热门标签
热门文章
- 1设置hive的执行引擎_0506如何将Hue4.0版本中默认执行引擎设置为Hive而非Impala
- 2高校导师在微信群里公然委托关照考研复试,学校通报处理情况!
- 3腾讯AniPortrait开源:音频合成逼真人脸动画,对标阿里EMO_腾讯aniportrait 模型下载
- 4stable diffusion常用的模型_stable diffusion 常用模型
- 5基于Kafka+Flink+Redis的电商大屏实时计算案例
- 6前端自动化测试(二)Vue Test Utils + Jest_vue+jest 测试api
- 7【前端】从零开始学习编写HTML
- 820240624 每日AI必读资讯
- 9数据结构之冒泡排序图文详解及代码(C++实现)_c++冒泡算法代码
- 10Dagger2 在 Android SystemUI 中的应用_android systemui11 dagger2
当前位置: article > 正文
【算法整理】快慢指针-链表的环检测_链表的环的检测快慢指针
作者:知新_RL | 2024-07-28 18:27:08
赞
踩
链表的环的检测快慢指针
【算法整理】快慢指针-链表的环检测
算法解决的问题
链表是编程中最常见的数据结构,当我们遍历链表时如果链表中存在闭环(如下图),会造成无限循环的情况。为了解决这个问题我们需要在遍历之前对链表做环检测。

算法解决方案-快慢指针
我们设置两个指针如下图

然后快指针每次移动两个节点,慢指针每次移动一个节点,就像两个人在操场上跑,一个跑得快一个跑得慢,那么如果一直跑下去两人总会相遇。当两个指针相遇就代表链表存在闭环。此时的代码实现应该是这样的:
LinkedNode<T>* checkCycle() { LinkedNode<T> *fast, *slow; fast = this->head; slow = this->head; while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (fast == slow) { std::cout << "存在闭环,相遇点的值:" << fast->value << std::endl; return fast; } } return nullptr; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
这个时候我们已经可以确定链表是否有闭环,那么在进一步我们还可以找到闭环的入口。就是上图6的节点。
闭环点分析
如下图所示,设链表中环外部分的长度为 L。指针进入环后,又走了 E的距离与 fast 相遇。此时,fast 指针已经走完了环的 n 圈,环长C。由于我们设定快指针是慢指针的2倍速度。因此有:R+E=n*C,演算过程如下:
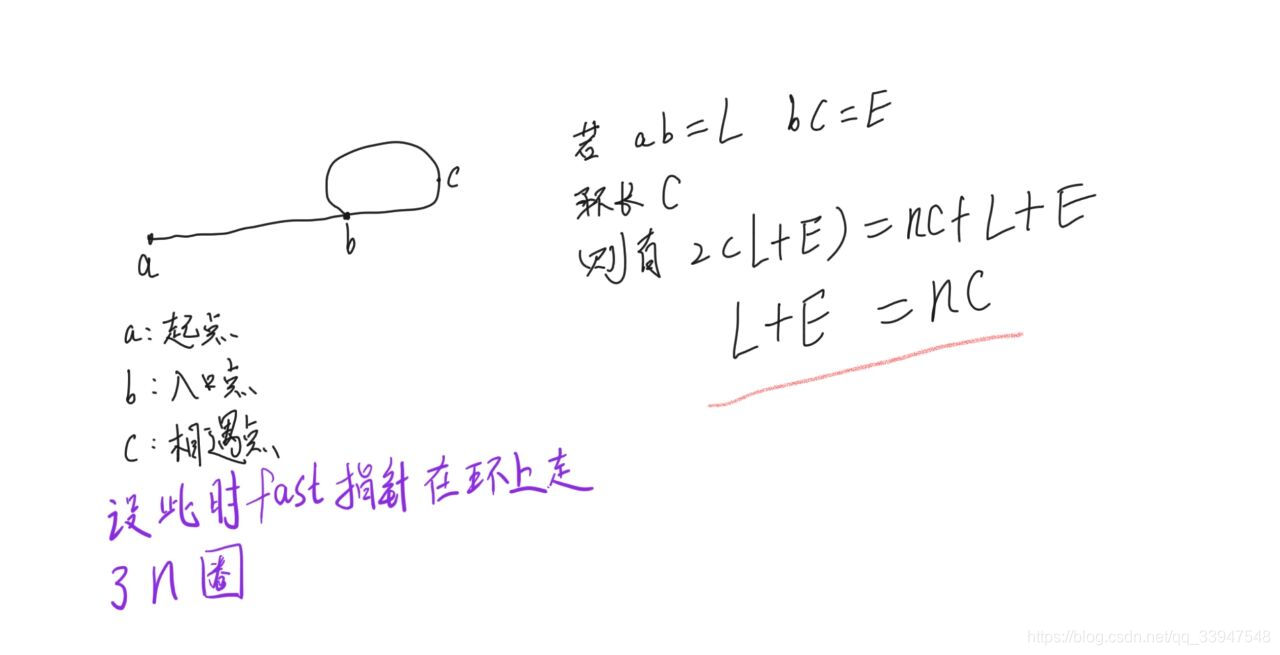
由以上结果可知:如果此时第三个指针以和慢指针一样的速度从链表头开始出发,它和慢指针一定会在c点相遇,那么可以得知它们的第一次相遇点就是环入口。进一步完善上面的代码:
LinkedNode<T>* checkCycle() { LinkedNode<T> *fast, *slow; fast = this->head; slow = this->head; while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (fast == slow) { std::cout << "存在闭环,相遇点的值:" << fast->value << std::endl; fast = this->head; while (fast != slow) { fast = fast->next; slow = slow->next; } std::cout << "环入口值: " << fast->value << std::endl; return fast; } } return nullptr; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
全部代码
/* List的单向链表实现 */ template <class T> class LinkedNode { public: T value; LinkedNode *next; LinkedNode(T value) { this->value = value; next = nullptr; } LinkedNode() { // value = default(); next = nullptr; } }; template <class T> class LinkedList { public: LinkedNode<T> *head; LinkedList(LinkedNode<T> *head) { this->head = head; } // 尾插法 bool add(LinkedNode<T> *node) { // 滑动指针 LinkedNode<T> *temp = this->head; while (temp->next != nullptr) { temp = temp->next; } temp->next = node; return true; } bool add(T t) { LinkedNode<T> *node = new LinkedNode<T>(t); this->add(node); return true; } int size() { if (checkLoop() != nullptr) { // 存在闭环则返回-1 return -1; } LinkedNode<T> *temp; temp = this->head; int size = 0; while (temp != nullptr) { size++; temp = temp->next; } return size; } LinkedNode<T>* checkLoop() { LinkedNode<T> *fast, *slow; fast = this->head; slow = this->head; while (fast->next != nullptr && fast->next->next != nullptr) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (fast == slow) { std::cout << "存在闭环,相遇点的值:" << fast->value << std::endl; fast = this->head; while (fast != slow) { fast = fast->next; slow = slow->next; } std::cout << "环入口值: " << fast->value << std::endl; return fast; } } return nullptr; } // 遍历操作 void foreach( void(*fun)(T item, int index)) const { LinkedNode<T> *temp = this->head->next; int i = 0; while (temp != nullptr) { fun(temp->value, i++); temp = temp->next; } } // 映射操作 template<typename V> LinkedList<V> map(V(*fun)(T item, int index)) { LinkedList<V> newList(new LinkedNode<V>()); LinkedNode<T> *temp = this->head->next; int i = 0; while (temp != nullptr) { V res = fun(temp->value, i++); newList.add(res); temp = temp->next; } return newList; } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/知新_RL/article/detail/895329
推荐阅读
相关标签



