- 1VirtualBox: CentOS7.5 install VBoxLinuxAdditions
- 2bundle内存 unity_Unity3D 关于资源加载(Resources和AssetBundle)和内存管理
- 3CTFshow web(php命令执行 55-59)
- 4ROS2 For Unity:高性能的通信解决方案_ros for unity
- 5组织病理学的生存模型综述_whole slide image survey
- 6Unity 贴图有接缝_unityhdrp法线有接缝
- 7HarmonyOS应用开发者高级认证学习认证知识答疑笔记_元服务包每个hap包不得超过,以提供秒开体验
- 8解决Build failed:Could not resolve com.android.tools.build:gradle:7.4.0-alpha10.
- 9Python 语音转文本_python将语音转化为文字
- 10envi提取纹理信息并进行地物可分离性指数分析,选取最合适窗口的纹理特征_envi纹理提取
ResNet详解+PyTorch实现_pytorch resnet
赞
踩
1.Resnet简介
深度残差网络(Deep residual network, ResNet)的提出是CNN图像史上的一件里程碑事件,由于其在公开数据上展现的优势,作者何凯明也因此摘得CVPR2016最佳论文奖。
Resnet是残差网络(Residual Network)的缩写,该系列网络广泛用于目标分类等领域以及作为计算机视觉任务主干经典神经网络的一部分,典型的网络有resnet50, resnet101等。Resnet网络证明网络能够向更深(包含更多隐藏层)的方向发展。
解决问题:网络退化
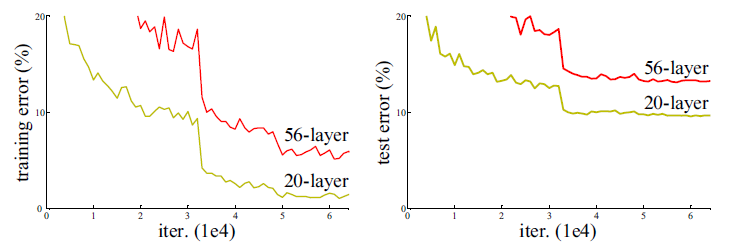
从经验来看,网络的深度对模型的性能至关重要,当增加网络层数后,网络可以进行更加复杂的特征模式的提取,所以当模型更深时理论上可以取得更好的结果,从图2中也可以看出网络越深而效果越好的一个实践证据。但是更深的网络其性能一定会更好吗?实验发现深度网络出现了退化问题(Degradation problem):网络深度增加时,网络准确度出现饱和,甚至出现下降。这个现象可以在图3中直观看出来:56层的网络比20层网络效果还要差。这不会是过拟合问题,因为56层网络的训练误差同样高。我们知道深层网络存在着梯度消失或者爆炸的问题,这使得深度学习模型很难训练。但是现在已经存在一些技术手段如BatchNorm来缓解这个问题。因此,出现深度网络的退化问题是非常令人诧异的。
2. RnsNet网络结构
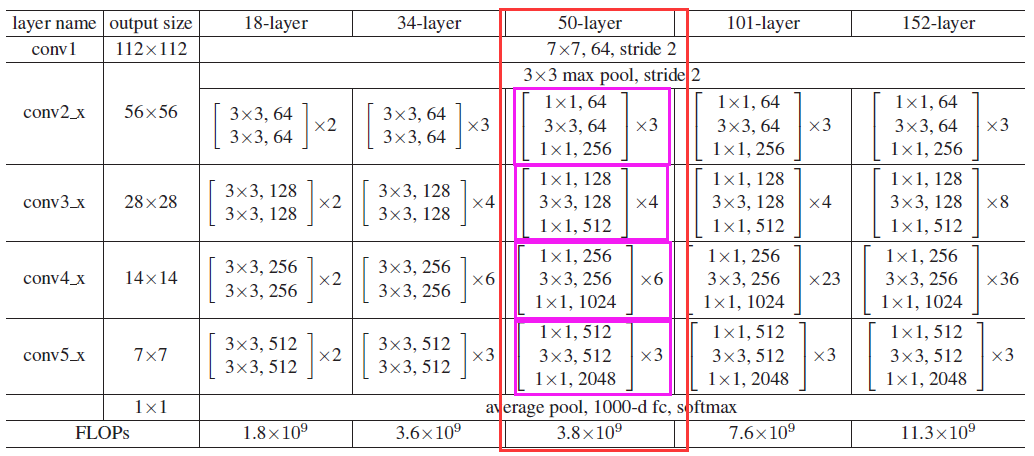
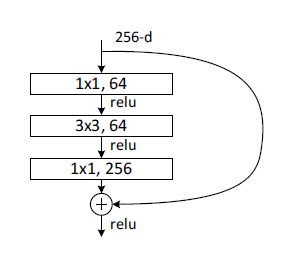
ResNet网络是参考了VGG19网络,在其基础上进行了修改,并通过短路机制加入了残差单元,如图5所示。变化主要体现在ResNet直接使用stride=2的卷积做下采样,并且用global average pool层替换了全连接层。ResNet的一个重要设计原则是:当feature map大小降低一半时,feature map的数量增加一倍,这保持了网络层的复杂度。从图5中可以看到,ResNet相比普通网络每两层间增加了短路机制,这就形成了残差学习,其中虚线表示feature map数量发生了改变。图5展示的34-layer的ResNet,还可以构建更深的网络如表1所示。从表中可以看到,对于18-layer和34-layer的ResNet,其进行的两层间的残差学习,当网络更深时,其进行的是三层间的残差学习,三层卷积核分别是1x1,3x3和1x1,一个值得注意的是隐含层的feature map数量是比较小的,并且是输出feature map数量的1/4。
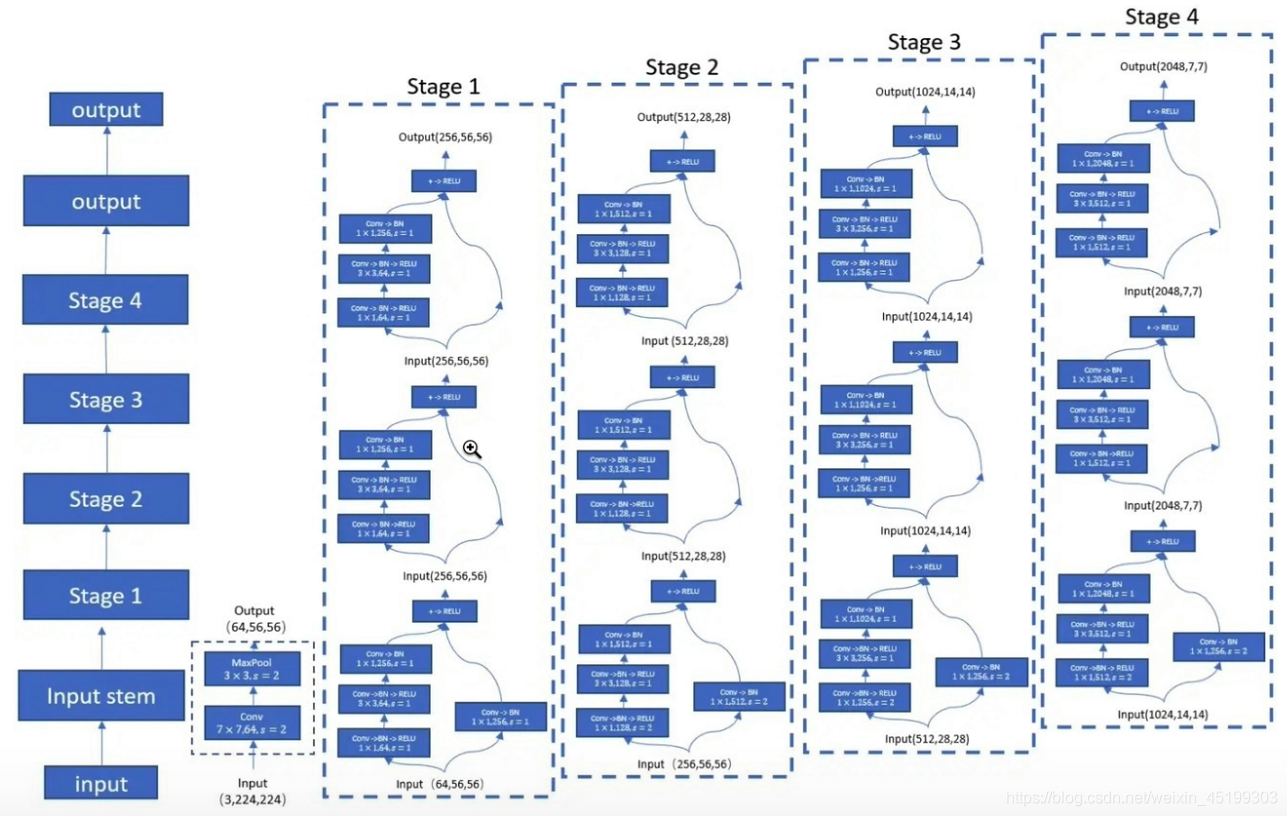
重点展示一下ResNet50网络,resnet50分为conv1、conv2_x、conv3_x、conv4_x、conv5_x 共5大层。1+1+3*3+4*3+6*3+3*3=50(前面一层卷积+一层池化+4组卷积 不考虑最后面的全连接、池化层)。
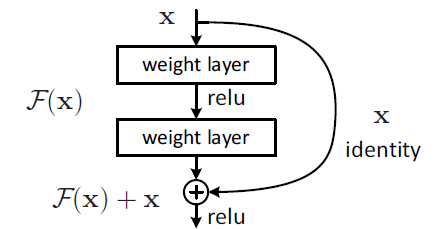
basic_block=identity_block,此结构保证了输入和输出相等,实现网络的串联。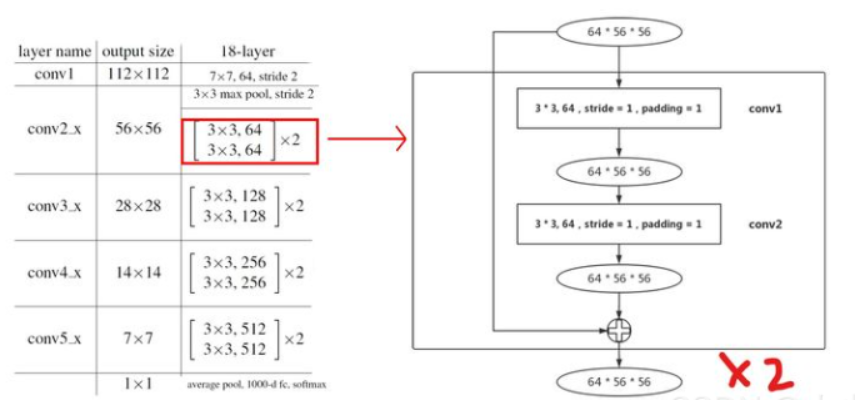
左conv-block 右 identity-block。右图可以看到,通过stride=2实现了图像下采样,并扩充了通道数。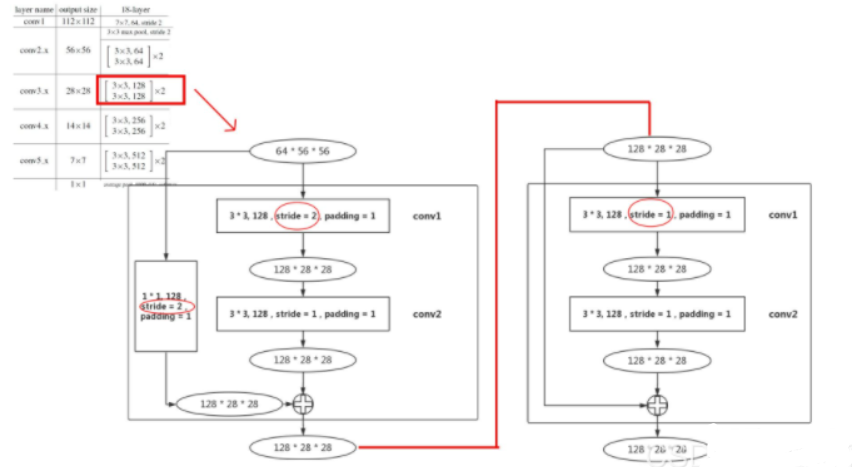
进一步,在下图可以多个模板中同时存在conv-block 和 identity-block两种模式。本质区别就是有没有下采样downsample和通道转换
3. PyTorch模型
定义网络中的resnet18, resnet34, resnet50, resnet101网络架构
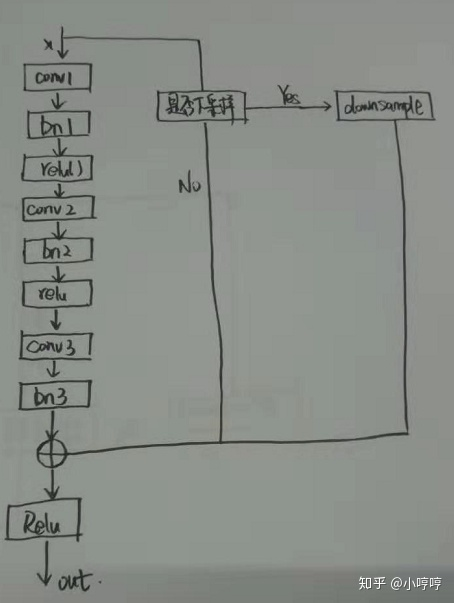
import torch.nn as nn import math import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo # 这个文件内包括6中不同的网络架构 __all__ = ['ResNet', 'resnet18', 'resnet34', 'resnet50', 'resnet101', 'resnet152'] # 每一种架构下都有训练好的可以用的参数文件 model_urls = { 'resnet18': 'https://s3.amazonaws.com/pytorch/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth', 'resnet34': 'https://s3.amazonaws.com/pytorch/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth', 'resnet50': 'https://s3.amazonaws.com/pytorch/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth', 'resnet101': 'https://s3.amazonaws.com/pytorch/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth', 'resnet152': 'https://s3.amazonaws.com/pytorch/models/resnet152-b121ed2d.pth', } # 常见的3x3卷积 def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1): "3x3 convolution with padding" return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False) # 这是残差网络中的basicblock,实现的功能如下方解释: class BasicBlock(nn.Module): expansion = 1 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None): # inplanes代表输入通道数,planes代表输出通道数。 super(BasicBlock, self).__init__() # Conv1 self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # Conv2 self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) # 下采样 self.downsample = downsample self.stride = stride def forward(self, x): residual = x out = self.conv1(x) out = self.bn1(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.bn2(out) if self.downsample is not None: residual = self.downsample(x) # F(x)+x out += residual out = self.relu(out) return out
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
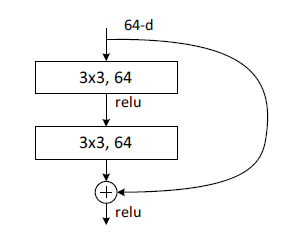
1.BasicBlock类中的init()函数是先定义网络架构,forward()的函数是前向传播,实现的功能就是残差块,BasicBlock:
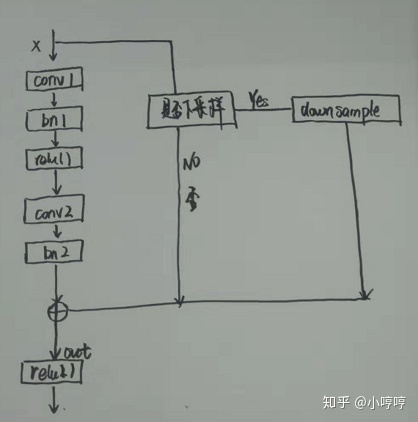
一位博主的手绘图:
Bottleneck:
class Bottleneck(nn.Module): expansion = 4 # 输出通道数的倍乘 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None): super(Bottleneck, self).__init__() # conv1 1x1 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) # conv2 3x3 self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) # conv3 1x1 self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * 4) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.downsample = downsample self.stride = stride def forward(self, x): residual = x out = self.conv1(x) out = self.bn1(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.bn2(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv3(out) out = self.bn3(out) if self.downsample is not None: residual = self.downsample(x) out += residual out = self.relu(out) return out
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
2.Bottleneck类是另一种blcok类型,同上,init()函数是预定义网络架构,forward函数是进行前向传播。该block中有三个卷积,分别是1x1,3x3,1x1,分别完成的功能就是维度压缩,卷积,恢复维度!故bottleneck实现的功能就是对通道数进行压缩,再放大。注意:这里的plane不再是输出的通道数,输出通道数应该就是plane*expansion,即4*plane。
附赠:
这两个class讲清楚的话,后面的网络主体架构就还蛮好理解的了,6中架构之间的不同在于basicblock和bottlenek之间的不同以及block的输入参数的不同。因为ResNet一般有4个stack,每一个stack里面都是block的堆叠,所以[3, 4, 6, 3]就是每一个stack里面堆叠block的个数,故而造就了不同深度的ResNet。
resnet18: ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2])
resnet34: ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3])
resnet50:ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3])
resnet101:ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3])
resnet152:ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3])
# resnet18 def resnet18(pretrained=False): """Constructs a ResNet-18 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2]) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet18'])) return model # resnet34 def resnet34(pretrained=False): """Constructs a ResNet-34 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3]) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet34'])) return model # resnet50 def resnet50(pretrained=False): """Constructs a ResNet-50 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3]) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet50'])) return model # resnet101 def resnet101(pretrained=False): """Constructs a ResNet-101 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3]) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet101'])) return model # resnet152 def resnet152(pretrained=False): """Constructs a ResNet-152 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3]) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet152'])) return model
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
最后的ResNet类其实可以根据列表大小来构建不同深度的resnet网络架构。resnet一共有5个阶段,第一阶段是一个7x7的卷积,stride=2,然后再经过池化层,得到的特征图大小变为原图的1/4。_make_layer()函数用来产生4个layer,可以根据输入的layers列表来创建网络。
class ResNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000): # layers=参数列表 block选择不同的类 self.inplanes = 64 super(ResNet, self).__init__() # 1.conv1 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,bias=False) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 2.conv2_x self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0]) # 3.conv3_x self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2) # 4.conv4_x self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2) # 5.conv5_x self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2) self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7) self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes) # 初始化权重 for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n)) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): m.weight.data.fill_(1) m.bias.data.zero_() def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1): downsample = None if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion: downsample = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion), ) layers = [] layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample)) # 每个blocks的第一个residual结构保存在layers列表中。 self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion for i in range(1, blocks): layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes)) # 该部分是将每个blocks的剩下residual 结构保存在layers列表中,这样就完成了一个blocks的构造。 return nn.Sequential(*layers) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) x = self.bn1(x) x = self.relu(x) x = self.maxpool(x) x = self.layer1(x) x = self.layer2(x) x = self.layer3(x) x = self.layer4(x) x = self.avgpool(x) x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # 将输出结果展成一行 x = self.fc(x) return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
ResNet50网络特征提取框架
import math import torch.nn as nn from torchvision.models.utils import load_state_dict_from_url class Bottleneck(nn.Module): expansion = 4 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None): super(Bottleneck, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * 4) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.downsample = downsample self.stride = stride def forward(self, x): residual = x out = self.conv1(x) out = self.bn1(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.bn2(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv3(out) out = self.bn3(out) if self.downsample is not None: residual = self.downsample(x) out += residual out = self.relu(out) return out class ResNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000): #-----------------------------------# # 假设输入进来的图片是600,600,3 #-----------------------------------# self.inplanes = 64 super(ResNet, self).__init__() # 600,600,3 -> 300,300,64 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 300,300,64 -> 150,150,64 self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, ceil_mode=True) # 150,150,64 -> 150,150,256 self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0]) # 150,150,256 -> 75,75,512 self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2) # 75,75,512 -> 38,38,1024 到这里可以获得一个38,38,1024的共享特征层 self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2) # self.layer4被用在classifier模型中 self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2) self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7) self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes) for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n)) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): m.weight.data.fill_(1) m.bias.data.zero_() def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1): downsample = None #-------------------------------------------------------------------# # 当模型需要进行高和宽的压缩的时候,就需要用到残差边的downsample #-------------------------------------------------------------------# if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion: downsample = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion), ) layers = [] layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample)) self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion for i in range(1, blocks): layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes)) return nn.Sequential(*layers) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) x = self.bn1(x) x = self.relu(x) x = self.maxpool(x) x = self.layer1(x) x = self.layer2(x) x = self.layer3(x) x = self.layer4(x) x = self.avgpool(x) x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) x = self.fc(x) return x def resnet50(pretrained = False): model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3]) if pretrained: state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url("https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth", model_dir="./model_data") model.load_state_dict(state_dict) #----------------------------------------------------------------------------# # 获取特征提取部分,从conv1到model.layer3,最终获得一个38,38,1024的特征层 #----------------------------------------------------------------------------# features = list([model.conv1, model.bn1, model.relu, model.maxpool, model.layer1, model.layer2, model.layer3]) #----------------------------------------------------------------------------# # 获取分类部分,从model.layer4到model.avgpool #----------------------------------------------------------------------------# classifier = list([model.layer4, model.avgpool]) features = nn.Sequential(*features) classifier = nn.Sequential(*classifier) return features, classifier
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
ResNet是一般性网络,后期也有很多学者进行调优,比如Highway Network,简单的说,就是将 x l = H ( x l − 1 ) + x l − 1 x_l = H(x_{l-1}) + x_{l-1} xl=H(xl−1)+xl−1变换为 x l = H ( x l − 1 ) × T ( x ) + x l − 1 × ( 1 − T ( x ) ) ) x_l = H(x_{l-1})\times T(x)+x_{l-1}\times (1-T(x))) xl=H(xl−1)×T(x)+xl−1×(1−T(x))),就是给增加了两个门的开关呢。Facebook团中(包含何凯明大佬)再2017的CVPR论文中也对ResNet网络进行了进一步的提升,在不增加大量参数的情况下,通过分组卷积,提升了模型的检测精度,详细可参考ResNext文章呢。当然,还有一种改用堆叠的形式,而不是短路连接,相似但有一些区别,也得到了更深的网络,建议大家都可以看看呢
可参考:DenseNet详细内容学习



