- 1【FLink-17-Flink监控metric】
- 2Python之列表推导式_pthon 列表推导
- 3OTA自动化测试解决方案——实车级OTA测试系统PAVELINK.OTABOX:实车级OTA自动化系统|系统级OTA通道测试系统|系统级OTA压力测试系统|PAVELINK.OTABOX解决方案_自动化测试平台方案
- 4容易被黑客攻击的10个漏洞_服务器上的jar包有漏洞,会使黑客侵入吗
- 5散列表(Hash Table)
- 6C++标准模板(STL)- 低层内存管理 - 分配函数(operator new, operator new[])
- 7sqlserver2012用ip远程连接设置_remote dac enable
- 8微软蓝屏事件揭示的网络安全深层问题与未来应对策略_蓝屏漏洞攻击与防御策略研究论文
- 9git生成个人令牌Access Token
- 10oracle数据库面试题目汇总_如果服务器是在共享模式下的则有可能没有对应于该客户所使用的通信协议的调度进程
有限状态机
赞
踩
在实际的软件开发中,状态机并不常用,但是在能够用得到的场景中,可以发挥出很大的作用。状态机常用在游戏、工作流引擎等系统开发中,其实现方式有分支逻辑法、查表法、状态模式等。
1. 概念
1.1 定义
有限状态机(Finite State Machine,FSM)简称状态机。状态机有三个组成部分:状态(State)、事件(Event)、动作(Action),事件(转移条件)触发状态的转移和动作的执行。动作的执行不是必须的,可以只转移状态,不指定任何动作。总体而言,状态机是一种用以表示有限个状态以及这些状态之间的转移和动作的执行等行为的数学模型。
状态机可以用公式 State(S) x Event(E) -> Actions (A), State(S’)表示,即在处于状态S的情况下,接收到了事件E,使得状态转移到了S’,同时伴随着动作A的执行。
1.2 举例
在游戏“超级马里奥”中,马里奥的形态转变就是一个状态机。马里奥有小马里奥、超级马里奥、火焰马里奥、斗篷马里奥等形态,在遇到不同的游戏情节时,会发生形态改变,同时产生积分的增减。比如小马里奥吃了蘑菇之后会变成超级马里奥,同时增加100积分。
在超级马里奥中,马里奥的不同形态就是状态机中的“状态”,游戏情节就是状态机中的“事件”,加减积分就是状态——机中的“动作”。
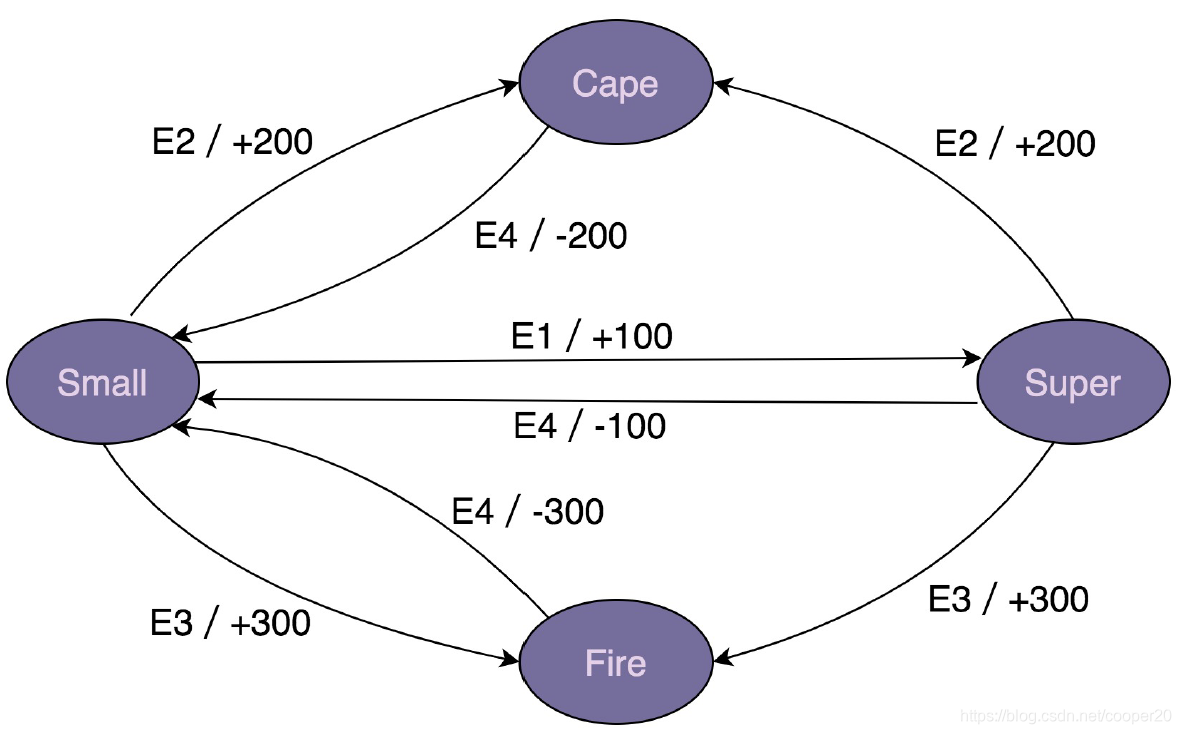
其中,事件E1~E4分别表示吃蘑菇、获得斗篷、获得火焰、遇到怪物。
2. 分支逻辑法
分支逻辑法是状态机最简单的实现方式,利用if-else或者switch-case,参照状态转移图,将每一种状态转移直接翻译成代码。
对于简单的状态机,分支逻辑法的实现方式可以接受。对于复杂的状态机,分支逻辑法容易漏写、错写某些状态转移。除此之外,代码中充斥着大量的if-else,可读性、可维护性都很差。
定义状态枚举
public enum State { SMALL(0), SUPER(1), FIRE(2), CAPE(3); private int value; private State(int value) { this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
状态机实现
public class MarioStateMachine { // 积分 private int score; // 状态 private State currentState; public MarioStateMachine() { this.score = 0; this.currentState = State.SMALL; } // 事件处理:在不同状态下事件所触发的状态转移、动作执行 public void obtainMushRoom() { if (currentState.equals(State.SMALL)) { this.currentState = State.SUPER; this.score += 100; } } public void meetMonster() { if (currentState.equals(State.SUPER)) { this.currentState = State.SMALL; this.score -= 100; return; } if (currentState.equals(State.CAPE)) { this.currentState = State.SMALL; this.score -= 200; return; } if (currentState.equals(State.FIRE)) { this.currentState = State.SMALL; this.score -= 300; return; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
3. 查表法
查表法适用于实现状态、事件类型很多、状态转移比较复杂的状态机,利用二维数组表示状态转移图,能极大的提高代码的可读性和可维护性。当把数组存在配置文件中,在状态机变更时甚至不需要修改代码。
在二维数组的表示形式中,用数组transitionTable和actionTable分别表示状态转移和动作执行。在这两个数组中,横坐标都表示当前状态,纵坐标都表示发生的事件,值则分别表示转移后的新状态和需要执行的动作。
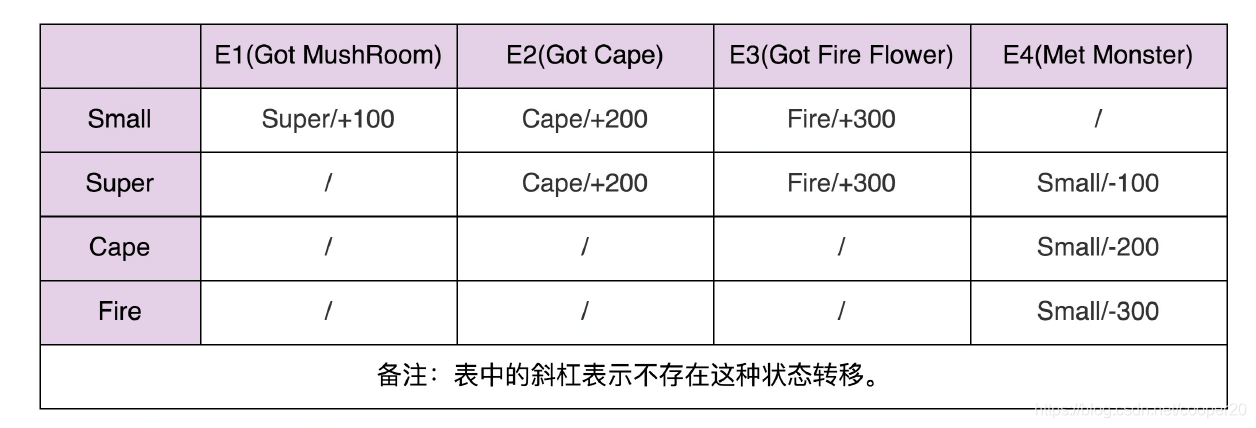
查表法的actionTable有一定的局限性,表示数值操作比较容易,表示复杂的业务逻辑会比较困难,此时,用状态模式会更加合适。当然,也可以将动作的类型用枚举表示,这样就可以用放入数组之中。
定义事件
public enum Event { GOT_MUSHROOM(0), GOT_CAPE(1), GOT_FIRE(2), MET_MONSTER(3); private int value; private Event(int value) { this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
状态机实现
public class MarioStateMachine { private int score; private State currentState; private static final State[][] TRANSITION_TABLE = { {SUPER, CAPE, FIRE, SMALL}, {SUPER, CAPE, FIRE, SMALL}, {CAPE, CAPE, CAPE, SMALL}, {FIRE, FIRE, FIRE, SMALL} }; private static final int[][] ACTION_TABLE = { {+100, +200, +300, +0}, {+0, +200, +300, -100}, {+0, +0, +0, -200}, {+0, +0, +0, -300} }; public MarioStateMachine() { this.score = 0; this.currentState = State.SMALL; } // 事件处理:根据当前状态和事件,查询TRANSITION_TABLE和ACTION_TABLE表,获得转移后的新状态和需要执行的动作 public void executeEvent(Event event) { int stateValue = currentState.getValue(); int eventValue = event.getValue(); this.currentState = TRANSITION_TABLE[stateValue][eventValue]; this.score = ACTION_TABLE[stateValue][eventValue]; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
4. 状态模式
状态模式用以实现状态不多、状态转移简单,但是事件触发动作所包含的业务逻辑比较复杂的状态机。将不同状态下事件所触发的状态转移和动作执行,拆分到不同的状态类中,来避免分支判断逻辑。
当状态模式会引入较多的状态类,对于状态比较多的推荐使用查表法;而对于状态比较少,但是动作复杂的,状态模式更加适合。
状态接口
IMario是状态的接口,定义了所有事件的响应方法。
public interface IMario {
State getName();
//以下是定义的事件
void obtainMushRoom();
void obtainCape();
void obtainFireFlower();
void meetMonster();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
状态类实现
SmallMario、SuperMario等是状态的具体实现类,分别对应状态机中的4个状态。具体实现了在当前状态下,每个事件的状态转移和动作执行,这些原本在MarioStateMachine中,现在分散到具体的状态类中了。
public class SmallMario implements IMario { // 状态类也依赖于状态机,用于修改其状态。 private MarioStateMachine stateMachine; public SmallMario(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) { this.stateMachine = stateMachine; } // 实现事件的具体逻辑:状态转移、动作执行 @Override public void obtainMushRoom() { stateMachine.setCurrentState(new SuperMario(stateMachine)); stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 100); } @Override public void obtainCape() { stateMachine.setCurrentState(new CapeMario(stateMachine)); stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 200); } @Override public void obtainFireFlower() { stateMachine.setCurrentState(new FireMario(stateMachine)); stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 300); } @Override public void meetMonster() { // do nothing... } @Override public State getName() { return State.SMALL; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
状态机
状态机持有状态,响应事件并调用具体状态类的实现来执行具体的逻辑。状态机和状态类之间是双向依赖,状态机持有状态,状态类需要反向修改状态机的状态。
public class MarioStateMachine { private int score; // 使用状态类而不是状态枚举表示当前状态 private IMario currentState; public MarioStateMachine() { this.score = 0; this.currentState = new SmallMario(this); } // 调用具体状态类的事件方法 public void obtainMushRoom() { this.currentState.obtainMushRoom(); } public void obtainCape() { this.currentState.obtainCape(); } public void obtainFireFlower() { this.currentState.obtainFireFlower(); } public void meetMonster() { this.currentState.meetMonster(); } // getter、setter public int getScore() { return this.score; } public State getCurrentState() { return this.currentState.getName(); } public void setScore(int score) { this.score = score; } public void setCurrentState(IMario currentState) { this.currentState = currentState; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
实现优化
可以将状态类设计成单例,对于状态类依赖于状态机,可以通过方法传参将状态机传入状态类。
public interface IMario { State getName(); void obtainMushRoom(MarioStateMachine stateMachine); void obtainCape(MarioStateMachine stateMachine); void obtainFireFlower(MarioStateMachine stateMachine); void meetMonster(MarioStateMachine stateMachine); } public class SmallMario implements IMario { private static final SmallMario instance = new SmallMario(); private SmallMario() { } public static SmallMario getInstance() { return instance; } @Override public State getName() { return State.SMALL; } @Override public void obtainMushRoom(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) { stateMachine.setCurrentState(SuperMario.getInstance()); stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 100); } @Override public void obtainCape(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) { stateMachine.setCurrentState(CapeMario.getInstance()); stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 200); } @Override public void obtainFireFlower(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) { stateMachine.setCurrentState(FireMario.getInstance()); stateMachine.setScore(stateMachine.getScore() + 300); } @Override public void meetMonster(MarioStateMachine stateMachine) { // do nothing... } } public class MarioStateMachine { private int score; private IMario currentState; public MarioStateMachine() { this.score = 0; this.currentState = SmallMario.getInstance(); } public void obtainMushRoom() { this.currentState.obtainMushRoom(this); } public void obtainCape() { this.currentState.obtainCape(this); } public void obtainFireFlower() { this.currentState.obtainFireFlower(this); } public void meetMonster() { this.currentState.meetMonster(this); } public int getScore() { return this.score; } public State getCurrentState() { return this.currentState.getName(); } public State getCurrentState() { return this.currentState.getName(); } public void setScore(int score) { this.score = score; } public void setCurrentState(IMario currentState) { this.currentState = currentState; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
参考
《设计模式之美》——极客时间



