热门标签
热门文章
- 1iOS:多效果的CategoryView_ios jxcategorytitleview加个数角标
- 2Docker(五)
- 3Leetcode3190. 使所有元素都可以被 3 整除的最少操作数
- 4音乐人值得尝试的十大文本转音乐AI平台
- 5【大唐杯备考】——5G网元功能与接口(学习笔记)_5g网络功能之间的信息交互可以基于两种方式表示的优缺点
- 6LLM Agents调研_有哪些经典的 single agent
- 7【Hadoop大数据技术】——Hive数据仓库(学习笔记)_启动数据仓库之前需要hadoop
- 8Pandas API 文档索引中文翻译版(一)—— Series_pandas中文api
- 9Java面试:分布式框架面试题合集_分布式架构面试题
- 10C语言的数据结构:图的操作
当前位置: article > 正文
【C++】“.wts”权重文件内容读取详解_wts文件
作者:小舞很执着 | 2024-06-30 13:17:44
赞
踩
wts文件
为方便大家理解加载“.wts”权重文件的过程,本文通过示例对加载的过程进行详细解读,包括如何读取,以什么形式读取,读取后数据是什么形式等。
此处使用的是“.pt”转“.wts”,再转“.engine”,进行tensorrt加速过程中的“.wts”文件读取的过程。
加载权重部分代码
std::map<std::string, nvinfer1::Weights> loadWeights(const std::string file){ std::cout << "Loading weights: " << file << std::endl; std::map<std::string, nvinfer1::Weights> WeightMap; //file文件,第一行是总层个数,第二行到最后是相应的层名称和权重。每一行先是名称,然后该行数量,最后是数值 std::ifstream input(file); assert(input.is_open() && "Unable to load weight file. please check if the .wts file path is right!!!!!!"); //定义一个 int32_t类型数值 int32_t count; //从input中读取一个int32_t的数值给count,是层的个数,即权重的个数 input>>count ; assert(count > 0 && "Invalid weight map file."); while(count--){ //定义wt,包括里边包含的内容,从下面可知是精度类型、权重值和权重个数 nvinfer1::Weights wt{nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0}; uint32_t size; std::string name; //十进制 input >> name >> std::dec >> size; wt.type = nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT; //reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*> 这是一个类型转换。它将malloc返回的void*类型的指针转换为uint32_t*类型的指针。 //因为C++不允许直接将一个类型的指针赋值给另一个类型,除非进行显式类型转换。 //uint32_t* val; -先定义一个指向uint32_t类型的指针变量val。 uint32_t* val = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(malloc(sizeof(val) * size)); for(uint32_t x = 0, y = size; x < y; x++){ //输出格式为16进制 input >> std::hex >> val[x]; } //赋值和保存 wt.values = val; wt.count = size; WeightMap[name] = wt; } return WeightMap; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
为方便理解其中的内容,进行摘选,运用示例进行详解。
#include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <string> int main() { std::ifstream input("example.txt"); // 替换为你的文件路径 if (!input.is_open()) { std::cerr << "Unable to open file!" << std::endl; return 1; // 返回非零错误代码 } //定义一个 int32_t类型数值 int32_t count; //从input中读取一个int32_t的数值给count,是层的个数,即权重的个数 input >> count; std::cout << "count: " << count<< std::endl; while (count--) { uint32_t size; std::string name; //十进制 input >> name >> std::dec >> size; std::cout << "name: " << name << std::endl; std::cout << "size: " << size << std::endl; //reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*> 这是一个类型转换。它将malloc返回的void*类型的指针转换为uint32_t*类型的指针。 //因为C++不允许直接将一个类型的指针赋值给另一个类型,除非进行显式类型转换。 //uint32_t* val; -先定义一个指向uint32_t类型的指针变量val。 uint32_t* val = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(malloc(sizeof(val) * size)); for (uint32_t x = 0, y = size; x < y; x++) { //输出格式为16进制 input >> std::hex >> val[x]; std::cout <<"val: " << val << std::endl; } //std::cout<<"name: " <<name<<" " << "val: " << val << std::endl; } input.close(); return 0; // 正常退出 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
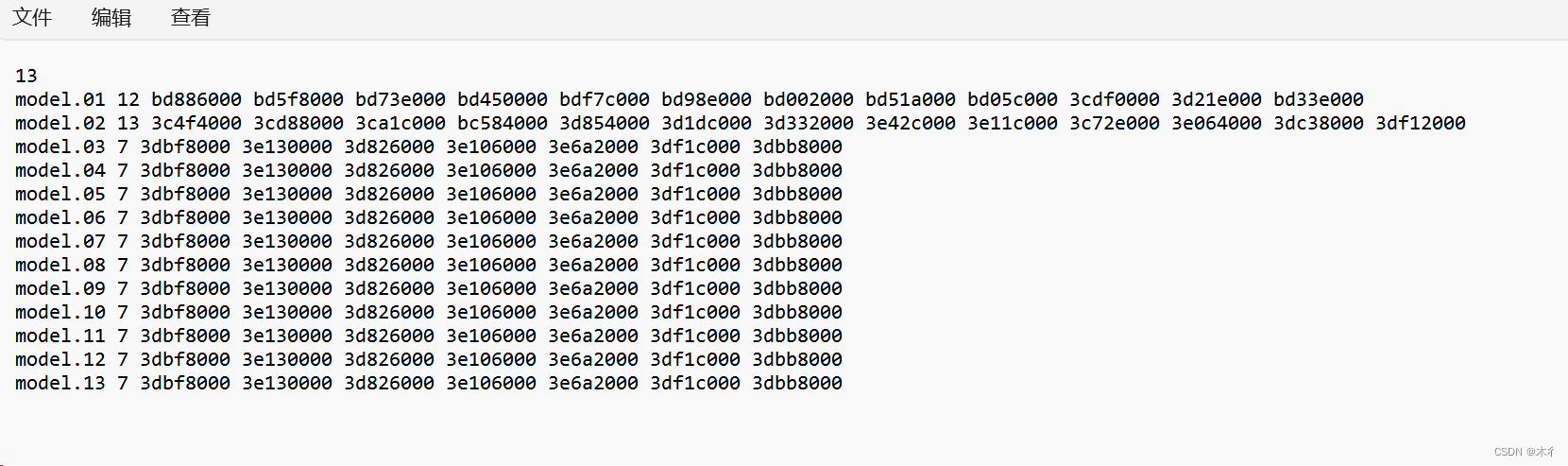
“example.txt”文件中的内容。
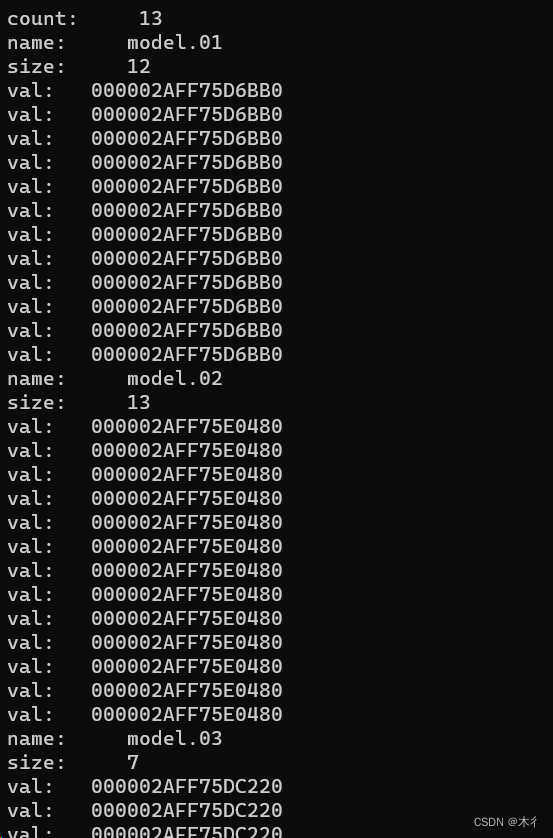
运行程序,部分输出结果。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小舞很执着/article/detail/772700
推荐阅读
相关标签



