- 1【华为云技术分享】漫谈LiteOS-Huawei_IoT_Link_SDK_OTA 开发指导_华为wi-fi设备ota流程
- 2Echarts控制台告警Can't get dom width or height
- 3深入Facebook的世界:探索数字化社交的无限可能性
- 4Python实现循环的最快方式(for、while等速度对比)_pyhon一个循环比较
- 5HyperDock 1.8.0.10(Dock优化工具)
- 6appium使用过程中的踩坑集_no route found for /wd/hub/session
- 7【ChatGPT】开源软件:ChatALL —— 我是 GitHub 榜一!(PS: 其实,小编本地 build run 了一下,就是一个组装 Chat UI ……)
- 8[LangChain核心模块]模型的输入和输出->Prompts
- 9鸿蒙设备学习|初识BearPi-HM Micro开发板
- 10荣耀手机现在是鸿蒙,荣耀手机也要升级鸿蒙,更新名单曝光,V30/30系列有望下月开测?...
C/C++编程:优先队列priority_queue_c++ priority_queue遍历
赞
踩
priority_queue
- priority_queue叫做优先队列,其内部的元素并非按照被压入的顺序排列,而是自动根据元素的权值排列(通常权值以实数表示)。权值最高的,排在最前面
- 由于这是一个queue,因此只能从最前面取出元素,从最后面新增元素,除此之外没有其他存取元素的途径
- priority_queue缺省情况下【以vector实现的完全二叉树 + max-heap处理规则】来实现。
- 那它为什么叫做xxxx_queue呢,是因为它的接口和queue非常像,只是它的下一个元素是优先级最高的元素
- 如果同时存在若干个优先级一样的元素,那么就不能确实是哪一个会入选

声明

- 即
priority_queue<Type, Container, Functional>中:Type为数据类型Container为保存数据的容器,它必须是用数组实现的容器,比如vector,deque等等,但不能用list。 STL里面默认用的是vector。Functional为元素比较方式。- 比较方式默认用
operator<,所以如果把后面2个参数缺省的话,优先队列就是大顶堆(降序),队头元素最大。特别注意pair的比较函数。 - 如果要用到小顶堆,则一般要把模板的3个参数都带进去。STL里面定义了一个仿函数
greater<>,基本类型可以用这个仿函数声明小顶堆。
- 比较方式默认用
核心接口

priority_queue没有迭代器
priority_queue中的所有元素,进出都有一定的规则,只有queue顶端的元素(权值最高的元素),才有机会被外界取用。因此priority_queue不提供遍历功能,也不提供迭代器
实现
priority_queue内部使用的是STL的heap算法

关于priority_queue中元素的比较
#include <functional>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
template<typename T> void print_queue(T& q) {
while(!q.empty()) {
std::cout << q.top() << " ";
q.pop();
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
当有限队列中的元素是简单类型,比如int时,
- 默认情况下,优先级队列元素从大到小排列,类似最大堆, 队头是值最大的那个元素
- 如果要用到小顶堆,则一般要把模板的3个参数都带进去。STL里面定义了一个仿函数greater<>,compare参数传入greator就是小根堆了
int main() { //-----------------------------如果想要降序------------------------------------- std::priority_queue<int >q; // 等同于 std::priority_queue<int,std::vector<int> , std::less<int> >q; for(int n : {1,8,5,6,3,4,0,9,7,2}) q.push(n); print_queue(q); // ---------------------------如果想要升序------------------------------ std::priority_queue<int,std::vector<int> , std::greater<int> >q2; for(int n : {1,8,5,6,3,4,0,9,7,2}) q2.push(n); print_queue(q2); //------------------------自定义lambar比较------------------------------ // Using lambda to compare elements. auto cmp = [](int left, int right) { return (left ^ 1) < (right ^ 1); }; std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>, decltype(cmp)> q3(cmp); for(int n : {1,8,5,6,3,4,0,9,7,2}) q3.push(n); print_queue(q3); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
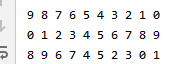
优先级队列的元素类型是复合类型,如pair
- 默认情况下,排序规则是先按照pair的first的属性降序排列,如果first相等,则按照second属性降序排序
- 同理,传入std::greator后,排序规则是先按照pair的first的属性升序排列,如果first相等,则按照second属性升序排列
int main() {
// 默认先按照pair的first元素降序,first元素相等时,再按照second元素降序:
std::priority_queue<std::pair<int, int>>q;
// 下面是:先按照pair的first元素升序,first元素相等时,再按照second元素升序:
// std::priority_queue<pair<int,int>, std::vector<pair<int,int> >, std::greater<pair<int,int> > > q;
std::pair<int,int> a(3,4);
std::pair<int,int> b(3,5);
std::pair<int,int> c(4,3);
q.push(a);
q.push(b);
q.push(c);
print_queue(q);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
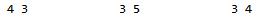
- 还可以自定义排序,比如,按照second来排序,first无所谓。second大的放在最前面:
struct cmp{
template<typename T, typename U>
bool operator()(T const& left, U const &right) {
if (left.second < right.second) return true;
return false;
}
};
...
int main(){
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
mp[3]=4;
mp[2]=44;
mp[12]=432;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, cmp> pq(mp.begin(), mp.end());//完成pq的初始化
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
对于自定义类型,则必须重载operator<或者重写仿函数。
- 重载operator<的例子:返回true时,说明左边形参的优先级低于右边形参
#include <functional> #include <queue> #include <vector> #include <iostream> struct Node{ int x, y; Node(int a = 0, int b = 0):x(a), y(b){}; }; bool operator < (Node a, Node b){ //返回true时,说明a的优先级低于b //x值较大的Node优先级低(x小的Node排在队前) //x相等时,y大的优先级低(y小的Node排在队前) if( a.x== b.x ) return a.y> b.y; return a.x> b.x; } int main() { std::priority_queue<Node>q; for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { q.push(Node(std::rand(), std::rand())); } while (!q.empty()){ std::cout << q.top().x << ' ' << q.top().y << std::endl; q.pop(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
-
自定义类型重载operator<后,声明对象时就可以只带一个模板参数。
-
但此时不能像基本类型这样声明
priority_queue<Node,vector<Node>,greater<Node> >,原因是greater<Node>没有定义,如果想用这种方法定义则可以重载operator >。
例子:返回的是小顶堆。但不怎么用,习惯是重载operator<。
#include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct Node{ int x, y; Node( int a= 0, int b= 0 ): x(a), y(b) {} }; bool operator>( Node a, Node b ){//返回true,a的优先级大于b //x大的排在队前部;x相同时,y大的排在队前部 if( a.x== b.x ) return a.y> b.y; return a.x> b.x; } int main(){ priority_queue<Node,vector<Node>,greater<Node> > q; for( int i= 0; i< 10; ++i ) q.push( Node( rand(), rand() ) ); while( !q.empty() ){ cout << q.top().x << ' ' << q.top().y << endl; q.pop(); } return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
当priority_queue的元素类型为指针的时候,重载< 的方法不能有效的给指针元素排序。这时候可以考虑以下的解决方案,定义cmp结构体类型,在内部重载()
#include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct Node{ int x, y; Node( int a= 0, int b= 0 ): x(a), y(b) {} }; struct cmp{ bool operator() ( Node a, Node b ){//默认是less函数 //返回true时,a的优先级低于b的优先级(a排在b的后面) if( a.x== b.x ) return a.y> b.y; return a.x> b.x; } }; int main(){ priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, cmp> q; for( int i= 0; i< 10; ++i ) q.push( Node( rand(), rand() ) ); while( !q.empty() ){ cout << q.top().x << ' ' << q.top().y << endl; q.pop(); } return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
自定义类型有多个排序规则时
首先定义个结构体A
typedef struct A
{
int l;
int r;
int label;
}a;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
接下来就可以定义优先队列,容器中的元素是结构体A
#include <queue>
priority_queue<a, vector<a>, greater<a> > que1;
priority_queue<a, vector<a>, less<a> > que2;
- 1
- 2
- 3
优先队列里面的greater和less是针对标准数据类型来的,greater是从小到大,less是从大到小
优先队列里面默认是从大到小排序
我们如果要按照结构体A中的r的大小进行排序,就需要重载运算符:
bool operator < (A a1, A a2){
return a1.r < a2.r;
}
bool operator > (A a1, A a2){
return a1.l > a2.l;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
其中:
- 大于号 > 的重载对应了greater的重载,是根据重载规则从小到大排序
- 小于号 < 的重载对应了less的重载,是根据重载规则从大到小排序
#include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef struct _A { int l; int r; int label; }A; bool operator < (A a1, A a2){ return a1.r < a2.r; } bool operator > (A a1, A a2){ return a1.l > a2.l; } priority_queue<A, vector<A>, greater<A> > que1; // 递增 - 对应> priority_queue<A, vector<A>, less<A> > que2; // 递减 - 对应< int main() { // l r label A a1 = {1, 2, 1}; A a2 = {6, 7, 2}; A a3 = {3, 5, 3}; A a4 = {2, 3, 4}; A a5 = {4, 10, 5}; que1.push(a1); que1.push(a2); que1.push(a3); que1.push(a4); que1.push(a5); que2.push(a1); que2.push(a2); que2.push(a3); que2.push(a4); que2.push(a5); cout << "按照l递增:"; while(!que1.empty()){ cout << "a" << que1.top().label << "<"; que1.pop(); } cout << endl; cout << "按照r递减:"; while(!que2.empty()){ cout << "a" << que2.top().label << ">"; que2.pop(); } cout << endl; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
输出:
- 按照l递增:a1<a4<a3<a5<a2
- 按照r递减:a5>a2>a3>a4>a1
继续探讨:
如果我在重载对应greater的大于符号的时候,返回的是小于的判定结论,结果如何?
对称地,如果在重载对应less的小于符号的时候返回的是大于的判定结论:
bool operator > (A a1, A a2){
return a1.l < a2.l;
}
bool operator < (A a1, A a2){
return a1.r > a2.r;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
最终的结果:
按照l递增:a2<a5<a3<a4<a1
按照r递减:a1>a4>a3>a2>a5
当然了,上面的大于和小于关系是不正确的,此时按照l应该是个递减的顺序,按照r应该是递增的顺序,也就是相反的结果,greater用于从大到小,less用于从小到大,他们的顺序取决于重载函数中的具体实现。
应该可以看出这个输出结果和上面的输出结果正好是倒序的。



