热门标签
热门文章
- 1c语言文件(万字)(超详细)_c语言文档
- 2git 大文件上传以及下载_gitbash 下载大文件
- 3小程序开发---uniapp---商城项目002---分类_uniapp实现商品分类展示组件
- 4ARP协议及抓包详解_arp抓包
- 5解决obsidian无法加载第三方插件(社区插件)的问题_obsidian无法加载社区插件
- 6UI管理面板_panal name
- 7前端实现sql格式化,Mybatis语法_sqlformatter.js+paramtypes
- 8机器学习原理之 -- XGboost原理详解
- 9数据库课设(图书管理系统)_数据库设置管理图书馆保管和借还的数据库
- 10Oracle数据库ORA-报错大全
当前位置: article > 正文
SVM兵王问题详解_clear all;fid = fopen('krkopt.data');c = fread(fid
作者:爱喝兽奶帝天荒 | 2024-06-29 01:10:26
赞
踩
clear all;fid = fopen('krkopt.data');c = fread(fid, 3);vec = zeros(6,1);
(一) 识别系统的性能度量
- 上接纸面笔记记录:
- 不能仅用识别率来判断系统的性能。单纯用系统的识别率来判断系统的好坏,是没有意义的。例如,瞎猜的准确率为80%,那么你svm识别率为%95,那么还算高吗?
(1)几个重要的度量系统性能的标准
(1)混淆矩阵(confusion matrix)

1.0 解释上图:
TP: T 代表正确true, TP代表读正样本(positive)正确;对了,把P读成P
TN: T代表正确true, N,negative,TN 代表读负样本正确;对了,把N读成N
FP:代表读正样本错误;错了,读成P(把谁读成P会错呢?)
FN:代表读负样本错误;错了,读成N
显然,正负样本的总数是固定的;那么可以概率化,归一化;
2.0 那么系统的识别率是多少呢?
识别成功个数:TP+TN; 总个数: TP+TN+FP+FN; 除一下就可以。99.61%
3.0 瞎猜的概率:由于负样本过多,所以全为负样本:TN + FP 89.96%
显然,这样的结果还可以,但是并不是非常好。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
概率形式:
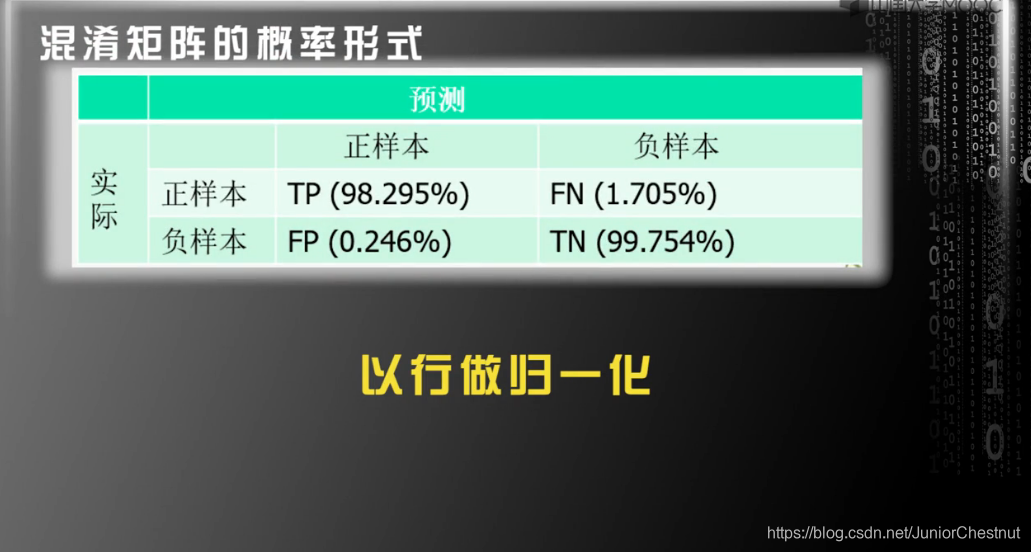
1.0 显然:TP+FN = 1; FP+TN = 1;
2.0 见下图:
- 1
- 2


【注】因为阈值下降,TP和FP通过率都上去(为正的概率)

(2)引入ROC曲线
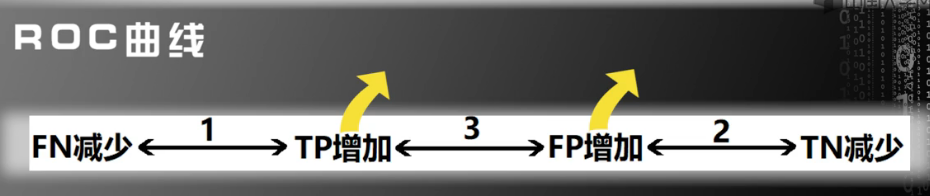
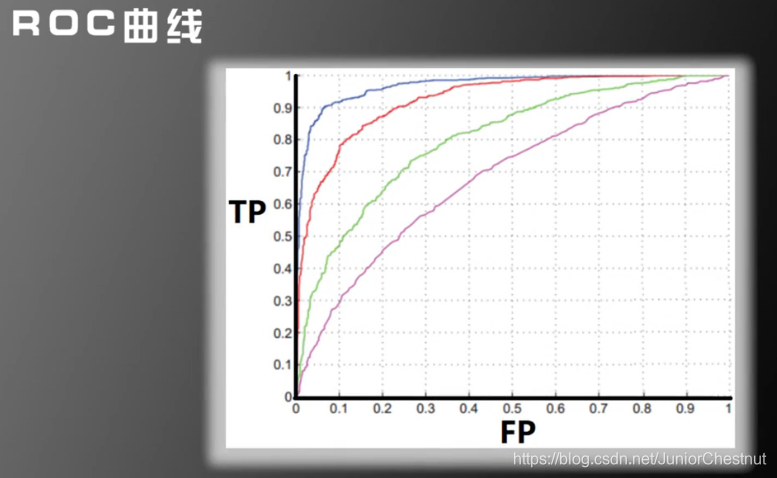

1.0 解释ROC曲线:是以FP和TP为横终坐标画成;
2.0 对每个测试样本,计算上图公式:
3.0 然后 将得到的值从小到大开始排序;
4.0 把每一个值当作阈值,计算此时的TP和FP;连成一条曲线;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
(2.1)通过ROC曲线获得系统性能度量
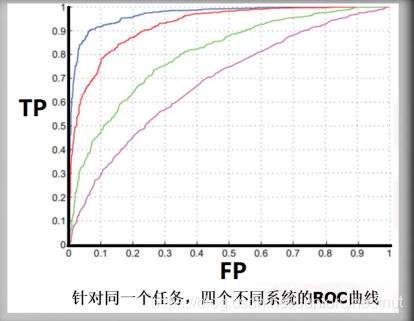
蓝色线最好,紫色线最差;因为在FP不变的情况下,TP越大越好。
(2.2)AUC指标
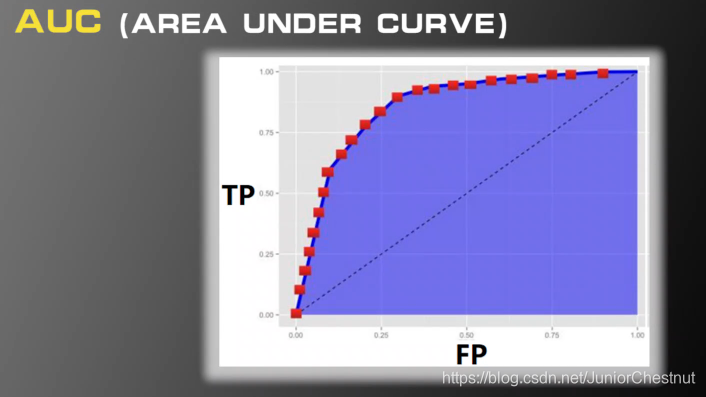
阴影面积越大越好。
(2.3)ERR
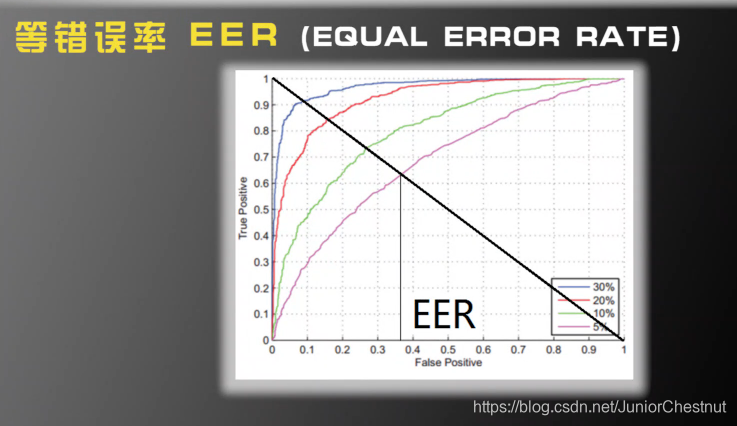
画一条45度线,EER为交点处的横坐标,显然,EER越小越好。
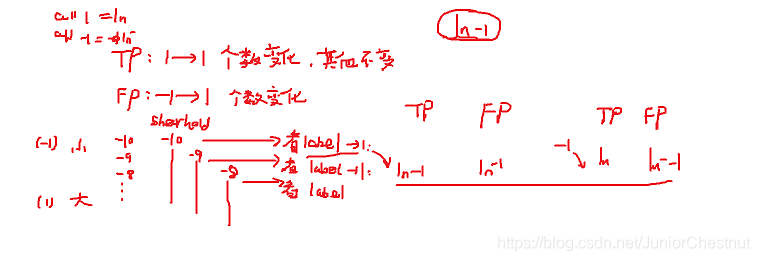
(2.4)ROC曲线代码解析

关键部分:通过当前得label去计算下一个得TP和FP
%Test the model on the remaining testing data and obtain the recognition rate. clear all; load model.mat; load xTesting.mat; load yTesting.mat; % yPred 是对每个样本预测的标签; accuracy是在测试集上整体的识别率 % decisionValue: 是w^TX + b 的值;就是根据这个值贴标签 [yPred,accuracy,decisionValues] = svmpredict(yTesting,xTesting,model); %draw ROC [totalScores,index] = sort(decisionValues); % 先排序 labels = yTesting; for i = 1:length(labels) labels(i) = yTesting(index(i)); % 将decisionValue与标签值对应起来。 end; truePositive = zeros(1,length(totalScores)+1); trueNegative = zeros(1,length(totalScores)+1); falsePositive = zeros(1,length(totalScores)+1); falseNegative = zeros(1,length(totalScores)+1); % 计算TP和FP的总的个数. 索引数一直为1; for i = 1:length(totalScores) if labels(i) == 1 truePositive(1) = truePositive(1)+1; else falsePositive(1) = falsePositive(1) +1; end; end; % FP: 是如何得出来的: 原本是不能通过,认成了pass, label = -1; % 由于排好序列了,那么,TP 和 FP的个数,其实是递减的。 for i = 1:length(totalScores) if labels(i) == 1 truePositive(i+1) = truePositive(i)-1; falsePositive(i+1) = falsePositive(i); else falsePositive(i+1) = falsePositive(i)-1; truePositive(i+1) = truePositive(i); end; end; % 概率化; truePositive = truePositive/truePositive(1); falsePositive = falsePositive/falsePositive(1); plot(falsePositive, truePositive); inc = 0.001; startIndex = 1; endIndex = length(falsePositive) pointerIndex = 1; pointerValue = falsePositive(1); newFalsePositive = []; newTruePositive = []; while pointerIndex<=length(falsePositive) while pointerIndex<=length(falsePositive) && falsePositive(pointerIndex)>falsePositive(startIndex)-inc pointerIndex = pointerIndex +1; end; newFalsePositive = [newFalsePositive, falsePositive(startIndex)]; newTruePositive = [newTruePositive, mean(truePositive(startIndex:min(pointerIndex,length(truePositive))))]; startIndex = pointerIndex; end; plot(newFalsePositive, newTruePositive);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
clear all; % Read the data. fid = fopen('krkopt.DATA'); c = fread(fid, 3); vec = zeros(6,1); xapp = []; % 接收六维的数据,先声明 yapp = []; % 接收所有的标签,先声明 while ~feof(fid) string = []; c = fread(fid,1); flag = flag+1; while c~=13 % 13代表回车; // 这里是读一行 string = [string, c]; c=fread(fid,1); end; fread(fid,1); % 这里是处理一行 if length(string)>10 vec(1) = string(1) - 96; % 把a变为整数1; vec(2) = string(3) - 48; vec(3) = string(5) - 96; vec(4) = string(7) - 48; vec(5) = string(9) - 96; vec(6) = string(11) - 48; xapp = [xapp,vec]; if string(13) == 100 % 13是因为第13个是draw(和棋)100是d; yapp = [yapp,1]; else yapp = [yapp,-1]; end; end; end; fclose(fid); [N,M] = size(xapp); % [N,M]是获取xapp的维度,例如3*4,N = 3,M = 4 p = randperm(M); % 直接打乱了训练样本,并且把列数作为行向量保存 % 1~M的整数随机置换 numberOfSamplesForTraining = 5000; xTraining = []; yTraining = []; for i=1:numberOfSamplesForTraining xTraining = [xTraining,xapp(:,p(i))]; % 这是从总样本中,取随机一列的全部元素 yTraining = [yTraining,yapp(p(i))]; % 这是取上面元素对应的标签 end; xTraining = xTraining'; % 取转置 yTraining = yTraining'; xTesting = []; yTesting = []; for i=numberOfSamplesForTraining+1:M % 遍历剩下的数据作为测试数据 xTesting = [xTesting,xapp(:,p(i))]; % 注意同样用的p(i) yTesting = [yTesting,yapp(p(i))]; end; xTesting = xTesting'; % 取转置 yTesting = yTesting'; %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %Normalization 归一化 [numVec,numDim] = size(xTraining); avgX = mean(xTraining); % 这里是对每一列求平均值 stdX = std(xTraining); % 对每一列求方差 for i = 1:numVec % 以行遍历所有数据 xTraining(i,:) = (xTraining(i,:)-avgX)./stdX; end; [numVec,numDim] = size(xTesting); for i = 1:numVec xTesting(i,:) = (xTesting(i,:)-avgX)./stdX; end; %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %SVM Gaussian kernel %Search for the optimal C and gamma, K(x1,x2) = exp{-||x1-x2||^2/gamma} to %make the recognition rate maximum. %Firstly, search C and gamma in a crude scale (as recommended in 'A practical Guide to Support Vector Classification')) CScale = [-5, -3, -1, 1, 3, 5,7,9,11,13,15]; gammaScale = [-15,-13,-11,-9,-7,-5,-3,-1,1,3]; C = 2.^CScale; gamma = 2.^gammaScale; maxRecognitionRate = 0; for i = 1:length(C) % 找到最佳的超参数 c 和 gama 的下标 for j = 1:length(gamma) % svm训练参数设置: cmd=['-t 2 -c ',num2str(C(i)),' -g ',num2str(gamma(j)),' -v 5']; recognitionRate = svmtrain(yTraining,xTraining,cmd); %训练数据和参数 if recognitionRate>maxRecognitionRate maxRecognitionRate = recognitionRate maxCIndex = i; maxGammaIndex = j; end; end; end; %Then search for optimal C and gamma in a refined scale. n = 10; % 用最好的超参数,重新训练 %max 是返回最大的数 minCScale = 0.5*(CScale(max(1,maxCIndex-1))+CScale(maxCIndex)); maxCScale = 0.5*(CScale(min(length(CScale),maxCIndex+1))+CScale(maxCIndex)); newCScale = [minCScale:(maxCScale-minCScale)/n:maxCScale]; minGammaScale = 0.5*(gammaScale(max(1,maxGammaIndex-1))+gammaScale(maxGammaIndex)); maxGammaScale = 0.5*(gammaScale(min(length(gammaScale),maxGammaIndex+1))+gammaScale(maxGammaIndex)); newGammaScale = [minGammaScale:(maxGammaScale-minGammaScale)/n:maxGammaScale]; newC = 2.^newCScale; newGamma = 2.^newGammaScale; maxRecognitionRate = 0; for i = 1:length(newC) for j = 1:length(newGamma) cmd=['-t 2 -c ',num2str(newC(i)),' -g ',num2str(newGamma(j)),' -v 5']; recognitionRate = svmtrain(yTraining,xTraining,cmd); if recognitionRate>maxRecognitionRate maxRecognitionRate = recognitionRate maxC = newC(i); maxGamma = newGamma(j); end; end; end; %Train the SVM model by the optimal C and gamma. cmd=['-t 2 -c ',num2str(maxC),' -g ',num2str(maxGamma)]; model = svmtrain(yTraining,xTraining,cmd); save model.mat model; save xTesting.mat xTesting; save yTesting.mat yTesting; % plot(falsePositive,truePositive);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/爱喝兽奶帝天荒/article/detail/767897
推荐阅读
相关标签



