- 1目标检测算法:anchor_free系列解读_anchorfree是什么意思
- 2CSdn积分获取方法_csdn积分怎么获取
- 3Midjourney | 电商产品图换背景_midjourney 产品 替换背景
- 4什么是Eureka?
- 5【EI会议征稿通知】第三届电子技术与人工智能国际学术会议(ETAI 2024)_第三届国际人工智能会议
- 62020年前端技术方向都在这里了_前端js小专利有哪些
- 7Linux协议栈-netfilter(3)-NAT_nat操作在协议栈中的哪个位置上?
- 8AWS RDS & ElasticCache 监控可观测最佳实践_cloudwatch 监控 rds
- 9牛客刷题笔记-数据库选择题(201-300)_设有如下两个事务,t1读x y=x+4
- 10leetcode刷题记录35-419. 甲板上的战舰
SpringCloud Feign基础入门与使用实践总结_feign+ribbon
赞
踩
【1】Feign是什么
Feign是一个声明式Web服务客户端。使用Feign能让编写Web服务客户端更加简单,它的使用方法是定义一个接口,然后在上面添加注解,同时也支持JAX-RS标准的注解。
Feign也支持可插拔式的编码器和解码器。
SpringCloud对Feign进行了封装,使其支持了SpringMVC标准注解和HttpMessageConverters。
Feign可以与Eureka和Ribbon组合使用以支持负载均衡。
官网文档地址:http://projects.spring.io/spring-cloud/spring-cloud.html#spring-cloud-feign
源码地址:https://github.com/OpenFeign/feign
【2】Feign能干什么
Feign旨在使编写Java Http客户端变得更加容易。
前面在使用Ribbon+RestTemplate时,利用了RestTemplate对http请求的封装处理,形成了一套模板化的调用方法。但是在实际开发中,由于对服务依赖的调用可能不止一处,往往一个接口会被多处调用,所以通常都会针对每个微服务自行封装一些客户端类来包装这些依赖服务的调用。
Feign在此基础上做了进一步封装,由他来帮助我们定义和实现依赖服务接口的定义。在Feign的实现下,我们只需创建一个接口并使用注解的方式来配置(比如以前是一个Dao接口上面标注@Mapper注解,现在是一个微服务接口上面标注一个Feign注解即可),即可完成对服务提供方的接口绑定,简化了使用Spring Cloud Ribbon时自动封装服务调用客户端的开发量。
Feign集成了Ribbon
前面我们利用Ribbon维护了MicroServiceCloud-Dept的服务列表信息,并且通过轮询实现了客户端的负载均衡。而与Ribbon不同的是,通过Feign只需要定义服务绑定接口且以声明式的方法,优雅而简单的实现了服务调用。
【3】Feign项目实战
① 创建feign工程
参考microservicecloud-consumer-dept-80项目创建microservicecloud-consumer-dept-feign
② pom中添加对Feign的支持
<dependencies> <dependency><!-- 自己定义的api --> <groupId>com.web.springcloud</groupId> <artifactId>microservicecloud-api</artifactId> <version>${project.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- Cloud-Feign相关 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Cloud-Ribbon相关 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-ribbon</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Spring Boot相关 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 修改后立即生效,热部署相关 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>springloaded</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
③ 修改microservicecloud-api Module
pom中添加feign依赖
<!-- Cloud-Feign相关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
com.web.springcloud.service包下添加DeptClientService
package com.web.springcloud.service; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.FeignClient; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import com.web.springcloud.entities.Dept; //绑定服务实例与接口 @FeignClient(value = "MICROSERVICECLOUD-DEPT")//注意这里 public interface DeptClientService{ @RequestMapping(value = "/dept/get/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") long id); @RequestMapping(value = "/dept/list", method = RequestMethod.GET) public List<Dept> list(); @RequestMapping(value = "/dept/add", method = RequestMethod.POST) public boolean add(Dept dept); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
④ 修改microservicecloud-consumer-dept-feign 的Controller
方法实现交给DeptClientService 远程调用服务提供方。
@RestController public class DeptController_Consumer { @Autowired private DeptClientService service; //引入公共Module(api)中的DeptClientService ,直接调用 @RequestMapping(value = "/consumer/dept/get/{id}") public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id) { return this.service.get(id); } @RequestMapping(value = "/consumer/dept/list") public List<Dept> list() { return this.service.list(); } @RequestMapping(value = "/consumer/dept/add") public Object add(Dept dept) { return this.service.add(dept); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
由此可见Feign只是又进一步进行了封装,使得调用服务更加方便。
⑤ 修改microservicecloud-consumer-dept-feign 的主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages={"com.web.springcloud"})//启用Feign
@ComponentScan("com.web.springcloud")
public class DeptConsumer80_Feign_App
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(DeptConsumer80_Feign_App.class, args);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
⑥ 测试
依次启动服务中心 7001 7002 7003和服务提供者 8001 8002 8003,最后启动microservicecloud-consumer-dept-feign。
浏览器访问http://localhost/consumer/dept/list如下:
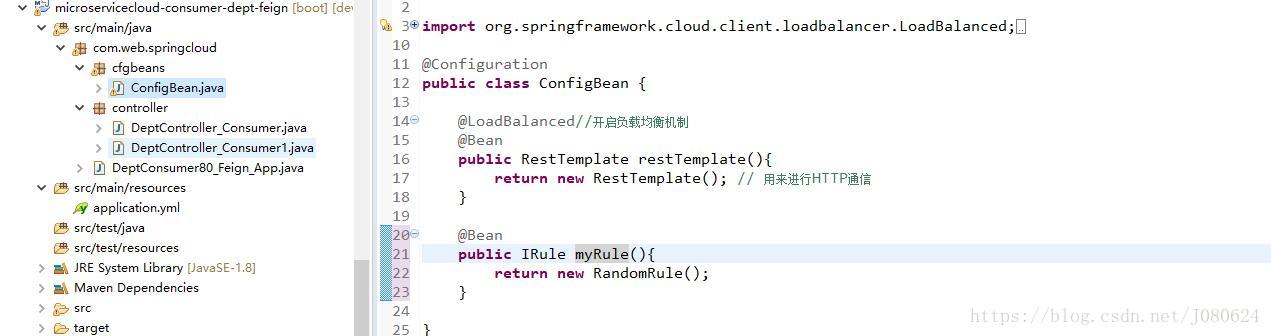
默认使用轮询算法,当然此时使用RestTemplate+Ribbon也是可以正常访问。
如下图所示,注册自定义IRule,则可以更改默认轮询算法:
【4】@FeignClient注解
@FeignClient 是 Feign 框架中的一个关键注解,用于标记接口,使其成为 Feign 客户端的一部分。这使得你可以以声明式的方式调用远程 HTTP 服务,就像调用本地方法一样。
/** * Annotation for interfaces declaring that a REST client with that interface should be * created (e.g. for autowiring into another component). If ribbon is available it will be * used to load balance the backend requests, and the load balancer can be configured * using a <code>@RibbonClient</code> with the same name (i.e. value) as the feign client. * * @author Spencer Gibb * @author Venil Noronha */ @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface FeignClient { // 服务实例名称 @AliasFor("name") String value() default ""; /** * 服务ID *// 已经过时,使用name替代 * @deprecated use {@link #name() name} instead */ @Deprecated String serviceId() default ""; //服务实例名称 @AliasFor("value") String name() default ""; // 即,ServiceId===name===value // 指定@Qualifier String qualifier() default ""; // 一个绝对URL或者可解析的hostname String url() default ""; // 定义404是解析还是抛出异常FeignExceptions boolean decode404() default false; //自定义配置类 可以实现自定义配置 Class<?>[] configuration() default {}; // 回调服务 Class<?> fallback() default void.class; //定义回调工厂,其可以产生回调服务实例 Class<?> fallbackFactory() default void.class; // 方法级别的映射前缀 String path() default ""; //是否为primary boolean primary() default true; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
@FeignClient 是 Feign 框架中的一个关键注解,用于标记接口,使其成为 Feign 客户端的一部分。这使得你可以以声明式的方式调用远程 HTTP 服务,就像调用本地方法一样。下面是一些关于 @FeignClient 注解的重要细节:
配置选项
@FeignClient 提供了多种配置选项,包括:
- name:必需的属性,表示要调用的服务名。
- url:可选属性,直接指定服务的 URL,而不是通过服务名。
- configuration:指定一个或多个配置类,用于自定义 Feign 客户端的行为,如设置编码器、解码器、日志级别等。
- fallback:指定一个备选类,在远程调用失败时使用,实现接口的所有方法,提供默认或异常处理逻辑。
- fallbackFactory:类似于
fallback,但工厂模式提供更灵活的错误处理。 - decoder、
encoder、contract、loggerLevel等:直接指定解码器、编码器、合约类型和日志级别。
【5】FeignClientsConfiguration
Feign Client的配置类:
@Configuration public class FeignClientsConfiguration { // 请求/响应信息转换器 @Autowired private ObjectFactory<HttpMessageConverters> messageConverters; @Autowired(required = false) private List<AnnotatedParameterProcessor> parameterProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); @Autowired(required = false) private List<FeignFormatterRegistrar> feignFormatterRegistrars = new ArrayList<>(); @Autowired(required = false) private Logger logger; @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public Decoder feignDecoder() { return new ResponseEntityDecoder(new SpringDecoder(this.messageConverters)); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public Encoder feignEncoder() { return new SpringEncoder(this.messageConverters); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public Contract feignContract(ConversionService feignConversionService) { return new SpringMvcContract(this.parameterProcessors, feignConversionService); } // 注册FormattingConversionService--数据类型转换 @Bean public FormattingConversionService feignConversionService() { FormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService(); for (FeignFormatterRegistrar feignFormatterRegistrar : feignFormatterRegistrars) { feignFormatterRegistrar.registerFormatters(conversionService); } return conversionService; } // 与Hystrix整合 @Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({ HystrixCommand.class, HystrixFeign.class }) protected static class HystrixFeignConfiguration { @Bean @Scope("prototype") @ConditionalOnMissingBean @ConditionalOnProperty(name = "feign.hystrix.enabled", matchIfMissing = false) public Feign.Builder feignHystrixBuilder() { return HystrixFeign.builder(); } } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public Retryer feignRetryer() { return Retryer.NEVER_RETRY; } @Bean @Scope("prototype") @ConditionalOnMissingBean public Feign.Builder feignBuilder(Retryer retryer) { return Feign.builder().retryer(retryer); } //如果缺少FeignLoggerFactory就注册FeignLoggerFactory @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(FeignLoggerFactory.class) public FeignLoggerFactory feignLoggerFactory() { return new DefaultFeignLoggerFactory(logger); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
【6】@EnableFeignClients 注解
@EnableFeignClients 是一个重要的注解,主要用于启用 Feign 客户端功能。当你在 Spring Boot 或 Spring Cloud 应用程序中使用 Feign 进行远程服务调用时,这个注解是必不可少的。它告诉 Spring 框架去识别和配置带有 @FeignClient 注解的接口,从而允许你以声明式的方式来调用远程服务。
以下是一些关键点:
-
启用 Feign 客户端:
@EnableFeignClients注解使 Spring 能够识别并处理@FeignClient注解,从而自动配置 Feign 客户端。 -
扫描路径:你可以通过
basePackages或basePackageClasses属性来指定哪些包下的@FeignClient接口应该被扫描和配置。如果不指定这些属性,那么默认会扫描应用主类所在的包及其子包。 -
默认配置:通过
defaultConfiguration属性,你可以指定一个或多个配置类,这些配置类中的配置将应用于所有 Feign 客户端,比如设置编码器、解码器、重试策略等。 -
特定客户端:
clients属性允许你显式地列出应被配置的 Feign 客户端接口。 -
元注解:
@EnableFeignClients本身是一个元注解,它通过@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)来导入FeignClientsRegistrar类,这个类负责实际的 Feign 客户端注册和配置。 -
整合其他框架:通常与
@SpringBootApplication和@EnableDiscoveryClient等注解一起使用,以便整合 Spring Cloud 的服务发现、断路器等功能。
使用 @EnableFeignClients 的基本例子可能如下所示:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = {"com.example.feign.clients"})
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
在这个例子中,所有位于 com.example.feign.clients 包及其子包内的 @FeignClient 接口都将被扫描并配置为可用的 Feign 客户端。
//扫描那些声明为feign client 的接口 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Documented @Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class) public @interface EnableFeignClients { // 同 basePackages String[] value() default {}; // 基础扫描包 String[] basePackages() default {}; // 指定扫描的基础类型,可以与basePackages共同使用 Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {}; // 自定义配置 Class<?>[] defaultConfiguration() default {}; // 显式列出标注了@FeignClient的类,如果不为空,则禁用路径扫描 Class<?>[] clients() default {}; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
本篇博文项目地址:https://github.com/JanusJ/SpringCloud/
【7】设置超时时间
在使用Feign时,我们可以使用两种方式来设置超时时间:一种是通过全局配置,另一种是通过接口级别的配置。
① 全局配置
你可以在application.yml或application.properties文件中进行配置。例如,如果你想设置连接超时时间为3秒,读取超时时间为5秒,你可以这样配置:
# application.yml
feign:
client:
config:
default:
connectTimeout: 3000
readTimeout: 5000
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
或者
# application.properties
feign.client.config.default.connectTimeout=3000
feign.client.config.default.readTimeout=5000
- 1
- 2
- 3
② 接口级别配置
你也可以在Feign的接口上使用@FeignClient注解来设置超时时间。例如:
@FeignClient(name = "service-name", configuration = FeignConfig.class)
public interface ServiceClient {
//...
}
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
public Request.Options options() {
return new Request.Options(3000, 5000);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
在上面的例子中,我们创建了一个名为FeignConfig的配置类,并在其中定义了一个Request.Options的bean,用于设置连接超时时间和读取超时时间。然后我们在ServiceClient接口上使用了configuration属性来引用这个配置类。
【8】OpenFeign
源码地址:https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign
Feign 和 OpenFeign 都是用于微服务架构中的声明式HTTP客户端,它们允许开发者以一种简单且类型安全的方式来定义HTTP API客户端。然而,它们之间存在一些关键性的区别,主要体现在以下方面:
起源与归属
- Feign 最初由Netflix开发,是Netflix OSS(Open Source Software)套件的一部分,用于简化客户端对服务端接口的调用,特别适合于Spring Cloud环境。
- OpenFeign 是Spring Cloud团队在Feign的基础上进行的扩展和封装,以便更好地融入Spring Cloud生态系统,尤其是在Spring Boot 2.0及更高版本中。
依赖管理
- Feign 使用的依赖是
spring-cloud-starter-feign。 - OpenFeign 使用的依赖是
spring-cloud-starter-openfeign。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
注解支持
- Feign 直接在接口上使用其自身的注解,如
@FeignClient和@RequestMapping等,但这些注解的使用方式与Spring MVC的注解有所不同。 - OpenFeign 支持标准的Spring MVC注解,如
@GetMapping,@PostMapping等,这使得它可以无缝地集成到Spring MVC的框架中。
版本兼容性
- Feign 可能在Spring Boot较新版本中支持不佳或需要额外配置,因为它的设计更早,可能没有考虑到Spring Boot后续的变化。
- OpenFeign 是为了适应Spring Boot 2.0及以后版本的改进而设计的,因此在新的Spring Boot项目中使用更加推荐。
社区支持与更新
- OpenFeign 作为Spring Cloud官方维护的项目,通常会有更好的文档、示例和社区支持,以及更频繁的更新和bug修复。
总结
OpenFeign可以看作是Feign的进化版本,它修正了一些Feign的不足,并且更加紧密地集成了Spring Boot和Spring Cloud的特性。如果你正在构建一个新的项目或者你正在使用的Spring Boot版本高于2.0,那么使用OpenFeign会是一个更佳的选择。
【9】日志打印功能
Feign 提供了日志打印功能,我们可以通过配置来调整日志级别,从而了解 Feign 中 Http 请求的细节。
说白了就是对Feign接口的调用情况进行监控和输出。
① 日志级别
NONE:默认的,不显示任何日志;
BASIC:仅记录请求方法、URL、响应状态码及执行时间;
HEADERS:除了 BASIC 中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的头信息;
FULL:除了 HEADERS 中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的正文及元数据。
② 配置类
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig
{
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel()
{
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
③ yml文件修改
logging:
level:
# feign日志以什么级别监控哪个接口
com.springcloud.service.PaymentFeignService: debug
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4