热门标签
热门文章
- 1数据结构(C语言)-排序_c语言简单排序概念是什么
- 2Python测试框架之pytest详解_pytest-xdist怎么导入
- 3strongSwan编译_gnu multi precision library gmp not found
- 4智能合约与数据验证技术:保障区块链系统的安全与可靠性
- 5基于微信山西太原某健身房私教预约小程序系统设计与实现 研究背景和意义、国内外现状_线上健身系统研究现状_健身馆预约管理系统的国内外研究现状
- 6常见机器学习算法_dtw筛选变量
- 7Spring Boot从入门到精通【一】
- 8python 模块xlrd 读取.xls文件_python xlrd读取xls文件
- 9【裂缝识别】基于matlab GUI路面裂缝识别(带面板)【含Matlab源码 1648期】
- 102024年运维最全Linux 下安装 Git,作为一个Linux运维程序员你还不会JetPack_linux 安装git
当前位置: article > 正文
sklearn实现逻辑回归_以python为工具【Python机器学习系列(十)】_python逻辑回归模型from sklearn_sklearn非线性回归
作者:小桥流水78 | 2024-06-22 23:55:37
赞
踩
sklearn非线性回归
第三步,训练模型
logistic = LogisticRegression()
logistic.fit(x_data, y_data)
# 截距
print(logistic.intercept_)
# 系数:theta1 theta2
print(logistic.coef_)
# 预测
pred = logistic.predict(x_data)
# 输出评分
score = logistic.score(x_data, y_data)
print(score)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
输出结果如下图所示:
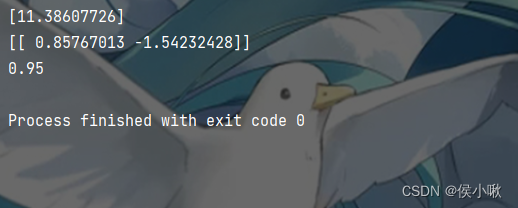
绘制出带有决策边界的散点图:
# 绘制散点
plot_logi()
# 绘制决策边界
x_test = np.array([[-4], [3]])
y_test = -(x_test\*logistic.coef_[0, 0]+logistic.intercept_)/logistic.coef_[0, 1]
plt.plot(x_test, y_test)
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
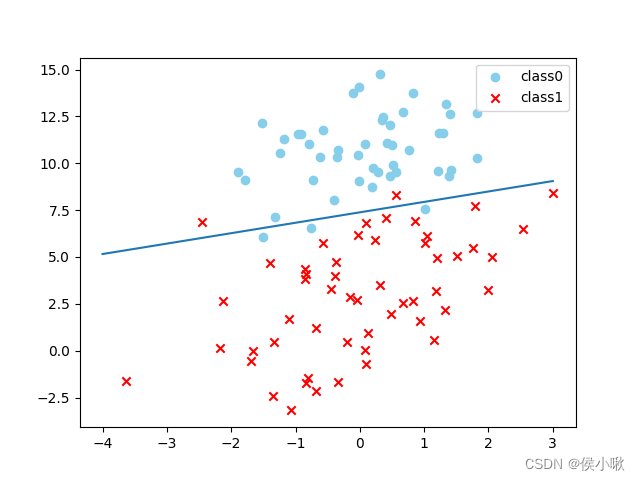
2.非线性逻辑回归
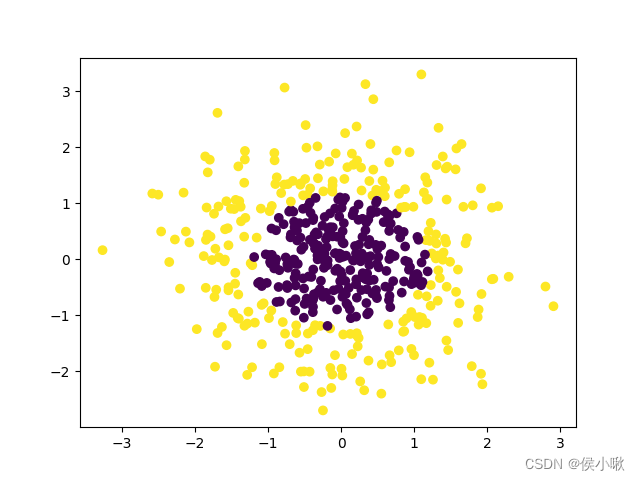
python实现非线性逻辑回归,首先使用make_gaussian_quantiles获取一组高斯分布的数据集,代码及数据分布如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.datasets import make_gaussian_quantiles
# 获取高斯分布的数据集,500个样本,2个特征,2分类
x_data, y_data = make_gaussian_quantiles(n_samples=500, n_features=2, n_classes=2)
# 绘制散点图
plt.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1],c=y_data)
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
描述数据分布的散点图如图所示:
然后转换数据并训练模型以实现非线性逻辑回归:
# 数据转换,最高次项为五次项
poly_reg = PolynomialFeatures(degree=5)
x_poly = poly_reg.fit_transform(x_data)
# 定义逻辑回归模型
logistic = linear_model.LogisticRegression()
logistic.fit(x_poly, y_data)
score = logistic.score(x_poly, y_data)
print(score)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
评分结果如图所示,达0.996:

3.乳腺癌数据集案例
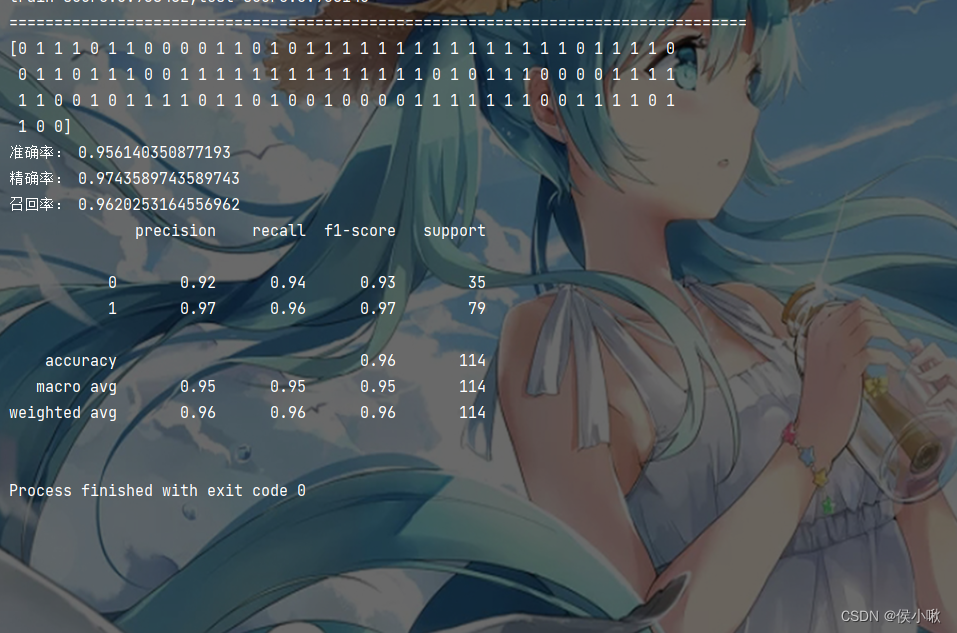
以乳腺癌数据集为例,建立线性逻辑回归模型,并输出准确率,精确率,召回率三大指标,代码如下所示:
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import recall_score from sklearn.metrics import precision_score from sklearn.metrics import classification_report from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score import warnings warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") # 获取数据 cancer = load_breast_cancer() # 分割数据 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(cancer.data, cancer.target, test_size=0.2) # 创建估计器 model = LogisticRegression() # 训练 model.fit(X_train, y_train) # 训练集准确率 train_score = model.score(X_train, y_train) # 测试集准确率 test_score = model.score(X_test, y_test) print('train score:{train\_score:.6f};test score:{test\_score:.6f}'.format(train_score=train_score, test_score=test_score)) print("==================================================================================") # 再对X\_test进行预测 y_pred = model.predict(X_test) print(y_pred) # 准确率 所有的判断中有多少判断正确的 accuracy_score_value = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) # 精确率 预测为正的样本中有多少是对的 precision_score_value = precision_score(y_test, y_pred) # 召回率 样本中有多少正样本被预测正确了 recall_score_value = recall_score(y_test, y_pred) print("准确率:", accuracy_score_value) print("精确率:", precision_score_value) print("召回率:", recall_score_value) # 输出报告模型评估报告 classification_report_value = classification_report(y_test, y_pred) print(classification_report_value)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
程序输出结果如下图所示:
本次分享就到这里,小啾感谢您的关注与支持!
本文内容由网友自发贡献,转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小桥流水78/article/detail/748020
推荐阅读
相关标签
Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。



