- 1pydub、playsound、pygame播放声音;gradio、streamlit页面播放声音;gradio 页面图像、视频及调用摄像头_gradio视频无法播放
- 2面试 vivo 大模型算法岗(实习),被疯狂拷打。。。_vivo南京算法岗实习
- 3Python面向对象-类_f'hello {person.name}')
- 4[大模型]MiniCPM-2B-chat transformers 部署调用_minicpm 多块显卡部署
- 5(附源码)python电影院信息管理系统 毕业设计 021844_基于python的管理系统任务书
- 6美团民宿跨端复用框架设计与实践_接口层面设计符合行业规范,提供实时、非实时、文件交互等方式,可根据业务需求进行
- 7python(Django之html模板继承)_{% block title %}主页{% endblock %} {% block css %}
- 8【开发篇】十九、SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ(SpringAMQP)_springboot amqp
- 9使用Docker安装运行RabbitMQ---阿里云服务器_docker 运行rabbitmq镜像
- 1002ShardingSphere-MySQL主从同步配置_shardingsphere连接多机mysql
Pytest 使用简介及常用方法_pytest用法
赞
踩
目录
1.1也可以用于模块级别,跳过当前模块里所有的测试用例。(注:参数allow_module_level的值设为True)
2.@pytest.mark.skip(用于函数外,跳过测试用例)
3.@pytest.mark.skipif(用于函数外,条件condition,跳过原因reason="xxx")
前言
最近在听极客时间的课程,里面的讲师极力推崇 pytest 框架,鄙视 unittest 框架,哈哈!然后查了些资料,发现了一条 python 鄙视链:pytest 鄙视 > unittest 鄙视 > robotframework 。
pytest 是 python 的第三方单元测试框架,比自带 unittest 更简洁和高效,支持315种以上的插件,同时兼容 unittest 框架。这就使得我们在 unittest 框架迁移到 pytest 框架的时候不需要重写代码。接下来我们在文中来对分析下 pytest 有哪些简洁、高效的用法。
一、安装
首先使用 pip 安装 pytest
pip3 install pytest
查看 pytest 是否安装成功
pip3 show pytest
二、简单使用
1.创建 test_sample.py 文件,代码如下:
- #!/usr/bin/env python
- # coding=utf-8
- import pytest
-
- def inc(x):
- return x + 1
-
- def test_answer():
- assert inc(3) == 5
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main()
执行结果:
- test_sample.py F [100%]
-
- ================================== FAILURES ===================================
- _________________________________ test_answer _________________________________
-
- def test_answer():
- > assert inc(3) == 5
- E assert 4 == 5
- E + where 4 = inc(3)
-
- test_sample.py:19: AssertionError
- ============================== 1 failed in 0.41s ==============================
从上面的例子可以看出,pytest 中断言的用法直接使用 assert ,和 unittest 中断言 self.assert 用法有所区别。
2.使用 pytest 执行测试需要遵行的规则:
-
.py 测试文件必须以test_开头(或者以_test结尾)
-
测试类必须以Test开头,并且不能有 init 方法
-
测试方法必须以test_开头
-
断言必须使用 assert
3.pytest.ini 配置文件
- [pytest]
- addopts = -v -s --html=py_test/scripts/report/report.html -p no:warnings --reruns=10
- testpaths = ./py_test/scripts
- python_files= test_rerun.py
- python_classes = Test*
- python_function = test*
- xfail_strict = true
4.addopts: OPTS 命令行参数集
-s:表示输出调试信息,包括 print打印的信息
-v:显示更详细的信息
-vs:这两个参数一起用
-n :支持多线程或者分布式运行测试用例
如:pytest -vs ./testcase/test_login.py -n 2
--html : 测试报告位置
--reruns :失败重跑
-p no:warnings :取消警告
--ff :先执行上次失败的用例
--lf :只执行上次失败的用例
-x :遇到测试用例fail,就结束测试
--maxfail=num:遇到num条测试用例fail, 就结束测试
-k :根据测试用例的部分字符串指定测试用例
如:pytest -vs ./testcase -k “ao”
三、常用方法
1.参数化
pytest 内置装饰器 @pytest.mark.parametrize 可以让测试数据参数化,把测试数据单独管理,类似 ddt 数据驱动的作用,方便代码和测试数据分离。
1.1一次传多个参数
- import pytest
-
- @pytest.mark.parametrize('x,y',[(1,2),(3,4)])
- def test_sum(x,y):
- sum = x + y
- print(sum)
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py','-s'])
执行结果:
- test_sample.py
- 3
- .
- 7
- .
-
- ============================== 2 passed in 0.06s ==============================
1.2组合传参:
注意:这种方式一共传递了4组参数 (1,3)、(1,4)、(2,3)、(2,4)。这种方式可以简化测试数据,不用手动再将参数组合。
- import pytest
-
- @pytest.mark.parametrize('x',[1,2])
- @pytest.mark.parametrize('y',[3,4])
- def test_sum(x,y):
- sum = x + y
- print(sum)
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py','-s'])
执行结果:
- test_sample.py
- 4
- .
- 5
- .
- 5
- .
- 6
- .
-
- ============================== 4 passed in 0.14s ==============================
2、@pytest.fixture()
pytest 提供的 fixture 实现 unittest 中 setup/teardown 功能,可以在每次执行case之前初始化数据。不同点是,fixture 可以只在执行某几个特定 case 前运行,只需要在运行 case 前调用即可。比 setup/teardown 使用起来更灵活。
2.1fixture scope 作用范围
先看下 fixture 函数的定义:
- def fixture(scope="function", params=None, autouse=False, ids=None, name=None):
- """
- :arg scope: 可选四组参数:function(默认)、calss、module、package/session
- :arg params: 一个可选的参数列表,它将导致多个参数调用fixture函数和所有测试使用它。
- :arg autouse: 如果为True,则fixture func将为所有测试激活可以看到它。如果为False(默认值),则需要显式激活fixture。
- :arg ids: 每个参数对应的字符串id列表,因此它们是测试id的一部分。如果没有提供id,它们将从参数中自动生成。
- :arg name: fixture的名称。 这默认为装饰函数的名称。 如果fixture在定义它的同一模块中使用,夹具的功能名称将被请求夹具的功能arg遮蔽; 解决这个问题的一种方法是将装饰函数命名 “fixture_ <fixturename>”然后使用”@ pytest.fixture(name ='<fixturename>')”。
- """
重点说下 scope 四组参数的意义:
-
function:每个方法(函数)都会执行一次。
-
class:每个类都会执行一次。类中有多个方法调用,只在第一个方法调用时执行。
-
module:一个 .py 文件执行一次。一个.py 文件可能包含多个类和方法。
-
package/session:多个文件调用一次,可以跨 .py 文件。
2.2获取被调用函数返回值
- import pytest
-
- @pytest.fixture(scope='function')
- def login():
- accesstoken = '197ce8083c38467f'
-
- return accesstoken
-
-
- def test_sum(login):
- token = login
- print(token)
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py','-s'])
执行结果:
- test_sample.py
- 197ce8083c38467f
- .
-
- ============================== 1 passed in 0.04s ==============================
若被调用函数返回多个参数:
- import pytest
-
- @pytest.fixture(scope='function')
- def login():
- accesstoken = '197ce8083c38467f'
- customerguid = '096799f5-e040-11e9-8c01-0242ac11000d'
-
- return accesstoken,customerguid
-
-
- def test_sum(login):
- token = login[0]
- guid = login[1]
- print(token)
- print(guid)
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py','-s'])

执行结果:
- test_sample.py
- 197ce8083c38467f
- 096799f5-e040-11e9-8c01-0242ac11000d
- .
-
- ============================== 1 passed in 0.07s ==============================
2.3单个用例调用多个函数
- import pytest
-
- @pytest.fixture(scope='function')
- def login():
- print('登录')
-
- @pytest.fixture(scope='function')
- def conn():
- print('连接数据库')
-
- def test_1(login,conn):
- print('测试用例1')
-
- def test_2():
- print('测试用例2')
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py','-s'])

执行结果:
- test_sample.py
- 登录
- 连接数据库
- 测试用例1
- .
- 测试用例2
- .
-
- ============================== 2 passed in 0.05s ==============================
2.4yield
我们刚刚实现了在每个用例之前执行初始化操作,那么用例执行完之后如需要 清除数据(或还原)操作,可以使用 yield 来实现。
- #!/usr/bin/env python
- # coding=utf-8
- import pytest
-
- @pytest.fixture(scope='function')
- def login():
- print("登录")
- yield
- print("注销登录")
-
- def test_1():
- print('测试用例1')
-
- def test_2(login):
- print('测试用例2')
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py','-s'])

执行结果:
- test_sample.py
- 测试用例1
- .
- 登录
- 测试用例2
- .注销登录
-
- ============================== 2 passed in 0.08s ==============================
3.conftest
上面的案例都是写在同一个.py 文件内的。倘若有多个.py 文件需要调用 login() 方法,就必须把 login() 方法写在外面,这里引用了conftest.py 配置文件。test_xxx.py 测试文件中无需 import conftest,pytest 会自动搜索同级目录中的 conftest.py 文件。
conftest.py 与测试文件目录层级关系
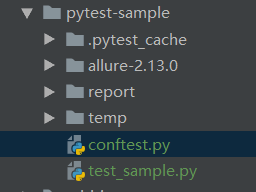
- # 新建conftest.py,和 test_sample.py 同级目录
- import pytest
-
- @pytest.fixture(scope='function')
- def login():
- print("登录")
-
-
-
-
- # test_sample.py 代码如下
- import pytest
-
- def test_1():
- print('测试用例1')
-
- def test_2(login):
- print('测试用例2')
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py','-s'])

执行结果:
- test_sample.py
- 测试用例1
- .
- 登录
- 测试用例2
- .
-
- ============================== 2 passed in 0.01s ==============================
4、重试机制
有的时候用例执行失败了,然后排查发现不是代码问题,可能和环境或者网络不稳定有关系,这个时候可以引入重试机制,排除一些外在因素。
1、安装 pytest-rerunfailures
pip3 install pytest-rerunfailures
2、重试的两种方法
1)使用装饰器 @pytest.mark.flaky(reruns=5, reruns_delay=2)
- reruns :最大重试次数
- reruns_delay :重试间隔时间,单位是秒
- #!/usr/bin/env python
- # coding=utf-8
- import pytest
-
-
- @pytest.mark.flaky(reruns=5, reruns_delay=2)
- def test():
- assert 0==1
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py','-s'])
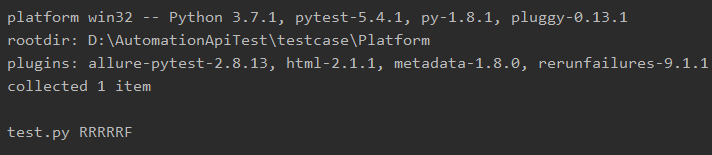
R表示用例失败后正在重试,尝试5次。
2)也可以使用命令行 pytest --reruns 5 --reruns-delay 2 -s ,参数与装饰器 @pytest.mark.flaky 一致,这个就不多说了。
5、测试用例分类@pytest.mark.smoke
有时候我们只需执行部分测试用例,比如从用例集当中挑选 smoke 测试,要怎么做呢?通过装饰器 @pytest.mark.smoke,smoke 是可以自定义的,运行时加上命令‘-m=smoke’,pytest 就会挑选带有装饰器的类或函数运行。
- import pytest
-
- @pytest.fixture(scope='function')
- def login():
- accesstoken = '197ce8083c38467f'
- customerguid = '096799f5-e040-11e9-8c01-0242ac11000d'
-
- return accesstoken,customerguid
-
- @pytest.mark.smoke
- def test_sum(login):
- token = login[0]
- guid = login[1]
- print(token)
- print(guid)
-
- def test_2():
- print('测试用例')
-
- if __name__ =="__main__":
- pytest.main(['test_sample.py','-s','-m=smoke'])

执行结果:
- test_sample.py
- 197ce8083c38467f
- 096799f5-e040-11e9-8c01-0242ac11000d
- .
-
- ======================= 1 passed, 1 deselected in 0.02s =======================
6、skipif-跳过测试
1.pytest.skip (用于函数内,跳过测试用例)
- def test_2():
- if 1 < 2:
- pytest.skip('1111111')
- pass
1.1也可以用于模块级别,跳过当前模块里所有的测试用例。(注:参数allow_module_level的值设为True)
- if 1==1:
- pytest.skip('1111111',allow_model_level=True)
-
- def test_1():
- pass
-
- def test_2():
- pass
2.@pytest.mark.skip(用于函数外,跳过测试用例)
- @pytest.mark.skip(reason='feature not implemented')
- def test_1():
- pass
-
- # 模块级别跳过。(注:参数allow_module_level的值设为True)
- pytest.skip('skip all tests', allow_module_level=True)
3.@pytest.mark.skipif(用于函数外,条件condition,跳过原因reason="xxx")
- @pytest.mark.skipif(condition='1<2',reason='feature not implemented')
- def test_1():
- pass
7、控制执行顺序
order-执行顺序
1、控制用例执行顺序的方法
2、在需要调整用例执行顺序的函数(或方法)前增加,如@pytest.mark.run(order=x),x表示数字
3、执行顺序,由小到大、由正到负、未标记的在正数后、负数前执行,顺序为:1,2,3,无标记,-3,-2,-1
4、提示:需要下载 pytest_ordering 依赖包,否则@pytest.mark.run(order=x)既不报错也不会生效
- class Testpytest(object):
-
- @pytest.mark.run(order=-1)
- def test_two(self):
- print("test_two, 测试用例")
-
- @pytest.mark.run(order=3)
- def test_one(self):
- print("test_one, 测试用例")
-
- @pytest.mark.run(order=1)
- def test_three(self):
- print("test_three, 测试用例")
8、预期失败
1.xfail-预期失败
xfail-预期失败的函数语法xfail(condition, reason):
--condition 预期失败的条件
--reason 预期失败的原因
- # condition 条件相等判断失败
- @pytest.mark.xfail(condition='1==1', reason="The test case")
- def test_1():
- print("\n-------")
-
- # condition 条件不等判断成功
- @pytest.mark.xfail(condition='1==2', reason="The test case")
- def test_2():
- print("\n-------")


