热门标签
热门文章
- 1实用篇 | 做自己的管理系统 :Pycharm+django+mysql_做管理系统要用到django吗
- 2贝叶斯神经网络对梯度攻击的鲁棒性
- 3第三讲 知识抽取与挖掘I_面向结构化的知识抽取是什么
- 4MISCONF Redis is configured to save RDB snapshots, but is currently not able to persist on disk
- 5[翻译Pytorch教程]NLP从零开始:使用字符级RNN进行姓名分类_nlp from scratch: classifying names with a charact
- 6c++优先队列(priority_queue)小顶堆 大顶堆_priority_queue默认大顶堆
- 7css设置文字铺满盒子
- 8全国计算机等级考试二级MS Office考试大纲(2023版)_计算机二级考试的考纲
- 9基于深度学习的木材表面缺陷检测系统(网页版+YOLOv8/v7/v6/v5代码+训练数据集)
- 10在Idea里,执行npm命令 : 无法加载文件 ***\Nodejs\node_global\npm.ps1,因为在此系统上禁止运行脚本_无法加载文件 nodejs\node_global\react-native.psl
当前位置: article > 正文
第一篇 Java核心技术细讲之ArrayList_arraylist常用的业务场景推荐
作者:笔触狂放9 | 2024-03-27 04:48:35
赞
踩
arraylist常用的业务场景推荐

一、开篇导言
- 你好,我是暗余。本专栏为我的原创专栏,也是我的第一部精品专栏,谢谢你的观看与支持!
- 今天我们来讲一下ArrayList。日常工作中,它是我们使用最为频繁的一个集合类;相信每一位Java同学都有接触过它。如何使用好ArrayList,如何深入浅出的理解ArrayList,是每一位同学的必修课;
- 学好ArrayList有什么作用呢?
- 集合在整个流程中都有它的存在。从数据库批量查询需要集合接收;作为我们业务逻辑承载的容器,它能够满足各种各样的业务逻辑和功能(数据的筛选、分页、排序、合并、切分等等);以及返回给前端的数据集。
- 学好集合能够让我们处理复杂业务游刃有余;在普通场景下,我们可以通过业务来选择是否使用ArrayList还是LinkedList;在并发场景下,我们可以根据实际场景来选择synchronized包装集合,还是选择current 包下的其他集合类或currentHashmap?在数据复杂的业务操作下,如何利用Stream更方便的处理我们的业务问题?
- 虽然我们经常在用它,但是很多时候没有完整、多角度的去认识它。面试的时候也经常会问到ArrayList,可涉及到一些底层知识的时候,又开始迷惘了;
- 接下来,我们一起来领略ArrayList 的魅力吧!
二、理论知识
2.1 ArrayList关系图谱
-
Java集合是一个大类,它主要由两个部分组成:
- Collection接口下的所有List,其中ArrayList是其实现类之一,存放的是单一元素;
- Map接口下的所有键值对,其中HashMap是其实现类之一,存放的是Key-Value形式的数据;(下一篇会讲到)。
-
在List集合下面,分成了三个部分:
- List:元素是可重复的,是有序的;
- Set:元素是不可重复的,往往是无序的,但是TreeSet实现了有序;
- Queue:按照特定规则来确定先后顺序,存储的元素是有序、可重复的;
-
ArrayList,由Java库中提供的一个动态数组集合类;这是它的类关系图:
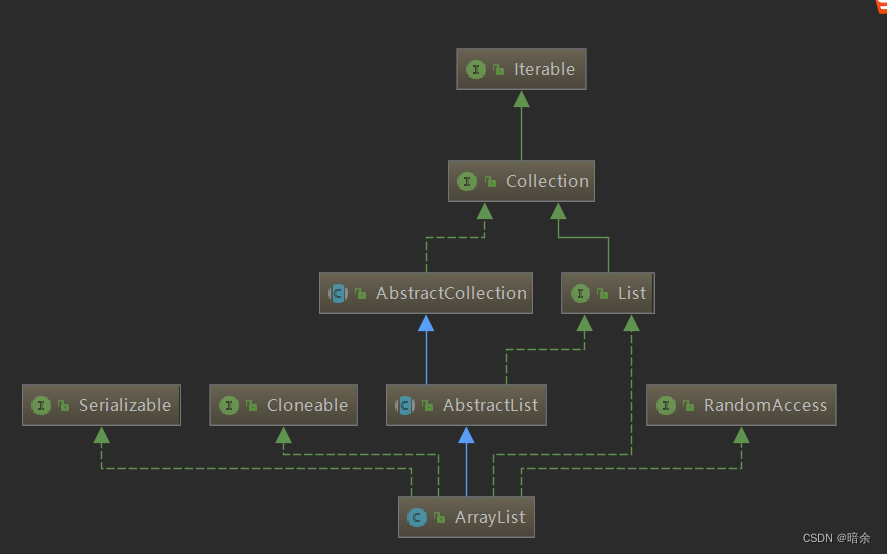
-
我们来看看它的特点:

2.2 ArrayList与LinkedList对比
| ArrayList | LinkedList | |
|---|---|---|
| 数据结构 | 数组 | 链表 |
| 扩容形式 | 数组拷贝方式扩容 | 天然支持扩容 |
| 随机读取 | 根据下标读取,时间复杂度O(1) | 从头部节点向下遍历匹配,时间复杂度O(n) |
| 新增元素 | 位置不同性能损耗不同,如果在头部添加,后面所有元素需要往后挪一位;尾部添加直接加 | 修改前后节点的引用地址,都指向新节点即可,总的来说性能更好 |
| 删除元素 | 删除指定元素,后面的元素需要逐次前挪一位,删除位置效率不同 | 直接指针修改引用地址,跳过被删除元素即可(仍然需要先遍历找到该元素),总的来说性能更好 |
2.3 ArrayList常用功能介绍
| 功能 | 使用方式 |
|---|---|
| 创建ArrayList的方式 | new ArrayList()、Lists.newArrayList()、Immuntable.of()(不支持扩容) |
| 常用增删查改、批量新增 | List自带api、allAll()、CollectionUtils.addAll() |
| 求和、统计平均值等统计 | stream流的sum等函数,Bigdecial的reduce |
| 排序 | CollectionUtils工具类、Stream流 sorted 排序 |
| 集合拆分、合并 | Lists.partition( List集合, 拆分成几个集合); Stream流合并 |
| 分页 | Stream 流的limit/skip |
| 转为其他的集合、Map | 遍历逐个转换、foreach、stream流的map再collect |
| 分组 | stream流的groupby |
| … |
三、实战操作
在理论章节中我们介绍到了ArrayList的一些功能,在本节中将展示对应的demo示例
3.1 创建ArrayList的方式
/** * @author csdn 暗余 * @date 2022-05-26 23:30 */ public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. new 关键字创建集合 List<String> strings = new ArrayList<>(); // 2. Lists创建集合 List<Integer> integers = Lists.newArrayList(); // 3. 创建不可变(不支持扩容)的集合 List<String> immutableStrings= ImmutableList.of("hello", "world!"); List<Integer> immutableIntegers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); List<Integer> list4 = Collections.nCopies(5, 1); // JDK9 才支持哦! List<Integer> list9 = List.of(1,2,3); // 4. 创建指定大小的集合, ps:你有兴趣了解他们之间的区别吗? List<String> strings10= Lists.newArrayListWithCapacity(10); List<String> strings20= Lists.newArrayListWithExpectedSize(20); // 5. 利用stream创建 List<Integer> streamList = Stream.of(1, 2, 3).collect(Collectors.toList()); // 6. 匿名内部类 List<Integer> anonymous= new ArrayList() {{ add(1); add(2); add(3); }}; // 还有一些可以通过其他方式转为List,就不具体描述啦! } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
3.2 常用增删查改
/** * @author csdn 暗余 * @date 2022-05-26 23:30 */ public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> strings = new ArrayList<>(); // 1. 新增 strings.add("hello"); strings.add(1,"world"); // [hello, world] System.out.println(strings); // 删除 strings.remove("hello"); // [world] System.out.println(strings); strings.remove(0); // [] System.out.println(strings); // 批量新增 strings.addAll(Lists.newArrayList("hello","world")); CollectionUtils.addAll(strings, ImmutableList.of("!")); // [hello, world, !] System.out.println(strings); // 查询 // hello System.out.println(strings.get(0)); // 查询指定位置元素 // 修改 strings.set(1,"CSDN暗余"); // [hello, CSDN暗余, !] System.out.println(strings); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
3.3 ArrayList与Stream结合的常用统计方法
/** * @author csdn 暗余 * @date 2022-05-26 23:30 */ public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = ImmutableList.of(1,2,3,4,5); long sum = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(integer -> integer)).getSum(); long count = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(integer -> integer)).getCount(); int max = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(integer -> integer)).getMax(); int min = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(integer -> integer)).getMin(); double average = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(integer -> integer)).getAverage(); // bigDecimal 求和 List<BigDecimal> bigDecimals = ImmutableList.of(BigDecimal.ONE, BigDecimal.TEN, BigDecimal.valueOf(5)); final BigDecimal bigDecimalSum= bigDecimals.stream().reduce(BigDecimal::add).orElse(BigDecimal.ZERO); // 15 System.err.println(sum); // 5 System.err.println(count); // 5 System.err.println(max); // 1 System.err.println(min); // 3.0 System.err.println(average); // 16 System.err.println(bigDecimalSum); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
3.4 ArrayList之排序
/** * @author csdn 暗余 * @date 2022-05-26 23:30 */ public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> sortList1 = Lists.newArrayList(1,9,3,2,8,2); Collections.sort(sortList1); // [1, 2, 2, 3, 8, 9] System.err.println(sortList1); List<Integer> sortList2= Lists.newArrayList(9, 7, 6, 54, 34, 4, 7, 1); sortList2.sort(Comparator.comparing(Integer::intValue)); // [1, 4, 6, 7, 7, 9, 34, 54] System.err.println(sortList2); List<Integer> sortList3 = Lists.newArrayList(3, 6, 45, 7, 2, 7, 8, 2, 65, 1); List<Integer> sortResult3= sortList3.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList()); // [1, 2, 2, 3, 6, 7, 7, 8, 45, 65] System.err.println(sortResult3); // 倒序排 List<Integer> sortDescResult3= sortList3.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Integer::intValue).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList()); // [65, 45, 8, 7, 7, 6, 3, 2, 2, 1] System.err.println(sortDescResult3); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
3.5 ArrayList之拆分集合、合并集合
/** * @author csdn 暗余 * @date 2022-05-26 23:30 */ public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = Lists.newArrayList(1, 9, 3, 2, 8, 2); // 将一个集合拆成每份三条数据,故上面集合会被拆成每三条为一个,总共为2个list: List<List<Integer>> partition = Lists.partition(list, 3); //[[1, 9, 3], [2, 8, 2]] System.err.println(partition); // 我们将两个集合合并起来 List<Integer> list1 = partition.get(0); List<Integer> list2 = partition.get(1); // 合并到集合1中 // list1.addAll(list2); // [1, 9, 3, 2, 8, 2] // System.err.println(list1); // 合并集合后需要做其他操作,我们可以使用stream流来进行合并操作 下面是合并结果后过滤掉小于等于1的数据: List<Integer> filterList= Stream.of(list1, list2).flatMap(Collection::stream) .filter(value -> value > 1) .collect(Collectors.toList()); //[9, 3, 2, 8, 2] System.err.println(filterList); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
3.6 ArrayList与其他容器之间的转换
/** * @author csdn 暗余 * @date 2022-05-26 23:30 */ public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Student student1 = new Student(); Student student2 = new Student(); student1.setName("zhangsan"); student1.setAge(18); student2.setName("暗余"); student2.setAge(27); // 将List集合转为Map是我们常用的转换 Map<String, Integer> map= ImmutableList.of(student1, student2).stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getName, Student::getAge)); Integer anYuAge = map.get("暗余"); // 27 System.err.println(anYuAge); // 将集合转为数组 List<Integer> integerList = ImmutableList.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); Integer[] integers = integerList.toArray(new Integer[0]); // 将集合转为字符串,这个我们也经常用到 String list2Str= integerList.stream().map(String::valueOf).collect(Collectors.joining(",")); // 1,2,3,4,5 System.err.println(list2Str); // 谷歌集合转字符串 String list2StrByGoogle = Joiner.on(",").join(integers); // 1,2,3,4,5 System.err.println(list2StrByGoogle ); // 集合转set Set<Integer> set= new HashSet<>(integerList); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] System.err.println(set); Set<Integer> set2= integerList.stream().filter(value -> value > 1).collect(Collectors.toSet()); // [2, 3, 4, 5] System.err.println(set2); } public static class Student { private String name; private Integer age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } Integer getAge() { return age; } void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
集合与流的配合十分紧密。我们可以通过Stream流对集合完成我们需要的许多业务逻辑操作!更多关于Stream流的讲解,我将在后面的章节为你介绍;
四、扩展阅读
4.1 手写一个简单版的ArrayList:
public class SequenceList<T>{ // 存储元素的数组 private T[] eles; // 记录当前顺序表中的元素个数 private int N; // 构造方法 public SequenceList(int capacity){ // 初始化数组 this.elses = (T[])new Object[capacity]; this.N =0; } // 将一个线性表置为空表 public void clear(){ this.N = 0; } // 判断当前线性表是否为空表 public boolean isEmpty(){ return N == 0; } // 获取线性表的长度 public int length(){ return N; } // 获取指定位置的元素 public T get(int i){ return eles[i]; } // 向线性表中添加元素t public void insert(T t){ eles[N++]=t; } // 在i元素处插入元素t public void insert(int i, T t){ // 先把i索引处的元素及其后面的元素依次向后移动一位 for(int index = N-1; index > i; index --){ eles[index] = eles[index -1]; } // 再把t元素放到i索引处即可 eles[i] = t; // 元素个数+1 N++; } // 删除指定位置i处的元素,并返回该元素 public T remove(int i){ // 记录索引i处的值 T current = eles[i]; // 索引i后面元素依次向前移动一位即可 for(int index = i; index < N-1; index ++){ eles[index] = eles[index + 1]; } // 元素个数 -1 N --; return current; } // 查找t元素第一次出现的位置 public int indexOf(T t){ for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){ if(eles[i].equals(t)){ return i; } } return -1; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
4.2 从源码分析ArrayList的新增扩容机制
add方法有两个,分别是在指定的索引处add,一个是默认在最后面add。
- 默认的不带索引的add方法执行逻辑
- 这里是整体的逻辑,分为扩容检查、赋值、返回成功三个部分;
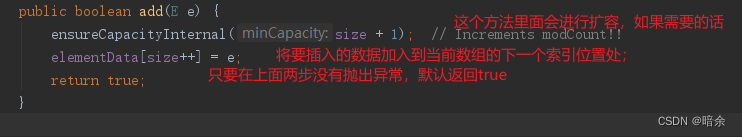
- 判断当前集合是否是空集合,如果是的话,则要在DEFAULT_CAPACITY与minCapacity之间求出一个最大值;
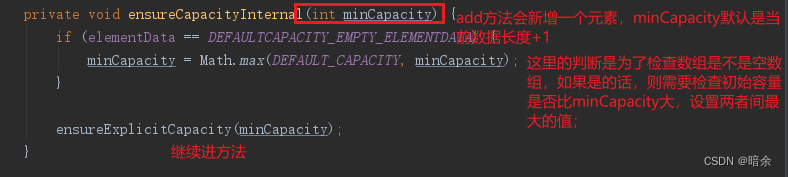
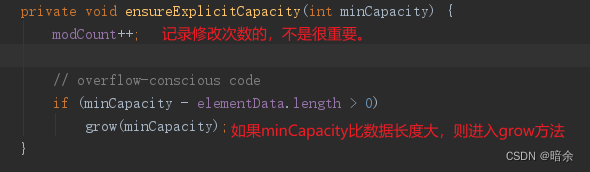
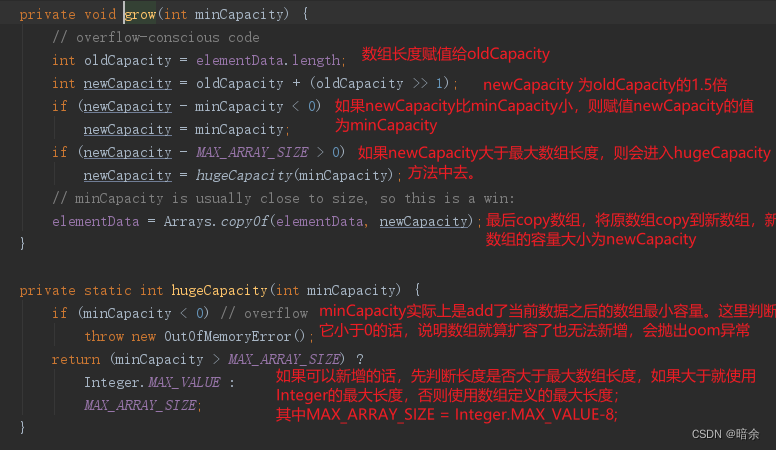
- 这里是整体的逻辑,分为扩容检查、赋值、返回成功三个部分;
- 带索引的add新增方法:
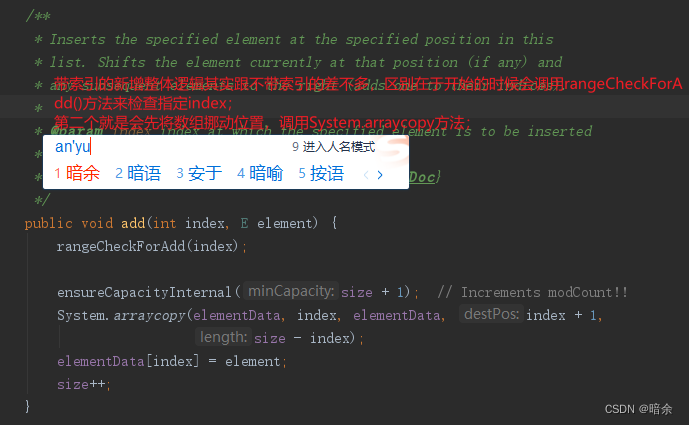
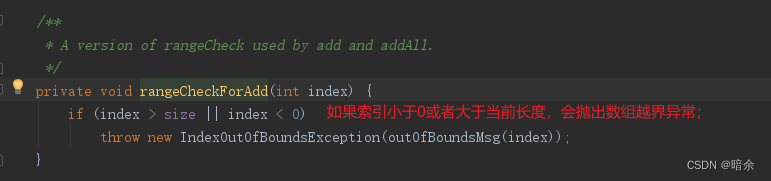
默认的add方法是直接在尾部新增,所以不需要挪动位置,而按照指定索引新增需要将指定位置的数组往后挪一位,这也是为什么数组新增修改常常比LinkedList性能差的原因;
4.3 ArrayList与其他集合类的对比
| 对比项 | Vector | ArrayList | LinkedList | HashSet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 是否线程安全 | 线程安全 | 线程不安全 | 线程不安全 | 线程不安全 |
| 数据结构 | 数组 | 数组 | 链表 | 由HashMap封装,故为数组+链表 |
| 特点 | 不建议使用 | 随机查询多、增删少、对存入数据有顺序要求的场景 | 增删多,随机查询少,对插入数据数量未知的场景 | 不要求存入顺序、元素不重复的场景 |
| 扩容机制 | 拷贝扩容 | 拷贝扩容 | 不需要扩容,新数据直接链接到节点最后 | 参照HashMap扩容机制 |
4.4 如何根据实际选择List集合?
- 根据上面的对比我们可以知道每个List集合实现类都有一些各自的特点,需要咱们根据实际的业务场景去选用;
- 如果是要求元素唯一,使用Set里面的一些实现类可以很好的满足要求,比如HashSet。如果同时需要排序,可以考虑使用TreeSet;
- 如果要求查询效率很快且不唯一,使用List里面的一些实现类可以很好的满足要求,比如ArrayList。ArrayList的优势在于随机查询非常快,但缺点是扩容会耗费性能;故如果存在频繁增删我们也可以选用LinkedList;
4.5 看透ArrayList的本质
- 首先经过我们手写的ArrayList,能够清楚它的底层是数组;我们做的一系列增删查改操作实际上就是对数组进行操作;故ArrayList的优缺点可以宽泛的与数组的优缺点联系起来;因为数组不支持扩容,所以ArrayList的扩容才会需要进行数组拷贝;而LinkedList不需要扩容是因为它底层是链表;
- 链表和顺序表(数组)是都是线性表的子集,故它们是连续的存储元素,所以为什么ArrayList能够元素的先后顺序而Set不能;
- 对List 进行增强、功能增多,能够形成各种不同种类的集合。我们根据它们的优缺点适配到什么样的业务场景中,决不能一个ArrayList走天下!
- 为什么我们日常中不使用数组而是ArrayList呢?首先,ArrayList在数组基础上进行了增强,具备自动扩容等特性,开发效率上更好。其次,我们的机器性能日益提高,使用ArrayList比直接使用数组带来的收益大于损失。但是如果你是在开发一些公共框架、底层应用、或者对性能要求很高的场景,那么你可以试试使用数组来实现。
五、面试锦题
- ArrayList初始化时Object数组的长度是多少呢?
- 初始化时,数组为空;只有当第一次插入的时候会新建一个默认长度为10的数组;
- ArrayList与LinkedList的区别?
- 可以参照我们上一节中的
各集合对比;
- 可以参照我们上一节中的
- ArrayList是线程不安全的,为什么还用?
- 我们一般业务场景是线程安全的环境,每个线程的数据是独立的;如果涉及到线程不安全的场景,可以对应切换合适的集合;
- ArrayList与LinkedList相比遍历性能怎样?
- ArrayList > LinkedList,因为它的内存空间是连续的,同时CPU有查询优化;
- 为什么ArrayList 的新增或者删除效率很低呢?
- 当遇到扩容操作的时候,效率会比较低。因为它会涉及到执行arraycopy的操作;删除的时候如果在中间或者前面,会导致后面的数据往前挪动,所以越靠前效率越低;
- ArrayList的扩容机制是什么样的?
- 首先不能无限扩容,最大长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE;
- 其次正常扩容时每次1.5倍大小;如果不能满足minCapacity要求,就会按照minCapacity继续扩容;
- 最后在扩容之后将数据复制到新数组,使用Arrays.copyof();
本篇总结
- 在开篇导言中,我们了解了
ArrayLis的重要性; - 在理论知识中我们学习了ArrayList的一些知识:
- ArrayList的类继承关系
- ArrayList的一些特点
- ArrayList与LinkedList的区别
- ArrayList在实际业务中常常会用到的功能;
- 我们在实战操作中,对实际业务常用功能进行了Demo 演示,比如常用的增删查改、统计方法、排序、拆分、归并、转为Map等示例;
- 也在扩展阅读中进行了手写ArrayList简单版的代码演示;
- 最后在面试锦题环节讲述了一些常考的ArrayList集合知识点;ArrayList与LinkedList的对比、扩容机制是常考点。
最后,也请我介绍一下自己,我是暗余,感谢你能够看完;咱们下期再见!
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/笔触狂放9/article/detail/321941
推荐阅读
相关标签



