- 1unity 内存释放分析_unloadunusedassets
- 2激活函数总结(Sigmoid、Tanh、Relu、LeakyRelu、pRelu、Elu、softplus)
- 3怎么复制一台虚拟机到另外一台电脑上_已有ubuntu虚拟机
- 4ChatGPT科研阅读论文应用插件(txyz.ai)使用初探
- 5node.js常用命令
- 6Apollo规划代码ros移植-混合A*_apollo混合a*算法
- 7【TypeScript】TS自定义类型之对象属性必选、对象属性可选_ts 可选
- 8MATLAB练习题:质数(Prime number)的判断
- 9聊天机器人-意图识别类,开源库推荐_聊天机器人意图识别数据库
- 10Anaconda默认安装在C:\Users\xxx\.conda\envs中_anaconda 默认安装路径
基于ROS的OMPL库RRT*算法代码学习_extract the robot's (x,y,z) position from its stat
赞
踩
本文是在学习路径规划算法中的一篇学习记录,由于对c++掌握粗浅,将整个代码进行了详细的梳理,由于代码中有很多是之前梳理过的《基于ROS的A*算法代码学习》中的,对本文graph_searcher.h注释可参考上一篇的Astar_searcher.h; node.h注释可参考上一篇的node.h; graph_searcher.cpp注释可参考Astar_searcher.cpp; waypoint_generator.cpp可参考上一篇的waypoint_generator.cpp.本文在参考其他博主总结的基础上,整理出了多种代码实现的方法.
(代码注释中英夹杂,英文注释是原来作者的注释,中文注释是本人后来添加的)
过程演示
1.编译功能包.

2.Ctrl+Shift+t新建窗口打开roscore.

3.Ctrl+Shift+t新建窗口打开rviz.
记得要source devel/setup.sh,告诉这个窗口你功能包的位置,否则3d Nav Goal插件会找不到.

4.在rviz中打开demo.rviz(路径src/grid_path_searcher/launch/rviz_config).

5.Ctrl+Shift+t新建窗口加载地图.
记得source.

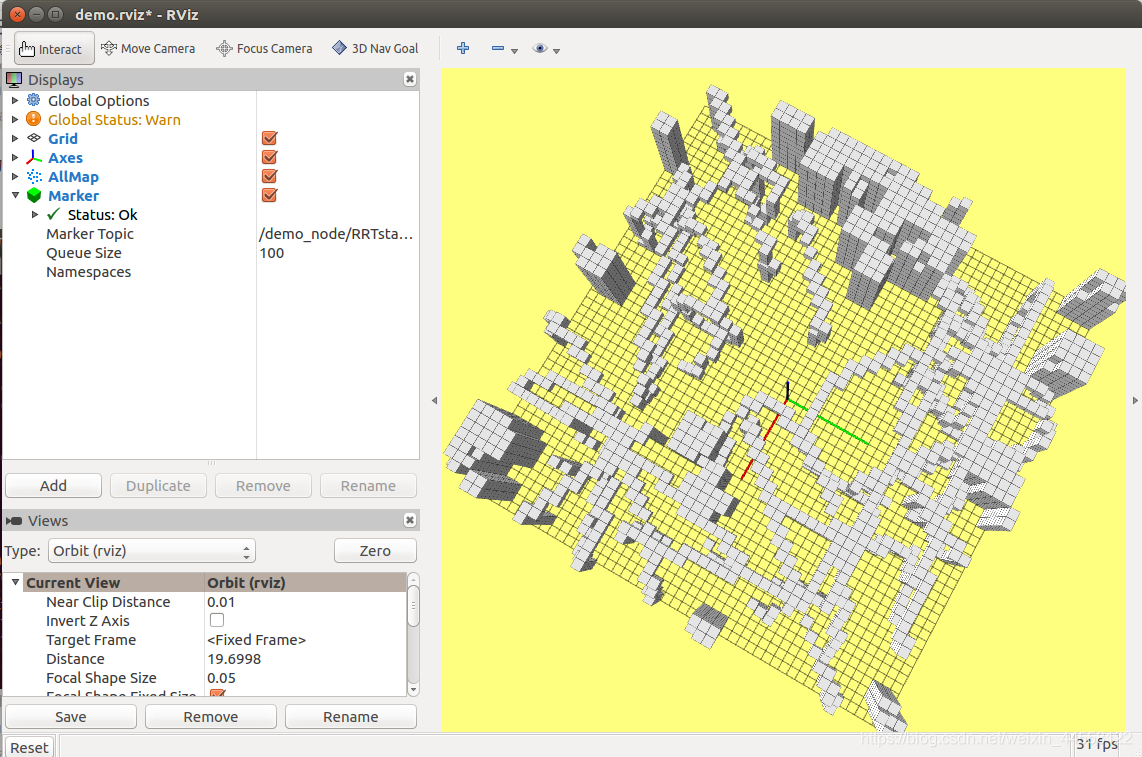
6.RRT*路径搜索.
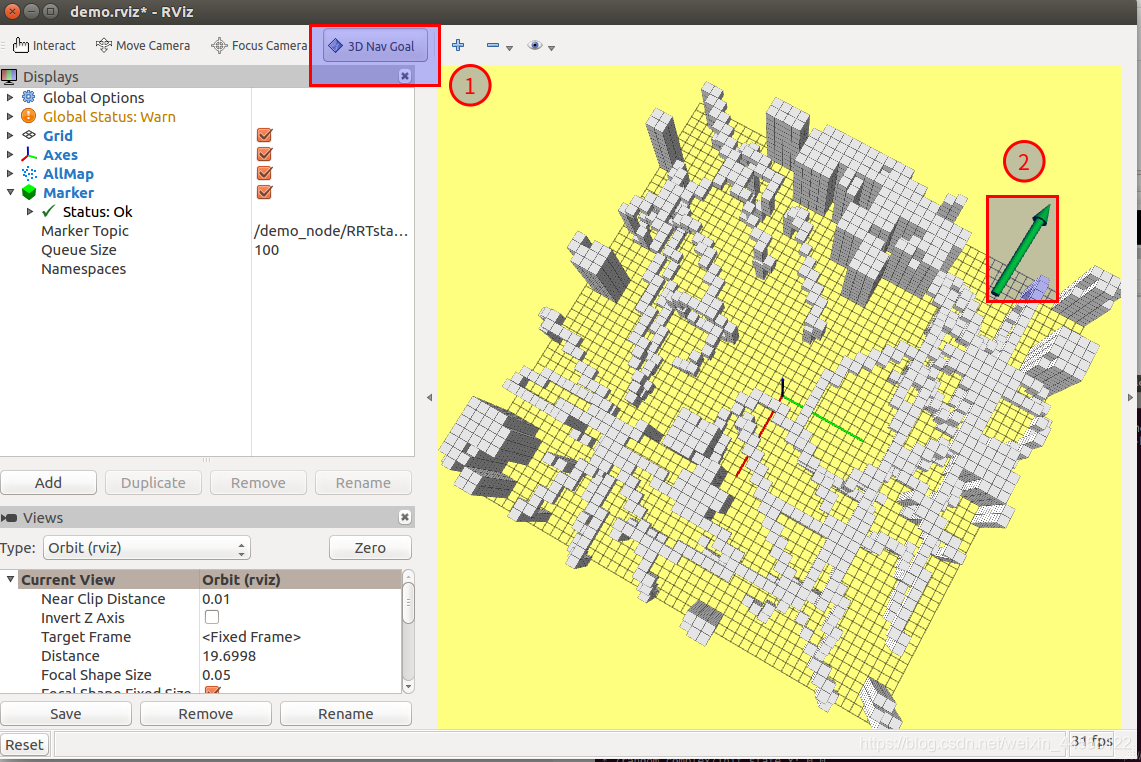
下面是结果

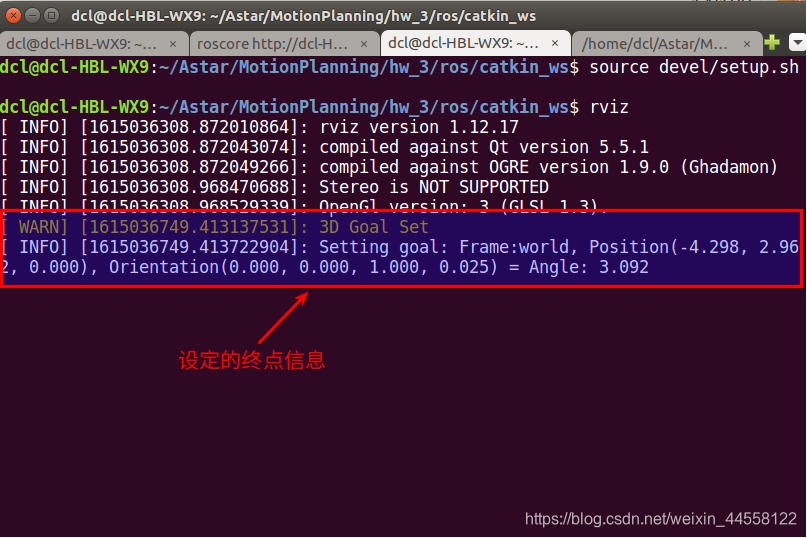
这是终端里的信息

ROS包

主要程序文件demo_node.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <math.h> #include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <ros/ros.h> #include <ros/console.h> #include <sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h> #include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h> #include <nav_msgs/Path.h> #include <geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h> #include <visualization_msgs/MarkerArray.h> #include <visualization_msgs/Marker.h> #include <ompl/config.h> #include <ompl/base/StateSpace.h> #include <ompl/base/Path.h> #include <ompl/base/spaces/RealVectorBounds.h> #include <ompl/base/spaces/RealVectorStateSpace.h> #include <ompl/base/StateValidityChecker.h> #include <ompl/base/OptimizationObjective.h> #include <ompl/base/objectives/PathLengthOptimizationObjective.h> #include <ompl/geometric/planners/rrt/RRTstar.h> #include <ompl/geometric/SimpleSetup.h> #include "graph_searcher.h" #include "backward.hpp" using namespace std; using namespace Eigen; namespace ob = ompl::base; namespace og = ompl::geometric; namespace backward { backward::SignalHandling sh; } // simulation param from launch file double _resolution, _inv_resolution, _cloud_margin; double _x_size, _y_size, _z_size; // useful global variables bool _has_map = false; Vector3d _start_pt; Vector3d _map_lower, _map_upper; int _max_x_id, _max_y_id, _max_z_id; // ros related ros::Subscriber _map_sub, _pts_sub; ros::Publisher _grid_map_vis_pub, _RRTstar_path_vis_pub; RRTstarPreparatory * _RRTstar_preparatory = new RRTstarPreparatory(); void rcvWaypointsCallback(const nav_msgs::Path & wp); void rcvPointCloudCallBack(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 & pointcloud_map); void pathFinding(const Vector3d start_pt, const Vector3d target_pt); void visRRTstarPath(vector<Vector3d> nodes ); void rcvWaypointsCallback(const nav_msgs::Path & wp) { if( wp.poses[0].pose.position.z < 0.0 || _has_map == false ) return; Vector3d target_pt; target_pt << wp.poses[0].pose.position.x, wp.poses[0].pose.position.y, wp.poses[0].pose.position.z; ROS_INFO("[node] receive the planning target"); pathFinding(_start_pt, target_pt); } void rcvPointCloudCallBack(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 & pointcloud_map) { if(_has_map ) return; pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud; pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_vis; sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 map_vis; pcl::fromROSMsg(pointcloud_map, cloud); if( (int)cloud.points.size() == 0 ) return; pcl::PointXYZ pt; for (int idx = 0; idx < (int)cloud.points.size(); idx++) { pt = cloud.points[idx]; // set obstalces into grid map for path planning _RRTstar_preparatory->setObs(pt.x, pt.y, pt.z); // for visualize only Vector3d cor_round = _RRTstar_preparatory->coordRounding(Vector3d(pt.x, pt.y, pt.z)); pt.x = cor_round(0); pt.y = cor_round(1); pt.z = cor_round(2); cloud_vis.points.push_back(pt); } cloud_vis.width = cloud_vis.points.size(); cloud_vis.height = 1; cloud_vis.is_dense = true; pcl::toROSMsg(cloud_vis, map_vis); map_vis.header.frame_id = "/world"; _grid_map_vis_pub.publish(map_vis); _has_map = true; } // Our collision checker. For this demo, our robot's state space class ValidityChecker : public ob::StateValidityChecker { public: // 单冒号(:)的作用是表示后面是初始化列表,可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/lusirking/article/details/83988421 // ob::StateValidityChecker父类构造的时候要传入一个状态空间信息(si) ValidityChecker(const ob::SpaceInformationPtr& si) : ob::StateValidityChecker(si) {} // Returns whether the given state's position overlaps the // circular obstacle bool isValid(const ob::State* state) const { // We know we're working with a RealVectorStateSpace in this // example, so we downcast state into the specific type. const ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType* state3D = state->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>(); /** * * STEP 1: Extract the robot's (x,y,z) position from its state * * */ auto x = (*state3D)[0]; auto y = (*state3D)[1]; auto z = (*state3D)[2]; return _RRTstar_preparatory->isObsFree(x, y, z); } }; // Returns a structure representing the optimization objective to use // for optimal motion planning. This method returns an objective which // attempts to minimize the length in configuration space of computed // paths. ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr getPathLengthObjective(const ob::SpaceInformationPtr& si) { return ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr(new ob::PathLengthOptimizationObjective(si)); } ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr getThresholdPathLengthObj(const ob::SpaceInformationPtr& si) { ob::OptimizationObjectivePtr obj(new ob::PathLengthOptimizationObjective(si)); obj->setCostThreshold(ob::Cost(1.51)); return obj; } void pathFinding(const Vector3d start_pt, const Vector3d target_pt) { // ompl使用一般步骤: // 1.实例化一个状态空间; // 2.实例化一个控制空间(可选); // 3.实例化一个空间信息类; // 4.实例化一个问题描述; // 5.实例化一个规划器; // 6.路径简化器. // 不熟悉ompl库的使用流程可以参考下面的网站简单学习一下: // https://blog.csdn.net/wjydym/article/details/104593543 // Construct the robot state space in which we're planning. // 构造一个三维的状态空间 ob::StateSpacePtr space(new ob::RealVectorStateSpace(3)); // Set the bounds of space to be in [0,1]. // 边界条件设置 ob::RealVectorBounds bounds(3); bounds.setLow(0, - _x_size * 0.5); bounds.setLow(1, - _y_size * 0.5); bounds.setLow(2, 0.0); bounds.setHigh(0, + _x_size * 0.5); bounds.setHigh(1, + _y_size * 0.5); bounds.setHigh(2, _z_size); // 将设置的边界赋予状态空间space,其中as的作用是类型转换 space->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace>()->setBounds(bounds); // Construct a space information instance for this state space // 构造状态空间信息SpaceInformation,后面的一些操作需要用到状态空间信息 ob::SpaceInformationPtr si(new ob::SpaceInformation(space)); // Set the object used to check which states in the space are valid // 为状态空间设置状态检查函数StateValidChecker,ValidityChecker肯定要知道状态的信息,也就是si si->setStateValidityChecker(ob::StateValidityCheckerPtr(new ValidityChecker(si))); // 载入设置 si->setup(); // Set our robot's starting state // 设定起点 ob::ScopedState<> start(space); /** * * STEP 2: Finish the initialization of start state * * */ // todo can I simply it? // 方法1: // start[0] = (&start_pt)->operator[](0) ; // start[1] = (&start_pt)->operator[](1) ; // start[2] = (&start_pt)->operator[](2) ; // 方法2: // start[0] = start_pt(0); // start[1] = start_pt(1); // start[2] = start_pt(2); // 方法3: // start->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->values[0] = start_pt(0); // start->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->values[1] = start_pt(1); // start->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->values[2] = start_pt(2); // 方法4: start->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](0) = start_pt(0); start->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](1) = start_pt(1); start->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](2) = start_pt(2); // Set our robot's goal state // 设定终点 ob::ScopedState<> goal(space); /** * * STEP 3: Finish the initialization of goal state * * */ // 方法1: // goal[0] = (&target_pt)->operator[](0) ; // goal[1] = (&target_pt)->operator[](1) ; // goal[2] = (&target_pt)->operator[](2) ; // 方法2: // goal[0] = target_pt(0); // goal[1] = target_pt(1); // goal[2] = target_pt(2); // 方法3: // goal->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->values[0] = target_pt(0); // goal->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->values[1] = target_pt(1); // goal->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->values[2] = target_pt(2); // 方法4: goal->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](0) = target_pt(0); goal->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](1) = target_pt(1); goal->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](2) = target_pt(2); // Create a problem instance /** * * STEP 4: Create a problem instance, please define variable as pdef * * */ // 构造问题实例,传入之前构造的状态空间信息SpaceInformation auto pdef(std::make_shared<ob::ProblemDefinition>(si)); // Set the start and goal states // 为问题实例设置起点和终点 pdef->setStartAndGoalStates(start, goal); // Set the optimization objective /** * * STEP 5: Set the optimization objective, the options you can choose are defined earlier: getPathLengthObjective() and getThresholdPathLengthObj() * * */ // 该语句为本问题设置了一个长度优化器,来自于ompl库自带的路径长度优化类 // 方法1: // pdef->setOptimizationObjective(getPathLengthObjective(si)); // 方法2: pdef->setOptimizationObjective(std::make_shared<ob::PathLengthOptimizationObjective>(si)); // Construct our optimizing planner using the RRTstar algorithm. /** * * STEP 6: Construct our optimizing planner using the RRTstar algorithm, please define varible as optimizingPlanner * * */ // 构造一个使用RRTstar算法对状态空间进行规划的规划器 ob::PlannerPtr optimizingPlanner(new og::RRTstar(si)); // Set the problem instance for our planner to solve // 传入问题实例给规划器 optimizingPlanner->setProblemDefinition(pdef); // 调用setup()将设置载入。 optimizingPlanner->setup(); // attempt to solve the planning problem within one second of // planning time ob::PlannerStatus solved = optimizingPlanner->solve(1.0); // 如果有解,就将得到的路径压入堆栈,将路径在rviz中显示出来 if (solved) { // get the goal representation from the problem definition (not the same as the goal state) // and inquire about the found path og::PathGeometric* path = pdef->getSolutionPath()->as<og::PathGeometric>(); vector<Vector3d> path_points; for (size_t path_idx = 0; path_idx < path->getStateCount (); path_idx++) { const ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType *state = path->getState(path_idx)->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>(); /** * * STEP 7: Trandform the found path from path to path_points for rviz display * * */ // 方法1: // auto x = state->operator[](0); // auto y = state->operator[](1); // auto z = state->operator[](2); // 方法2: // auto x = (*state)[0]; // auto y = (*state)[1]; // auto z = (*state)[2]; // 方法3: auto x = state->values[0]; auto y = state->values[1]; auto z = state->values[2]; Vector3d temp_mat(x,y,z); path_points.push_back(temp_mat); } visRRTstarPath(path_points); } } int main(int argc, char** argv) { ros::init(argc, argv, "demo_node"); ros::NodeHandle nh("~"); _map_sub = nh.subscribe( "map", 1, rcvPointCloudCallBack ); _pts_sub = nh.subscribe( "waypoints", 1, rcvWaypointsCallback ); _grid_map_vis_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("grid_map_vis", 1); _RRTstar_path_vis_pub = nh.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("RRTstar_path_vis",1); nh.param("map/cloud_margin", _cloud_margin, 0.0); nh.param("map/resolution", _resolution, 0.2); nh.param("map/x_size", _x_size, 50.0); nh.param("map/y_size", _y_size, 50.0); nh.param("map/z_size", _z_size, 5.0 ); nh.param("planning/start_x", _start_pt(0), 0.0); nh.param("planning/start_y", _start_pt(1), 0.0); nh.param("planning/start_z", _start_pt(2), 0.0); _map_lower << - _x_size/2.0, - _y_size/2.0, 0.0; _map_upper << + _x_size/2.0, + _y_size/2.0, _z_size; _inv_resolution = 1.0 / _resolution; _max_x_id = (int)(_x_size * _inv_resolution); _max_y_id = (int)(_y_size * _inv_resolution); _max_z_id = (int)(_z_size * _inv_resolution); _RRTstar_preparatory = new RRTstarPreparatory(); _RRTstar_preparatory -> initGridMap(_resolution, _map_lower, _map_upper, _max_x_id, _max_y_id, _max_z_id); ros::Rate rate(100); bool status = ros::ok(); while(status) { ros::spinOnce(); status = ros::ok(); rate.sleep(); } delete _RRTstar_preparatory; return 0; } void visRRTstarPath(vector<Vector3d> nodes ) { visualization_msgs::Marker Points, Line; Points.header.frame_id = Line.header.frame_id = "world"; Points.header.stamp = Line.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); Points.ns = Line.ns = "demo_node/RRTstarPath"; Points.action = Line.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD; Points.pose.orientation.w = Line.pose.orientation.w = 1.0; Points.id = 0; Line.id = 1; Points.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::POINTS; Line.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::LINE_STRIP; Points.scale.x = _resolution/2; Points.scale.y = _resolution/2; Line.scale.x = _resolution/2; //points are green and Line Strip is blue Points.color.g = 1.0f; Points.color.a = 1.0; Line.color.b = 1.0; Line.color.a = 1.0; geometry_msgs::Point pt; for(int i = 0; i < int(nodes.size()); i++) { Vector3d coord = nodes[i]; pt.x = coord(0); pt.y = coord(1); pt.z = coord(2); Points.points.push_back(pt); Line.points.push_back(pt); } _RRTstar_path_vis_pub.publish(Points); _RRTstar_path_vis_pub.publish(Line); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
参考引用
demo_node.cpp注释参考了https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43795921/article/details/102674696.
代码来源:https://github.com/KailinTong/Motion-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots/tree/master/hw_3.
相关知识来源:深蓝学院<<移动机器人运动规划>>



