- 1linux 修改22默认端口和扩展其他端口_22端口和其他端口
- 2git@gitee.com: Permission denied (publickey)_git上传了公钥还是permission denied (publickey).
- 3CorelDRAW Graphics Suite2024简体中文版本发布更新介绍_coreldraw 2024 25.1.1.328
- 4【MySQL 基础知识】
- 5如何在 PyTorch 上进行性能分析_vtune和torch profiler
- 6区块链开发者观点:来自 Carbon 的 Nick Pai_hedera postgresql
- 7crt批量增加session模板与脚本_crt.session
- 8解决因jbd2导致mysql性能过低问题
- 9XML的三大解析方式解析_解析xml文件的三种方式
- 10什么是提示词注入攻击?大语言模型为Web安全带来的新风险!
(超全)python图像处理详细解析(3)
赞
踩
23.保存视频每一帧图像
import cv2 from skimage import io import os class AVILoader: def __init__(self, video_file): self.video_file = video_file self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(self.video_file) def __call__(self, frame): self.cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES, frame) ret, frame = self.cap.read() if ret: return cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) else: return None video_file = 'sp.mp4' av_loader = AVILoader(video_file) frames = range(0, 100, 20) output_folder = 'frames' os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True) # 保存每一帧为图像文件 for frame in frames: img = av_loader(frame) if img is not None: filename = os.path.join(output_folder, f'frame_{frame}.jpg') io.imsave(filename, img) io.imshow(img) # 显示图像 io.show() # 显示图像窗口 # 创建图像集合 ic = io.ImageCollection(os.path.join(output_folder, '*.jpg')) # 输出图像集合
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
24.把png图像转换成jpg并保存
from skimage import io, transform, color import numpy as np def convert_gray(f): rgb = io.imread(f) gray = color.rgb2gray(rgb) dst = transform.resize(gray, (256, 256)) return dst # 指定文件夹路径 #data_dir = 'D:\rgzn\wl' # 读取文件夹中的所有png文件 image_dir = 'D:/rgzn/wl' str=image_dir+'/*.png' coll = io.ImageCollection(str, load_func=convert_gray) # 保存处理后的图像 for i in range(len(coll)): # 保存为jpg格式,注意文件路径和文件名的拼接 io.imsave("D:/rgzn/wl1" + np.str(i) + '.jpg', coll[i])
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
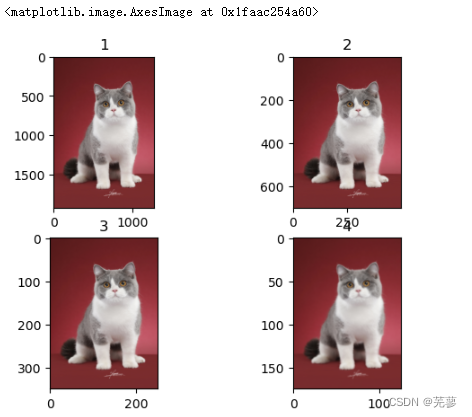
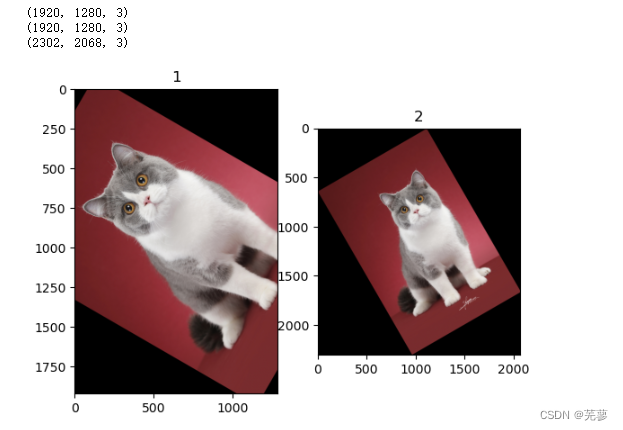
25.改变图像尺寸
改变图片尺寸resize(200,200)
函数格式为:
skimage.transform.resize(image, output_shape)
image: 需要改变尺寸的图片
output_shape: 新的图片尺寸
from skimage import transform,data,io import matplotlib.pyplot as plt img=io.imread('mao.jpg') a=img.shape plt.subplot(2,2,1) plt.title('1') plt.imshow(img) plt.subplot(2,2,2) plt.title('2') dst=transform.resize(img,(700,500)) plt.imshow(dst) plt.subplot(2,2,3) plt.title('3') dst=transform.resize(img,(350,250)) plt.imshow(dst) plt.subplot(2,2,4) plt.title('4') dst=transform.resize(img,(175,125)) plt.imshow(dst)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24

26.改变图像比例
按比例缩放rescale
from skimage import transform,data,io
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img=io.imread('mao.jpg')
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.title('1')
plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.title('2')
#将原始图像放缩到原来的0.1倍
dst=transform.rescale(img,0.1)
plt.imshow(dst)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13

27.旋转图像
旋转 rotate
from skimage import transform,data,io import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 读取图像 img = io.imread('mao.jpg') print(img.shape) # 旋转图像 img1 = transform.rotate(img, 60) print(img1.shape) img2 = transform.rotate(img, 30, resize=True) print(img2.shape) # 使用同一个窗口显示两个旋转后的图像 plt.figure('resize') # 创建子图布局 plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.title('1') plt.imshow(img1, plt.cm.gray) plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.title('2') plt.imshow(img2, plt.cm.gray) # 显示窗口 plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
28.亮度调整
图像亮度与对比度的调整,是放在skimage包的exposure模块里面
对原图像的像素,进行幂运算,得到新的像素值。公式中的g就是gamma值。
如果gamma>1, 新图像比原图像暗
如果gamma<1,新图像比原图像亮
函数格式为:skimage.exposure.adjust_gamma(image, gamma=1)
gamma参数默认为1,原像不发生变化 。
import numpy as np from skimage import transform,exposure,img_as_float import matplotlib.pyplot as plt img=io.imread('iii.jpg') #gam1是原始图像调暗3倍,而gam2是原始图像调亮0.1倍。 gam1= exposure.adjust_gamma(img,3) #调暗 gam2= exposure.adjust_gamma(img,0.1) #调亮 plt.figure('adjust_gamma',figsize=(8,8)) plt.subplot(131) plt.title('1') plt.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray) plt.axis('off') plt.subplot(132) plt.title('2') plt.imshow(gam1,plt.cm.gray) plt.axis('off') plt.subplot(133) plt.title('3') plt.imshow(gam2,plt.cm.gray) plt.axis('off') plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26

29.log对数调整
与gamma相反
import numpy as np from skimage import transform,exposure,img_as_float,io import matplotlib.pyplot as plt img = io.imread('iii.jpg') #使用exposure模块中的adjust_log函数对读取的图像进行对数变换 gam1 = exposure.adjust_log(img) #创建一个名为'adjust_gamma'的图表,设置图表大小为(8,8)。 plt.figure('adjust_gamma',figsize=(8,8)) plt.subplot(121) plt.title('origin image') #图中显示变量img的图像,使用灰度色彩映射。 plt.imshow(img,plt.cm.gray) plt.axis('off') plt.subplot(122) plt.title('log') plt.imshow(gam1,plt.cm.gray) plt.axis('off') plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22

30.判断图像对比度
函数:is_low_contrast(img)
from skimage import exposure,img_as_float,io
img1 = io.imread('liii.png')
#判断图像是否为低对比度图像
result=exposure.is_low_contrast(img1)
print(result)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
运行结果:
False
31.调整强度
(1)强度调节
import numpy as np
from skimage import exposure
#创建一个包含三个元素的一维数组,元素值分别为51, 102, 153,数据类型为无符号8位整数。
image = np.array([51, 102, 153], dtype=np.uint8)
#rescale_intensity函数对输入的图像强度进行重新缩放
mat=exposure.rescale_intensity(image)
print(mat)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
运行结果:
[ 0 127 255]
(2)uint8转float
通过img_as_float()函数将unit8类型转换为float型,实际上还有更简单的方法,就是乘以1.0
import numpy as np
image = np.array([51, 102, 153], dtype=np.uint8)
print(image*1.0)
- 1
- 2
- 3
运行结果:
[ 51. 102. 153.]
float类型的范围是[0,1],因此对float进行rescale_intensity 调整后,范围变为[0,1],而不是[0,255]
import numpy as np
from skimage import exposure
image = np.array([51, 102, 153], dtype=np.uint8)
tmp=image*1.0
#rescale_intensity函数对输入的图像强度进行重新缩放
mat=exposure.rescale_intensity(tmp)
print(mat)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
运行结果:
[0. 0.5 1. ]
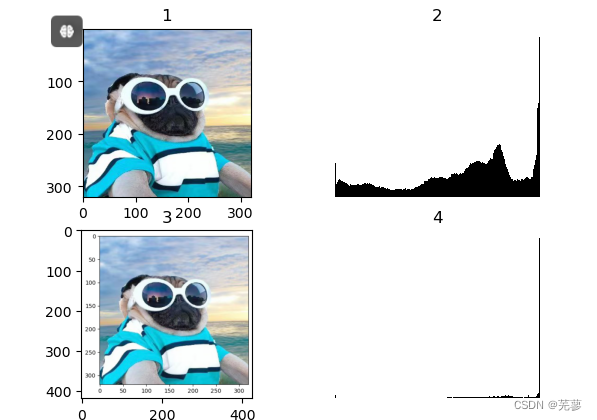
32.绘制直方图和均衡化
绘图都可以调用matplotlib.pyplot库来进行,其中的hist函数可以直接绘制直方图。
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(arr, bins=10, normed=0, facecolor='black', edgecolor='black',alpha=1,histtype='bar')
- 1
hist的参数非常多,但常用的就这六个,只有第一个是必须的,后面四个可选
arr: 需要计算直方图的一维数组
bins: 直方图的柱数,可选项,默认为10
normed: 是否将得到的直方图向量归一化。默认为0
facecolor: 直方图颜色
edgecolor: 直方图边框颜色
alpha: 透明度
histtype: 直方图类型,‘bar’, ‘barstacked’, ‘step’, ‘stepfilled’
from skimage import io import matplotlib.pyplot as plt img = io.imread('iii.jpg') img1 = io.imread('liii.png') plt.figure('hist') plt.subplot(221) plt.title('1') plt.imshow(img) plt.subplot(222) plt.title('2') #绘制图像直方图 n, bins, patches = plt.hist(img.ravel(), bins=256, density=True, edgecolor='None', facecolor='black') plt.axis('off') plt.subplot(223) plt.title('3') plt.imshow(img1) plt.subplot(224) plt.title('4') #绘制图像直方图 n, bins, patches = plt.hist(img1.ravel(), bins=256, density=True, edgecolor='None', facecolor='black') plt.axis('off') plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
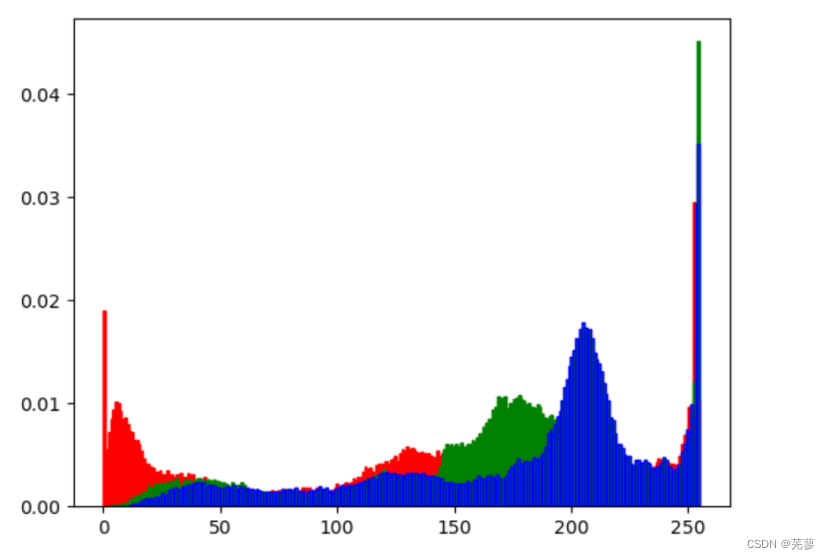
33.彩色图片三通道直方图
from skimage import io
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img=io.imread('iii.jpg')
ar=img[:,:,0].flatten()
plt.hist(ar,bins=256,density=True,facecolor='r',edgecolor='r')
ag=img[:,:,1].flatten()
plt.hist(ag,bins=256,density=True,facecolor='g',edgecolor='g')
ab=img[:,:,2].flatten()
plt.hist(ab,bins=256,density=True,facecolor='g',edgecolor='b')
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11