- 1Pytorch基础及实战(3)——深入浅出PyTorch数据读取机制_继承dataset类__len__
- 2人工智能-聚类算法、误差评估、算法优化、特征降维
- 3实不相瞒,字节跳动的大模型、推荐、特效算法……都是在这里跑出来的
- 4Pytorch中Dataset类的继承使用方法(创建自己的图片数据集)(自己记录加强印象的,大家别喷我)_怎样继承自torch中的dataset
- 5易感-感染-易感(SIS)模型的实现方式_sis模型
- 6机器学习实战教程(二):线性回归_线性回归实战 这是一个关于初创企业的小数据集,由51行和5列组成。我们的目标是根
- 7springcloud异常:org.springframework.web.client.HttpClientErrorException$BadRequest: 400 null_nested exception is org.springframework.web.client
- 8王咏刚《AI的产品化和工程化挑战》_人工智能工程化挑战
- 9在线SM2验签工具_sm2在线验签
- 10基于ChatGPT函数调用来实现C#本地函数逻辑链式调用助力大模型落地_chatgpt vb代码转c#
自然语言处理—RNN循环神经网络_self.rnn
赞
踩
1. RNN基本介绍
(参见吴恩达深度学习—RNN篇https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV16r4y1Y7jv?p=152&spm_id_from=pageDriver)
1.1 基本介绍
RNN神经网络可以用来处理时间序列类型的数据,一段文字也可以看成一个时间序列。比如,
The cat ate many food that was delicious was full
其中,上标代表第
个样本,
代表时间,下面将不再样本的标记
进行分析。一般的神经网络处理时间序列时存在两个问题:i) 输入维度不确定,且如果是one-hot编码,则向量维度高;ii) 一般神经网络不能捕捉序列之间的信息。因此,有循环神经网络来处理时间序列数据。
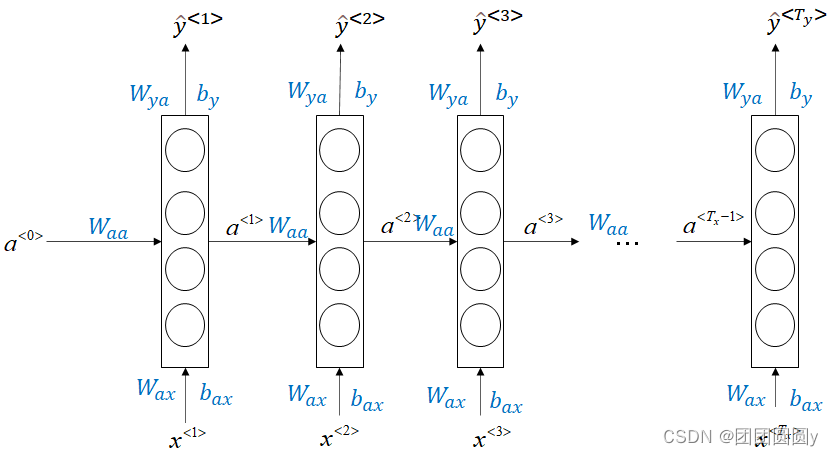
图1. RNN神经网络模型结果
前向传播
在RNN中,每一时刻所使用的参数
、
、
以及
、
、
都是一致的。模型的forward-propagation如下:
(1)
其中,。
反向传播
每一个时刻,都有损失函数:
总的损失为。其back-propagation如下图所示,
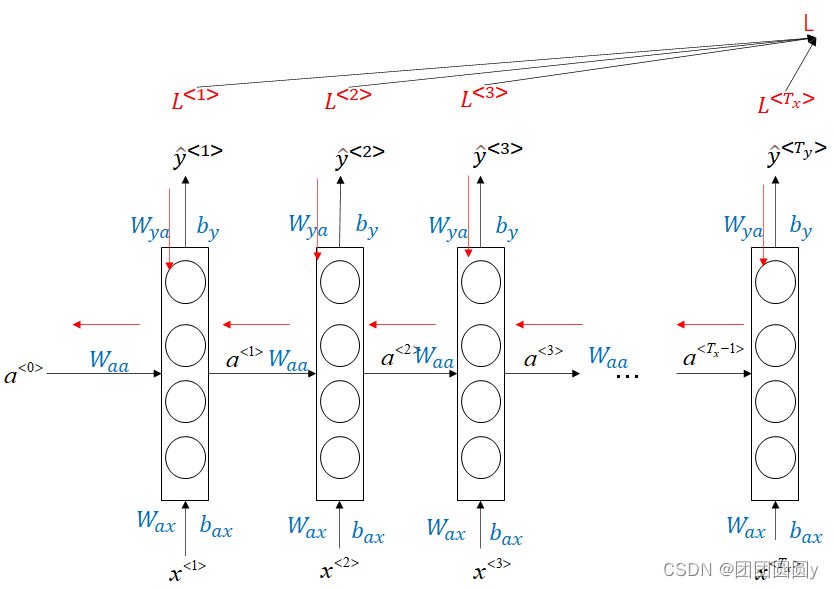
图2. RNN反向传播示意图
上面展示的是的情形,即输入和输出一样多,根据
和
,有以下多种网络形式。
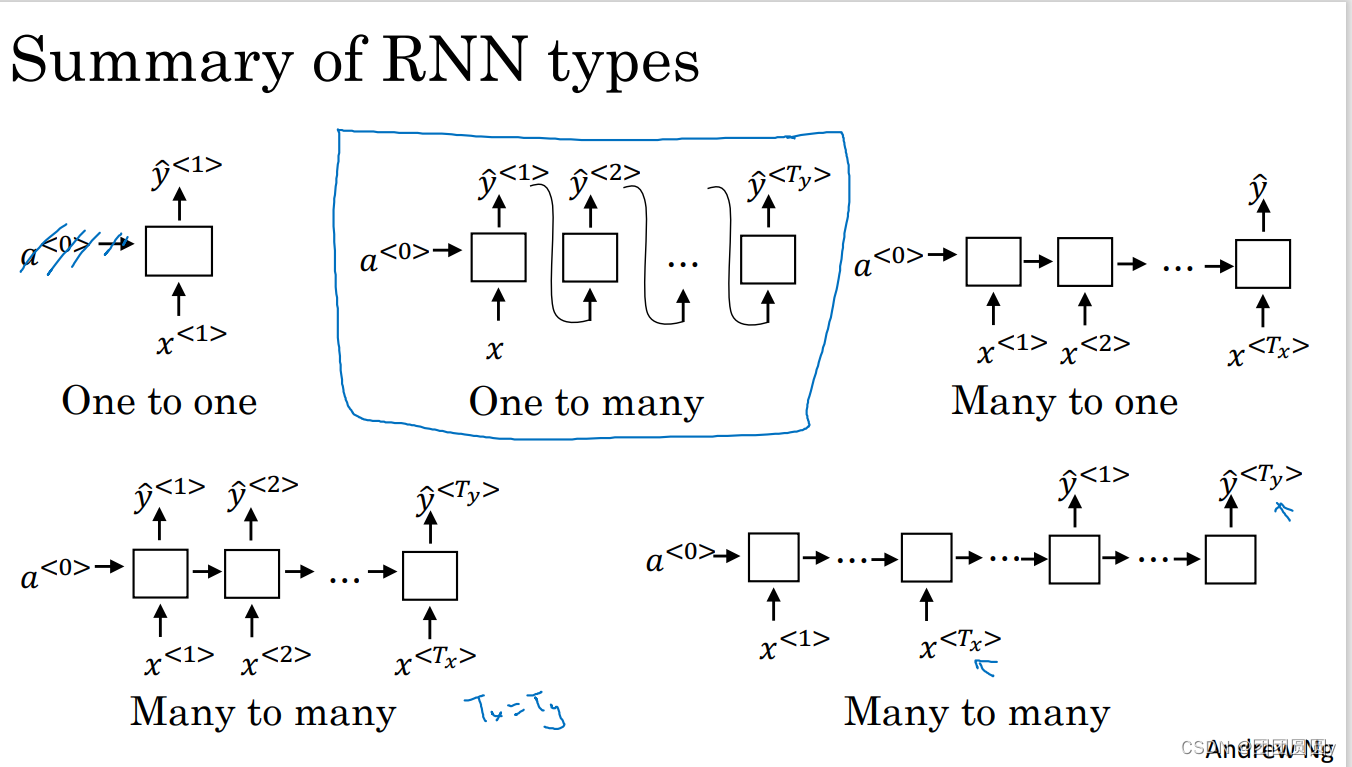
图3. 多种类型的RNN模型
1.2 解决RNN的梯度消失
和深度神经网络一样,RNN同样存在梯度消失和梯度爆炸的问题(复合函数求导,若每一步梯度>1则容易产生梯度爆炸,梯度<1则容易产生梯度消失,参见https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/68579467),导致更新网络参数无效或者震荡太大。梯度爆炸容易观察,但是梯度消失不易观察,针对RNN,专门有GRU和LSML两种模型解决。
GRU简单理解为,每个时刻引入一个记忆值
,记忆值
和激活值
相等。根据门控
(gate)决定是否用新得到的
更新当前的c^{t},
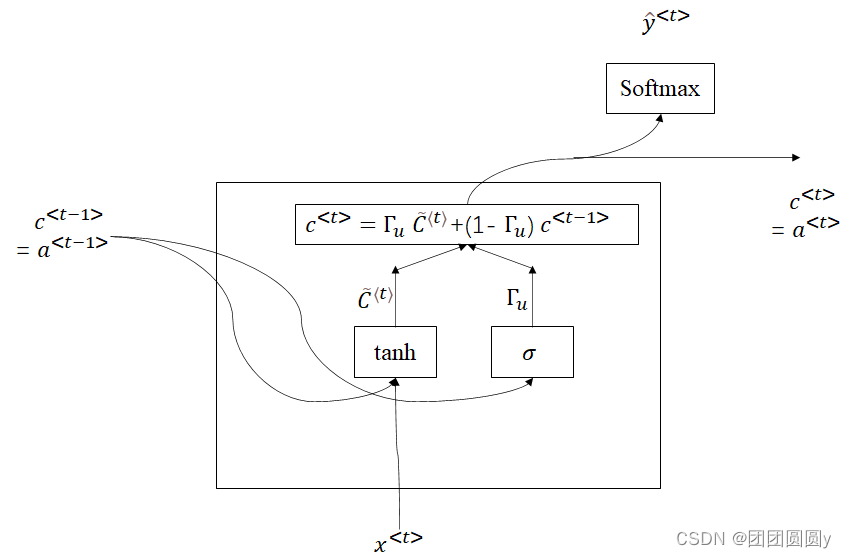
图4. GRU示意图
更新公式如下:
(2.1)
(2.2)
(2.3)
(2.4)
(2.5)
与图4中只有一个门控不同的是,在计算
的时候有另外一个相关性的门控
。
LSMT和GRU不同的是,和
并不相等,引入了其他的门控
和
,其中
取代了式(2.4)中的
,作为单独的遗忘门控;
用以更新激活值
,如下:
(3.1)
(3.2)
(3.3)
(3.4)
(3.5)
(3.6)
2. 实例
2.1 pytorch中语法
Torch.nn.RNN为内置的RNN网络。序列的激活值用
表示,计算公式如下,
初始化一个RNN网络语法:
rnn=torch.nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers,nonlinearity, bias,batch_first,dropout, bidirectional)参数
其中,一般用到的参数为input_size, hidden_size, num_layers,nonlinearity, bias,batch_first。
input_size:输入序列每个字节的维度
hidden_size:隐含层中的激活值的维度
num_layers:隐含层的层数
nonlinearity:默认:激活函数为tanh,也可以设置为relu等
bias:是否有偏重,默认为true
网络输入
Input—X:[seq_len, batch_size, input_size]
seq_len:输入的句子/序列的字节长度
batch_size:样本量
input_size:字节维度
Input—h0: [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
num_layers:多少层隐含层,多少层的激活值
batch_size:样本量
hidden_size:激活值的维度
当网络的设置中batch_first为True时,输入为Input—X:[seq_len, batch_size, input_size],Input—h0: [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
网络输出
out-out(n-n类型RNN)
[seq_len,batch_size,hidden_size]
out-h(最后一个字节对应的激活值)
[seq_len,batch_size,hiden_size]
参加pytorch官网https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.RNN.html#torch.nn.RNN、(超详细!!)Pytorch循环神经网络(RNN)快速入门与实战_Hello3q3q的博客-CSDN博客_rnn循环神经网络
示例
设计一个含有2层隐含层的RNN,输入输出示意图如下,
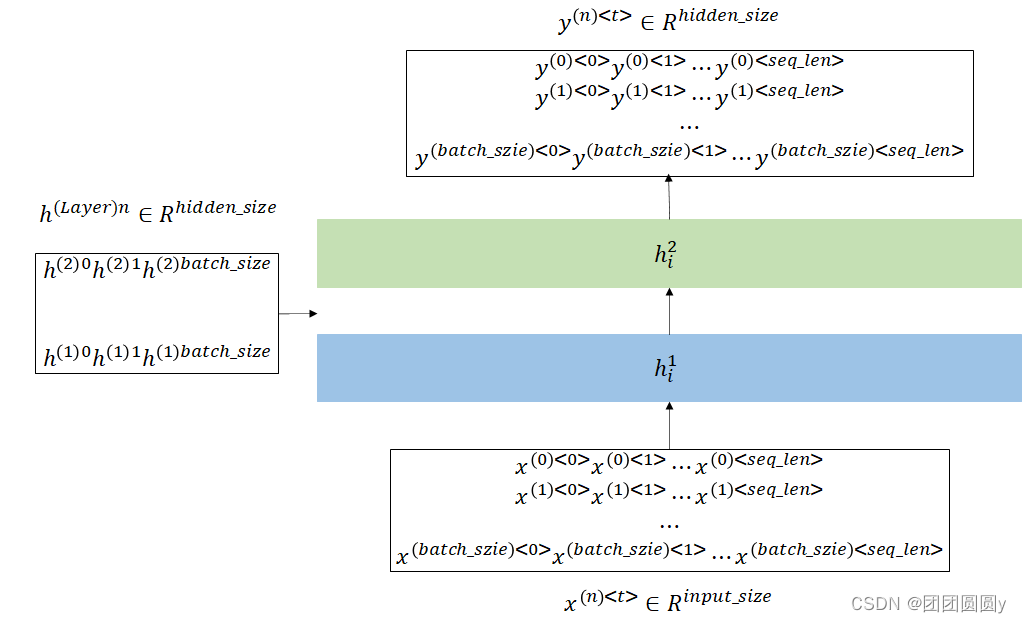
图5. 2层RNN输入批量数据输出示意图
在该例中,输入样本量的
,序列长度
,每个字节的维度为
。设计隐含层2层,激活值的维度为
。代码示例如下:
- '''
- RNN
- input_size:输入序列每个字节的维度
- hidden_size:隐含层中的激活值的维度
- num_layers:隐含层的层数
- Input—X
- seq_len:输入的句子/序列的字节长度
- batch_size:样本量
- input_size:字节维度
- Input—h(初始化的激活层)
- num_layers:多少层隐含层,多少层的激活值
- batch_size:样本量
- hidden_size:激活值的维度
- out-out
- seq_len,batch_size,hidden_size
- out-h
- seq_len,batch_size,hiden_size
- '''
- input_size = 10
- hidden_size = 3
- num_layers = 2
- output_size = 2
- rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=input_size,hidden_size=hidden_size,
- num_layers=num_layers, batch_first=True)
-
- seq_len = 3
- batch_size = 2
- x = torch.randn(batch_size,seq_len,input_size) # 输入数据
- h0 = torch.zeros(batch_size,num_layers,hidden_size) # 输入数据
-
- out, h = rnn(x, h0) # 输出数据
- linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
-
- print("out.shape:",out.shape)
- print("h.shape:",h.shape)
- print("out",out)
- out = linear(out)
- print(out)

其中,linear层将输出由
的维度转变为我们想要的维度
。
结果如下,
- out.shape: torch.Size([2, 3, 3]) # [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size]
- h.shape: torch.Size([2, 2, 3]) # [batch_size, Layers_num, hidden_size]
- out tensor([[[-0.1594, -0.4284, -0.0468], # 样本1字节1
- [ 0.0161, -0.5916, -0.1567], # 样本1字节2
- [-0.0266, -0.6426, -0.1186]], # 样本1字节3
-
- [[ 0.1776, 0.2767, 0.3266], # 样本2字节1
- [ 0.0168, 0.1360, 0.0264], # 样本2字节2
- [ 0.1708, -0.0948, 0.2696]]], grad_fn=<TransposeBackward1>) # 样本2字节3
- tensor([[[-0.2269, -0.0797], # 样本1字节1
- [-0.1802, 0.0406], # 样本1字节2
- [-0.1426, 0.0049]], # 样本1字节1
-
- [[-0.7844, -0.0692], # 样本2字节1
- [-0.6108, -0.0201], # 样本2字节2
- [-0.5674, -0.0560]]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>) # 样本2字节1

(注:这里,为方便理解,RNN的参数batch_first=True,初始化x和h0的时候使用了对应的顺序,但是规范的方法应该是使用torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequence)
2.2 网络训练
构建RNN模型,训练网络
- class RNN_model(torch.nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size,num_layers, output_size):
- super(RNN_model,self).__init__()
- self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size = input_size,
- hidden_size = hidden_size,
- num_layers = num_layers,
- batch_first=False)
- self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
- def forward(self, x, h0):
- out, h = self.rnn(x, h0)
- out = self.linear(out)
- return out
-
- input_size = 10
- hidden_size = 3
- num_layers = 2
- output_size = 2
- model = RNN_model(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, output_size)
- model = model.to(device)

使用GRU训练,基本一致,将nn.RNN替换为nn.GRU
- class RNN_model(torch.nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size,num_layers, output_size):
- super(RNN_model,self).__init__()
- self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size = input_size,
- hidden_size = hidden_size,
- num_layers = num_layers,
- batch_first=False)
- self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
- def forward(self, x, h0):
- out, h = self.gru(x, h0)
- out = self.linear(out)
- return out
-
- input_size = 10
- hidden_size = 3
- num_layers = 2
- output_size = 2
- model = RNN_model(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, output_size)
- model = model.to(device)

训练过程如下,
- seq_len = 3 # 句子长度
- batch_size = 2
- x = torch.randn(seq_len,batch_size,input_size) # 输入数据
- h0 = torch.zeros(num_layers,batch_size,hidden_size) # 输入数据
- target = torch.randn(seq_len,batch_size,output_size) # 输出数据
-
- board = SummaryWriter('/kaggle/working/ML_RNN/logs')
- loss_function = nn.MSELoss()
- opt = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.003, weight_decay=1e-3)
- Epochs = 100
- for epoch in range(Epochs):
- pred = model(x, h0)
- loss = loss_function(pred, target)
- #一般下面三行指令是放一起的
- opt.zero_grad()
- loss.backward()
- opt.step()
- print('epoch=',epoch,' train_loss=',loss.item())
- board.add_scalar("Train_loss", loss.item(), epoch)
- board.close()

误差图如下,
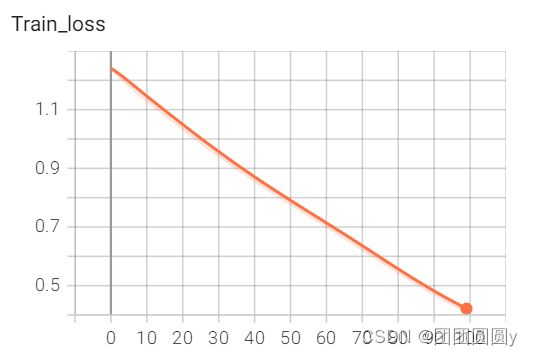
图6. 误差图
从误差图可以看到,训练到100步的时候,还未收敛。


