- 12023版教你pycharm如何配置python环境_pycharm选择环境
- 2AI绘画之三_StableDiffusion_界面操作_sd-webui-roop 换脸不生效
- 3ChatGPT:AI在编程领域的革新——改变代码创作方式
- 4Invalid keystore format 报错解决_db2 ssl invaild keystore format
- 5安卓面试题多线程 61-65
- 6Vue3 ElementPlus Admin
- 7Android Studio 配置国内镜像源、HTTP代理(详细步骤)_android studio 国内源
- 8Huawei Cloud EulerOS(Linux)常用命令汇总_euleros系统常用指令
- 9好记性不如烂笔头--校园网下Parsec远程控制软件的使用_parsec校园网
- 10c语言程序设计课程测试试卷,2014年韩山师范学院本科插班生考试《C语言程序设计》课程试卷...
面试官再问你什么是反射,就把这篇文章发给他!_什么是反射 面试
赞
踩
1 什么是反射?
反射是一种可以间接操作目标对象的机制。当使用反射时,JVM 在运行的时候才动态加载类,对于任意类,知道其属性和方法,并不需要提前在编译期知道运行的对象是谁,允许运行时的 Java 程序获取类的信息并对其进行操作。
对象的类型在编译期就可以确定,但程序运行时可能需要动态加载一些类(之前没有用到,故没有加载进 jvm),使用反射可以在运行期动态生成对象实例并对其进行操作。
2 反射的原理
在获取到 Class 对象之后,反向获取和操作对象的各种信息。
3 反射的使用
我们先建一个类
public class People { private int age; private String name; private People() { age = 18; name = "Tony"; } public People(int age,String name) { this.age = age; this.name = name; } private void print() { System.out.println(this.toString()); } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
获得 Class 对象
获取 Class 对象有三种方法:
- 调用对象的 getClass 方法
- 任何数据类型都拥有的 class 属性
- 通过 Class 类的静态方法 forName(String className) 进行调用,该方法最常用
在运行期间,一个类只能有一个 Class 对象产生
获取类的构造函数
通过 getDeclaredConstructors 方法我们可以得到类的所有构造方法。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Class c = People.class; //得到类的所有构造方法 Constructor[] constructors = c.getDeclaredConstructors(); for(int i = 0; i < constructors.length; i++) { //获得构造方法的类型 System.out.println("构造方法的类型:" + Modifier.toString(constructors[i].getModifiers())); //获得构造方法的所有参数 Class[] parametertypes = constructors[i].getParameterTypes(); for (int j = 0; j < parametertypes.length; j++) { System.out.print(parametertypes[j].getName() + " "); } System.out.println(""); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
返回结果如下:

通过该方法,我们可以获取类中所有构造方法和构造方法中的参数。
获取类中特定的构造方法
在 getDeclaredConstructor 方法中,我们未传入参数,表示希望得到类的特定构造方法。同时在代码中要进行异常捕获,因为可能不存在对应的构造方法。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ Class c = People.class; Constructor constructor; try { //得到类的特定构造方法,无参构造方法不传参数 constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(); //获得构造方法的类型 System.out.println("构造方法的类型:" + Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers())); //获得构造方法的所有参数 System.out.println("构造方法的参数:"); Class[] parametertypes = constructor.getParameterTypes(); for (int j = 0; j < parametertypes.length; j++) { System.out.print(parametertypes[j].getName() + " "); } } catch (Exception e) {} } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
结果如下:
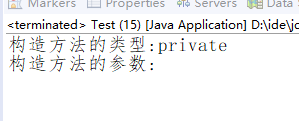
如果我们想得到这个构造函数
public People(int age,String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
在 getDeclaredConstructor 方法中,我们可以传入一个 Class 数组,里面包含 int 和 java.lang.String 的 Class 对象。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ Class c = People.class; Class[] p = {int.class,String.class}; Constructor constructor; try { //得到类的特定构造方法,这次传入int和java.lang.String两个参数 constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(p); //获得构造方法的类型 System.out.println("构造方法的类型:" + Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers())); //获得构造方法的所有参数 System.out.println("构造方法的参数:"); Class[] parametertypes = constructor.getParameterTypes(); for (int j = 0; j < parametertypes.length; j++) { System.out.print(parametertypes[j].getName() + " "); } } catch (Exception e) {} } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
结果如下:

调用构造方法
在上面。我们已经学习了如何获取类中特定的构造方法,在这里,我们不仅要获取,还要对类的构造方法进行调用。
我们先修改类的两个构造函数,分别加上一打印语句,代码如下:
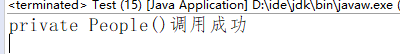
private People() {
age = 18;
name = "Tony";
System.out.println("private People()调用成功");
}
public People(int age,String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
System.out.println("public People(int age,String name)调用成功");
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
我们先使用这个 public 访问类型的构造函数
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Class c = People.class;
Class[] p = {int.class,String.class};
Constructor constructor;
try {
constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(p);
//创建实例
constructor.newInstance(10,"HaWei");
} catch (Exception e) {}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
结果如下

那么我们如何通过反射调用类的 private 访问类型的构造函数呢?其实大体与上面一样,只是我们需要设置constructors.setAccessible(true);罢了。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Class c = People.class;
Constructor constructor;
try {
//获取类的无参构造函数
constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor();
constructor.setAccessible(true);
//创建实例
constructor.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
结果如下
调用类的私有方法
我们尝试调用一下类的这个私有方法
private void print() {
System.out.println(this.toString());
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
关于调用方法,我们可以通过 getDeclaredMethod 来获取该方法,然后通过调用 invoke 执行。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ Class c = People.class; Constructor constructor; try { //获取类的无参构造函数 constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(); constructor.setAccessible(true); //创建实例 People obj = (People) constructor.newInstance(); //获取需要调用的方法,需要两个参数,第一个参数是方法名,第二个参数是参数类型(本例不需要传入参数) Method method = c.getDeclaredMethod("print"); method.setAccessible(true); //调用方法,需要两个参数,第一个参数是类的实例,第二个参数是方法参数 method.invoke(obj); } catch (Exception e) {} } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
结果如下:

获取类的私有字段并修改值
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ Class c = People.class; Constructor constructor; try { //获取类的无参构造函数 constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(); constructor.setAccessible(true); //创建实例 People obj = (People) constructor.newInstance(); //修改之前的name字段值 System.out.println("修改之前:" + obj.getName()); //获取类的name字段 Field field = c.getDeclaredField("name"); field.setAccessible(true); //修改类的私有字段 field.set(obj,"HaWei"); //修改之后的name字段值 System.out.println("修改之后:" + obj.getName()); } catch (Exception e) {} } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
结果如下:

4 反射的优点
可以在运行时获得类的内容,对于 Java 这种先编译再运行的语言,能够让我们很方便的写出灵活的代码,这些代码可以在运行时装配,无需在组件之间进行源代码的链接,更加容易实现面向对象。
5 反射的缺点
- 会消耗一定的系统资源
- 反射调用方法时可以忽略权限检查,因此可能会破坏封装性从而导致安全问题
6 反射的用途
- 进行反编译,把 .class 文件变为 .java 文件
- 通过反射机制访问 java 对象的属性,方法
- 开发各种通用框架(例如 Spring),许多框架都是配置化的,为了保证框架的通用性,可能需要根据配置文件加载不同的类或者对象,调用不同的方法,这个时候就必须使用到反射了,运行时动态加载需要的加载的对象
- 可以通过反射运行配置文件内容,利用反射和配置文件可以使应用程序更新时,对源码无需进行任何修改,只需要将新类发送给客户端,并修改配置文件即可
- 可以通过反射越过泛型检查,泛型使用在编译期,编译过后泛型擦除,反射作用在运行期,所以是可以通过反射越过泛型检查的



