- 1如何培养程序员的领导力?_程序员如何培养自己的管理能力
- 2【1】MongoDB的安装以及连接_mongodb怎么连接
- 3Linux 安装 Gitblit_gitblit linux 安装
- 42022卡塔尔世界杯互动游戏|运营策略_世界杯 运营 活动 游戏
- 5vivado的RTL设计与联合modelsim仿真_vivado可以生成rtl
- 6目前常见的Linux操作系统_linux操作系统分类
- 7京东软件测试岗:不忍直视的三面,幸好做足了准备,月薪18k,已拿offer_京东测开三面
- 8视觉应用线扫相机速度反馈(倍福CX7000PLC应用)
- 9GPT3.5、GPT4、GPT4o的性能对比_gpt3.5和gpt4o
- 10【C语言题解】1、写一个宏来计算结构体中某成员相对于首地址的偏移量;2、写一个宏来交换一个整数二进制的奇偶位
SpringBoot——单元测试之JUnit5_springboot junit5
赞
踩
文章目录:
2.1 @DisplayName、@Disabled、@BeforeEach、@AfterEach、@BeforeAll、@AfterAll
1.JUnit5的变化
Spring Boot 2.2.0 版本开始引入 JUnit 5 作为单元测试默认库
作为最新版本的JUnit框架,JUnit5与之前版本的Junit框架有很大的不同。由三个不同子项目的几个不同模块组成。
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
JUnit Platform: Junit Platform是在JVM上启动测试框架的基础,不仅支持Junit自制的测试引擎,其他测试引擎也都可以接入。
JUnit Jupiter: JUnit Jupiter提供了JUnit5的新的编程模型,是JUnit5新特性的核心。内部 包含了一个测试引擎,用于在Junit Platform上运行。
JUnit Vintage: 由于JUint已经发展多年,为了照顾老的项目,JUnit Vintage提供了兼容JUnit4.x,Junit3.x的测试引擎。

注意:SpringBoot 2.4 以上版本移除了默认对 Vintage 的依赖。如果需要兼容junit4需要自行引入(不能使用junit4的功能 @Test)
JUnit 5’s Vintage Engine Removed from
spring-boot-starter-test,如果需要继续兼容junit4需要自行引入vintage
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
- <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
- <scope>test</scope>
- <exclusions>
- <exclusion>
- <groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
- <artifactId>hamcrest-core</artifactId>
- </exclusion>
- </exclusions>
- </dependency>
如果只使用JUnit5的特性,那么就需要添加下面的依赖。
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
- <scope>test</scope>
- </dependency>
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
- import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
-
- @SpringBootTest
- class SpringbootActuatorApplicationTests {
-
- @Test
- void contextLoads() {
- }
-
- }
2.JUnit5常用注解及测试
JUnit5的注解与JUnit4的注解有所变化
- @Test :表示方法是测试方法。但是与JUnit4的@Test不同,他的职责非常单一不能声明任何属性,拓展的测试将会由Jupiter提供额外测试
- @ParameterizedTest :表示方法是参数化测试,下方会有详细介绍
- @RepeatedTest :表示方法可重复执行,下方会有详细介绍
- @DisplayName :为测试类或者测试方法设置展示名称
- @BeforeEach :表示在每个单元测试之前执行
- @AfterEach :表示在每个单元测试之后执行
- @BeforeAll :表示在所有单元测试之前执行
- @AfterAll :表示在所有单元测试之后执行
- @Tag :表示单元测试类别,类似于JUnit4中的@Categories
- @Disabled :表示测试类或测试方法不执行,类似于JUnit4中的@Ignore
- @Timeout :表示测试方法运行如果超过了指定时间将会返回错误
- @ExtendWith :为测试类或测试方法提供扩展类引用
2.1 @DisplayName、@Disabled、@BeforeEach、@AfterEach、@BeforeAll、@AfterAll
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- //----------------------------常用注解----------------------------
- @DisplayName("测试DisplayName注解---方法1")
- @Test
- public void testDisplayName1() {
- System.out.println(123);
- }
-
- @Disabled
- @DisplayName("测试DisplayName注解---方法2")
- @Test
- public void testDisplayName2() {
- System.out.println(456);
- }
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- }

我们再把 testDisplayName2 方法上的@Disabled注解打开。可以看到,这个测试方法已经被禁用了。

2.2 @Timeout
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @DisplayName("测试Timeout注解")
- @Timeout(value = 5, unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
- @Test
- public void testTimeout() throws InterruptedException {
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- }
-
- }

2.3 @RepeatedTest
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @RepeatedTest(5)
- @Test
- public void testRepeatedTest() {
- System.out.println(1);
- }
-
- }

3.断言
断言(assertions)是测试方法中的核心部分,用来对测试需要满足的条件进行验证。这些断言方法都是 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions 的静态方法。JUnit 5 内置的断言可以分成如下几个类别:
检查业务逻辑返回的数据是否合理。
所有的测试运行结束以后,会有一个详细的测试报告;
3.1 简单断言
用来对单个值进行简单的验证。如:
| 方法 | 说明 |
| assertEquals | 判断两个对象或两个原始类型是否相等 |
| assertNotEquals | 判断两个对象或两个原始类型是否不相等 |
| assertSame | 判断两个对象引用是否指向同一个对象 |
| assertNotSame | 判断两个对象引用是否指向不同的对象 |
| assertTrue | 判断给定的布尔值是否为 true |
| assertFalse | 判断给定的布尔值是否为 false |
| assertNull | 判断给定的对象引用是否为 null |
| assertNotNull | 判断给定的对象引用是否不为 null |
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- //----------------------------断言----------------------------
-
- /**
- * 如果前面的断言失败,则后面的代码不会再执行
- */
- @DisplayName("测试简单断言")
- @Test
- public void testSimpleAssertions() {
- int result = cal(1,2);
- assertEquals(5,result,"业务逻辑计算结果出错....");
- Object obj1 = new Object();
- Object obj2 = new Object();
- assertSame(obj1,obj2);
- }
-
- public int cal(int x, int y) {
- return x + y;
- }
-
- }
assertEquals方法判断出运算结果不同,也即此时第一个断言失败了,那么后面的assertSame不会再执行。

当我们修改assertEquals方法使其断言成功,那么后续的assertSame将会继续执行。
此时看到的就是assertSame方法打印的异常信息(两个对象不相等)。
assertEquals(3,result,"业务逻辑计算结果出错....");
3.2 数组断言
通过 assertArrayEquals 方法来判断两个对象或原始类型的数组是否相等。
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- //----------------------------断言----------------------------
- @DisplayName("测试数组断言1")
- @Test
- public void testArrayAssertions1() {
- assertArrayEquals(new int[]{1,2}, new int[]{1,2});
- }
-
- @DisplayName("测试数组断言2")
- @Test
- public void testArrayAssertions2() {
- assertArrayEquals(new int[]{3,4}, new int[]{1,2}, "数组内容不相等....");
- }
-
- }


3.3 组合断言
assertAll 方法接受多个 org.junit.jupiter.api.Executable 函数式接口的实例作为要验证的断言,可以通过 lambda 表达式很容易的提供这些断言。
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- //----------------------------断言----------------------------
- @DisplayName(("测试组合断言"))
- @Test
- public void testAllAssertions() {
- assertAll("testAll",
- () -> assertTrue(true && true),
- () -> assertEquals(1,2));
- //当以上两个断言全部成功时,才会打印下面的内容
- System.out.println("success!!!");
- }
-
- }
组合断言中,当所有断言都成功时,代码才会顺利向下执行。assertTrue虽然执行成功了,但是assertEquals失败了,所有下面的sout不会执行。

3.4 异常断言
在JUnit4时期,想要测试方法的异常情况时,需要用@Rule注解的ExpectedException变量还是比较麻烦的。而JUnit5提供了一种新的断言方式Assertions.assertThrows() ,配合函数式编程就可以进行使用。
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
-
- //----------------------------断言----------------------------
- @DisplayName("测试异常断言")
- @Test
- public void testExceptionAssertions() {
- assertThrows(ArithmeticException.class,() -> {
- int i = 10 / 2; //此时断言会执行
- //int j = 10 / 0; //此时断言不会执行
- },"业务逻辑居然正常运行???");
- }
-
- }
如果代码执行 int i = 10 / 2 运行正确,不会出现 ArithmeticException 异常,所以此时assertThrows断言会执行。反之则不会执行。

3.5 超时断言
Junit5还提供了Assertions.assertTimeout() 为测试方法设置了超时时间。
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
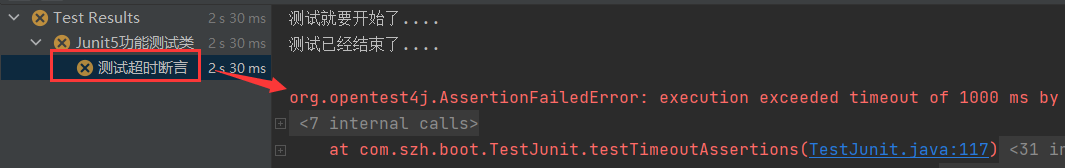
- @DisplayName("测试超时断言")
- @Test
- public void testTimeoutAssertions() {
- assertTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(1000), () -> Thread.sleep(2000));
- }
-
- }
3.6 快速失败
通过 fail 方法直接使得测试失败。
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
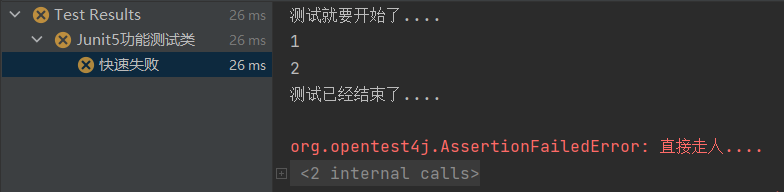
- @DisplayName("快速失败")
- @Test
- public void testFailAssertions() {
- System.out.println(1);
- System.out.println(2);
- fail("直接走人....");
- System.out.println(3);
- System.out.println(4);
- }
-
- }
4.前置条件
JUnit 5 中的前置条件(assumptions【假设】)类似于断言,不同之处在于不满足的断言会使得测试方法失败,而不满足的前置条件只会使得测试方法的执行终止。前置条件可以看成是测试方法执行的前提,当该前提不满足时,就没有继续执行的必要。
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
-
- import java.time.Duration;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- *
- */
- //@SpringBootTest
- @DisplayName("Junit5功能测试类")
- public class TestJunit {
-
- @BeforeEach
- public void testBeforeEach() {
- System.out.println("测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterEach
- public void testAfterEach() {
- System.out.println("测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void testBeforeAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了....");
- }
-
- @AfterAll
- public static void testAfterAll() {
- System.out.println("所有测试已经结束了....");
- }
-
- //----------------------------前置条件----------------------------
- @DisplayName("测试前置条件")
- @Test
- public void testAssumptions() {
- Assumptions.assumeTrue(true, "结果不是true....");
- System.out.println(111);
- }
-
- }

将 Assumptions.assumeTrue(false, "结果不是true...."); 中的 true 改为 false,此时因为 true != false,所以不满足该前置条件,则直接导致测试方法被终止执行。

5.嵌套测试
JUnit 5 可以通过 Java 中的内部类和@Nested 注解实现嵌套测试,从而可以更好的把相关的测试方法组织在一起。在内部类中可以使用@BeforeEach 和@AfterEach 注解,而且嵌套的层次没有限制。
- package com.szh.boot;
-
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.Nested;
- import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
-
- import java.util.EmptyStackException;
- import java.util.Stack;
-
- import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
-
- /**
- * 嵌套测试中,外层的@Test不能驱动内层的@Before(After)Each/All之类的方法提前/之后运行
- * 内层的@Test可以驱动外层的@Before(After)Each/All之类的方法提前/之后运行
- */
- @DisplayName("A stack")
- public class TestingAStackDemo {
-
- Stack<Object> stack;
-
- @Test
- @DisplayName("is instantiated with new Stack()")
- void isInstantiatedWithNew() {
- new Stack<>();
- }
-
- @Nested
- @DisplayName("when new")
- class WhenNew {
-
- @BeforeEach
- void createNewStack() {
- stack = new Stack<>();
- }
-
- @Test
- @DisplayName("is empty")
- void isEmpty() {
- assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());
- }
-
- @Test
- @DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when popped")
- void throwsExceptionWhenPopped() {
- assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::pop);
- }
-
- @Test
- @DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when peeked")
- void throwsExceptionWhenPeeked() {
- assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::peek);
- }
-
- @Nested
- @DisplayName("after pushing an element")
- class AfterPushing {
- String anElement = "an element";
-
- @BeforeEach
- void pushAnElement() {
- stack.push(anElement);
- }
-
- @Test
- @DisplayName("it is no longer empty")
- void isNotEmpty() {
- assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());
- }
-
- @Test
- @DisplayName("returns the element when popped and is empty")
- void returnElementWhenPopped() {
- assertEquals(anElement, stack.pop());
- assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());
- }
-
- @Test
- @DisplayName("returns the element when peeked but remains not empty")
- void returnElementWhenPeeked() {
- assertEquals(anElement, stack.peek());
- assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());
- }
- }
- }
- }
6.参数化测试
参数化测试是JUnit5很重要的一个新特性,它使得用不同的参数多次运行测试成为了可能,也为我们的单元测试带来许多便利。
利用@ValueSource等注解,指定入参,我们将可以使用不同的参数进行多次单元测试,而不需要每新增一个参数就新增一个单元测试,省去了很多冗余代码。
@ValueSource: 为参数化测试指定入参来源,支持八大基础类以及String类型,Class类型
@NullSource: 表示为参数化测试提供一个null的入参
@EnumSource: 表示为参数化测试提供一个枚举入参
@CsvFileSource:表示读取指定CSV文件内容作为参数化测试入参
@MethodSource:表示读取指定方法的返回值作为参数化测试入参(注意方法返回需要是一个流)
7.JUnit4 → Junit5
在进行迁移的时候需要注意如下的变化:
- 注解在 org.junit.jupiter.api 包中,断言在 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions 类中,前置条件在 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions 类中。
- 把@Before 和@After 替换成@BeforeEach 和@AfterEach。
- 把@BeforeClass 和@AfterClass 替换成@BeforeAll 和@AfterAll。
- 把@Ignore 替换成@Disabled。
- 把@Category 替换成@Tag。
- 把@RunWith、@Rule 和@ClassRule 替换成@ExtendWith。


