- 1让Sora和ChatGPT更可靠!只需这个知识价值定量评估新框架
- 2maven打包自定义包名_assembly打包 包名
- 3burpsuite安装HTTPS证书_burp证书
- 4Android 编译系统(Build System)剖析_system_ext_specific
- 5学点Java打小工_Day2Day3_一点作业
- 6快手匿名直播间提取工具,可采集匿名用户信息,UID评论内容都可以,源码分享仅供学_获取快手用户头像api
- 7算法的学习-基础篇_算法主要学什么
- 8网上租房售房管理系统/二手房智能选取与推荐系统/房屋租赁管理系统/中原房产中介登记系统的设计与实现(源码+论文)_java_312_作为网络房屋租赁销售求租系统,在系统中有注册会员和各类的房屋信息要管理员
- 9wazuh agent功能详解
- 10TCPIP协议总结
生产者与消费者问题算法 C++(一对多)_生产者消费者问题c++代码
赞
踩
目录
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
前言
一、实验内容
1.问题描述
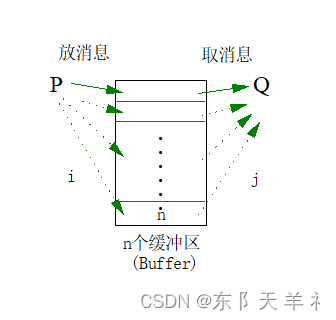
一组生产者向多组消费者提供消息,它们共享一个有界缓冲池,生产者向其中投放消息,消费者从中取得消息。假定这些生产者和消费者互相等效,只要缓冲池未满,生产者可将消息送入缓冲池,只要缓冲池未空,消费者可从缓冲池取走一个消息。
2.功能要求
根据进程同步机制,编写一个解决上述问题的程序,可显示缓冲池状态、放数据、取数据等过程。
二、背景知识
生产者消费者问题(英语:Producer-consumer problem),也称有限缓冲问题(英语:Bounded-buffer problem),是一个多线程同步问题的经典案例。该问题描述了共享固定大小缓冲区的两个线程——即所谓的“生产者”和“消费者”——在实际运行时会发生的问题。生产者的主要作用是生成一定量的数据放到缓冲区中,然后重复此过程。与此同时,消费者也在缓冲区消耗这些数据。该问题的关键就是要保证生产者不会在缓冲区满时加入数据,消费者也不会在缓冲区中空时消耗数据。
三、思路
要解决该问题,就必须让生产者在缓冲区满时休眠(要么干脆就放弃数据),等到下次消费者消耗缓冲区中的数据的时候,生产者才能被唤醒,开始往缓冲区添加数据。同样,也可以让消费者在缓冲区空时进入休眠,等到生产者往缓冲区添加数据之后,再唤醒消费者。通常采用进程间通信的方法解决该问题,常用的方法有信号灯法[1]等。如果解决方法不够完善,则容易出现死锁的情况。出现死锁时,两个线程都会陷入休眠,等待对方唤醒自己。该问题也能被推广到多个生产者和消费者的情形。
四、核心代码
数据说明
- int mutex = 1; //互斥信号量
- // mutex =1 代表进程空闲, mutex =0代表进程正在使用
- int full; //缓冲区非空个数
- const int n = 5; //缓冲区大小为 10
- int empty = n; //空缓冲区个数
- char buffer[n]; //定义缓冲区
- int pfull = 0; //产品资源非空信号量
- //可用于多生产者时进行区分产品类不同对应的消费
- int in = 0, out = 0; //定义存取指针的初始位置
- // in 指定生产产品当前的位置, out 指定消费产品当前的位置
- int choose = 1; //选择,首次产生产品P
1.生产者类
- //生产者类
- class Producer
- {
- private:
- int m_mutex;
- int m_full;
- int m_pfull;
- int m_in;
-
- public:
- Producer( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int pin )
- {
- m_mutex = mu;
- m_full = fu;
- m_pfull = pfu;
- m_in = in;
- }
- void showP()
- {
- if( mutex == 1 )//mutex = 1代表没有进程进行
- {
- if( full == n )//进程满了
- {
- cout << "缓冲区空间已满!" << endl;
- exit( 0 );//退出
- }
- mutex = 0;//mutex = 0代表有进程正在进行
- cout << "--------------------------------------------" << endl;
- cout << "生产者进程P:产生产品P" << endl;
- full++;//产品数量存储+1
- pfull++;//生产者进程P生产数量
- while( buffer[in] == 'P' )//避免重复位置替换产品P
- {
- in = ( in + 1 ) % n;//循环队列计数
- }
- buffer[ in ] = 'P';
- showbuffer( buffer );
- in = ( in + 1 ) % n;
- }
- else/// mutex = 0的情况
- {
- cout << "进程P正在使用!" << endl;
- }
- choice();
- }
- };

2.消费者类
- //消费者类
- class Consumer{
- private:
- int m_mutex;
- int m_full;
- int m_pfull;
- int m_out;
- char m_c;
- public:
- Consumer( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int ou, char c = '0' )
- {
- m_mutex = mu;
- m_full = fu;
- m_pfull = pfu;
- m_out = ou;
- m_c = c;
- }
-
- void showC( )
- {
- if( mutex == 1 )//mutex = 1代表没有进程进行
- {
- if( full == 0 )
- {
- cout << "没有进程可消费!" << endl;
- exit( 0 );
- }
- else{
- mutex = 0;
- if( pfull == 0 )
- {
- cout << " 消费者进程C没有可消费的!" << endl;
- exit( 0 );
-
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "--------------------------------------------" << endl;
- cout << "消费者进程C" << m_c << ":把产品P消费了->" << m_c << endl;
- full--;
- pfull--;
- buffer[ out ] = m_c;
- showbuffer( buffer );
- buffer[ out ] = '~';
- out = ( out + 1 ) % n;
- }
- }
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "进程C" << m_c << "正在使用!" << endl;
- }
- choice();
- }
- };

2.1 消费者子类1
- //消费者类 1
- class C1:public Consumer
- {
- public:
- C1( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int ou, char c1 = '1' ):Consumer( mu, fu, pfu, ou, c1 )
- {}
-
- void showC1()
- {
- Consumer::showC();
- }
- };
2.2 消费者子类2
- //消费者类 2
- class C2:public Consumer
- {
- public:
- C2( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int ou, char c1 = '2' ):Consumer( mu, fu, pfu, ou, c1 )
- {}
-
- void showC2()
- {
- Consumer::showC();
- }
- };
2.3 消费者子类3
- //消费者类 3
- class C3:public Consumer
- {
- public:
- C3( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int ou, char c1 = '3' ):Consumer( mu, fu, pfu, ou, c1 )
- {}
-
- void showC3()
- {
- Consumer::showC();
- }
- };
3.主函数
- int main()
- {
- Producer p( mutex, full, pfull, in );
- Consumer c( mutex, full, pfull, out );
- C1 c1( mutex, full, pfull, out );
- C2 c2( mutex, full, pfull, out );
- C3 c3( mutex, full, pfull, out );
- while( choose != 0 )
- {
- switch( choose )
- {
- case 1:
- p.showP();
- break;
- case 2:
- c1.showC1();
- break;
- case 3:
- c2.showC2();
- break;
- case 4:
- c3.showC3();
- break;
- }
- }
- }

五、源代码
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
-
- int mutex = 1; //互斥信号量
- // mutex =1 代表进程空闲, mutex =0代表进程正在使用
- int full; //缓冲区非空个数
- const int n = 10; //缓冲区大小为 10
- int empty = n; //空缓冲区个数
- char buffer[n]; //定义缓冲区
- int pfull = 0; //产品资源非空信号量
- //可用于多生产者时进行区分产品类不同对应的消费
- int in = 0, out = 0; //定义存取指针的初始位置
- // in 指定生产产品当前的位置, out 指定消费产品当前的位置
- int choose = 1; //选择,首次产生产品P
-
- //选择
- void choice()
- {
- cout << "按f或F继续,按q或Q退出程序:" << endl;
- cout << "--------------------------------------------" << endl;
- char ch;
- cin >> ch;
- if( ch == 'q' || ch == 'Q' )
- {
- mutex = 1;//把进程释放出来
- exit( 0 );//退出
- }
- else if( ch == 'f' || ch == 'F' )
- {
- mutex = 1;//把进程释放出来
- cout << "输入选择继续:" << endl;
- cin >> choose;
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "输入非法!" << endl;
- choice(); //重新选择
- }
- }
-
- //显示缓冲区情况函数
- void showbuffer( char a[10] )
- {
- cout << "缓冲区存储情况为( ~ 为已消费资源):" ;
- for( int i = 0; i < 10; i ++ )
- {
- cout << a[i] << " ";//输出缓冲区情况
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
-
- ///--------------------------------生产者--------------------------------------------------
- //生产者类
- class Producer
- {
- private:
- int m_mutex;
- int m_full;
- int m_pfull;
- int m_in;
-
- public:
- Producer( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int pin )
- {
- m_mutex = mu;
- m_full = fu;
- m_pfull = pfu;
- m_in = in;
- }
- void showP()
- {
- if( mutex == 1 )//mutex = 1代表没有进程进行
- {
- if( full == n )//进程满了
- {
- cout << "缓冲区空间已满!" << endl;
- exit( 0 );//退出
- }
- mutex = 0;//mutex = 0代表有进程正在进行
- cout << "--------------------------------------------" << endl;
- cout << "生产者进程P:产生产品P" << endl;
- full++;//产品数量存储+1
- pfull++;//生产者进程P生产数量
- while( buffer[in] == 'P' )//避免重复位置替换产品P
- {
- in = ( in + 1 ) % n;//循环队列计数
- }
- buffer[ in ] = 'P';
- showbuffer( buffer );
- in = ( in + 1 ) % n;
- }
- else/// mutex = 0的情况
- {
- cout << "进程P正在使用!" << endl;
- }
- choice();
- }
- };
-
- ///--------------------------------------消费者-------------------------------------------
- //消费者类
- class Consumer{
- private:
- int m_mutex;
- int m_full;
- int m_pfull;
- int m_out;
- char m_c;
- public:
- Consumer( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int ou, char c = '0' )
- {
- m_mutex = mu;
- m_full = fu;
- m_pfull = pfu;
- m_out = ou;
- m_c = c;
- }
-
- void showC( )
- {
- if( mutex == 1 )//mutex = 1代表没有进程进行
- {
- if( full == 0 )
- {
- cout << "没有进程可消费!" << endl;
- exit( 0 );
- }
- else{
- mutex = 0;
- if( pfull == 0 )
- {
- cout << " 消费者进程C没有可消费的!" << endl;
- exit( 0 );
-
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "--------------------------------------------" << endl;
- cout << "消费者进程C" << m_c << ":把产品P消费了->" << m_c << endl;
- full--;
- pfull--;
- buffer[ out ] = m_c;
- showbuffer( buffer );
- buffer[ out ] = '~';
- out = ( out + 1 ) % n;
- }
- }
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "进程C" << m_c << "正在使用!" << endl;
- }
- choice();
- }
- };
-
- //消费者类 1
- class C1:public Consumer
- {
- public:
- C1( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int ou, char c1 = '1' ):Consumer( mu, fu, pfu, ou, c1 )
- {}
-
- void showC1()
- {
- Consumer::showC();
- }
- };
-
- //消费者类 2
- class C2:public Consumer
- {
- public:
- C2( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int ou, char c1 = '2' ):Consumer( mu, fu, pfu, ou, c1 )
- {}
-
- void showC2()
- {
- Consumer::showC();
- }
- };
-
- //消费者类 3
- class C3:public Consumer
- {
- public:
- C3( int mu, int fu, int pfu, int ou, char c1 = '3' ):Consumer( mu, fu, pfu, ou, c1 )
- {}
-
- void showC3()
- {
- Consumer::showC();
- }
- };
-
- int main()
- {
- Producer p( mutex, full, pfull, in );
- Consumer c( mutex, full, pfull, out );
- C1 c1( mutex, full, pfull, out );
- C2 c2( mutex, full, pfull, out );
- C3 c3( mutex, full, pfull, out );
- while( choose != 0 )
- {
- switch( choose )
- {
- case 1:
- p.showP();
- break;
- case 2:
- c1.showC1();
- break;
- case 3:
- c2.showC2();
- break;
- case 4:
- c3.showC3();
- break;
- }
- }
- }

六、运行结果
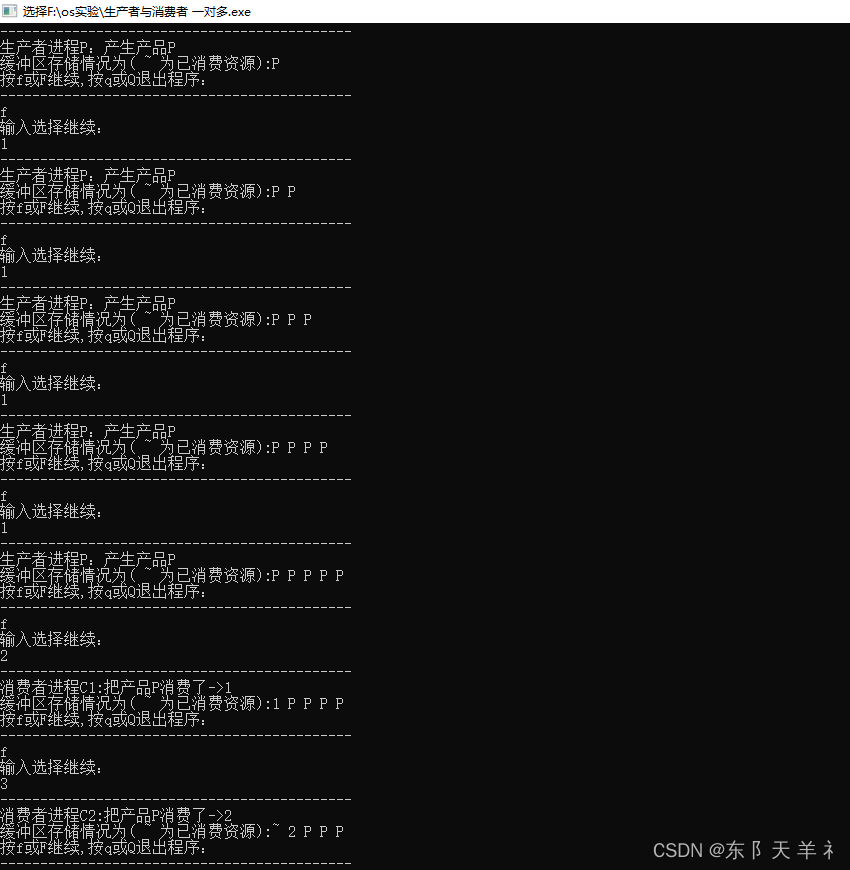
这里以缓冲区大小为 5 来测试
不同的消费者进程消费产品后转换成的结果不同
正常生产和消费,当生产者依次顺序占用缓冲区时,消费者也是依次顺序消费,当前队列到尽头时,采用循环继续,生产者在空缓冲区继续执行生产命令。

当缓冲区已满时,进程提示空间已满,程序正常状态退出!
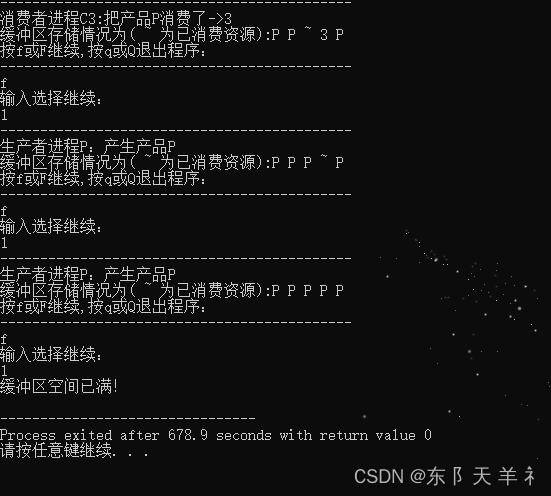
当缓冲区没有产品时,消费者无法进行消费,此时进程提示没有进程可消费,程序正常状态退出!

更多测试结果请阅读者亲测~
七.结论
以上便是本次生产者与消费者问题的基本算法,生产者和消费者可以一对一、一对多或是多对多,只要分析清楚它们之间的同步互斥变量,共用的缓冲区资源的使用情况,解决好同步互斥问题,可以有效避免出现死锁的情况。通过生产者与消费者的问题算法,加深对信号量机制的理解和了解信号量的使用。
代码为原创,如有类似可联系了解情况,若有大神提出修改精进,欢迎评论区讨论!