- 1【Spring Boot】掌握Spring Boot:深入解析配置文件的使用与管理_springboot properties配置数据库
- 2AI绘画Stable Diffusion 如何安装插件?保姆级教程带你全方位了解SD的插件安装与使用!_sd安装中文插件
- 3elasticsearch时间格式DateFormat的含义_elasticsearch date format
- 4基于CNN 对车牌数字进行识别,(二)_车牌识别opencv+cnn
- 55G 室内融合定位白皮书_5g+人员定位和uwb人员定位
- 6bert4keras、transformers 加载预训练bert模型、句向量cls,字向量提取;tokenizer使用_bert4keras预训练模型
- 7【大话数据结构】第八章-查找(1)_如果在查找过程中需要大量的插入元素该查找表采用的储存结构是
- 8【好用的工具】Mac 配置 Java 开发环境_mac jdk1.8
- 9台湾应广OTP系列单片机_1脚为电源的otp单片机
- 10Elasticsearch7 单节点与集群部署_es7.15.1集群部署及认证
从零入门激光SLAM(八)——ROS常用消息_std::msgs
赞
踩
大家好呀,我是一个SLAM方向的在读博士,深知SLAM学习过程一路走来的坎坷,也十分感谢各位大佬的优质文章和源码。随着知识的越来越多,越来越细,我准备整理一个自己的激光SLAM学习笔记专栏,从0带大家快速上手激光SLAM,也方便想入门SLAM的同学和小白学习参考,相信看完会有一定的收获。如有不对的地方欢迎指出,欢迎各位大佬交流讨论,一起进步。 博主创建了一个科研互助群Q:772356582,欢迎大家加入讨论。
目录
ROS很重要一点就是可以对不同类型的消息进行接收与发送,并且能够对数据进行实时的可视化,ROS官网已经给出了很多的消息类型供我们使用。
一、std_msgs
1.1 简介
std_msgs是一种标准消息类型包,包含了一些常用的基本数据类型的消息定义。
1.2 基本类别
std_msgs/Bool:表示布尔值(True或False)
std_msgs/Int8、Int16、Int32、Int64:表示有符号的8、16、32和64位整数
std_msgs/UInt8、UInt16、UInt32、UInt64:表示无符号的8、16、32和64位整数
std_msgs/Float32、Float64:表示单精度和双精度浮点数
std_msgs/String:表示字符串
std_msgs还包括其他类型的消息,例如:
std_msgs/Time:表示ROS的时间戳
std_msgs/Duration:表示时间段
std_msgs/Header:表示ROS消息头,其中包括时间戳、坐标系和序列号等信息。
1.3 使用模板
发布接收字符串
- #include "ros/ros.h"
- #include "std_msgs/String.h"
- #include "std_msgs/Int32.h"
-
- void callback_string(const std_msgs::String::ConstPtr& msg)
- {
- ROS_INFO("Received string: %s", msg->data.c_str());
- // 创建一个新的std_msgs::String类型消息
- std_msgs::String output_msg;
- output_msg.data = "Received string: " + msg->data;
- // 发布新消息
- pub.publish(output_msg);
- }
-
-
- void callback_int(const std_msgs::Int32::ConstPtr& msg)
- {
- ROS_INFO("Received integer: %d", msg->data);
- // 创建一个新的std_msgs::String类型消息
- std_msgs::String output_msg;
- output_msg.data = "Received integer: " + std::to_string(msg->data);
- // 发布新消息
- pub.publish(output_msg);
- }
-
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
- {
- // 初始化ROS节点
- ros::init(argc, argv, "listener_and_talker");
- // 创建ROS节点句柄和两个订阅节点对象,以及一个发布者对象
- ros::NodeHandle nh;
- ros::Subscriber sub_string = nh.subscribe("my_topic_string", 10, callback_string);
- ros::Subscriber sub_int = nh.subscribe("my_topic_int", 10, callback_int);
- ros::Publisher pub = nh.advertise<std_msgs::String>("my_topic_output", 10);
- // 运行ROS节点
- ros::spin();
- return 0;
-
- }

二、geometry_msgs
2.1 简介
ROS中的geometry_msgs是一个包含了各种几何形状相关的消息类型的软件包,主要用于机器人运动控制和感知相关应用中。
2.2 基本类别
- Point:用于表示三维空间中的一个点。
- Quaternion:用于表示四元数,通常用于表示机器人末端执行器的姿态。
- Pose:用于表示三维空间中的一个位姿,即位置和姿态。
- Vector3:用于表示三维空间中的一个向量。
- Twist:用于表示机器人在三维空间中的线速度和角速度。
- Transform:用于表示两个坐标系之间的变换关系,即一个坐标系相对于另一个坐标系的平移和旋转。
- PoseStamped:用于表示带有时间戳的三维空间中的位姿。
- TwistStamped:用于表示带有时间戳的机器人在三维空间中的线速度和角速度。
- TransformStamped:用于表示带有时间戳的两个坐标系之间的变换关系。
- Accel:用于表示机器人在三维空间中的线加速度和角加速度。
- AccelStamped:用于表示带有时间戳的机器人在三维空间中的线加速度和角加速度。
更多使用方法见官网https://wiki.ros.org/geometry_msgs?distro=melodic
2.3 使用模板
- 发布接收位置
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h>
-
- void poseCallback(const geometry_msgs::PoseStamped::ConstPtr& msg)
- {
- // 在回调函数中处理接收到的消息
- ROS_INFO("Received a pose at time %f", msg->header.stamp.toSec());
- ROS_INFO("Position: x=%f, y=%f, z=%f", msg->pose.position.x, msg->pose.position.y, msg->pose.position.z);
- ROS_INFO("Orientation: x=%f, y=%f, z=%f, w=%f", msg->pose.orientation.x, msg->pose.orientation.y, msg->pose.orientation.z, msg->pose.orientation.w);
- }
-
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
- {
- ros::init(argc, argv, "pose_node"); // 初始化ROS节点
- ros::NodeHandle nh;
-
- // 创建一个用于接收pose消息的订阅者
- ros::Subscriber sub = nh.subscribe<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>("pose_topic", 10, poseCallback);
-
- // 创建一个用于发送pose消息的发布者
- ros::Publisher pub = nh.advertise<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>("pose_topic", 10);
-
- // 设置消息的头部信息
- geometry_msgs::PoseStamped pose_msg;
- pose_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
- pose_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
-
- // 设置消息的内容
- pose_msg.pose.position.x = 1.0;
- pose_msg.pose.position.y = 2.0;
- pose_msg.pose.position.z = 3.0;
- pose_msg.pose.orientation.x = 0.0;
- pose_msg.pose.orientation.y = 0.0;
- pose_msg.pose.orientation.z = 0.0;
- pose_msg.pose.orientation.w = 1.0;
-
- // 发布消息
- pub.publish(pose_msg);
- ros::spin();
- return 0;
- }

三、sensor_msgs
3.1 简介
ROS中的sensor_msgs是一种消息类型,用于在ROS节点之间传输与传感器数据相关的消息。sensor_msgs包含了许多常用传感器的消息类型,例如激光雷达、相机、IMU、GPS等。
3.2 基本类别
- Imu:姿态、角速度和线性加速度等信息。
- MagneticField:磁场强度数据。
- NavSatFix:GPS定位数据。
- NavSatStatus:GPS定位状态数据。
- Joy:手柄控制器数据。
- JoyFeedback:手柄反馈数据。
- JoyFeedbackArray:手柄反馈数组数据。
- LaserScan:激光雷达数据。
- PointCloud:点云数据。
- PointCloud2:点云数据,支持RGB信息。
- CameraInfo:相机内参数据。
- Image:图像数据。
- CompressedImage:压缩图像数据。
- FluidPressure:液压数据。
- TFMessage:坐标系变换数据。
- NavSatFix:GPS数据。
- TimeReference:时间参考数据。
- MultiArrayDimension:多维数组数据的维度信息。
- MultiArrayLayout:多维数组数据的布局信息。
- ImageProjection:用于三维重建的图像投影数据。
- PointField:点云数据的字段信息。
- RegionOfInterest:感兴趣区域数据。
- RelativePose:相对位姿数据。
- RelativePoseStamped:相对位姿和时间戳数据。
- NavSatCartesian:GPS坐标转换为笛卡尔坐标数据。
- CompressedNavSatFix:压缩GPS数据。
3.3 使用模板
发布接收点云
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h>
-
- void pointCloudCallback(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& input_cloud_msg)
-
- {
- // TODO: 这里添加处理输入点云的代码
- // 将处理后的点云发布到 /output_pointcloud 话题上
- pub.publish(output_cloud_msg);
- }
-
-
-
- int main(int argc, char** argv)
-
- {
- ros::init(argc, argv, "point_cloud_node");
- ros::NodeHandle nh;
- // 订阅 /input_pointcloud 话题上的点云消息
- ros::Subscriber sub = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/input_pointcloud", 1, pointCloudCallback);
- // 发布处理后的点云消息到 /output_pointcloud 话题上
- ros::Publisher pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/output_pointcloud", 1);
- ros::spin();
- return 0;
- }

四、shape_msgs
4.1 简介
ROS中的shape_msgs是一个定义了常见几何形状(例如点,线,多边形,立方体等)的ROS消息类型。它是ROS的标准消息之一,常用于描述机器人的形状和姿态,以及环境中的障碍物等。shape_msgs消息并不能直接在rviz中可视化,需要将其转换为visualization_msgs/Marker消息才能在rviz中显示。而visualization_msgs/Marker消息则可以直接在rviz中可视化,并且提供了多种不同的可视化方式,例如用线、面、箭头等方式显示几何形状。
4.2 基本类别
- Point: 一个三维空间中的点,由x、y和z三个浮点数表示。
- Quaternion: 一个四元数,由x、y、z和w四个浮点数表示。
- Vector3: 一个三维向量,由x、y和z三个浮点数表示。
- Pose: 一个位姿,由位置(Point)和方向(Quaternion)组成。
- PoseStamped: 带有时间戳的位姿。
- Twist: 一个刚体的线速度和角速度,由线速度(Vector3)和角速度(Vector3)组成。
- Polygon: 一个平面内的多边形,由多个点(Point)组成。
- Mesh: 一个三维模型,由多个三角形(Triangle)组成。
- SolidPrimitive: 一个固体的基本几何形状,例如立方体、球体、圆柱体等。
- MeshTriangle: 一个三角形,由三个顶点的索引组成,用于描述Mesh消息中的三角形。
4.3 使用模板
发送三角形顶点坐标
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <shape_msgs/Polygon.h>
- #include <geometry_msgs/Point32.h>
-
-
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
-
- {
- // 初始化ROS节点
- ros::init(argc, argv, "polygon_publisher");
- // 创建节点句柄
- ros::NodeHandle nh;
- // 创建一个publisher发布名为"/polygon"的shape_msgs/Polygon消息
- ros::Publisher polygon_pub = nh.advertise<shape_msgs::Polygon>("/polygon", 10);
- // 设置消息发布频率
- ros::Rate loop_rate(10);
- while (ros::ok())
- {
- // 创建shape_msgs/Polygon消息并填充数据
- shape_msgs::Polygon polygon;
- geometry_msgs::Point32 p1, p2, p3;
- p1.x = 0.0;
- p1.y = 0.0;
- p1.z = 0.0;
- p2.x = 1.0;
- p2.y = 0.0;
- p2.z = 0.0;
- p3.x = 0.0;
- p3.y = 1.0;
- p3.z = 0.0;
- polygon.points.push_back(p1);
- polygon.points.push_back(p2);
- polygon.points.push_back(p3);
-
- // 发布消息
- polygon_pub.publish(polygon);
- // 按照指定频率循环发布消息
- loop_rate.sleep();
- }
- return 0;
-
- }

接收三角形顶点坐标
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <shape_msgs/Polygon.h>
- #include <geometry_msgs/Point32.h>
-
- void polygonCallback(const shape_msgs::Polygon::ConstPtr& msg)
- {
- // 输出消息内容
- ROS_INFO("Received polygon message:");
- for (int i = 0; i < msg->points.size(); i++)
- {
-
- ROS_INFO("Point %d: (%f, %f, %f)", i+1, msg->points[i].x, msg->points[i].y, msg->points[i].z);
- }
- }
-
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
- {
- // 初始化ROS节点
- ros::init(argc, argv, "polygon_subscriber");
- // 创建节点句柄
- ros::NodeHandle nh;
- // 创建一个subscriber订阅名为"/polygon"的shape_msgs/Polygon消息
- ros::Subscriber polygon_sub = nh.subscribe("/polygon", 10, polygonCallback);
- // 循环处理回调函数
- ros::spin();
- return 0;
- }

五、trajectory_msgs
5.1 简介
trajectory_msgs 是一个ROS消息包,包含用于描述机器人或其它物体运动的消息类型。其主要包含以下消息类型:
5.2 基本类型
- JointTrajectory: 描述机器人关节运动轨迹,包含关节位置、速度、加速度、时间戳等信息。
- JointTrajectoryPoint: 描述一个时刻的机器人关节状态,包含关节位置、速度、加速度等信息。
- MultiDOFJointTrajectory: 描述机器人多自由度运动轨迹,包含多个关节的位置、速度、加速度、时间戳等信息。
- MultiDOFJointTrajectoryPoint: 描述一个时刻的机器人多自由度状态,包含多个关节的位置、速度、加速度等信息。
5.3 基本类型
发布者周期性地创建一个 JointTrajectory 消息并发布到话题 joint_trajectory 上,而订阅者则通过回调函数 jointTrajectoryCallback 接收到这些消息并打印出其中的关节信息。
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectory.h>
- #include <trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectoryPoint.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
- {
- ros::init(argc, argv, "joint_trajectory_publisher_subscriber");
- ros::NodeHandle nh;
- // 创建一个发布者,用于发布机器人的关节轨迹
- ros::Publisher joint_trajectory_pub = nh.advertise<trajectory_msgs::JointTrajectory>("joint_trajectory", 10);
- // 创建一个订阅者,用于接收机器人的关节轨迹
- ros::Subscriber joint_trajectory_sub = nh.subscribe("joint_trajectory", 10, jointTrajectoryCallback);
- ros::Rate loop_rate(10); // 发布频率为10Hz
- while (ros::ok())
- {
- // 创建一个JointTrajectory消息
- trajectory_msgs::JointTrajectory trajectory_msg;
- trajectory_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
- trajectory_msg.joint_names.push_back("joint_1");
- trajectory_msg.joint_names.push_back("joint_2");
- trajectory_msg.joint_names.push_back("joint_3");
-
- // 创建一个JointTrajectoryPoint消息
- trajectory_msgs::JointTrajectoryPoint point_msg;
- point_msg.positions.push_back(0.5);
- point_msg.positions.push_back(0.5);
- point_msg.positions.push_back(0.5);
- point_msg.velocities.push_back(0.0);
- point_msg.velocities.push_back(0.0);
- point_msg.velocities.push_back(0.0);
- point_msg.time_from_start = ros::Duration(1.0); // 在1秒的时间内到达目标位置
- trajectory_msg.points.push_back(point_msg); // 将JointTrajectoryPoint添加到JointTrajectory中
- // 发布JointTrajectory消息
- joint_trajectory_pub.publish(trajectory_msg);
- ros::spinOnce();
- loop_rate.sleep();
- }
- return 0;
- }
-
- // 订阅者回调函数,用于接收机器人的关节轨迹
- void jointTrajectoryCallback(const trajectory_msgs::JointTrajectory& msg)
- {
- ROS_INFO("Received JointTrajectory message");
- // 打印出轨迹中的关节信息
- for (int i = 0; i < msg.joint_names.size(); i++)
- {
- ROS_INFO("%s position: %f, velocity: %f, acceleration: %f",
- msg.joint_names[i].c_str(),
- msg.points[0].positions[i],
- msg.points[0].velocities[i],
- msg.points[0].accelerations[i]);
- }
-
- }

六、nav_msgs
6.1 简介
ROS中的nav_msgs是一组与导航相关的消息(messages)和服务(services)类型的软件包。它包含了一些用于导航任务的标准消息格式,比如机器人当前的位姿信息、目标点、障碍物等信息。
6.2 基本类型
- Odometry(里程计消息):提供机器人当前的位姿、速度等信息。
- Path(路径消息):提供机器人的路径信息,可以用于可视化机器人在地图上的运动轨迹。
- MapMetaData(地图元数据消息):提供地图的基本信息,如分辨率、地图的起始点和终点等。
- OccupancyGrid(占据栅格地图消息):提供机器人周围的环境地图信息,包括障碍物和自由空间。
- GetMap(获取地图服务):用于从地图服务器中获取占据栅格地图。
6.3 使用模板
发布接收一个Path,Path可以直接在RVIZ可视化
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <nav_msgs/Path.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char** argv)
- {
- // 初始化ROS节点
- ros::init(argc, argv, "path_publisher");
- ros::NodeHandle nh;
- // 创建一个发布者,发布类型为nav_msgs::Path,话题名为/path
- ros::Publisher path_pub = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("path", 10);
- // 创建一个订阅者,订阅类型为nav_msgs::Path,话题名为/path
- ros::Subscriber path_sub = nh.subscribe<nav_msgs::Path>("path", 10, pathCallback);
-
-
- // 循环发布消息
- ros::Rate loop_rate(10);
- while (ros::ok())
- {
- // 创建一个新的Path消息
- nav_msgs::Path path_msg;
- // 将路径信息添加到Path消息中,此处省略具体代码
- ...
- // 发布Path消息
- path_pub.publish(path_msg);
- // 循环等待
- ros::spinOnce();
- loop_rate.sleep();
- }
- return 0;
- }
-
-
-
- // 接收到Path消息时的回调函数
- void pathCallback(const nav_msgs::Path::ConstPtr& path_msg)
- {
- // 处理接收到的Path消息,此处省略具体代码
- ...
- }

七、visualization_msgs
7.1 简介
visualization_msgs是ROS中的一个用于可视化的消息类型软件包。它包含了一些用于在ROS中进行可视化的标准消息格式,如点、线、箭头、网格、文字、标记等。
7.2 基本类型
- Marker(标记消息):用于将点、线、箭头、网格、文字等可视化为三维空间中的对象。
- MarkerArray(标记数组消息):用于同时发布多个Marker消息。
- ImageMarker(图像标记消息):用于将图像可视化为三维空间中的对象。
- InteractiveMarker(交互式标记消息):用于添加可以与用户交互的可视化元素,如移动、旋转、缩放等。
https://wiki.ros.org/visualization_msgs?distro=melodic
7.3 marker使用模板
- *发布接收
- 发布Marker消息
- ros::Publisher vis_pub = nh.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>( "visualization_marker", 0, markerCallback);
- 接收Marker消息
- ros::Subscriber sub = nh.subscribe<visualization_msgs::Marker>("marker_topic", 10, markerCallback);
- *消息内容
- //基本信息
- visualization_msgs::Marker marker;
- marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
- marker.header.stamp = ros::Time();
- marker.ns = "my_namespace";
- marker.id = 0;
- marker.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::SPHERE;//确定类型
- marker.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD;
- //位置信息
- marker.pose.position.x = 1;
- marker.pose.position.y = 1;
- marker.pose.position.z = 1;
- marker.pose.orientation.x = 0.0;
- marker.pose.orientation.y = 0.0;
- marker.pose.orientation.z = 0.0;
- marker.pose.orientation.w = 1.0;
- //Marker范围
- marker.scale.x = 1;
- marker.scale.y = 0.1;
- marker.scale.z = 0.1;
- //Marker颜色
- marker.color.a = 1.0; // Don't forget to set the alpha!
- marker.color.r = 0.0;
- marker.color.g = 1.0;
- marker.color.b = 0.0;
- //加载地图
- marker.mesh_resource="package://pr2_description/meshes/base_v0/base.dae";
- //发布消息
- vis_pub.publish( marker );

建立一个箭头
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <visualization_msgs/Marker.h>
-
- int main( int argc, char** argv )
- {
- ros::init(argc, argv, "basic_shapes");
- ros::NodeHandle n;
- ros::Rate r(1);
- ros::Publisher marker_pub = n.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("visualization_marker", 1);
-
- while (ros::ok())
- {
- visualization_msgs::Marker marker;
- marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
- marker.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
- marker.ns = "basic_shapes";
- marker.id = 0;
- marker.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::ARROW;
- marker.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD;
-
- marker.scale.x = 1.0;
- marker.scale.y = 0.1;
- marker.scale.z = 0.1;
-
- marker.color.r = 1.0f;
- marker.color.g = 0.0f;
- marker.color.b = 0.0f;
- marker.color.a = 1.0;
-
- marker.pose.position.x = 0;
- marker.pose.position.y = 0;
- marker.pose.position.z = 0;
-
- marker.pose.orientation.x = 0.0;
- marker.pose.orientation.y = 0.0;
- marker.pose.orientation.z = 0.0;
- marker.pose.orientation.w = 1.0;
-
- marker_pub.publish(marker);
-
- r.sleep();
- }
- }

建立一个cube list
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <visualization_msgs/Marker.h>
- int main( int argc, char** argv )
- {
- ros::init(argc, argv, "basic_shapes");
- ros::NodeHandle n;
- ros::Rate r(1);
- ros::Publisher marker_pub = n.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("visualization_marker", 1);
-
- visualization_msgs::Marker marker;
- marker.header.frame_id = "base_link";
- marker.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
- marker.ns = "basic_shapes";
- marker.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::CUBE_LIST;
- marker.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD;
-
- marker.scale.x = 0.1;
- marker.scale.y = 0.1;
- marker.scale.z = 0.1;
-
- marker.color.r = 0.0f;
- marker.color.g = 1.0f;
- marker.color.b = 0.0f;
- marker.color.a = 1.0;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
- {
- for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
- {
- for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++)
- {
- geometry_msgs::Point cube_point;
- cube_point.x = i * 0.1;
- cube_point.y = j * 0.1;
- cube_point.z = k * 0.1;
-
- marker.points.push_back(cube_point);
- }
- }
- }
-
- while (ros::ok())
- {
- marker_pub.publish(marker);
- r.sleep();
- }
- }

八、jsk_recognition _msgs
8.1 简介
jsk_recognition_msgs 是一个ROS消息包,它包含了一些用于机器人视觉和感知的常用消息类型。这些消息类型可以被用于在ROS系统中传递机器人感知和识别结果。
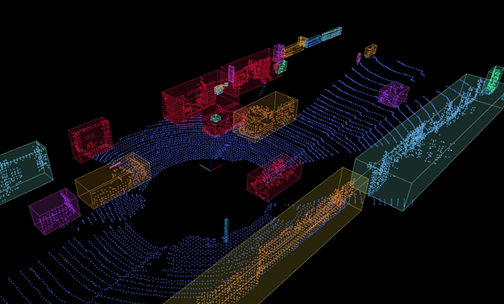
8.2 类别
主要包含以下消息类型:
- BoundingBox:用于表示物体的3D包围盒,包括其尺寸和位置等信息。
- BoundingBoxArray:一个由多个 BoundingBox 组成的数组,用于表示多个物体的包围盒。
- ClusterPointIndices:用于表示点云中的聚类信息,包括每个聚类的点的索引。
- ContactSensor:用于表示机器人接触传感器的测量值,例如触摸传感器和力传感器。
- Histogram:用于表示图像或点云的直方图信息。
- LabelArray:一个由多个标签组成的数组,用于表示图像或点云中每个像素或点的标签。
- ModelCoefficientsArray:一个由多个模型系数组成的数组,用于表示多个几何模型的系数。
- PolygonArray:一个由多个多边形组成的数组,用于表示多个物体的表面几何信息。
- RectArray:一个由多个矩形组成的数组,用于表示多个图像区域的位置和大小等信息。
- Segment:用于表示点云中的一个分割结果,包括每个点所属的分割标签和系数等信息。
- Segmentation:一个由多个 Segment 组成的数组,用于表示点云中的多个分割结果。
- TrackingObject:用于表示追踪物体的信息,包括其标识符、位置和速度等信息。
- jsk_recognition_msgs 包提供了一些方便的消息类型,可用于处理机器人感知和识别的数据。
8.3 使用模板
- 自定义发送
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <jsk_recognition_msgs/BoundingBoxArray.h>
- #include <jsk_recognition_msgs/BoundingBox.h>
-
- int main(int argc, char** argv)
- {
- ros::init(argc, argv, "custom_bounding_box_array_publisher");
- ros::NodeHandle nh;
-
- // 创建一个 BoundingBoxArray 发布者
- ros::Publisher bb_array_pub = nh.advertise<jsk_recognition_msgs::BoundingBoxArray>("bounding_box_array_topic", 10);
-
- // 创建一个 BoundingBoxArray 消息
- jsk_recognition_msgs::BoundingBoxArray bb_array_msg;
-
- // 设置 BoundingBoxArray 消息的 Header
- bb_array_msg.header.frame_id = "base_link";
- bb_array_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
-
- // 创建一个 BoundingBox 消息并添加到 BoundingBoxArray 消息中
- jsk_recognition_msgs::BoundingBox bb_msg;
- bb_msg.header = bb_array_msg.header;
- bb_msg.label = "object_1"; // 设置标签
- bb_msg.pose.position.x = 1.0; // 设置位置坐标
- bb_msg.pose.position.y = 2.0;
- bb_msg.pose.position.z = 3.0;
- bb_msg.dimensions.x = 0.5; // 设置尺寸
- bb_msg.dimensions.y = 0.3;
- bb_msg.dimensions.z = 0.2;
- bb_array_msg.boxes.push_back(bb_msg); // 将 BoundingBox 消息添加到 BoundingBoxArray 中
-
- // 发布 BoundingBoxArray 消息
- bb_array_pub.publish(bb_array_msg);
-
- ROS_INFO("Custom BoundingBoxArray published");
-
- ros::spin();
- return 0;
- }
-
- 接收获取坐标
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <jsk_recognition_msgs/BoundingBoxArray.h>
-
- void boundingBoxCallback(const jsk_recognition_msgs::BoundingBoxArray::ConstPtr& msg) {
- // 遍历BoundingBoxArray中的所有BoundingBox
- for (const auto& bbox : msg->boxes) {
- // 获取BoundingBox的尺寸
- const auto& dimensions = bbox.dimensions;
- float width = dimensions.x;
- float height = dimensions.y;
- float depth = dimensions.z;
-
- // 获取BoundingBox的坐标
- const auto& position = bbox.pose.position;
- float x = position.x;
- float y = position.y;
- float z = position.z;
-
- // 在控制台输出BoundingBox的尺寸和坐标
- ROS_INFO_STREAM("Bounding Box Dimensions (width, height, depth): " << width << ", " << height << ", " << depth);
- ROS_INFO_STREAM("Bounding Box Position (x, y, z): " << x << ", " << y << ", " << z);
- }
- }
-
- int main(int argc, char** argv) {
- // 初始化ROS节点
- ros::init(argc, argv, "bounding_box_subscriber");
-
- // 创建节点句柄
- ros::NodeHandle nh;
-
- // 订阅jsk_recognition_msgs::BoundingBoxArray消息
- ros::Subscriber sub = nh.subscribe<jsk_recognition_msgs::BoundingBoxArray>("bounding_box_topic", 1000, boundingBoxCallback);
-
- // 循环等待回调函数
- ros::spin();
-
- return 0;
- }

在上面的代码中,我们定义了一个回调函数 boundingBoxCallback() 来处理接收到的 jsk_recognition_msgs::BoundingBoxArray 消息。在这个回调函数中,我们遍历 BoundingBoxArray 中的所有 BoundingBox,并从每个 BoundingBox 中获取其尺寸和坐标信息。具体来说,我们使用 bbox.dimensions 来获取 BoundingBox 的尺寸,使用 bbox.pose.position 来获取 BoundingBox 的位置。最后,我们在控制台上输出每个 BoundingBox 的尺寸和坐标信息,以便我们可以在程序运行时检查它们。
到此,专栏的ROS讲解部分结束,你应该知道ROS能干啥和编写简单的发送接收消息的代码了,下一步我们将介绍SLAM的理论基础。


