- 12021国赛数据处理_乙醇偶合制备c4烯烃数学建模论文
- 2Unity光照渲染设置_unity渲染设置在哪
- 3【Transformer系列(4)】Transformer模型结构超详细解读_transformer结构
- 4万字讲解9种Web应用攻击与防护安全。XSS、CSRF、SQL注入等是如何实现的
- 5使用 PyTorch 构建 NLP 聊天机器人_使用pytorch搭建聊天机器人模型
- 6flutter Got socket error trying to find package nested at
- 7Android 和 iOS 漏洞加剧移动安全的威胁_cwe漏洞安卓
- 8python(8)---- pyltp5个核心函数_python pyltp包里的函数
- 9langchain+chatglm阅读理解天龙八部_langchain 直接调用chatglm回答,不构造本地知识库
- 10玩客云改造HP2130打印机服务器_刷打印服务器
Python 高性能 web 框架 - FastApi 全面指南_fasterapi
赞
踩
原文:Python 高性能 web 框架 - FastApi 全面指南 - 知乎
一、简介
FastAPI 是一个用于构建 API 的现代、快速(高性能)的 web 框架,使用 Python 3.6+ 并基于标准的 Python 类型提示。
它具有如下这些优点:
- 快速:可与 NodeJS 和 Go 比肩的极高性能(归功于 Starlette 和 Pydantic)
- 高效编码:提高功能开发速度约 200% 至 300%
- 更少 bug:减少约 40% 的人为(开发者)导致错误。
- 智能:极佳的编辑器支持。处处皆可自动补全,减少调试时间
- 简单:设计的易于使用和学习,阅读文档的时间更短
- 简短:使代码重复最小化。通过不同的参数声明实现丰富功能。bug 更少
- 健壮:生产可用级别的代码。还有自动生成的交互式文档
- 标准化:基于(并完全兼容)API 的相关开放标准:OpenAPI (以前被称为 Swagger) 和 JSON Schema。
二、安装
pip install fastapiASGI 服务器可以使用uvicorn:
pip install uvicorn[standard]三、简单示例
创建一个 main.py 文件并写入以下内容:
- from typing import Optional
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.get("/")
- def read_root():
- return {"Hello": "World"}
-
-
- @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
- def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
- return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
uvicorn main:app --reload访问URL:http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery,你将会看到如下 JSON 响应:
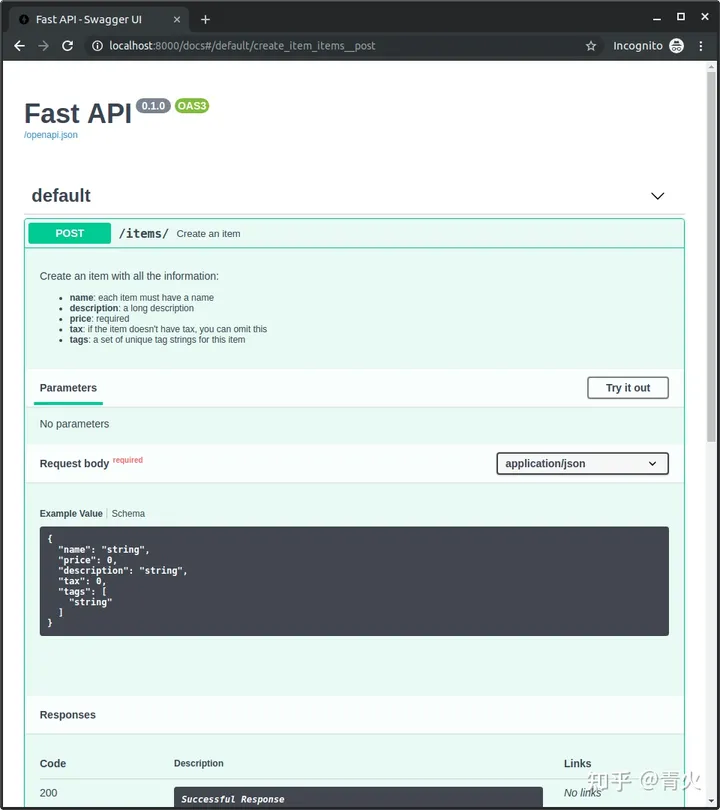
{"item_id": 5, "q": "somequery"}访问URL:http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs,你会看到自动生成的交互式 API 文档,由Swagger UI 生成:

访问URL:http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc,你会看到另一个自动生成的文档(由ReDoc生成):

四、请求
使用与 Python 格式化字符串相同的语法来声明路径"参数"或"变量":
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
-
- async def read_item(item_id):
-
- return {"item_id": item_id}
路径参数item_id的值将作为参数item_id传递给你的函数。声明不属于路径参数的其他函数参数时,它们将被自动解释为"查询字符串"参数:
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
- fake_items_db = [{"item_name": "Foo"}, {"item_name": "Bar"}, {"item_name": "Baz"}]
-
-
- @app.get("/items/")
-
- async def read_item(skip: int = 0, limit: int = 10):
-
- return fake_items_db[skip : skip + limit]
查询字符串是键值对的集合,这些键值对位于 URL 的?之后,并以&符号分隔。
可以使用Query对查询进行额外的校验:
- from typing import Optional
-
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.get("/items/")
- async def read_items(q: Optional[str] = Query(None, max_length=50)):
- results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
- if q:
- results.update({"q": q})
- return results
Query 有如下这些字段校验:
- min_length 最小长度
- max_length 最大长度
- regex 正则匹配
- Query 第一个参数为默认值,
...表示是必需的
Path和Query用法一样,也能对查询字段进行校验。
而且你还可以声明数值校验:
- from fastapi import FastAPI, Path, Query
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
- async def read_items(
- *,
- item_id: int = Path(..., title="The ID of the item to get", ge=0, le=1000),
- q: str,
-
- size: float = Query(..., gt=0, lt=10.5)
-
- ):
- results = {"item_id": item_id}
- if q:
- results.update({"q": q})
- return results

gt:大于ge:大于等于lt:小于le:小于等于
类似的还有Cookie:
- from typing import Optional
-
-
- from fastapi import Cookie, FastAPI
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.get("/items/")
- async def read_items(ads_id: Optional[str] = Cookie(None)):
- return {"ads_id": ads_id}
以及Header:
- from typing import Optional
-
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI, Header
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.get("/items/")
- async def read_items(user_agent: Optional[str] = Header(None)):
- return {"User-Agent": user_agent}
还可以为路径设置tags标签进行分组:
- from typing import Optional, Set
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI
- from pydantic import BaseModel
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- class Item(BaseModel):
- name: str
- description: Optional[str] = None
- price: float
- tax: Optional[float] = None
- tags: Set[str] = []
-
-
-
- @app.post("/items/", response_model=Item, tags=["items"])
-
- async def create_item(item: Item):
- return item
-
-
-
- @app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
-
- async def read_items():
- return [{"name": "Foo", "price": 42}]
-
-
-
- @app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
-
- async def read_users():
- return [{"username": "johndoe"}]


还可以设置summary 和 description:
- from typing import Optional, Set
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI
- from pydantic import BaseModel
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- class Item(BaseModel):
- name: str
- description: Optional[str] = None
- price: float
- tax: Optional[float] = None
- tags: Set[str] = []
-
-
- @app.post(
- "/items/",
- response_model=Item,
- summary="Create an item",
- description="Create an item with all the information, name, description, price, tax and a set of unique tags",
- )
- async def create_item(item: Item):
- return item

多行注释:
- from typing import Optional, Set
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI
- from pydantic import BaseModel
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- class Item(BaseModel):
- name: str
- description: Optional[str] = None
- price: float
- tax: Optional[float] = None
- tags: Set[str] = []
-
-
- @app.post("/items/", response_model=Item, summary="Create an item")
- async def create_item(item: Item):
-
- """
- Create an item with all the information:
- - **name**: each item must have a name
- - **description**: a long description
- - **price**: required
- - **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- - **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
- """
-
- return item

废弃路由:
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
- async def read_items():
- return [{"name": "Foo", "price": 42}]
-
-
- @app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
- async def read_users():
- return [{"username": "johndoe"}]
-
-
-
- @app.get("/elements/", tags=["items"], deprecated=True)
-
- async def read_elements():
- return [{"item_id": "Foo"}]


五、响应
使用response_model参数来声明用于响应的模型:
- from typing import List, Optional
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI
- from pydantic import BaseModel
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- class Item(BaseModel):
- name: str
- description: Optional[str] = None
- price: float
- tax: Optional[float] = None
- tags: List[str] = []
-
-
-
- @app.post("/items/", response_model=Item)
-
- async def create_item(item: Item):
- return item

response_model_exclude_unset=True:响应中将不会包含那些默认值,而是仅有实际设置的值response_model_include包含哪些属性response_model_exclude省略某些属性
status_code参数来声明用于响应的 HTTP 状态码:
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
-
- @app.post("/items/", status_code=201)
-
- async def create_item(name: str):
- return {"name": name}
表单字段时,要使用Form:
- from fastapi import FastAPI, Form
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.post("/login/")
- async def login(username: str = Form(...), password: str = Form(...)):
- return {"username": username}
File用于定义客户端的上传文件(接收上传文件,要预先安装python-multipart):
- from fastapi import FastAPI, File, UploadFile
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.post("/files/")
- async def create_file(file: bytes = File(...)):
- return {"file_size": len(file)}
-
-
- @app.post("/uploadfile/")
- async def create_upload_file(file: UploadFile = File(...)):
- return {"filename": file.filename}
向客户端返回 HTTP 错误响应,可以使用HTTPException。
- from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
- items = {"foo": "The Foo Wrestlers"}
-
-
- @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
- async def read_item(item_id: str):
- if item_id not in items:
- raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found")
- return {"item": items[item_id]}
使用response_description设置响应描述:
- from typing import Optional, Set
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI
- from pydantic import BaseModel
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- class Item(BaseModel):
- name: str
- description: Optional[str] = None
- price: float
- tax: Optional[float] = None
- tags: Set[str] = []
-
-
- @app.post(
- "/items/",
- response_model=Item,
- summary="Create an item",
- response_description="The created item",
- )
- async def create_item(item: Item):
- """
- Create an item with all the information:
- - **name**: each item must have a name
- - **description**: a long description
- - **price**: required
- - **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- - **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
- """
- return item


六、JSON兼容
在某些情况下,你可能需要把数据(例如Pydantic模型)转换成JSON形式,例如存储在数据库中,这时候你就需要用到jsonable_encoder()方法。
- from datetime import datetime
- from typing import Optional
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
- from fastapi.encoders import jsonable_encoder
-
- from pydantic import BaseModel
-
- fake_db = {}
-
-
- class Item(BaseModel):
- title: str
- timestamp: datetime
- description: Optional[str] = None
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- @app.put("/items/{id}")
- def update_item(id: str, item: Item):
-
- json_compatible_item_data = jsonable_encoder(item)
-
- fake_db[id] = json_compatible_item_data

七、依赖注入
FastAPI 提供了简单易用,但功能强大的依赖注入系统,可以让开发人员轻松地把组件集成至FastAPI。
什么是「依赖注入」?
依赖注入是一种消除类之间依赖关系的设计模式。把有依赖关系的类放到容器中,解析出这些类的实例,就是依赖注入。目的是实现类的解耦。
示例:
- from typing import Optional
-
- from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
-
- async def common_parameters(q: Optional[str] = None, skip: int = 0, limit: int = 100):
-
- return {"q": q, "skip": skip, "limit": limit}
-
-
-
- @app.get("/items/")
- async def read_items(commons: dict = Depends(common_parameters)):
- return commons
-
-
- @app.get("/users/")
- async def read_users(commons: dict = Depends(common_parameters)):
- return commons

本例中的依赖项预期接收如下参数:
- 类型为
str的可选查询参数q - 类型为
int的可选查询参数skip,默认值是0 - 类型为
int的可选查询参数limit,默认值是100
然后,依赖项函数返回包含这些值的 dict。
使用Class作为依赖:
- from typing import Optional
-
- from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- fake_items_db = [{"item_name": "Foo"}, {"item_name": "Bar"}, {"item_name": "Baz"}]
-
-
- class CommonQueryParams:
- def __init__(self, q: Optional[str] = None, skip: int = 0, limit: int = 100):
- self.q = q
- self.skip = skip
- self.limit = limit
-
-
- @app.get("/items/")
-
- async def read_items(commons: CommonQueryParams = Depends(CommonQueryParams)):
-
- response = {}
- if commons.q:
- response.update({"q": commons.q})
- items = fake_items_db[commons.skip : commons.skip + commons.limit]
- response.update({"items": items})
- return response

使用嵌套子依赖:
- from typing import Optional
-
- from fastapi import Cookie, Depends, FastAPI
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- def query_extractor(q: Optional[str] = None):
- return q
-
-
- def query_or_cookie_extractor(
- q: str = Depends(query_extractor), last_query: Optional[str] = Cookie(None)
- ):
- if not q:
- return last_query
- return q
-
-
- @app.get("/items/")
-
- async def read_query(query_or_default: str = Depends(query_or_cookie_extractor)):
-
- return {"q_or_cookie": query_or_default}

在路径中使用依赖:
- from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, Header, HTTPException
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- async def verify_token(x_token: str = Header(...)):
- if x_token != "fake-super-secret-token":
- raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="X-Token header invalid")
-
-
- async def verify_key(x_key: str = Header(...)):
- if x_key != "fake-super-secret-key":
- raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="X-Key header invalid")
- return x_key
-
-
-
- @app.get("/items/", dependencies=[Depends(verify_token), Depends(verify_key)])
-
- async def read_items():
- return [{"item": "Foo"}, {"item": "Bar"}]

全局依赖项,可以为所有路径操作应用该依赖项:
- from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, Header, HTTPException
-
-
- async def verify_token(x_token: str = Header(...)):
- if x_token != "fake-super-secret-token":
- raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="X-Token header invalid")
-
-
- async def verify_key(x_key: str = Header(...)):
- if x_key != "fake-super-secret-key":
- raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="X-Key header invalid")
- return x_key
-
-
-
- app = FastAPI(dependencies=[Depends(verify_token), Depends(verify_key)])
-
-
-
- @app.get("/items/")
- async def read_items():
- return [{"item": "Portal Gun"}, {"item": "Plumbus"}]
-
-
- @app.get("/users/")
- async def read_users():
- return [{"username": "Rick"}, {"username": "Morty"}]

八、安全
在许多框架和系统中,仅处理安全性和身份认证就会花费大量的精力和代码(在许多情况下,可能占编写的所有代码的 50% 或更多)。
FastAPI 提供了多种工具,可帮助你以标准的方式轻松、快速地处理安全性,而无需研究和学习所有的安全规范。
JWT 表示 「JSON Web Tokens」。
它是一个将 JSON 对象编码为密集且没有空格的长字符串的标准。字符串看起来像这样:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ.SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5c它没有被加密,因此任何人都可以从字符串内容中还原数据。
但它经过了签名。因此,当你收到一个由你发出的令牌时,可以校验令牌是否真的由你发出。
通过这种方式,你可以创建一个有效期为 1 周的令牌。然后当用户第二天使用令牌重新访问时,你知道该用户仍然处于登入状态。
一周后令牌将会过期,用户将不会通过认证,必须再次登录才能获得一个新令牌。而且如果用户(或第三方)试图修改令牌以篡改过期时间,你将因为签名不匹配而能够发觉。
OAuth2
OAuth2是一个规范,它定义了几种处理身份认证和授权的方法。
它是一个相当广泛的规范,涵盖了一些复杂的使用场景。
它包括了使用「第三方」进行身份认证的方法。
这就是所有带有「使用 Facebook,Google,Twitter,GitHub 登录」的系统背后所使用的机制。
下面演示了如何使用OAuth2 和 JWT进行用户验证。
- from datetime import datetime, timedelta
- from typing import Optional
-
- from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, HTTPException, status
- from fastapi.security import OAuth2PasswordBearer, OAuth2PasswordRequestForm
- from jose import JWTError, jwt
-
- from passlib.context import CryptContext
-
- from pydantic import BaseModel
-
- # to get a string like this run:
- # openssl rand -hex 32
- SECRET_KEY = "09d25e094faa6ca2556c818166b7a9563b93f7099f6f0f4caa6cf63b88e8d3e7"
- ALGORITHM = "HS256"
- ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES = 30
-
-
- fake_users_db = {
- "johndoe": {
- "username": "johndoe",
- "full_name": "John Doe",
- "email": "johndoe@example.com",
- "hashed_password": "$2b$12$EixZaYVK1fsbw1ZfbX3OXePaWxn96p36WQoeG6Lruj3vjPGga31lW",
- "disabled": False,
- }
- }
-
-
- class Token(BaseModel):
- access_token: str
- token_type: str
-
-
- class TokenData(BaseModel):
- username: Optional[str] = None
-
-
- class User(BaseModel):
- username: str
- email: Optional[str] = None
- full_name: Optional[str] = None
- disabled: Optional[bool] = None
-
-
- class UserInDB(User):
- hashed_password: str
-
-
-
- pwd_context = CryptContext(schemes=["bcrypt"], deprecated="auto")
-
-
- oauth2_scheme = OAuth2PasswordBearer(tokenUrl="token")
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
-
- def verify_password(plain_password, hashed_password):
-
- return pwd_context.verify(plain_password, hashed_password)
-
-
-
-
- def get_password_hash(password):
- return pwd_context.hash(password)
-
-
-
- def get_user(db, username: str):
- if username in db:
- user_dict = db[username]
- return UserInDB(**user_dict)
-
-
-
- def authenticate_user(fake_db, username: str, password: str):
- user = get_user(fake_db, username)
-
- if not user:
-
- return False
-
- if not verify_password(password, user.hashed_password):
-
- return False
-
- return user
-
-
-
- def create_access_token(data: dict, expires_delta: Optional[timedelta] = None):
- to_encode = data.copy()
- if expires_delta:
- expire = datetime.utcnow() + expires_delta
- else:
- expire = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(minutes=15)
- to_encode.update({"exp": expire})
- encoded_jwt = jwt.encode(to_encode, SECRET_KEY, algorithm=ALGORITHM)
- return encoded_jwt
-
-
- async def get_current_user(token: str = Depends(oauth2_scheme)):
- credentials_exception = HTTPException(
- status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
- detail="Could not validate credentials",
- headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
- )
- try:
- payload = jwt.decode(token, SECRET_KEY, algorithms=[ALGORITHM])
- username: str = payload.get("sub")
- if username is None:
- raise credentials_exception
- token_data = TokenData(username=username)
- except JWTError:
- raise credentials_exception
- user = get_user(fake_users_db, username=token_data.username)
- if user is None:
- raise credentials_exception
- return user
-
-
- async def get_current_active_user(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_user)):
- if current_user.disabled:
- raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Inactive user")
- return current_user
-
-
- @app.post("/token", response_model=Token)
- async def login_for_access_token(form_data: OAuth2PasswordRequestForm = Depends()):
- user = authenticate_user(fake_users_db, form_data.username, form_data.password)
- if not user:
- raise HTTPException(
- status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED,
- detail="Incorrect username or password",
- headers={"WWW-Authenticate": "Bearer"},
- )
- access_token_expires = timedelta(minutes=ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRE_MINUTES)
- access_token = create_access_token(
- data={"sub": user.username}, expires_delta=access_token_expires
- )
- return {"access_token": access_token, "token_type": "bearer"}
-
-
- @app.get("/users/me/", response_model=User)
- async def read_users_me(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
- return current_user
-
-
- @app.get("/users/me/items/")
- async def read_own_items(current_user: User = Depends(get_current_active_user)):
- return [{"item_id": "Foo", "owner": current_user.username}]

OAuth2PasswordBearer:访问tokenUrl地址,获取token并返回OAuth2PasswordRequestForm是一个类依赖项,声明了如下的请求表单:usernamepassword- 一个可选的
scope字段,是一个由空格分隔的字符串组成的大字符串 - 一个可选的
grant_type - 一个可选的
client_id - 一个可选的
client_secret
九、中间件
"中间件"是一个函数,它在每个请求被特定的路径操作处理之前,以及在每个响应返回之前工作。
要创建中间件你可以在函数的顶部使用装饰器 @app.middleware("http").
中间件参数接收如下参数:
request- 一个函数
call_next它将接收request作为参数- 这个函数将
request传递给相应的 路径操作 - 然后它将返回由相应的路径操作生成的
response
- 这个函数将
- 然后你可以在返回
response前进一步修改它
- import time
-
- from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
-
- @app.middleware("http")
-
- async def add_process_time_header(request: Request, call_next):
-
- start_time = time.time()
-
- response = await call_next(request)
-
- process_time = time.time() - start_time
- response.headers["X-Process-Time"] = str(process_time)
-
- return response

十、跨域设置
你可以在FastAPI应用中使用CORSMiddleware来配置跨域:
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
- from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- origins = [
- "http://localhost.tiangolo.com",
- "https://localhost.tiangolo.com",
- "http://localhost",
- "http://localhost:8080",
-
- ]
-
-
-
- app.add_middleware(
- CORSMiddleware,
- allow_origins=origins,
- allow_credentials=True,
- allow_methods=["*"],
- allow_headers=["*"],
-
- )
-
-
-
- @app.get("/")
- async def main():
- return {"message": "Hello World"}

它支持以下参数:
allow_origins- 一个允许跨域请求的源列表。例如['https://example.org', 'https://www.example.org']。你可以使用['*']允许任何源。allow_origin_regex- 一个正则表达式字符串,匹配的源允许跨域请求。例如'https://.*\.example\.org'。allow_methods- 一个允许跨域请求的 HTTP 方法列表。默认为['GET']。你可以使用['*']来允许所有标准方法。allow_headers- 一个允许跨域请求的 HTTP 请求头列表。默认为[]。你可以使用['*']允许所有的请求头。Accept、Accept-Language、Content-Language以及Content-Type请求头总是允许 CORS 请求。allow_credentials- 指示跨域请求支持 cookies。默认是False。另外,允许凭证时allow_origins不能设定为['*'],必须指定源。expose_headers- 指示可以被浏览器访问的响应头。默认为[]。max_age- 设定浏览器缓存 CORS 响应的最长时间,单位是秒。默认为600。
十一、APIRouter
使用APIRouter同样也能对路由进行操作:
- from fastapi import APIRouter
-
- router = APIRouter()
-
-
-
- @router.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
-
- async def read_users():
- return [{"username": "Rick"}, {"username": "Morty"}]
-
-
-
- @router.get("/users/me", tags=["users"])
-
- async def read_user_me():
- return {"username": "fakecurrentuser"}
-
-
-
- @router.get("/users/{username}", tags=["users"])
-
- async def read_user(username: str):
- return {"username": username}

为所有路径进行同样的操作:
- from fastapi import APIRouter, Depends, HTTPException
-
- from ..dependencies import get_token_header
-
-
- router = APIRouter(
- prefix="/items",
- tags=["items"],
- dependencies=[Depends(get_token_header)],
- responses={404: {"description": "Not found"}},
- )
-
-
-
- fake_items_db = {"plumbus": {"name": "Plumbus"}, "gun": {"name": "Portal Gun"}}
-
-
-
- @router.get("/")
-
- async def read_items():
- return fake_items_db
-
-
-
- @router.get("/{item_id}")
-
- async def read_item(item_id: str):
- if item_id not in fake_items_db:
- raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Item not found")
- return {"name": fake_items_db[item_id]["name"], "item_id": item_id}
-
-
- @router.put(
- "/{item_id}",
- tags=["custom"],
- responses={403: {"description": "Operation forbidden"}},
- )
- async def update_item(item_id: str):
- if item_id != "plumbus":
- raise HTTPException(
- status_code=403, detail="You can only update the item: plumbus"
- )
- return {"item_id": item_id, "name": "The great Plumbus"}

该示例,就为所有的路径添加了前缀,标签、依赖和返回,而不用在每个路径上单独声明,简化了代码。
十二、Background Tasks
background tasks 就是在返回响应之后立即运行的任务。
- from fastapi import BackgroundTasks, FastAPI
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- def write_notification(email: str, message=""):
- with open("log.txt", mode="w") as email_file:
- content = f"notification for {email}: {message}"
- email_file.write(content)
-
-
- @app.post("/send-notification/{email}")
- async def send_notification(email: str, background_tasks: BackgroundTasks):
- background_tasks.add_task(write_notification, email, message="some notification")
- return {"message": "Notification sent in the background"}

十三、静态文件
首先需要安装aiofiles:
pip install aiofiles 使用:
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
- from fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
- app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory="static"), name="static")
十四、子应用
如果你有2个独立的FastAPI的应用,你可以设置一个为主应用,另外一个为子应用:
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
-
-
-
- @app.get("/app")
-
- def read_main():
- return {"message": "Hello World from main app"}
-
-
-
- subapi = FastAPI()
-
-
- @subapi.get("/sub")
- def read_sub():
- return {"message": "Hello World from sub API"}
-
-
- app.mount("/subapi", subapi)

十五、代理
可以使用root_path来设置代理。
使用命令行:
uvicorn main:app --root-path /api/v1 或者在代码中设置:
- from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
-
-
- app = FastAPI(root_path="/api/v1")
-
-
-
- @app.get("/app")
- def read_main(request: Request):
- return {"message": "Hello World", "root_path": request.scope.get("root_path")}
十六、使用模板
你可以在FastAPI中使用任何模板,常用的选择是Jinja2。
pip install jinja2使用:
- from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
- from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
- from fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles
-
- from fastapi.templating import Jinja2Templates
-
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
- app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory="static"), name="static")
-
-
-
- templates = Jinja2Templates(directory="templates")
-
-
-
- @app.get("/items/{id}", response_class=HTMLResponse)
-
- async def read_item(request: Request, id: str):
- return templates.TemplateResponse("item.html", {"request": request, "id": id})

模板文件templates/item.html:
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Item Details</title>
- <link href="{{ url_for('static', path='/styles.css') }}" rel="stylesheet">
- </head>
- <body>
-
- <h1>Item ID: {{ id }}</h1>
-
- </body>
- </html>
十七:WebSockets
- from fastapi import FastAPI, WebSocket
-
- from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
- html = """
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Chat</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>WebSocket Chat</h1>
- <form action="" onsubmit="sendMessage(event)">
- <input type="text" id="messageText" autocomplete="off"/>
- <button>Send</button>
- </form>
- <ul id='messages'>
- </ul>
- <script>
- var ws = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8000/ws");
- ws.onmessage = function(event) {
- var messages = document.getElementById('messages')
- var message = document.createElement('li')
- var content = document.createTextNode(event.data)
- message.appendChild(content)
- messages.appendChild(message)
- };
- function sendMessage(event) {
- var input = document.getElementById("messageText")
- ws.send(input.value)
- input.value = ''
- event.preventDefault()
- }
- </script>
- </body>
- </html>
- """
-
-
- @app.get("/")
- async def get():
- return HTMLResponse(html)
-
-
-
- @app.websocket("/ws")
-
- async def websocket_endpoint(websocket: WebSocket):
- await websocket.accept()
- while True:
- data = await websocket.receive_text()
- await websocket.send_text(f"Message text was: {data}")

十八、startup - shutdown事件
你可以设置应用的启动和关闭事件回调函数:
- from fastapi import FastAPI
-
- app = FastAPI()
-
- items = {}
-
- @app.on_event("shutdown")
- def shutdown_event():
- with open("log.txt", mode="a") as log:
- log.write("Application shutdown")
-
-
- @app.on_event("startup")
- async def startup_event():
- items["foo"] = {"name": "Fighters"}
- items["bar"] = {"name": "Tenders"}
-
-
- @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
- async def read_items(item_id: str):
- return items[item_id]



