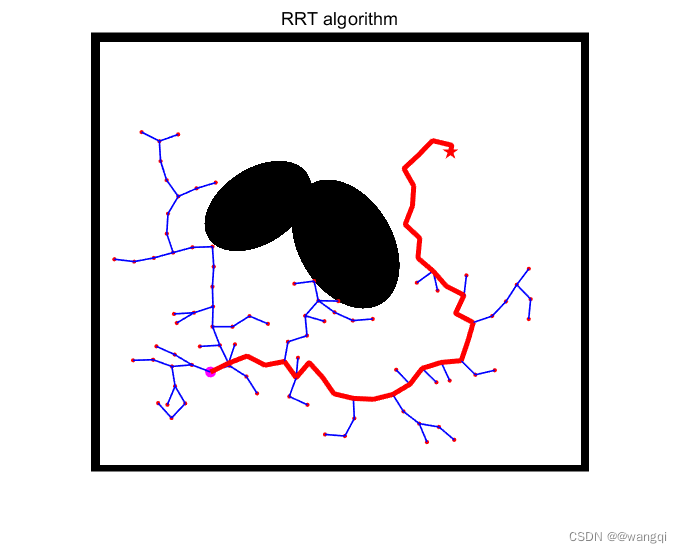

一、算法流程

二、rrt*与rrt的不同
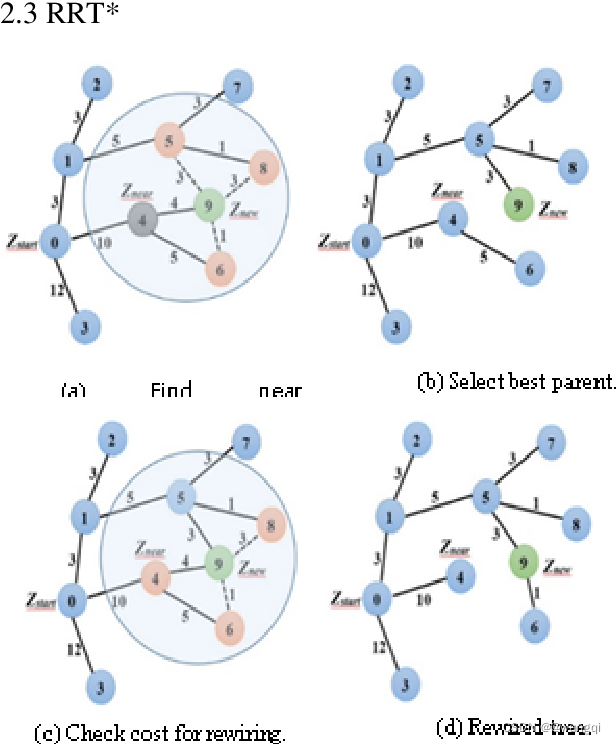
1、父节点的选取不同
rrt扩展完后,将距离其最近的节点作为其父节点;而rrt*是划定一个范围,将范围的节点均作为待选父节点,然后分别计算以它们为父节点时,
的cost值,选择使
的cost最小的节点作为其父节点。这一步使得扩展得新节点得cost尽可能得小。
2、重布线(rewire)
在完成新节点的父节点选取后,选取新节点的周边节点,假设将刚扩展的新节点作为它们的父节点,比较此时它们的cost值与其原先得cost值,如果此时cost值较小,则rewire,将新节点作为其父节点,并更新cost值。
三、matlab代码
这里只放两处关键代码,后面会上传github。
1、父节点的选取
- %以newnode节点为中心,半径R为半径搜索节点
- R=30/ceil(0.001*numel(nodes_list));
- dis2new=nodes_list(ind).cost+stepLength;
- minCostIndex=ind;
- nearNodeList=[];
- for index_near=1:N
- if norm(nodes_list(index_near).position-newnode)<R
- nearNodeList=[nearNodeList,nodes_list(index_near)]; %if node in the range, put it in the nearNodeList
- if norm(nodes_list(index_near).position-newnode)+nodes_list(index_near).cost<dis2new
- dis2new=norm(nodes_list(index_near).position-newnode)+nodes_list(index_near).cost;
- flag=collisionCheck(newnode,nodes_list(index_near).position,fig);
- if flag
- minCostIndex=index_near;
- end
- end
- end
- end
- lhandle=plot([nodes_list(minCostIndex).position(1),newnode(1)],[nodes_list(minCostIndex).position(2),newnode(2)],'b-','LineWidth',1);
- lhandlelist=[lhandlelist,lhandle];
- phandle=plot(newnode(1),newnode(2),'ro','MarkerFaceColor','r','MarkerSize',2);
- phandlelist=[phandlelist,phandle];
- drawnow;
- nodes_list(N+1).position=newnode;
- nodes_list(N+1).parentind=minCostIndex;
- nodes_list(N+1).cost=nodes_list(minCostIndex).cost+norm(near2rand);
- nodes_list(N+1).index=N+1;

2、rewire
- %% rewire
- NearNums=length(nearNodeList);
- for iterNear=1:NearNums
- nearNewCost=norm(nearNodeList(iterNear).position-newnode);
- if nearNewCost+nodes_list(N+1).cost<nearNodeList(iterNear).cost
- flag=collisionCheck(newnode,nearNodeList(iterNear).position,fig);
- if flag
- nodes_list(nearNodeList(iterNear).index).parentind=N+1;
- nodes_list(nearNodeList(iterNear).index).cost=nearNewCost+nodes_list(N+1).cost;
- %delete(lhandlelist(nearNodeList(iterNear).index-1));
- lhandlelist(nearNodeList(iterNear).index-1)=plot([nearNodeList(iterNear).position(1),newnode(1)],...
- [nearNodeList(iterNear).position(2),newnode(2)],'r-','LineWidth',2);
- drawnow;
- end
- end
- end
- if norm(newnode-goalPoint)<=stepLength && ~findflag
- findflag=1;
- nodes_list(N+2).position=goalPoint;
- nodes_list(N+2).parentind=N+1;
- nodes_list(N+2).cost=nodes_list(N+1).cost+norm(newnode-goalPoint);
- nodes_list(N+2).index=N+2;
- goalindex=N+2;
- %plot([newnode(1),goalPoint(1)],[newnode(2),goalPoint(2)],'b-');
- end
- title(['RRT* algorithm ','sampleNums:',num2str(j)]);
- if findflag
- updatepathcount=updatepathcount+1;
- if updatepathcount==50
- updatepathcount=0;
- m=2;
- path=[];
- path(1).position=goalPoint;
- pathIndex=nodes_list(goalindex).parentind;
- while 1
- path(m).position = nodes_list(pathIndex).position;
- pathIndex = nodes_list(pathIndex).parentind; % 沿终点回溯到起点
- if pathIndex == -1
- break
- end
- m=m+1;
- end
- for delete_index=1:length(pathhandlelist)
- delete(pathhandlelist(delete_index));
- end
- for m=2:length(path)
- pathhandle=plot([path(m).position(1),path(m-1).position(1)],[path(m).position(2),path(m-1).position(2)],'g-','LineWidth',3);
- pathhandlelist=[pathhandlelist,pathhandle];
- end
- end
- end

四、几点疑问
1、采样次数与时间复杂度的取舍,采样次数越多,路线越优化。
2、随着采样次数增多,后期的父节点选取及rewire的待选节点越多,这一点如何处理。(有人把搜索半径与采样次数关联,采样次数越多,搜索半径越小)。
3、搜索半径的问题,同样半径越大,路径会越优化,但会带来时间成本的增大。
五、参考文章
http://路径规划——改进RRT算法 - 搬砖的旺财的文章 - 知乎 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/51087819
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/笔触狂放9/article/detail/881284
推荐阅读
相关标签


