- 1Debian11 环境下用Docker 安装mysql 5.6.51和Web界面的管理工具Adminer_adminer 安装
- 2故障诊断——迁移学习整理_迁移学习故障诊断
- 3外校的打星的同学,学校名称填写自己的大学就行(>;_<;)
- 4Flutter和iOS原生通信_flutter ios fluttereventsink
- 5什么是Vercel?
- 6一文搞懂Stable Diffusion中的提示词
- 7MyBatis-Plus和SpringBoot的整合_
com.baomidou - 8计算机专业顶级学术会议
- 9AI绘画美女:StableDiffusion实操教程-完美世界-国漫女神云曦(附高清图下载)_ai国漫资源分享
- 10(贫民窟系列)Raspberry 树莓派+L298N+Python控制小车_树莓派python编程案例
Vision Transformer源码详解_vision transformer代码
赞
踩
Vision Transformer源码详解
前言
本篇文章主要分享视觉Transformer的Pytorch实现和代码细节问题。
一、模型架构
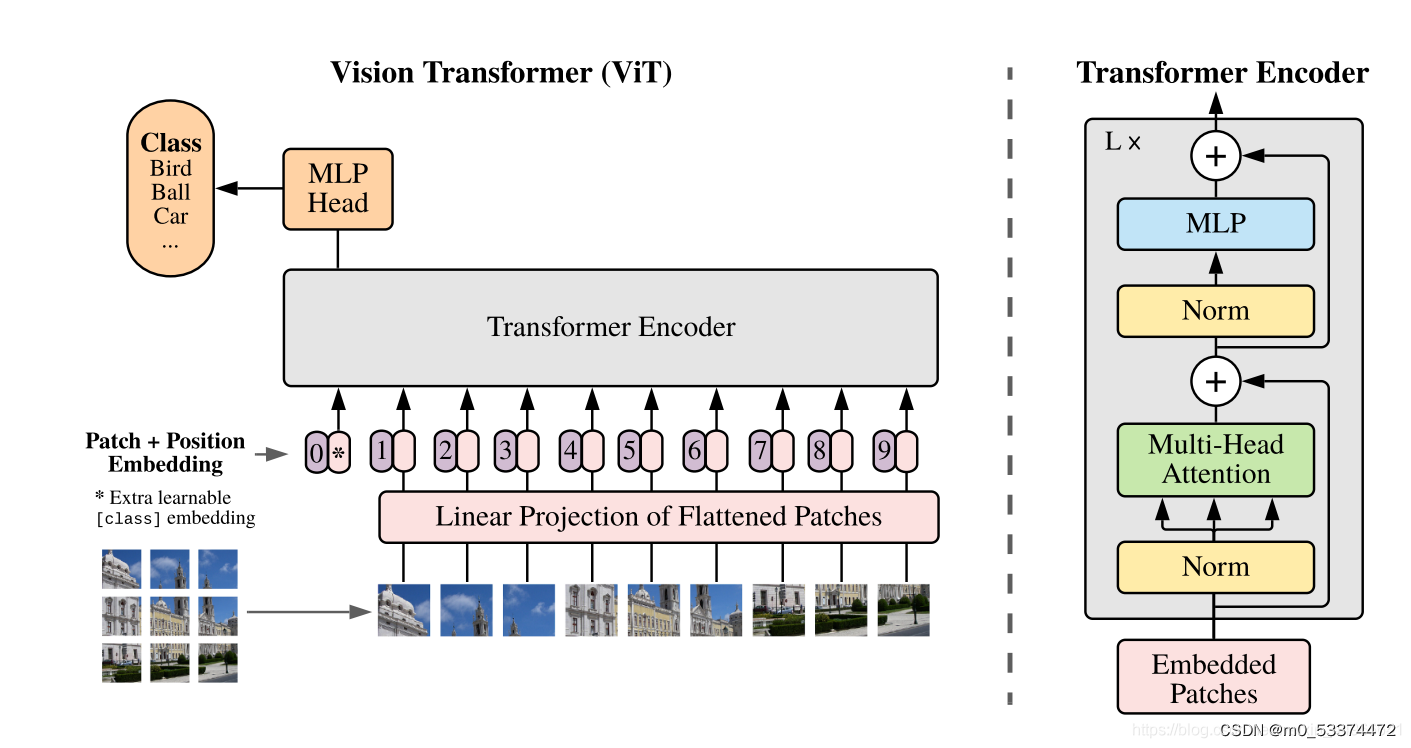
整体思路是将图片数据转换成序列数据,连接一个分类特征class_token,在加上位置信息,通过多层堆叠的Transformer Encoder,这个class_token融合了其他图片序列的特征,在经过多层感知机MLP后,输出最终分类结果。
二、整体代码
import numpy as np import torch import torch.nn as nn class Vit(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size=1, image_size=224, patch_size=16, in_channels=3, embed_dim=768, num_classes=1000, depth=12, num_heads=12, mlp_ratio=4, dropout=0, ): super(Vit, self).__init__() self.patch_embedding = PatchEmbedding(batch_size, image_size, patch_size, in_channels, embed_dim, dropout) self.encoder = Encoder(batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio, dropout, depth) self.classifier = Classification(embed_dim,num_classes,dropout) def forward(self, x): x = self.patch_embedding(x) x = self.encoder(x) x = self.classifier(x) return x class PatchEmbedding(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size, image_size, patch_size, in_channels, embed_dim, dropout): super(PatchEmbedding, self).__init__() n_patchs = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, embed_dim, patch_size, patch_size) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) self.class_token = torch.randn((batch_size, 1, embed_dim)) self.position = torch.randn((batch_size, n_patchs + 1, embed_dim)) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) # (batch,in_channel,h,w)-(batch,embed_dim,h/patch_size,w/patch_size)(1,768,14,14) x = x.flatten(2) # batch,embed_dim,h*w/(patch_size)**2 (1,768,196) x = x.transpose(1, 2) # batch,h*w/(patch_size)^^2,embed_dim (1,196,768) x = torch.concat((self.class_token, x), axis=1) # (1,197,768) x = x + self.position x = self.dropout(x) return x class Encoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio, dropout, depth): super(Encoder, self).__init__() layer_list = [] for i in range(depth): encoder_layer = EncoderLayer(batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio, dropout, ) layer_list.append(encoder_layer) self.layer = nn.Sequential(*layer_list) self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim) def forward(self, x): for layer in self.layer: x = layer(x) x = self.norm(x) return x class EncoderLayer(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio, dropout, ): super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__() self.attn_norm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim, eps=1e-6) self.attn = Attention(batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, ) self.mlp_norm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim, eps=1e-6) self.mlp = Mlp(embed_dim, mlp_ratio, dropout) def forward(self, x): h = x x = self.attn_norm(x) x = self.attn(x) x = x + h h = x x = self.mlp_norm(x) x = self.mlp(x) x = x + h return x class Attention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, ): super(Attention, self).__init__() self.qkv = embed_dim // num_heads self.batch_size = batch_size self.num_heads = num_heads self.W_Q = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.W_K = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.W_V = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) def forward(self, x): Q = self.W_Q(x).view(self.batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.qkv).transpose(1, 2) K = self.W_K(x).view(self.batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.qkv).transpose(1, 2) # (1,12,197,64) V = self.W_V(x).view(self.batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.qkv).transpose(1, 2) # (batch,num_heads,length,qkv_dim) att_result = CalculationAttention()(Q, K, V, self.qkv) # (batch,num_heads,length,qkv) att_result = att_result.transpose(1, 2).flatten(2) # (1,197,768) return att_result class CalculationAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, ): super(CalculationAttention, self).__init__() def forward(self, Q, K, V, qkv): score = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(2, 3)) / (np.sqrt(qkv)) score = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(score) score = torch.matmul(score, V) return score class Mlp(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embed_dim, mlp_ratio, dropout): super(Mlp, self).__init__() self.fc1 = nn.Linear(embed_dim,embed_dim*mlp_ratio) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(embed_dim*mlp_ratio,embed_dim) self.actlayer = nn.GELU() self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout) self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self,x): x = self.fc1(x) x = self.actlayer(x) x = self.dropout1(x) x = self.fc2(x) x = self.dropout2(x) return x class Classification(nn.Module): def __init__(self,embed_dim,num_class,dropout): super(Classification, self).__init__() self.fc1 = nn.Linear(embed_dim,embed_dim) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(embed_dim,num_class) self.relu = nn.ReLU(True) self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout) self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self,x): x = x[:,0] x = self.fc1(x) x = self.relu(x) x = self.dropout1(x) x = self.fc2(x) x = self.dropout2(x) return x def main(): ins = torch.randn((1, 3, 224, 224)) vitmodel = Vit() out = vitmodel(ins) print(out.shape) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
三、各模块代码详解
1. Vit()类
class Vit(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size=1, # 样本批量 image_size=224, # 输入图片大小 patch_size=16, # 所用卷积核尺寸,认为patch*patch块大小为一个序列数据 in_channels=3, #输入通道数 embed_dim=768, #输出通道数,即卷积核个数 num_classes=1000, # 分类个数 depth=12, # EncoderLayer层堆叠深度 num_heads=12, # 多头自注意力机制的heads数 mlp_ratio=4, # 隐藏层节点倍数 dropout=0, #Dropout发生概率 ): super(Vit, self).__init__() self.patch_embedding = PatchEmbedding(batch_size, image_size, patch_size, in_channels, embed_dim, dropout) self.encoder = Encoder(batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio, dropout, depth) self.classifier = Classification(embed_dim,num_classes,dropout) def forward(self, x): x = self.patch_embedding(x) x = self.encoder(x) x = self.classifier(x) return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
Vision Transfomer基本框架由PatchEmbedding层,Transfomer Encoder层和分类器Classifier构成
2.PatchEmbedding()类
class PatchEmbedding(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size, image_size, patch_size, in_channels, embed_dim, dropout): super(PatchEmbedding, self).__init__() n_patchs = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, embed_dim, patch_size, patch_size) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) self.class_token = torch.randn((batch_size, 1, embed_dim)) self.position = torch.randn((batch_size, n_patchs + 1, embed_dim)) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) # (batch,in_channel,h,w)-(batch,embed_dim,h/patch_size,w/patch_size)(1,768,14,14) x = x.flatten(2) # batch,embed_dim,h*w/(patch_size)**2 (1,768,196) x = x.transpose(1, 2) # batch,h*w/(patch_size)^^2,embed_dim (1,196,768) x = torch.concat((self.class_token, x), axis=1) # (1,197,768) x = x + self.position # (1,197,768) x = self.dropout(x) #(1,197,768) return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
PatchEmbedding类通过尺寸大小为16*16,步长为16,数量为768的卷积核实现了将输入[1,3,224,224]转化为[1,768,14,14],再通过flatten()将最后两位展平变为[1,768,196],transpose()转换维度为[1,196,768],concat()连接class_token变为[1,197,768],最后加上随机产生的位置信息。
3.Encoder()类
class Encoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio, dropout, depth): super(Encoder, self).__init__() layer_list = [] for i in range(depth): encoder_layer = EncoderLayer(batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio, dropout, ) layer_list.append(encoder_layer) self.layer = nn.Sequential(*layer_list) self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim) def forward(self, x): for layer in self.layer: x = layer(x) x = self.norm(x) return x class EncoderLayer(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio, dropout, ): super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__() self.attn_norm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim, eps=1e-6) self.attn = Attention(batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, ) self.mlp_norm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim, eps=1e-6) self.mlp = Mlp(embed_dim, mlp_ratio, dropout) def forward(self, x): residual = x # 残差 residual x = self.attn_norm(x) x = self.attn(x) x = x + residual residual = x # 残差 residual x = self.mlp_norm(x) x = self.mlp(x) x = x + residual return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
nn.Sequential(*layer_list)是将layer_list列表拆成一个个元素容纳
4.Attention()类
class Attention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, batch_size, embed_dim, num_heads, ): super(Attention, self).__init__() self.qkv = embed_dim // num_heads self.batch_size = batch_size self.num_heads = num_heads self.W_Q = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.W_K = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.W_V = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) def forward(self, x): Q = self.W_Q(x).view(self.batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.qkv).transpose(1, 2) K = self.W_K(x).view(self.batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.qkv).transpose(1, 2) # (1,12,197,64) V = self.W_V(x).view(self.batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.qkv).transpose(1, 2) # (batch,num_heads,length,qkv_dim) att_result = CalculationAttention()(Q, K, V, self.qkv) # (batch,num_heads,length,qkv) att_result = att_result.transpose(1, 2).flatten(2) # (1,197,768) return att_result class CalculationAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, ): super(CalculationAttention, self).__init__() def forward(self, Q, K, V, qkv): score = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(2, 3)) / (np.sqrt(qkv)) score = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(score) score = torch.matmul(score, V) return score
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
Attention()类产生Q,K,V矩阵,Calculation()类进行Attention的计算。Q,K,V矩阵利用nn.Linear()线性映射产生W_Q,W_K,W_V参数矩阵,与x相乘得到。
5.Mlp()类
class Mlp(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embed_dim, mlp_ratio, dropout): super(Mlp, self).__init__() self.fc1 = nn.Linear(embed_dim,embed_dim*mlp_ratio) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(embed_dim*mlp_ratio,embed_dim) self.actlayer = nn.GELU() # GELU>ELU>RELU>Sigmond self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout) self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self,x): x = self.fc1(x) x = self.actlayer(x) x = self.dropout1(x) x = self.fc2(x) x = self.dropout2(x) return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
多层感知机为多层线性映射,通过GELU()增加非线性,Dropout()防止过拟合
6.Classifier()类
class Classification(nn.Module): def __init__(self,embed_dim,num_class,dropout): super(Classification, self).__init__() self.fc1 = nn.Linear(embed_dim,embed_dim) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(embed_dim,num_class) self.relu = nn.ReLU(True) self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout) self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self,x): x = x[:,0] # 取class_token输入到分类器中进行最后的分类判别 x = self.fc1(x) x = self.relu(x) x = self.dropout1(x) x = self.fc2(x) x = self.dropout2(x) return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
分类器本质上也为多层感知机,与MLP相似,不过在前向传播过程中,需注意取最开始添加class_token进行最后分类判别。
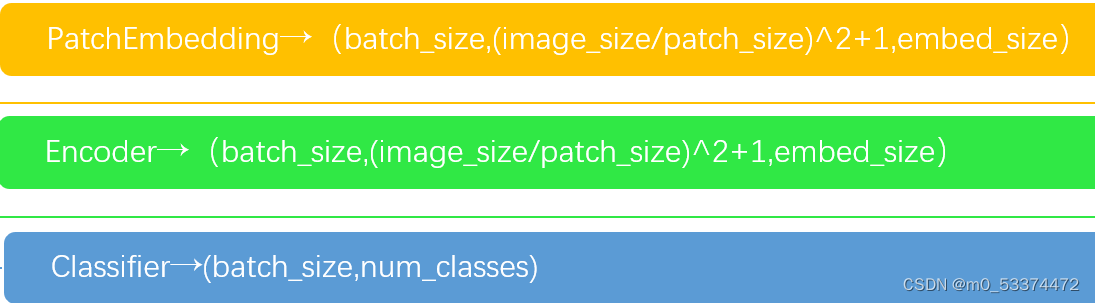
7.数据流图
四、总结
本篇着重在于Vision Transfomer的Pytorch实现,接下来会复现Vision Transformer Advanced,如有问题可或想法可相互交流.



