热门标签
热门文章
- 1运行git命令报错与xcode相关_error: you dont have xcode command line tools, but
- 2ARP协议详解,小白易懂_发送数据包的时候为什么需要知道目标地址的物理地址
- 37z命令行操作指南之最快压缩_-tzip
- 4python实现BP神经网络进行预测和误差分析(附源代码)_bp神经网络预测模型python
- 5手机助手无法启动备份服务器,华为手机助手备份数据无法恢复怎么办?华为手机助手备份数据无法恢复教程...
- 6Android 使用DataBinding 报错NullPointerException_com.android.databinding:compiler
- 7精讲▍一文读懂Python,Python为什么那么火,优缺点是啥?
- 8深度学习100例 | 第41天-卷积神经网络(CNN):UrbanSound8K音频分类(语音识别)_声音分类神经网络
- 9Pycharm使用(1)Pycharm中运行Python代码的几种方式_pycharm解析python脚本运行
- 10xshell连接android设备_android-x86_64-9.0-r2怎么xshell连接
当前位置: article > 正文
yolov5 obb旋转框 tensorrt部署_yolov5obb
作者:小蓝xlanll | 2024-04-06 04:27:31
赞
踩
yolov5obb
yolov5-obb tensorRT部署代码结合王新宇和fish-kong两者的代码,可以多batch批量检测旋转框
yolov5旋转框检测: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42754919/article/details/134145174
1.生成engine文件
首先需要将pt文件转换成wts文件,执行gen_wts.py文件,修改上面两个文件路径即可。
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Convert .pt file to .wts')
parser.add_argument('-w', '--weights', required=True, help='Input weights (.pt) file path (required)')
parser.add_argument('-o', '--output', help='Output (.wts) file path (optional)')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
修改yololayer.h中CLASS_NUM,INPUT_H和INPUT_W ,根据训练模型时的图像尺寸修改这三个参数。
static constexpr int MAX_OUTPUT_BBOX_COUNT = 1000;
static constexpr int CLASS_NUM = 2 + 180; // 类别数量 + 180个角度
static constexpr int INPUT_H = 128; //
static constexpr int INPUT_W = 1024; //
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
修改yolov5.cpp文件,主要是BATCH_SIZE ,确定几张图一起推理
#define USE_FP16 // set USE_INT8 or USE_FP16 or USE_FP32 设置量化
#define DEVICE 0 // GPU id
#define NMS_THRESH 0.4
#define CONF_THRESH 0.1
#define BATCH_SIZE 4
#define MAX_IMAGE_INPUT_SIZE_THRESH 3000 * 3000 // ensure it exceed the maximum size in the input images !
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
修改完毕执行如下操作:
cd build
rm -r *
cmake ..
make
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
执行完毕build文件夹内生成一个可执行文件yolov5,后续使用此文件生成engine和检测图像。
# ./yolov5 -s wts文件路径 engine文件路径 yolov5模型类型,s,n,l,m
./yolov5 -s ../wts ../engine n
- 1
- 2
等待生成engine文件。
2.检测图像
主要是解码和nms
yololayer.cu在王新宇代码的基础上增加了旋转角度的解码
__global__ void CalDetection(const float *input, float *output, int noElements, const int netwidth, const int netheight, int maxoutobject, int yoloWidth, int yoloHeight, const float anchors[CHECK_COUNT * 2], int classes, int outputElem) { int idx = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x * blockIdx.x; if (idx >= noElements) return; int total_grid = yoloWidth * yoloHeight; int bnIdx = idx / total_grid; idx = idx - total_grid * bnIdx; int info_len_i = 5 + classes; const float *curInput = input + bnIdx * (info_len_i * total_grid * (CHECK_COUNT)); for (int k = 0; k < CHECK_COUNT; ++k) { float box_prob = Logist(curInput[idx + k * info_len_i * total_grid + 4 * total_grid]); if (box_prob < IGNORE_THRESH) continue; int class_id = 0; float max_cls_prob = 0.0; for (int i = 5; i < info_len_i; ++i) { float p = Logist(curInput[idx + k * info_len_i * total_grid + i * total_grid]); if (p > max_cls_prob) { max_cls_prob = p; class_id = i - 5; } } // 解码:找到最大角度的索引作为角度值 int angle_id = 0; float max_angle = 0.0; for (int i = info_len_i - 180; i < info_len_i; ++i) { float p = Logist(curInput[idx + k * info_len_i * total_grid + i * total_grid]); if (p > max_angle) { max_angle = p; angle_id = i - (info_len_i - 180); } } float *res_count = output + bnIdx * outputElem; int count = (int)atomicAdd(res_count, 1); if (count >= maxoutobject) return; char *data = (char *)res_count + sizeof(float) + count * sizeof(Detection); Detection *det = (Detection *)(data); int row = idx / yoloWidth; int col = idx % yoloWidth; // Location // pytorch: // y = x[i].sigmoid() // y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i].to(x[i].device)) * self.stride[i] # xy // y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh // X: (sigmoid(tx) + cx)/FeaturemapW * netwidth det->bbox[0] = (col - 0.5f + 2.0f * Logist(curInput[idx + k * info_len_i * total_grid + 0 * total_grid])) * netwidth / yoloWidth; det->bbox[1] = (row - 0.5f + 2.0f * Logist(curInput[idx + k * info_len_i * total_grid + 1 * total_grid])) * netheight / yoloHeight; // W: (Pw * e^tw) / FeaturemapW * netwidth // v5: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/471 det->bbox[2] = 2.0f * Logist(curInput[idx + k * info_len_i * total_grid + 2 * total_grid]); det->bbox[2] = det->bbox[2] * det->bbox[2] * anchors[2 * k]; det->bbox[3] = 2.0f * Logist(curInput[idx + k * info_len_i * total_grid + 3 * total_grid]); det->bbox[3] = det->bbox[3] * det->bbox[3] * anchors[2 * k + 1]; det->conf = box_prob * max_cls_prob; det->angle_id = angle_id; det->class_id = class_id; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
common.hpp主要修改在nms,使用opencv cv::RotatedRect存放旋转角信息,使用rotatedRectangleIntersection获取旋转框重叠面积
void nms(std::vector<Yolo::BoxInfo> &res, float *output, float conf_thresh, float nms_thresh = 0.5) { int det_size = sizeof(Yolo::Detection) / sizeof(float); // std::cout << "det_size: " << det_size << std::endl; // std::cout << "output[0]: " << output[0] << std::endl; std::map<float, std::vector<Yolo::BoxInfo>> m; for (int i = 0; i < output[0] && i < Yolo::MAX_OUTPUT_BBOX_COUNT; i++) { if (output[1 + det_size * i + 4] <= conf_thresh) // output[0]表示当前图像里面有多少个检测目标 continue; Yolo::Detection det; memcpy(&det, &output[1 + det_size * i], det_size * sizeof(float)); if (m.count(det.class_id) == 0) m.emplace(det.class_id, std::vector<Yolo::BoxInfo>()); float cx = det.bbox[0]; float cy = det.bbox[1]; float w = det.bbox[2]; float h = det.bbox[3]; float conf = det.conf; int class_idx = det.class_id; float angle = 90 - det.angle_id; RotatedRect box = RotatedRect(Point2f(cx, cy), Size2f(w, h), angle); // 按类别存放box, socre, cls m[det.class_id].push_back(Yolo::BoxInfo{box, conf, class_idx}); } // std::cout << "m[det.class_id]: " << m[0].size() << std::endl; for (auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) { auto &dets = it->second; std::sort(dets.begin(), dets.end(), cmp); for (size_t m = 0; m < dets.size(); ++m) { auto &item = dets[m]; res.push_back(item); for (size_t n = m + 1; n < dets.size(); ++n) { float item_area = item.box.size.area(); float dets_area = dets[n].box.size.area(); std::vector<Point2f> intersectingRegion; rotatedRectangleIntersection(item.box, dets[n].box, intersectingRegion); if (intersectingRegion.empty()) { continue; } float inter = contourArea(intersectingRegion); float iou = inter / (item_area + dets_area - inter); if (iou > nms_thresh) { dets.erase(dets.begin() + n); --n; } } } } // std::cout << "res: " << res.size() << std::endl; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
然后执行:
// ./yolov5 -d engien 文件 图像路径
./yolov5 -d ../engine ../image
- 1
- 2
执行完毕生成推理结果。
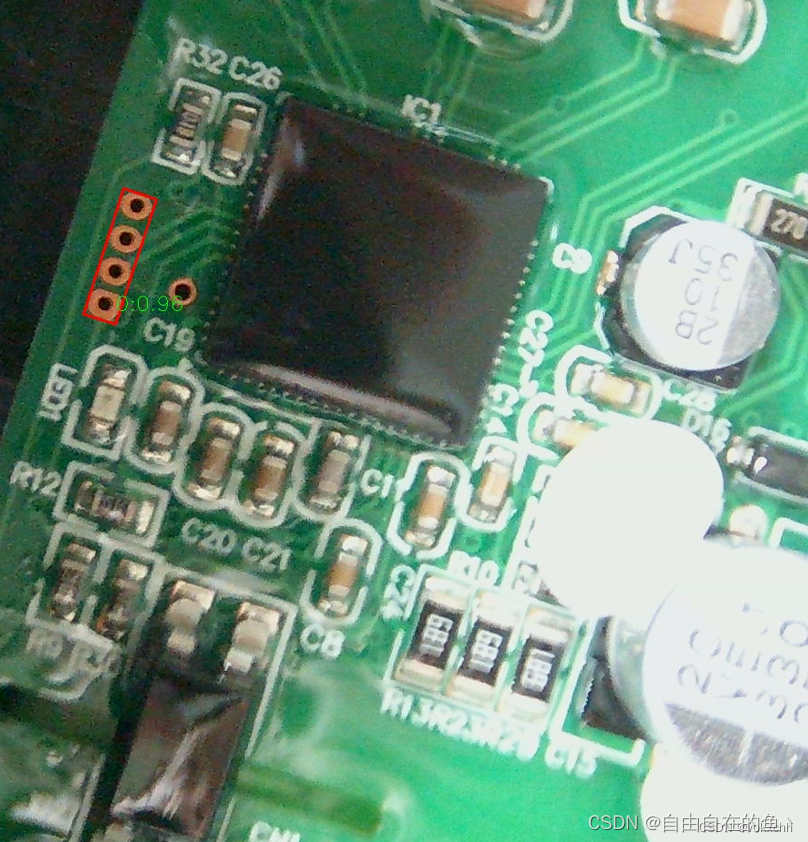
3.代码
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1m_k8Bwy3RIrszF06iGsy4g
提取码:1111
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小蓝xlanll/article/detail/369794
推荐阅读
相关标签



