- 1Android初始化系统语言为简体中文
- 2C# 操作IIS方法集合
- 3mysql数据库备份学习笔记
- 4mac.cornerstone+svn+androidstudio_conerstone切换分支
- 5软考网络工程师 第五章 第六节 WLAN安全
- 6gradle配置阿里云镜像_grable配置阿里云镜像
- 7OpenVINO™ Java API 应用RT-DETR做目标检测器实战
- 8com.google.gson.JsonSyntaxException: java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: ““
- 9python使用结巴分词(jieba)创建自己的词典/词库_jieba.load_userdict(file_name)
- 10分数排名_id为此表的上键,name为学生名,score为分数请根据分数统计排名ranks,分数相同排名
C++文件操作(超详细!!!简单快速上手)_c++代码创建文件
赞
踩
文件操作
读文件:把磁盘文件中的数据转移到内存中。 -------ofstream类
写文件:把内存中的数据转移到磁盘文件中。 --------ifstream类
读+写 ---------fstream类
一、写文本文件
写文件的四个步骤:
1、创建文件输出流对象
2、打开文件
3、向文件中写入数据
4、关闭文件
代码:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream> //文件操作类需要包含的头文件
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
-
- //STEP 1
- ofstream fout; //创建文件输出流对象
-
- //STEP 2
- fout.open("test.txt"); //打开文件,如果文件不存在,则创建它;如果文件已存在,则截断其内容
-
- //STEP 3
- fout << "hello 1\n"; //向文件中写入数据
- fout << "hello 2\n";
- fout << "hello 3\n";
-
- //STEP 4
- fout.close(); //关闭文件,fout对象失效前会自动调用close()
-
- cout << "写文件操作完成!\n";
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }

效果:

文件自动创建在项目文件下,一般自定义文件路径:
- string filename = "D:\\test.txt";
- fout.open(filename);
文件名一般用全路径,书写方法如下:
1)"D:\test.txt" //错误
2)R"(D:\test.txt)" //原始字面量,C++11标准
3)"D:\\test.txt" //转义字符
4)"D:/test.txt" //把斜线反着写
5)"/test.txt" //Linux系统采用的方法
STEP2也可以隐藏,在STEP1中,将原代码写为:
- //STEP1
- ofstream fout(filename);
-
- /*
- //STEP2
- ....
- */
可以支持创建打开文件。
输出流打开文件的模式:
ios::out 缺省值:会截断文件内容
ios::trunc 截断文件内容
ios::app 不截断文件内容,只在文件末尾追加文件
ios::binary 以二进制方式打开文件
其中,默认值(不填=out=trunc),会直接覆盖原文件内容(if 有)。
代码实例(以app模式为例):
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream> //文件操作类需要包含的头文件
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
- //
- string filename = "D:\\test.txt";
-
- /*
- 打开文件的模式:
- ios::out 缺省值:会截断文件内容
- ios::trunc 截断文件内容
- ios::app 不截断文件内容,只在文件末尾追加文件
- */
-
- //STEP 1
- ofstream fout(filename,ios::app); //创建文件输出流对象
-
- //STEP 2
- //fout.open(filename); //打开文件,如果文件不存在,则创建它;如果文件已存在,则截断其内容
-
- //STEP 3
- fout << "hello 1\n"; //向文件中写入数据
- fout << "hello 2\n";
- fout << "hello 3\n";
- //STEP 4
- fout.close(); //关闭文件,fout对象失效前会自动调用close()
-
- cout << "写文件操作完成!\n";
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }

运行两次,效果:
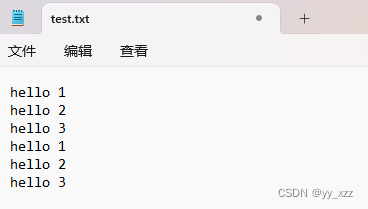
在实际开发中,STEP3 紧着STEP2是不理智的,因为打开文件不一定成功。
需要加上一行代码判断:
- if (fout.is_open() == false) {
- cout << "打开文件失败\n";
- return 0;
- }
失败的原因主要有三种:
1、目录不存在
2、磁盘空间已满
3、没有权限,Linux平台下很常见
二、读取文本文件
读文件的四个步骤:
1、创建文件输入流对象
2、打开文件
3、向文件中读取数据
4、关闭文件
代码:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream> //文件操作类需要包含的头文件
- #include <string>
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
- string filename = "D:\\test.txt";
-
- /*
- 输入流打开文件的模式:
- ios::in 缺省值
- */
-
- //STEP 1
- ifstream fin(filename,ios::in); //创建文件输入流对象
-
- if (fin.is_open() == false) {
- cout << "打开文件失败\n";
- return 0;
- }
-
- //STEP 3
- /*
- 读取文件内容的代码
- 文本文件一般以行的方式组织读取。-->getline()函数 (需要包含头文件 #include <string>)
- */
- string buffer; //用于存放从文件中读取的内容
- while (getline(fin, buffer)) { //从文本中读取一行数据存到buffer中,可使用循环读取全部数据,文件结束时getline()返回空
- cout << buffer << endl;
- }
-
- //STEP 4
- fin.close(); //关闭文件,fin对象失效前会自动调用close()
-
- cout << "读文件操作完成!\n";
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }

以上是读取文件的第一种方法,下面介绍第二种方法,可以直接修改STEP3的部分,
- //STEP 3
- /*
- 读取文件内容的代码
- 文本文件一般以行的方式组织读取。-->getline()函数 (需要包含头文件 #include <string>)
- */
- // 第一种方法
- //string buffer; //用于存放从文件中读取的内容
- //while (getline(fin, buffer)) { //从文本中读取一行数据存到buffer中,可使用循环读取全部数据,文件结束时getline()返回空
- // cout << buffer << endl;
- //}
- // 第二种方法
- char buffer[101]; //存放从文件中读取的内容
- //注意:如果使用ifstream.getline(),一定要保证缓冲区足够大。
- while (fin.getline(buffer, 100)) {
- cout << buffer << endl;
- }

注意:如果使用ifstream.getline(),一定要保证缓冲区足够大。
下面介绍第三种方法,推荐使用!
- //STEP 3
- /*
- 读取文件内容的代码
- 文本文件一般以行的方式组织读取。-->getline()函数 (需要包含头文件 #include <string>)
- */
- // 第一种方法
- //string buffer; //用于存放从文件中读取的内容
- //while (getline(fin, buffer)) { //从文本中读取一行数据存到buffer中,可使用循环读取全部数据,文件结束时getline()返回空
- // cout << buffer << endl;
- //}
- // 第二种方法
- //char buffer[101]; //存放从文件中读取的内容
- 注意:如果使用ifstream.getline(),一定要保证缓冲区足够大。
- //while (fin.getline(buffer, 100)) {
- // cout << buffer << endl;
- //}
- //第三种方法
- string buffer;
- while (fin >> buffer) {
- cout << buffer << endl;
- }

三、写二进制文件
雷同于写文本文件,代码如下:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream> //文件操作类需要包含的头文件
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
- string filename = "D:\\test.dat";
-
- /*
- 打开文件的模式:
- ios::binary 以二进制方式打开文件
- */
-
- //STEP 1
- ofstream fout(filename, ios::app | ios::binary); //创建文件输出流对象 追加+二进制打开
-
- if (fout.is_open() == false) {
- cout << "打开文件失败\n";
- return 0;
- }
-
- //自定义一个结构体
- struct Student {
- char name[20];
- int age;
- double weight;
- }yyxzz;
- yyxzz = { "yyxzz",25,140.5 };
- //STEP 3
- //向文件中写入数据
- fout.write((const char*)&yyxzz, sizeof(Student));
-
- //STEP 4
- fout.close(); //关闭文件,fout对象失效前会自动调用close()
-
- cout << "写文件操作完成!\n";
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }

主要注意点,1、打开文件时要用二进制打开方式
2、写入时要用write()方法
四、读二进制文件
读二进制文件需要知道二进制的格式,以上述写二进制文件代码为例,读二进制文件代码如下:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream> //文件操作类需要包含的头文件
-
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
- string filename = "D:\\test.dat";
-
- /*
- 输入流打开文件的模式:
- ios::in 缺省值
- ios::binary 二进制方式
- */
-
- //STEP 1
- ifstream fin(filename, ios::in| ios::binary); //创建文件输入流对象
-
- if (fin.is_open() == false) {
- cout << "打开文件失败\n";
- return 0;
- }
-
- //STEP 3
- //二进制文件以数据块(数据类型)的形式组织数据
- struct Student {
- char name[20];
- int age;
- double weight;
- }yyxzz; //需知道二进制格式
- while (fin.read((char*)&yyxzz, sizeof(yyxzz))) {
- cout << yyxzz.name << " " << yyxzz.age << " " << yyxzz.weight << endl;
- }
-
- //STEP 4
- fin.close(); //关闭文件,fin对象失效前会自动调用close()
-
- cout << "读文件操作完成!\n";
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }

五、fstream类的使用
fstream可以用于读,也可以用于写,上述代码中,将对应的ifstream或ofstream替换为fstream即可,但是这种写法是C语言的写法,且目的不明确,开放的权限过多,所以尽量不要用。
六、文件的位置指针
1、获取文件的位置指针
ofstream类的成员函数是tellp();
ifstream类的成员函数是tellg();
fstream类两个都有,效果相同。
代码演示,以写入文件为例:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream>
- using namespace std;
- int main()
- {
-
- //STEP 1
- ofstream fout;
- //STEP 2
- fout.open("D:\\test.txt",ios::out);
- //STEP 3
- cout << fout.tellp() << endl; 打印位置指针
- fout << "hello 1\n"; 向文件中写入数据
- cout << fout.tellp() << endl;
- fout << "hello 12\n";
- cout << fout.tellp() << endl;
- fout << "hello 123\n";
- cout << fout.tellp() << endl;
-
- //STEP 4
- fout.close();
- cout << "写文件操作完成!\n";
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }

效果展示:
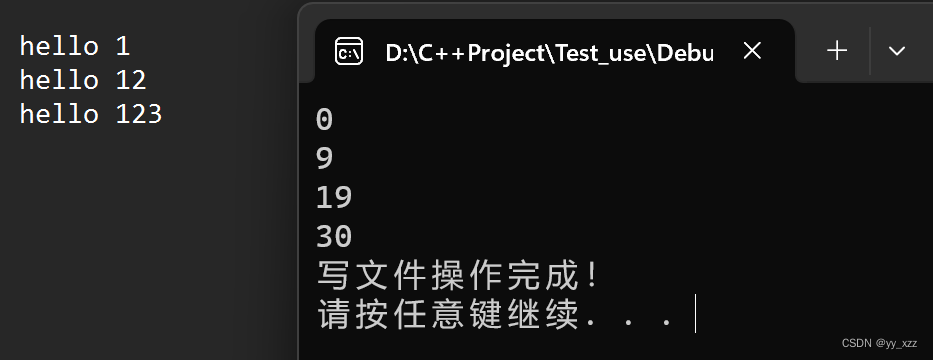
2、移动文件位置指针
ofstream类的函数是seekp();
ifstream类的函数是seekg();
fstream类两个都有,效果相同。
方法一:
- std::istream& seekg(std::streampos_Pos);
-
-
- fin.seekg(128); 把文件指针移动到第128字节
- fin.seekp(128);
-
- fin.seekg(ios::beg); 把文件指针移动到文件的开始
- fin.seekp(ios::beg);
-
- fin.seekg(ios::end); 把文件指针移动到文件的结尾
- fin.seekp(ios::end);
方法二:
- std::istream& seekg(std::streamoff_Off,std::ios::seekdir_Way);
-
-
- 在ios中定义的枚举类型:eum seek_dir{beg,cur,end};
- beg----文件的起始位置 cur----文件的当前位置 end----文件的结尾位置
-
-
-
- fin.seekg(30,ios::beg); 从文件的开始位置往后移30字节
- fin.seekg(-5,ios::cur); 从文件的当前位置往前移5字节
- fin.seekg(-10,ios::end); 从文件的结尾位置往前移10字节
注意换行在文件中为\r\n,写入后可能会导致文件换行消失,例如:



