- 1202104 美团优选2-1 算法_美团优选输入输出
- 2imazing破解版百度云2.17.3(附激活许可证下载)_imazing 2 许可证
- 3基于FPGA的VGA图像显示_vga显示fpga
- 4探索创新代码托管平台:GitCode上的Mosiki/Github镜像仓库
- 5Can We Edit Multimodal Large Language Models?阅读笔记
- 6【MySQL】MySQL分库分表详解_mysql 分表
- 7如何使用Whisper语音识别模型_whisper离线语音合成
- 8前端三大主流框架中文文档_web前端三大主流框架
- 9数据框的切片_数据框切片
- 10直接插入排序(C++实现)_直接插入排序数据结构c++
DEM山体阴影原理以及算法详解_地形阴影校正 公式
赞
踩
山体阴影原理以及算法详解
山体阴影基本原理:
山体阴影是假想一个光源在某个方向和某个太阳高度的模拟下,用过临近像元的计算来生成一副0-255的灰度图。
一、山体阴影的主要参数:
1、 太阳光线的入射角度:这个角度的量算起点是正北方向,按照顺时针的方向,角度的范围是0到360度,如下图所示,默认的角度是315度,西北方向,如下图所示:
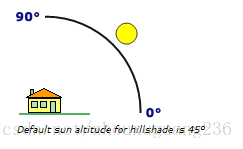
2、 太阳高度角:太阳高度角也简称太阳高度。是太阳光线和当地地平面之间的夹角,范围是0-90度,默认的太阳高度是45度,如下图所示:
二、山体阴影计算方法
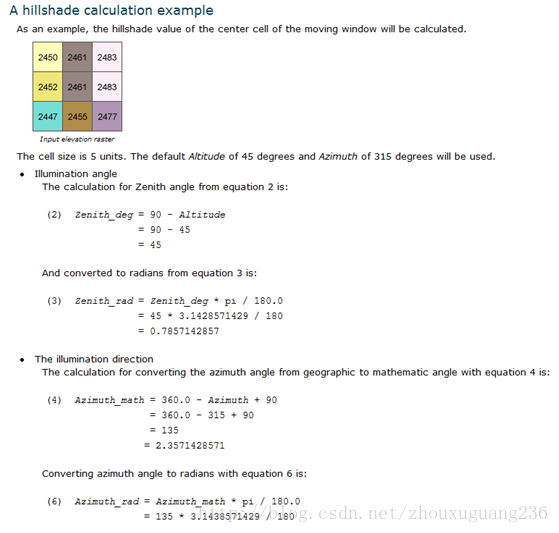
山体阴影的计算公式如下
(1) Hillshade = 255.0 * ((cos(Zenith_rad)* cos(Slope_rad)) +
(sin(Zenith_rad) * sin(Slope_rad) * cos(Azimuth_rad- Aspect_rad)))
如果Hillshade < 0, 则设Hillshade=0.
其中,Zenith_rad是太阳天顶角的的弧度数,Slope_rad是某一点的坡度弧度数,Azimuth_rad是指太阳光线方向角的弧度数,Aspect_rad是某一点的坡向弧度数。
计算山体阴影的照明光源的角度默认是太阳高度角,但是真正计算时,需要用到太阳天顶角,太阳天顶角的计算方法是90°-太阳高度角。所以有如下计算公式:
计算太阳天顶角弧度数:
(2) Zenith_deg = 90 - Altitude
转换为弧度数:
(3) Zenith_rad = Zenith * pi / 180.0
计算照明的方向:
照明的方向角是指定的角度数,山体阴影的计算公式需要弧度数。首先,需要将地理上的指南针方向转换为数学上的向右的方向,即向右为起算的方向;其次,需要将角度转换为弧度。
转为数学上的方向角:
(4) Azimuth_math = 360.0 - Azimuth + 90
注意如果 Azimuth_math >=360.0, 那么:
(5) Azimuth_math = Azimuth_math - 360.0
转换为弧度:
(6) Azimuth_rad = Azimuth_math * pi / 180.0
计算坡度和坡向
坡度和坡向是利用一个3*3的窗口在输入影像中访问每个像素,9个像素从左到右、从上到下分别用a-i表示,如图所示:
a b c d e f g h i
E像元X方向上的变化率采用如下的算法:
(7) [dz/dx] = ((c + 2f + i) - (a + 2d + g)) / (8 * cellsize)
E像元Y方向上的变化率采用如下的算法:
(8) [dz/dy] = ((g + 2h + i) - (a + 2b + c)) / (8 * cellsize)
坡度的弧度计算公式,考虑了Z因子(协调Z方向的单位和Xy平面上单位的一个系数):
(9) Slope_rad = atan (z_factor * sqrt ([dz/dx]2 + [dz/dy]2))
坡向通过下面的方法进行计算:
If [dz/dx] is non-zero:
Aspect_rad= atan2 ([dz/dy], -[dz/dx])
if Aspect_rad< 0 then
Aspect_rad= 2 * pi + Aspect_rad
If [dz/dx] iszero:
if [dz/dy] >0 then
Aspect_rad= pi / 2
else if [dz/dy]< 0 then
Aspect_rad= 2 * pi - pi / 2
else
Aspect_rad = Aspect_rad
山体阴影计算示例:出自arcgis10.0帮助文档。
最后,奉上OpenCL实现的代码:
- __kernel void hillshade_kernel( __global const float *pSrcData,
- __global float *pDestData,const int nWidth,const int nHeight
- , struct HillshadeOption hillOption)
- {
- int j = get_global_id(0);
- int i = get_global_id(1);
-
- if (j >= nWidth || i >= nHeight)
- return;
-
-
- int nTopTmp = i-1;
- int nBottomTmp = i+1;
- int nLeftTep = j-1;
- int nRightTmp = j+1;
-
- //处理边界情况
- if (0 == i)
- {
- nTopTmp = i;
- }
- if (0 == j)
- {
- nLeftTep = j;
- }
- if (i == nHeight-1)
- {
- nBottomTmp = i;
- }
- if (j == nWidth-1)
- {
- nRightTmp = j;
- }
- __local float afRectData[9];
- afRectData[0] = pSrcData[nTopTmp*nWidth+nLeftTep];
- afRectData[1] = pSrcData[nTopTmp*nWidth+j];
- afRectData[2] = pSrcData[nTopTmp*nWidth+nRightTmp];
-
- afRectData[3] = pSrcData[i*nWidth+nLeftTep];
- afRectData[4] = pSrcData[i*nWidth+j];
- afRectData[5] = pSrcData[i*nWidth+nRightTmp];
-
- afRectData[6] = pSrcData[nBottomTmp*nWidth+nLeftTep];
- afRectData[7] = pSrcData[nBottomTmp*nWidth+j];
- afRectData[8] = pSrcData[nBottomTmp*nWidth+nRightTmp];
-
- const float degreesToRadians = (M_PI_F / 180);
-
- float dx = ((afRectData[2]+ afRectData[5]*2 + afRectData[8]) -
- (afRectData[0] + afRectData[3]*2 + afRectData[6])) / (8 * hillOption.dbEwres);
-
- float dy = ((afRectData[6] + afRectData[7]*2 + afRectData[8]) -
- (afRectData[0]+ afRectData[1]*2 + afRectData[2])) / (8 * hillOption.dbNsres);
-
- //计算坡度(弧度)
- float key = sqrt(dx *dx + dy * dy);
- float dfSlope = atan( hillOption.dfzScaleFactor * key);
-
- //计算坡向(弧度)
- float dfAspect = 0;
- if (dx != 0)
- {
- dfAspect = atan2(dy,-dx);
- if (dfAspect < 0)
- {
- dfAspect += 2* M_PI_F;
- }
- }
-
- if (dx == 0)
- {
- if (dy > 0.0f)
- {
- dfAspect = M_PI_F / 2;
- }
-
- else if (dy < 0.0f)
- dfAspect = M_PI_F + M_PI_F / 2;
- }
-
- //将太阳高度和太阳光线角度转换为要求的格式
- float dfZenithDeg = hillOption.dfAltitude;
-
- float dfAzimuthRad = hillOption.dfAzimuth;
-
- //最后计算山体阴影值
- float dfHillshade = 255 * (cos(dfZenithDeg)*cos(dfSlope) +
- sin(dfZenithDeg)*sin(dfSlope)*cos(dfAzimuthRad-dfAspect));
- if (dfHillshade < 0)
- {
- dfHillshade = 0;
- }
-
- if (dfHillshade >= 255)
- {
- dfHillshade = 255;
- }
-
- pDestData[i*nWidth+j] = (int)(dfHillshade+1/2);
-
- }