- 1AWS RDS启用自动备份_aws rds备份
- 2项目管理模板_2021年会策划,用项目管理思维搞定!(附28个配套模板)
- 3Python 使用 WeChatFerry 搭建部署微信机器人详细教程(更新中)
- 4JDBC——详解注册驱动_在哪里修改jdbc的注册驱动
- 5PHP实现SM2算法(附完整源码)_php sm2
- 6c语言编程实现rm调度算法,浅析rm与edf实时调度算法.docx
- 7GIT常用操作整理(从本地创建仓库到提交到GitHub全流程)学习笔记_git新建一个仓库
- 8亚马逊云与生成式 AI 的融合:未来展望与综述_亚马逊生成式ai
- 9基于第三方开源框架xxl-sso单点登录的实现
- 10使用Spring Retry实现重试机制
ElasticSearch(ES)详解(一)_elasticsearch es
赞
踩
前言
众所周知,ElasticSearch是一个智能搜索,分布式的搜索引擎,下面就来简单的介绍一下。
一、Why ElasticSearch?
正如百度、电商的兴起,对于数据的搜索需求越来越大,基于Lucene开发的ElasticSearch搜索引擎顺势崛起。
1.Why not Mysql
为什么不用数据库去实现搜索功能?肯定很多人会这样问。关系型数据库如Mysql是很常用的基础数据库,它的事务操作给数据的安全性上是其他数据库很难超越的,面对目前多样的查询搜索上,他却体现出了局限性。
如下图,当我们要查询保利的物业,查询语句肯定是select * from xx where xx like ‘%保利%’,而mysql对于模糊查询使用的是全表扫描假设有1亿条数据可以想象一次查询的消耗是非常巨大的。
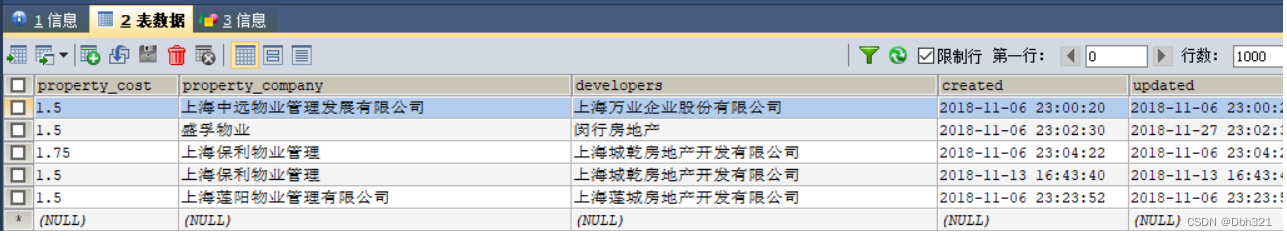
这里肯定很多人说利用索引,没错索引对于搜索的提升是非常大的,但是mysql的索引也有他的弊端:
1.mysql的索引是B+树的数据结构,若对于每列都加索引,对于存储的消耗是非常巨大的;
2.mysql利用多个索引字段进行组合查询时,只会利用一个索引查询,其他条件仍然是全文扫描。
2.倒排索引
ES的解决方案是利用倒排索引的方式,来提升查询效率,下面对倒排索引做一个介绍:
现在让我们想一首包含“前”字的诗文,肯定很难,但是让我们背一下《静夜思》,肯定能朗朗上口,而我们这种思维方式《静夜思》->床前明夜光,就是正向索引,根据诗歌标题记忆诗歌内容。反向索引简单点理解就是将内容(比如“窗前明月光”)进行分解成索引(比如“前”),而当检索包含“前”的诗句时,就想起内容,如下图。
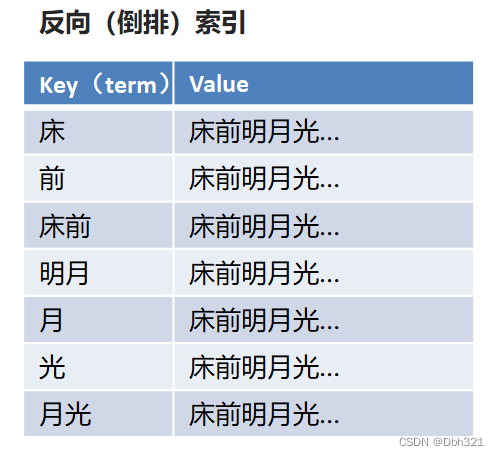
但是如果这样直接存诗句太占空间,可以将索引对应的连接为内容的唯一标识(比如诗歌名)
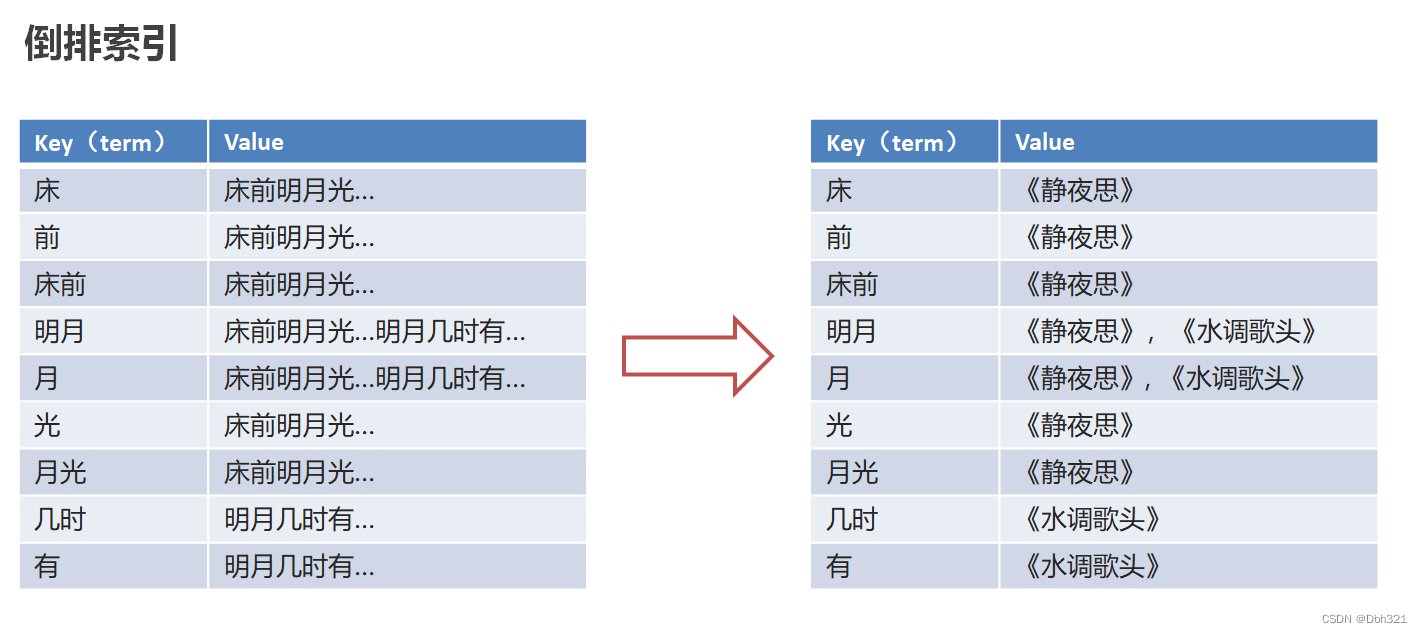
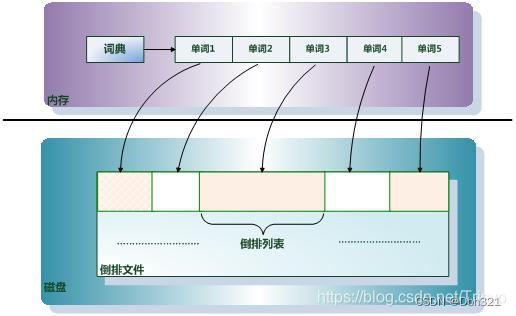
这便是倒排索引,这里肯定很多疑问,这样基于全文检索的倒排索引,相对于B+树岂不是更占空间,因此ES针对倒排索引的存储采用内存加磁盘的形式,将索引项(拆分的单词)放在内存,每个索引项(单词)指向一个倒排列表(里面存储包含单词的文档id以及单词在文档中出现的位置),而倒排列表通过倒排文件存储在磁盘中。当仍然过大可以采取分布式存储(后续写入)。
二、ElasticSearch简介
ES正是靠其独特的索引方式,实现了快速检索功能。下面对ES的组成和数据类型进行介绍。
1.核心部件
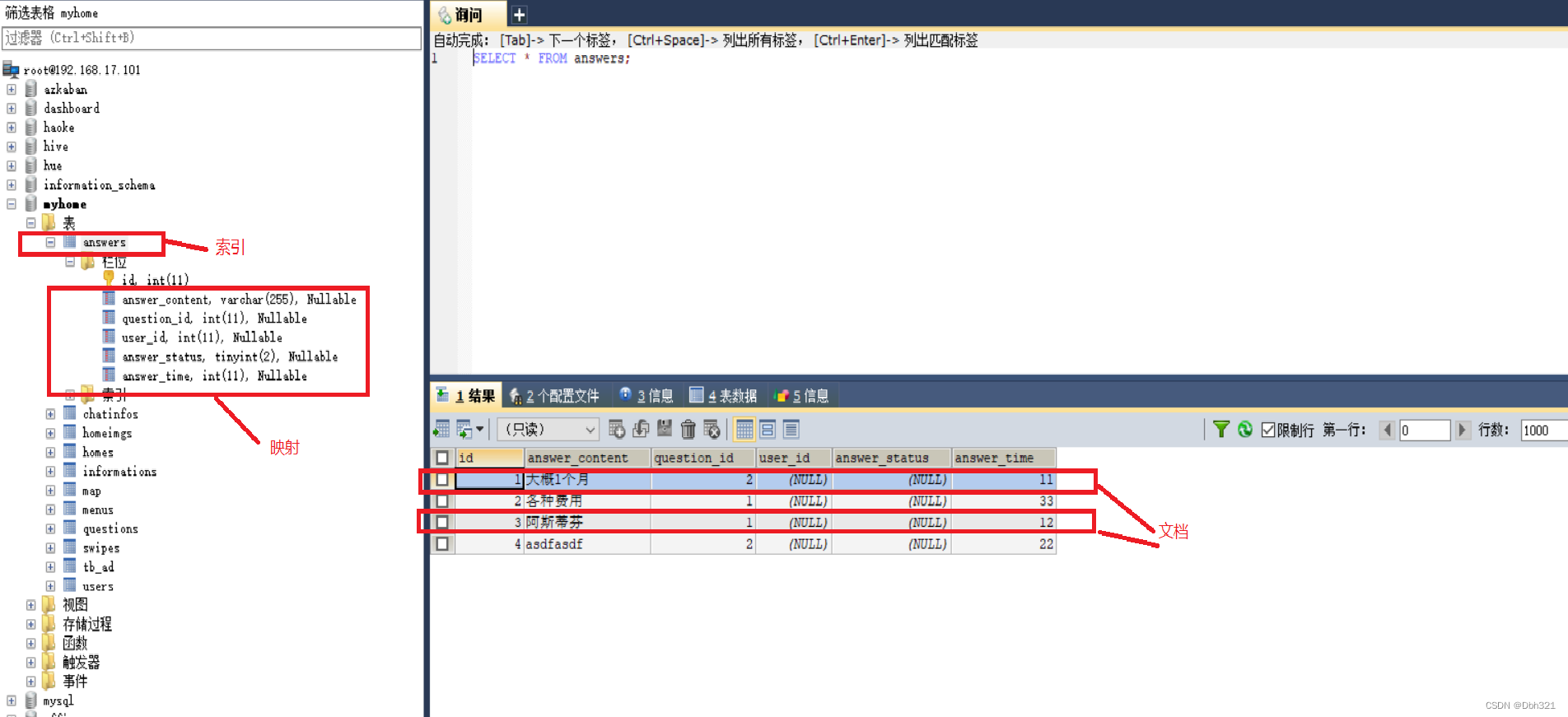
(1)索引(index)
不同于传统意义上的的索引,ES的索引为其存放数据的地方,类似于Mysql中的数据库。
(2)映射(mapping)
mapping定义了每个字段的类型、字段所使用的分词器等,用来描述索引的数据结构的,相当于Mysql中的表结构。
(3)文档(document)
就是存储的最终数据,是ES里面最小的数据单元,就好比Mysql表里面的一条数据。
(4)字段(field)
一个document有一个或者多个field组成,好比Mysql中列的概念。
2.数据类型
ES根据document中每个字段的数据类型来建立不同数据结构的索引,比如text类型建立倒排索引。ES数据类型可大致分为简单数据类型和复杂数据类型。
(1)简单数据类型
- 字符串
text:会分词,不支持聚合
keyword:不会分词,将全部内容作为一个词条,支持聚合(聚合:相当于mysql 中的sum(求和))
- 1
- 2
- 3
-
数值
-
布尔:boolean
-
二进制:binary
-
范围类型
integer_range, float_range, long_range, double_range, date_range
- 1
- 日期:date
(2)复杂数据类型
•数组:[ ] Nested: nested (for arrays of JSON objects 数组类型的JSON对象)
•对象:{ } Object: object(for single JSON objects 单个JSON对象)
3.ES安装
ES及插件安装参照下面链接Elasticsearch 安装详细步骤(保姆级安装)
三、ElasticSearch基本操作
ES基于RESTful风格的网络接口操作。因此可以使用PostMan等网络工具操作,也可以使用kibana控制台操作,这里主要介绍使用kibana控制台操作。
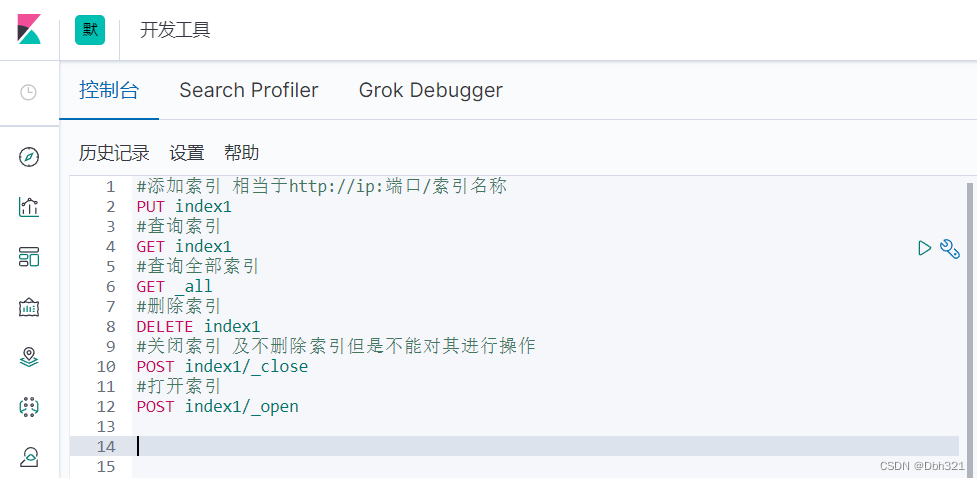
1.索引操作
2.映射操作
#新建映射 对已有索引添加 PUT index1/_mapping { "properties":{ "name":{ "type":"keyword" }, "age":{ "type":"integer" }, "address":{ "type":"text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" } } } #新建映射 创建索引时设置映射 PUT index2 { "mappings": { "properties": { "name":{ "type":"keyword" }, "age":{ "type":"integer" }, "address":{ "type":"text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" } } } } #添加字段 对已有映射添加项 POST index2/_mapping { "properties":{ "hobby":{ "type":"text", "analyzer":"ik_max_word" } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
这里特别说明,ES有一种情况会自己添加字段,在录入文档时,发现mapping中没有相应的字段,这里就会根据录入的数据,自己判断字段类型并给mapping新增该字段。
3.分词器
正如前面所讲,ES在text类型的字段存入时,会对该字段进行分词,并将分的词存入索引,分词器也就是干这个事的,但是在ES默认的分词器中对中文的兼容性很差,只能将中文分成单个字,所以需要自己下载第三方兼容中文的分词器IK分词器。
(1)分词器操作
GET _analyze { "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "text": "我们爱打乒乓球" } #返回消息 { "tokens" : [ { "token" : "我们", "start_offset" : 0, "end_offset" : 2, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 0 }, { "token" : "爱打", "start_offset" : 2, "end_offset" : 4, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 1 }, { "token" : "打乒乓球", "start_offset" : 3, "end_offset" : 7, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 2 }, { "token" : "乒乓球", "start_offset" : 4, "end_offset" : 7, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 3 }, { "token" : "乒乓", "start_offset" : 4, "end_offset" : 6, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 4 }, { "token" : "球", "start_offset" : 6, "end_offset" : 7, "type" : "CN_CHAR", "position" : 5 } ] }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
同时在mapping设定中,在指定字段类型的时候也可设置该字段的分词器
POST index2/_mapping
{
"properties":{
"hobby":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word" #分词器
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
(2)IK分词器下载及简介
参照链接(链接是在windows环境下部署,linux系统同理):ElasticSearch 入门(四)安装IK分析器
4.文档操作
在了解了分词器的概念后,我们看一下ES对文档的操作
#新建文档 自定义id PUT index1/_doc/1 { "name":"张三", "age":12, "address":"北京海淀区" } #新建文档 系统自建id POST index1/_doc { "name":"李四", "age":15, "address":"上海浦东区" } #删除文档 DELETE index1/_doc/1 #修改文档 同新建文档, 当id存在时及为修改 PUT index1/_doc/1 { "name":"张三", "age":14, "address":"北京海淀区" } #查询文档 #查看索引下全部文档 GET index1/_search #按词条查询 及查询的内容不会进行分词 GET index1/_search { "query": { "term": { "address": { "value": "海淀" } } } } } #按全文查询 全文查询会分析查询条件,先将查询条件进行分词,然后查询,求并集 GET index1/_search { "query": { "match": { "address": "北京海淀" } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
这里的操作指令其实是kibana进行了简化,可以看到ES的操作有规律可言的,按照Restful风格,通常put操作为添加操作,Post为修改,get为查询,delete为删除。
四、JAVA API
1.导入maven依赖
<!--引入es的坐标--> <dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId> <version>7.4.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId> <version>7.4.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId> <version>7.4.0</version> </dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2.创建RestHighLevelClient客服端对象
@BeforeAll
public void before() {
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(
RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost(
"192.168.17.101",//ES主机ip
9200 ,//端口号
"http"//传递协议
)));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3.操作ES
package com.db123; import com.dbh123.ElasticSearchDemoApp; import org.apache.http.HttpHost; import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.delete.DeleteIndexRequest; import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteRequest; import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteResponse; import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetRequest; import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse; import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest; import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse; import org.elasticsearch.action.support.master.AcknowledgedResponse; import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest; import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexResponse; import org.elasticsearch.client.IndicesClient; import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions; import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient; import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient; import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexRequest; import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexResponse; import org.elasticsearch.cluster.metadata.MappingMetaData; import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType; import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * @description: * @author: DBH123 * @date: 2022/6/27 23:09 */ @SpringBootTest(classes = ElasticSearchDemoApp.class) public class ElasticSearchTest { private static RestHighLevelClient client; @BeforeAll public static void before() { client = new RestHighLevelClient( RestClient.builder( new HttpHost("node1" , 9200 , "http") ) ); } /** * @Description 添加索引 * @Author: DBH123 * @Date: 2022/6/28 16:39 * @Params: * @Return: **/ @Test public void addIndex() throws IOException { // 1.使用client获取操作索引对象 IndicesClient indices = client.indices(); // 2.具体操作获取返回值 // 2.1 设置索引名 CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("student"); // 2.2 创建索引 CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = indices.create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); // 3.输出返回值 System.out.println(createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged()); } /** * @Description 添加索引并添加映射 * @Author: DBH123 * @Date: 2022/6/28 16:49 * @Params: * @Return: **/ @Test public void addIndexAndMapping() throws IOException { //1.使用client获取操作索引对象 IndicesClient indices = client.indices(); //2.具体操作获取返回值 //2.具体操作,获取返回值 CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("student1"); //2.1 设置mappings String mapping = "{\n" + " \"properties\" : {\n" + " \"address\" : {\n" + " \"type\" : \"text\",\n" + " \"analyzer\" : \"ik_max_word\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"age\" : {\n" + " \"type\" : \"long\"\n" + " },\n" + " \"name\" : {\n" + " \"type\" : \"keyword\"\n" + " }\n" + " }\n" + " }"; createIndexRequest.mapping(mapping, XContentType.JSON); CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = indices.create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); //3.根据返回值判断结果 System.out.println(createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged()); } /** * @Description 查询索引 * @Author: DBH123 * @Date: 2022/6/28 17:16 * @Params: * @Return: **/ @Test public void queryIndex() throws IOException { IndicesClient indices = client.indices(); GetIndexRequest getIndexRequest = new GetIndexRequest("student1"); GetIndexResponse getIndexResponse = indices.get(getIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); //获取结果 Map<String, MappingMetaData> mappings = getIndexResponse.getMappings(); for (String key : mappings.keySet()) { System.out.println(key+":" + mappings.get(key).getSourceAsMap()); } } /** * @Description 删除索引 * @Author: DBH123 * @Date: 2022/6/28 17:19 * @Params: [] * @Return: void **/ @Test public void deleteIndex() throws IOException { IndicesClient indices = client.indices(); DeleteIndexRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteIndexRequest("student"); AcknowledgedResponse response = indices.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(response.isAcknowledged()); } /** * @Description 判断索引是否存在 * @Author: DBH123 * @Date: 2022/6/28 17:19 * @Params: [] * @Return: void **/ @Test public void existIndex() throws IOException { IndicesClient indices = client.indices(); GetIndexRequest getRequest = new GetIndexRequest("student1"); boolean exists = indices.exists(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(exists); } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /** * @Description 添加文档,使用map作为数据 * @Author: DBH123 * @Date: 2022/6/28 17:20 * @Params: [] * @Return: void **/ @Test public void addDoc() throws IOException { //数据对象,map Map data = new HashMap(); data.put("address","重庆渝北"); data.put("name","张三"); data.put("age",20); //1.获取操作文档的对象 IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("student1").id("1").source(data); //添加数据,获取结果 IndexResponse response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); //打印响应结果 System.out.println(response.getId()); } /** * @Description 修改文档:添加文档时,如果id存在则修改,id不存在则添加 * @Author: DBH123 * @Date: 2022/6/28 17:21 * @Params: [] * @Return: void **/ @Test public void updateDoc() throws IOException { } /** * 根据id查询文档 */ @Test public void findDocById() throws IOException { GetRequest getReqeust = new GetRequest("student1","1"); //getReqeust.id("1"); GetResponse response = client.get(getReqeust, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); //获取数据对应的json System.out.println(response.getSourceAsString()); } /** * 根据id删除文档 */ @Test public void delDoc() throws IOException { DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("student1","1"); DeleteResponse response = client.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(response.getId()); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246




