- 1配置conda镜像源
- 22019年下半年1+X 证书 Web 前端开发初级理论考试题目原题+答案(超详细分析)_设置文字的大小为14,行高28,颜色为红色
- 3python清除typora垃圾图片_python去除typora未使用的图片
- 4动态规划(Dynamic Programming)理论篇_等价动态规划
- 5Kafka入门到精通(二)-安装Zookeeper
- 6Pycharm结合Git、GitHub配置与其常用操作_git access token pycharm
- 7Kali MSF攻击Win10_kali攻击win10
- 8【Python合集】我见过最有趣好玩强大的代码都在这里,涨见识啦~建议收藏起来慢慢学。(墙裂推荐)_好玩的python代码
- 9【打工日常】使用docker部署在线PDF工具_stirling-pdf
- 10Spark启动_authentication disabled; ui acls disabled; users w
Java数据结构——哈希表_java中哈希表
赞
踩
一.概念
哈希散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表
二. HashMap类
1. 概述
HashMap是基于哈希表的Map接口实现,属于双列集合的一种,其存储数据的特点是无序,不重复,无索引
2. 特有方法
HashMap的方法与Map基本一致\n\ngetOrDefault( key,默认值)\n\n判断哈希表中是否存在key,若存在则返回key的value值,不存在则返回默认值\n\n这个方法可厉害了,在力扣的部分解题中很有帮助\n\n如:如何让哈希表中的一个键key对应多个值\n\n首先我们肯定会想到值用链表结构类型,在每次找键插值时,我们要先获取key的链表,再将value插入链表中,最后再用put覆盖将链表再次插入到key中
三. HashMap代码实现
⑴底层基本原理
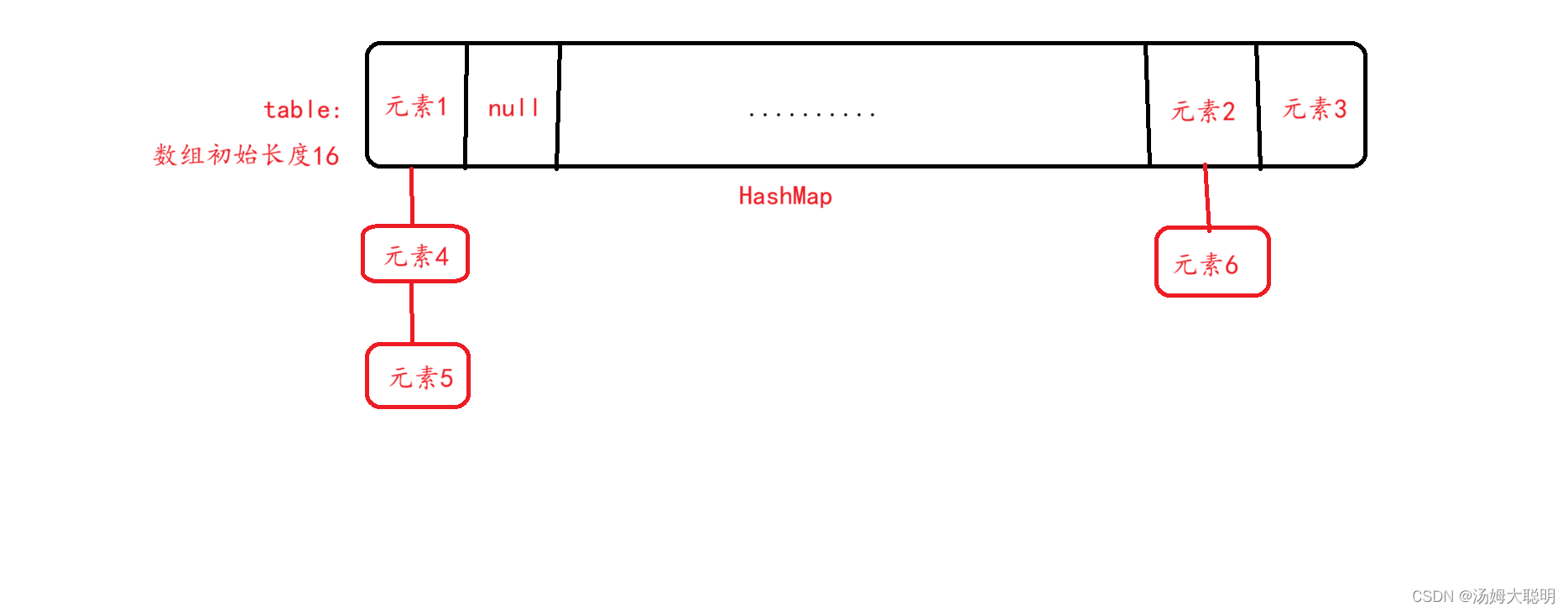
在JDK8以前,哈希表的底层结构是数组+链表,JDK8以后,为了优化性能,又加入了红黑树,当数组长度超过64且链表长度大于等于8,链表会优化为红黑树
下面我们主要来了解最初的底层结构原理
1.首先数组中存储的是键值对对象Entry
2.在创建哈希表时,会默认创建一个长度为16,加载因子为0.75的数组table
3.添加元素时,底层会根据键的哈希值与数组长度的关系计算出应插入的数组位置,若哈希值冲突,会将新元素以链表的形式添加到冲突位置的后面
⑵代码实现
知道了哈希表的基本底层原理,下面我们就来实现HashMap中最基本的操作
1.键值对对象Entry
首先键值对对象一定要有键key和值value以及用来计算存入位置的哈希码hash
又因为当哈希冲突时我们要将新元素以链表的形式添加,所以我们还需要一个用来记录键值对插入位置的指针next
- static class Entry<K, V> {
- /**
- * 键值对
- */
- final int hash;//键的哈希值
- final K key;//键唯一
- V value;//值
- Entry<K, V> next;//哈希值冲突的键值对用链表连接
- public Entry(int hash, K key, V value) {
- this.hash = hash;
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- }
- @Override
- public boolean equals(Object o) {
- if (this == o) return true;//地址值相同
- if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;//地址值不同
- Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry<?, ?>) o;
- return Objects.equals(key, entry.key);
- }
- @Override
- public final int hashCode() {
- return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return key+"="+value;
- }
- }

2.MyHashMap
我们主要实现哈希表的添加put,删除remove,查找get等操作
⑴初始成员变量
首先当我们创建哈希表的对象时,底层会自动创建一个默认长度为16且加载因子为0.75的数组table,当数组中已经存在的元素个数size大于数组的可存入最大数组长度(数组长度*加载因子)时,数组就要进行扩容
- Entry[] table = new Entry[16];//初始数组长度
- int size = 0;//已存数组长度
- final double DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75d;//加载因子
- int threshold = (int) (table.length * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);//可存入的最大数组长度
- public MyHashMap() {}
⑵添加put
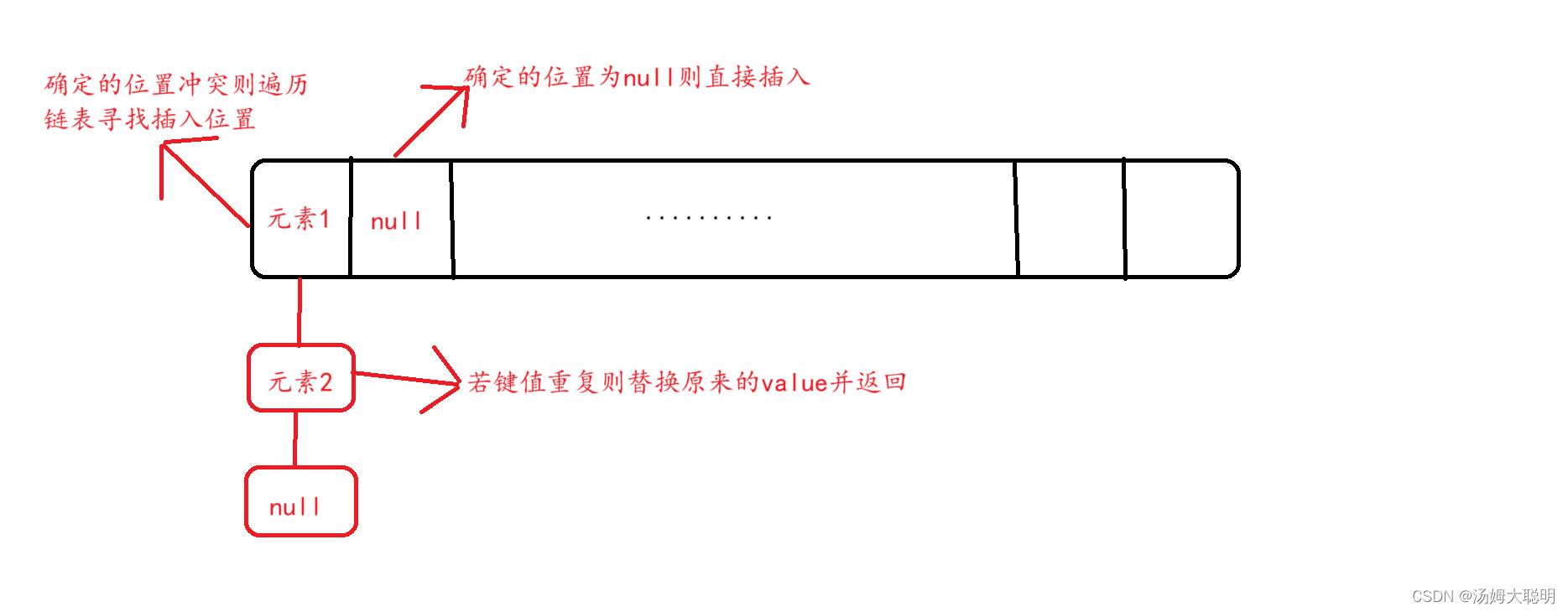
我们根据哈希码与数组长度的关系(hash&(数组长度-1))来确定键值对的位置
若确定的数组位置中没有元素null,则将元素直接插入
若确定的数组位置中有元素,则遍历此位置的链表,若键存在,则将原来的值覆盖并返回,若键不存在,则插入链表尾部
- public void put(K key, V value) {
- int hash = key.hashCode();
- int index = hash & (table.length - 1);
- if (table[index] == null) {
- table[index] = new Entry(hash, key, value);
- } else {
- Entry<K, V> p = table[index];
- while (true) {
- if (p.key.equals(key)) {//键已经存在,将原来键的值覆盖
- p.value = value;
- return;
- }
- if (p.next == null) {//键不存在,插入
- break;
- }
- p = p.next;
- }
- p.next = new Entry<>(hash, key, value);
- }
- size++;
- if (size >= threshold) {//检查数组长度是否超出最大数组长度,超出则扩容
- resize();
- }
- }

细节:为什么根据hash&(数组长度-1)来确定键值对的位置?
其实hash&(数组长度-1)等价于hash%数组长度,在数组长度为2^n的前提下
我们来看个例子:
十进制下:15%2=1
转化为二进制为:0001111%0000010=0000001
十进制下:15%4=3
转化为二进制为:0001111%0000100=0000011
十进制下:15%8=7
转化为二进制为:0001111%0001000=0000111
我们发现余数就是被除数保留的位数
因此为了提高运算的性能,我们可以对被除数进行&操作
0001111%0000010↔0001111&0000001=0000001
其中0000001为2^1-1
0001111%0000100↔0001111&0000011=0000011
0000011为2^2-1
那么综上:在数组长度为2^n的前提下,hash&(数组长度-1)等价于hash%数组长度
⑶扩容resize
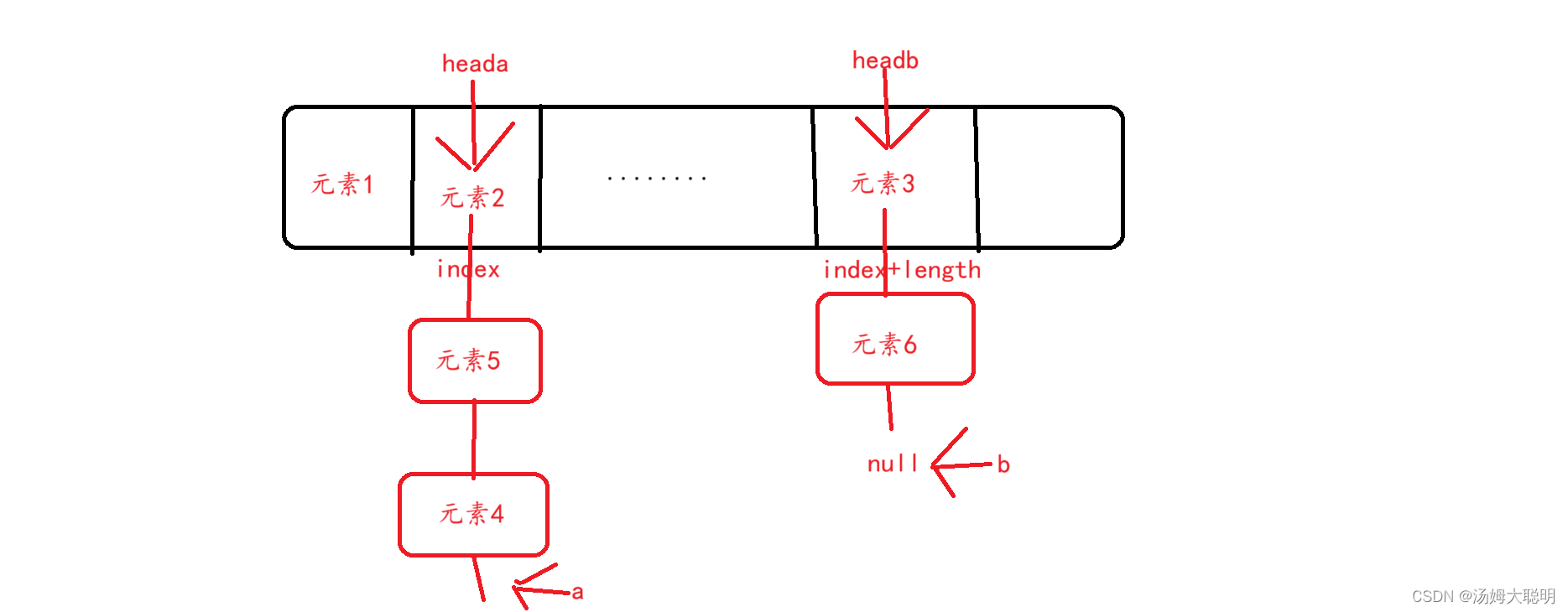
扩容的新数组容量为原来数组的2倍,扩容后我们要将数组每一位的键值对链表重装为两组
我们利用尾插法,若hash&数组长度==0则为一组,若hash&数组长度!=0则为另一组,最后我们将两组链表分装为2组
- private void resize() {
- Entry[] newtable = new Entry[table.length * 2];//扩容容量为原来数组的两倍
- for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) {
- Entry<K, V> p = table[i];//获取每一个位置的链表拆分为两部分进行重装
- if (p != null) {
- //尾查法
- Entry<K, V> a = null;//链表尾指针
- Entry<K, V> b = null;
- Entry<K, V> heada = null;//链表头指针,用来记录操作的链表
- Entry<K, V> headb = null;
- while (p != null) {
- //第一组:hash&数组长度==0 第二组:hash&数组长度!=0
- if ((p.hash & table.length) == 0) {
- if (a == null) {//刚开始添加,记录头指针
- heada = p;
- } else {
- a.next = p;
- }
- a = p;//尾指针后移
- } else {
- if (b == null) {//刚开始添加
- headb = p;
- } else {
- b.next = p;
- }
- b = p;//尾指针后移
- }
- p = p.next;
- }
- if (a != null) {//将尾指针指向null
- a.next = null;
- newtable[i] = heada;//将重装的链表分装到数组中
- }
- if (b != null) {
- b.next = null;
- newtable[i + table.length] = headb;
- }
- }
- }
- table = newtable;//覆盖原来的数组
- //更新最大数组长度
- threshold = (int) (table.length * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
- }

细节:为什么要根据hash&数组长度进行分组?
我们来看一个例子:在数组长度为2^n前提下
十进制下:2%4=2
6%4=2
二进制下:0000010%0000100=0000010
0000110%0000100=0000010
我们进行&操作,检查倒数第三位,按位与后若结果为0则为一组,否则为另一组
⑷删除remove
删除操作与链表的删除操作相似
- public V remove(K key) {
- int hash = key.hashCode();
- int index = hash & (table.length - 1);//位置
- if (table[index] == null) {
- return null;
- } else {
- Entry<K, V> p = table[index];
- Entry<K, V> pre = null;
- //遍历链表寻找要删除的键值对
- while (p != null) {
- if (p.key.equals(key)) {
- if (pre == null) {//链表头部元素
- table[index] = p.next;
- } else {
- pre.next = p.next;
- }
- size--;
- return p.value;
- }
- pre = p;
- p = p.next;
- }
- }
- return null;
- }

⑸获取get
- public V get(K key) {/**找对应键的值*/
- int hash = key.hashCode();
- //根据哈希值计算在数组中的位置
- int index = hash & (table.length - 1);//hash%table.length;
- if (table[index] == null) {
- return null;
- }
- Entry<K, V> p = table[index];
- //遍历链表,找到键对应的值
- while (p != null) {
- if (p.key.equals(key)) {
- return p.value;
- }
- p = p.next;
- }
- return null;

下面是我们实现的哈希表的完整的代码
- package myHashMap;
-
- import java.util.Objects;
- import java.util.StringJoiner;
-
- public class MyHashMap<K, V> {
- static class Entry<K, V> {
- /**
- * 键值对
- */
- final int hash;//键的哈希值
- final K key;//键唯一
- V value;//值
- Entry<K, V> next;//哈希值冲突的键值对用链表连接
- public Entry(int hash, K key, V value) {
- this.hash = hash;
- this.key = key;
- this.value = value;
- }
- @Override
- public boolean equals(Object o) {
- if (this == o) return true;//地址值相同
- if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;//地址值不同
- Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry<?, ?>) o;
- return Objects.equals(key, entry.key);
- }
- @Override
- public final int hashCode() {
- return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return key+"="+value;
- }
- }
- Entry[] table = new Entry[16];//初始数组长度
- int size = 0;//已存数组长度
- final double DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75d;//加载因子
- int threshold = (int) (table.length * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);//可存入的最大数组长度
- public MyHashMap() {}
- public V get(K key) {/**找对应键的值*/
- int hash = key.hashCode();
- //根据哈希值计算在数组中的位置
- int index = hash & (table.length - 1);//hash%table.length;
- if (table[index] == null) {
- return null;
- }
- Entry<K, V> p = table[index];
- //遍历链表,找到键对应的值
- while (p != null) {
- if (p.key.equals(key)) {
- return p.value;
- }
- p = p.next;
- }
- return null;
- }
- public void put(K key, V value) {
- int hash = key.hashCode();
- int index = hash & (table.length - 1);
- if (table[index] == null) {
- table[index] = new Entry(hash, key, value);
- } else {
- Entry<K, V> p = table[index];
- while (true) {
- if (p.key.equals(key)) {//键已经存在,将原来键的值覆盖
- p.value = value;
- return;
- }
- if (p.next == null) {//键不存在,插入
- break;
- }
- p = p.next;
- }
- p.next = new Entry<>(hash, key, value);
- }
- size++;
- if (size >= threshold) {//检查数组长度是否超出最大数组长度,超出则扩容
- resize();
- }
- }
- private void resize() {
- Entry[] newtable = new Entry[table.length * 2];//扩容容量为原来数组的两倍
- for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) {
- Entry<K, V> p = table[i];//获取每一个位置的链表拆分为两部分进行重装
- if (p != null) {
- //尾查法
- Entry<K, V> a = null;//链表尾指针
- Entry<K, V> b = null;
- Entry<K, V> heada = null;//链表头指针,用来记录操作的链表
- Entry<K, V> headb = null;
- while (p != null) {
- //第一组:hash&数组长度==0 第二组:hash&数组长度!=0
- if ((p.hash & table.length) == 0) {
- if (a == null) {//刚开始添加,记录头指针
- heada = p;
- } else {
- a.next = p;
- }
- a = p;//尾指针后移
- } else {
- if (b == null) {//刚开始添加
- headb = p;
- } else {
- b.next = p;
- }
- b = p;//尾指针后移
- }
- p = p.next;
- }
- if (a != null) {//将尾指针指向null
- a.next = null;
- newtable[i] = heada;//将重装的链表分装到数组中
- }
- if (b != null) {
- b.next = null;
- newtable[i + table.length] = headb;
- }
- }
- }
- table = newtable;//覆盖原来的数组
- //更新最大数组长度
- threshold = (int) (table.length * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner(",", "[", "]");
- for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) {
- Entry<K, V> p = table[i];
- while (p != null) {
- sj.add(p.toString());
- p = p.next;
- }
- }
- return sj.toString();
- }
- public V remove(K key) {
- int hash = key.hashCode();
- int index = hash & (table.length - 1);//位置
- if (table[index] == null) {
- return null;
- } else {
- Entry<K, V> p = table[index];
- Entry<K, V> pre = null;
- //遍历链表寻找要删除的键值对
- while (p != null) {
- if (p.key.equals(key)) {
- if (pre == null) {//链表头部元素
- table[index] = p.next;
- } else {
- pre.next = p.next;
- }
- size--;
- return p.value;
- }
- pre = p;
- p = p.next;
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
- }

实现完成后我们来运行代码来爽一下吧
首先我们来看一下put方法的添加以及覆盖能否实现
- MyHashMap<String,Integer> ha=new MyHashMap<>();
- ha.put("aa",1);
- ha.put("aa",5);
- System.out.println(ha);//[aa=5]
然后是数组的扩容操作
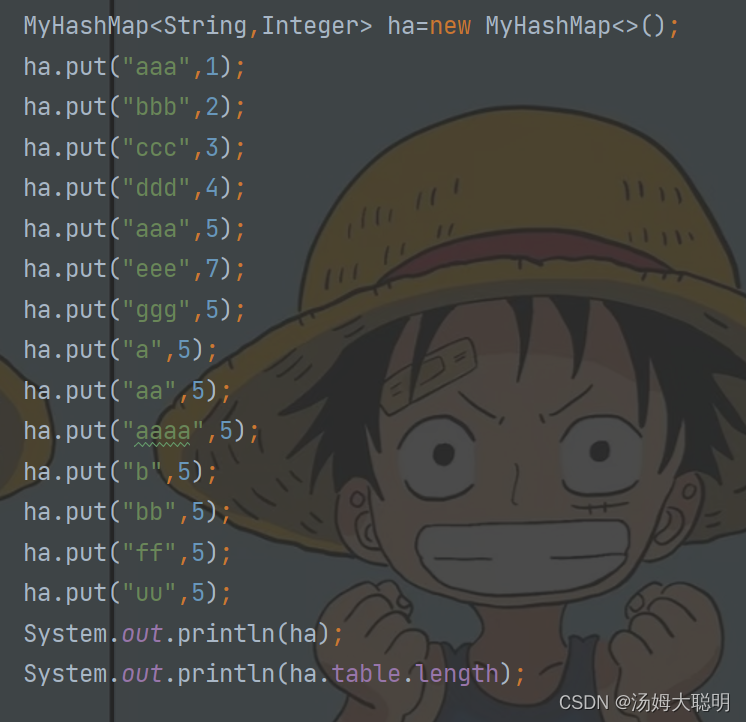

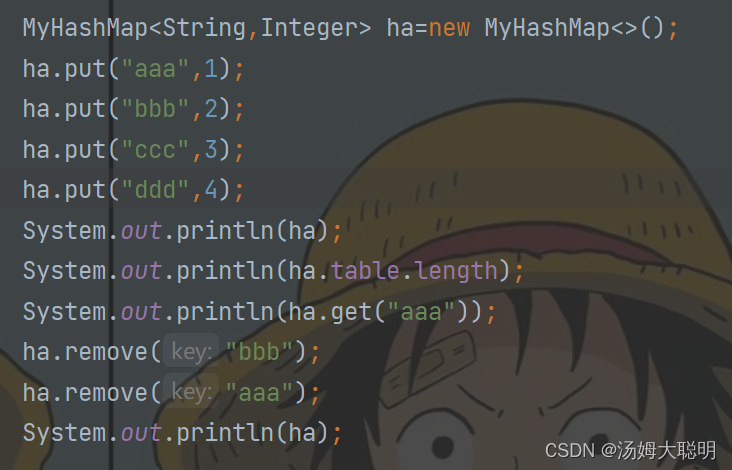
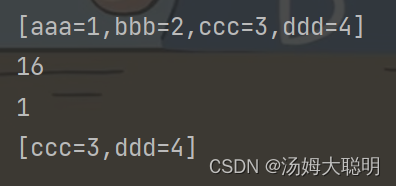
最后是remove以及get方法
四. 哈希表常见算法题
在算法练习中,熟练的运用哈希表可以使许多题目简单很多,下面我整理了一些力扣中的有关哈希表的经典算法题,希望会对各位有所帮助
常见的利用哈希表主要有三种题型
①数组哈希
②set哈希
③map哈希

若有不足,错误之处,望指出更正(*´I`*)


